Composition analysis of aromatics-rich extraction oil from FCC slurry
-
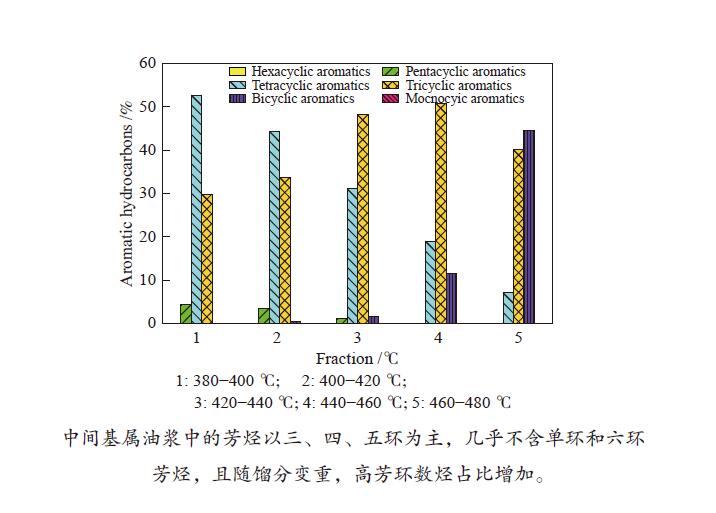
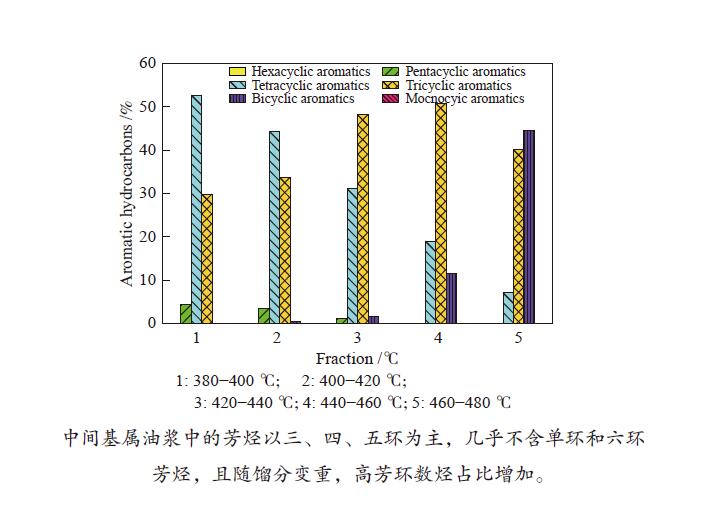
摘要: 以中间基属FCC油浆的抽出油为原料,采用实沸点减压蒸馏切割为每20 ℃一个窄馏分,测量其密度、残炭和运动黏度等基本物性,并结合元素分析、核磁共振波谱以及全二维气相色谱/飞行时间质谱等考察了窄馏分中芳烃组成和结构的变化。结果表明,随着沸点升高,窄馏分的密度、残炭、运动黏度均呈现递增趋势,沸点达420 ℃后变化尤为明显;440 ℃之前窄馏分中的芳烃主要以三、四环为主,其后五环芳烃含量急剧增加。FCC油浆中的芳烃具有较高的缩合度且芳环上仅含有少量较短的烷基侧链;油浆窄馏分中的杂原子化合物主要以硫化物和氧化物为主,氮化物和卤化物含量较低。Abstract: The extracted oil of intermediate base FCC slurry is split into eight narrow fractions with a boiling point interval of 20 °C by vacuum distillation. The aromatic composition and constitution of these narrow fractions were determined by measuring their density, carbon residue and kinematic viscosity as well as elemental analysis, 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography and time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC×GC TOF MS). The results indicate that the density, carbon residue and kinematic viscosity of each narrow fraction increase with the increase of boiling point, in particular with a boiling point higher than 420 °C. The aromatics consist of mainly tricyclic and tetracyclic aryl hydrocarbons in the narrow fractions with a boiling point lower than 440 °C; the content of pentacyclic aromatics increases rapidly with the increace of boling point over 440 °C, though the pentacyclic aromatics are also present in the narrow fractions with a boiling point of 400–420 °C. The aromatics in the FCC slurry are highly-condensed and contain a small amount of short-alkyl groups. The heteratomic compounds in the narrow fractions include mainly sulfur- and oxygen-containing compounds, whereas the content of nitrogen- and halogen-containing compounds is very low.
-
表 1 原料基本性质
Table 1 Primary properties of the FCC slurry
ρ20/(kg·m−3) M w(carbon residue)/% μ100/(mm2·s−1) w(SARA)/% saturates aromatics resins asphaltenes 1120.20 343 8.43 14.08 18.77 72.37 6.06 2.80 表 2 窄馏分收率分布
Table 2 Extraction yield of each narrow fraction from the FCC slurry
IBP−380 ℃ Yield w/% 480 ℃−FBP 380−400 ℃ 400−420 ℃ 420−440 ℃ 440−460 ℃ 460−480 ℃ 5.67 27.59 20.25 15.07 8.89 6.69 15.08 表 3 原料及产物性质检测方法
Table 3 Standards of testing methods of feedstock and products
Number Analysis item Method of analysis 1 ρ20, density at 20 °C, (kg·m−3) GB/T 2540—1981 2 M, average molecular weight SH/T 0583—1994 3 w,carbon residue,% GB/T 17144—1997 4 μ100,kinematic viscosity, (mm2·s−1) GB/T 11137—1989 表 4 窄馏分物性变化
Table 4 Physical properties of narrow fractions
Fraction ρ20/(kg·m−3) w (carbon residue)/% μ100/(mm2·s−1) 360−380 ℃ 1.1008 0.12 3.63 380−400 ℃ 1.1012 0.13 5.53 400−420 ℃ 1.1066 0.25 8.07 420−440 ℃ 1.1169 0.70 10.30 440−460 ℃ 1.1268 2.65 18.10 460−480 ℃ 1.1294 7.47 38.43 480−500 ℃ 1.1850 16.01 81.44 500 ℃−FBP 1.2250 25.28 132.50 表 5 C、H、S、N元素分析及VPO分子量
Table 5 Elemental composition and molecular weight of all narrow fractions
Fraction n(H)/n(C) w/% M H C S N 360−380 ℃ 0.89 6.88 90.61 2.17 0.10 208 380−400 ℃ 0.87 6.61 91.38 2.00 0.07 256 400−420 ℃ 0.86 6.59 91.76 1.86 0.06 263 420−440 ℃ 0.82 6.24 91.90 1.82 0.05 291 440−460 ℃ 0.82 6.27 91.78 1.72 0.06 313 460−480 ℃ 0.80 6.05 90.36 1.51 0.07 325 480−500 ℃ 0.79 6.05 92.12 1.44 0.05 334 500 ℃−FBP 0.74 5.67 92.66 1.06 0.05 − 表 6 窄馏分中不同化学位移氢的含量
Table 6 Content of hydrogen species (%) of different chemical shifts in each narrow fraction determined by 1H-NMR
Fraction w/% Hγ Hβ Hα HA IBP−380 ℃ 0.73 11.35 43.63 44.28 380−400 ℃ 0.89 10.98 43.30 44.83 400−420 ℃ 0.82 10.12 43.22 45.84 420−440 ℃ 0.64 9.48 43.83 46.05 440−460 ℃ 0.61 9.34 43.64 46.41 460−480 ℃ 0.71 9.58 41.61 48.11 480−500 ℃ 0.53 8.84 41.59 49.04 表 7 窄馏分核磁共振H谱结构参数
Table 7 Structural parameters of narrow fractions derived by the improved B-L method based on the 1H-NMR results
Fraction CT HT RA RT RN fa fN fP σ HAU/CA IBP−380 ℃ 15.69 14.20 2.57 3.74 1.17 0.75 0.22 0.03 0.33 0.80 380−400 ℃ 19.48 16.79 3.60 4.68 1.07 0.76 0.17 0.07 0.33 0.75 400−420 ℃ 20.08 17.20 3.80 4.79 0.99 0.77 0.15 0.09 0.32 0.75 420−440 ℃ 22.27 18.02 4.46 5.57 1.12 0.78 0.15 0.07 0.32 0.70 440−460 ℃ 23.90 19.47 4.88 5.84 0.96 0.78 0.12 0.10 0.32 0.71 460−480 ℃ 24.45 19.51 5.12 6.02 0.90 0.79 0.11 0.10 0.30 0.69 480−500 ℃ 25.62 20.02 5.49 6.36 0.87 0.80 0.10 0.10 0.30 0.68 表 8 窄馏分中不同化学位移碳的含量
Table 8 Fractions of carbon species (%) of different chemical shifts in each narrow fraction determined by 13C-NMR
Fraction $ f_{{\rm{a}}} $/% $ f^{{\rm{H}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $/% $f^{{\rm{B}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $/% $f^{{\rm{C}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $/% $f^{{\rm{O}}}_{{\rm{a}}}$/% $ f^{{\rm{C}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $/% $ f_{{\rm{al}}} $/% $ f^{{\rm{A}}}_{{\rm{al}}} $/% $ f^{{\rm{B}}}_{{\rm{al}}} $/% $ f^{{\rm{H}}}_{{\rm{al}}} $/% $ f^{{\rm{O}}}_{{\rm{al}}} $/% 360−380 ℃ 80.24 61.25 15.48 3.51 0 0 19.76 11.76 2.33 5.59 0.08 380−400 ℃ 80.05 57.61 17.66 4.79 0 0 19.95 12.31 2.44 5.20 0 400−420 ℃ 81.84 56.30 18.68 5.91 0.67 0.29 18.15 11.45 2.14 4.52 0.03 420−440 ℃ 80.85 55.05 19.58 5.88 0.34 0 19.15 11.98 2.45 4.72 0 440−460 ℃ 80.85 57.06 18.77 4.67 0.13 0.21 19.15 11.59 2.43 5.13 0 460−480 ℃ 84.37 56.14 20.37 6.69 1.18 0 15.63 10.60 2.23 2.80 0 480−500 ℃ 83.44 73.45 7.69 0 0 2.31 16.56 7.18 0.86 8.47 0 note: fa, aromatic carbon; $ f^{{\rm{H}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $, proton aromatic carbon; $ f^{{\rm{B}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $, bridgehead aromatic carbon; $ f^{{\rm{S}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $, lateral aromatic carbon; $ f^{{\rm{O}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $ oxygen-bonded aromatic carbon; $ f^{{\rm{C}}}_{{\rm{a}}} $, carbonyl aromatic carbon; $ f_{{\rm{al}}} $, saturated carbon; $f^ {\rm{A} }_{ {\rm{al} } }$, lipomethyl carbon; $ f^{B}_{{\rm{al}}} $, aromatic ring methyl carbon; $ f^{{\rm{H}}}_{{\rm{al}}} $, methylene and methine carbon; $ f^{{\rm{O}}}_{{\rm{al}}} $, oxygen connected saturated carbon -
[1] 刘丽强. 重油催化裂化油浆综合利用及进展[J]. 广州化工,2015,43(9):34−35+38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2015.09.014LIU Li-qiang. Comprehensive utilization and progress of RFCC slurry[J]. Guangzhou Chem Ind,2015,43(9):34−35+38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2015.09.014 [2] 程意茹, 蒋定建, 方晓玲. 催化裂化油浆的应用研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,2016,36(15):72−73, 75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2016.15.045CHENG Yi-ru, JIANG Ding-jian, FANG Xiao-ling. Application study of FCC slurry[J]. China Pet Chem Standard Quality,2016,36(15):72−73, 75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2016.15.045 [3] 李林, 徐海清. 催化油浆综合利用的技术措施[J]. 化学工业与工程技术,2013,34(1):20−24.LI Lin, XU Hai-qing. Technical measures for comprehensive utilization of catalytic slurry oil[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2013,34(1):20−24. [4] 兰翔, 许志明, 赵锁奇, 王仁安. 大庆和辽河油浆窄馏分的性质及组成[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版),2001,(6):74−77, 3.LAN Xiang, XU Zhi-ming, ZHAO Suo-qi, WANG Ren-an. Propertiep and components of narrow fractions of Daqing and Liaohe decanted oils[J]. J China Univ Pet (Ed Nat Sci),2001,(6):74−77, 3. [5] 兰翔, 赵锁奇, 许志明, 王仁安. 大庆、辽河油浆窄馏分的环状结构、组成的比较[J]. 石油学报(石油加工),2002,(2):14−19.LAN Xiang, XU Zhi-ming, ZHAO Suo-qi, WANG Ren-an. Comparison of structure and composition of rings in narrow fractions of DQ and LH decant oil[J]. Acta Pet Sin (Pet Process Sect),2002,(2):14−19. [6] 王遥. FCC油浆的结构表征及提高其抗老化性能的改性反应研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2018.WANG Yao. Characterization of FCC Slurry and Study of Modified Reaction to Increase Aging Resistance[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2018. [7] 常泽军, 刘熠斌, 冯翔, 杨朝合. 石蜡基属催化裂化轻油浆化学结构随沸点变化规律研究[J]. 石油学报(石油加工),2017,33(4):667−673.CHANG Ze-jun, LIU Yi-bin, FENG Xiang, YANG Chao-he. Variation regularity of chemical structure of paraffin-based FCC light slurry over boiling point[J]. Acta Pet Sin (Pet Process Sect),2017,33(4):667−673. [8] 张桧然, 沈本贤, 孙辉, 刘纪昌. 南海原油胶质、沥青质结构表征及原油降黏研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工,2015,46(12):31−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2015.12.011ZHANG Hui-ran, SHEN Ben-xian, SUN Hui, LIU Ji-chang. Structure characterization of resin and asphaltene and viscosity reduction of south China Sea crude oil[J]. China Pet Process Pet Technol,2015,46(12):31−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2015.12.011 [9] WANDAS R. Structural characterization of asphaltenes from raw and desulfurized vacuum residue and correlation between asphaltene content and the tendency of sediment formation in H-iol heavy products[J]. Pet Sci Technol,2007,25(1):153−168. [10] BROWN J K, LADNER W R. A comparison with infra-red measurement and the conversion to carbon structure[J]. Fuel,1960,39(1):87−96. [11] 郭琨, 周建, 刘泽龙. 全二维气相色谱-飞行时间质谱联用技术分析重馏分油中芳烃组成[J]. 色谱,2012,30(2):128−134.GUO Kun, ZHOU Jian, LIU Ze-long. Characterization of aromatic hydrocarbons in heavy gas oil using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Chromatography,2012,30(2):128−134. [12] 赵小宁. FCC油浆抽提分离工艺研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019.ZHAO Xiao-ning. Study on the extraction and separation technology of FCC slurry[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum, 2019. [13] 孙昱东, 赵小宁, 冯祎. FCC油浆抽提分离产物结构组成分析[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(8):937−941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.08.005SUN Yu-dong, ZHAO Xiao-ning, FENG Yi. Composition analysis of FCC slurry and its extraction products[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(8):937−941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.08.005 [14] 刘莹. 油系针状焦的研究与生产现状[J]. 中外能源,2019,24(11):65−69.LI Ying. Research and production status of oil-based needle coke[J]. Sino-Global Energy,2019,24(11):65−69. [15] 徐春明, 杨朝合. 石油炼制工程(第四版)[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009.XU Chun-ming, YANG Chao-he. Petroleum Refining Engineering (Fourth Edition)[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2009. -




 下载:
下载: