Pyrolysis behavior of coal in a moving bed with baffled internals under different residence times
-
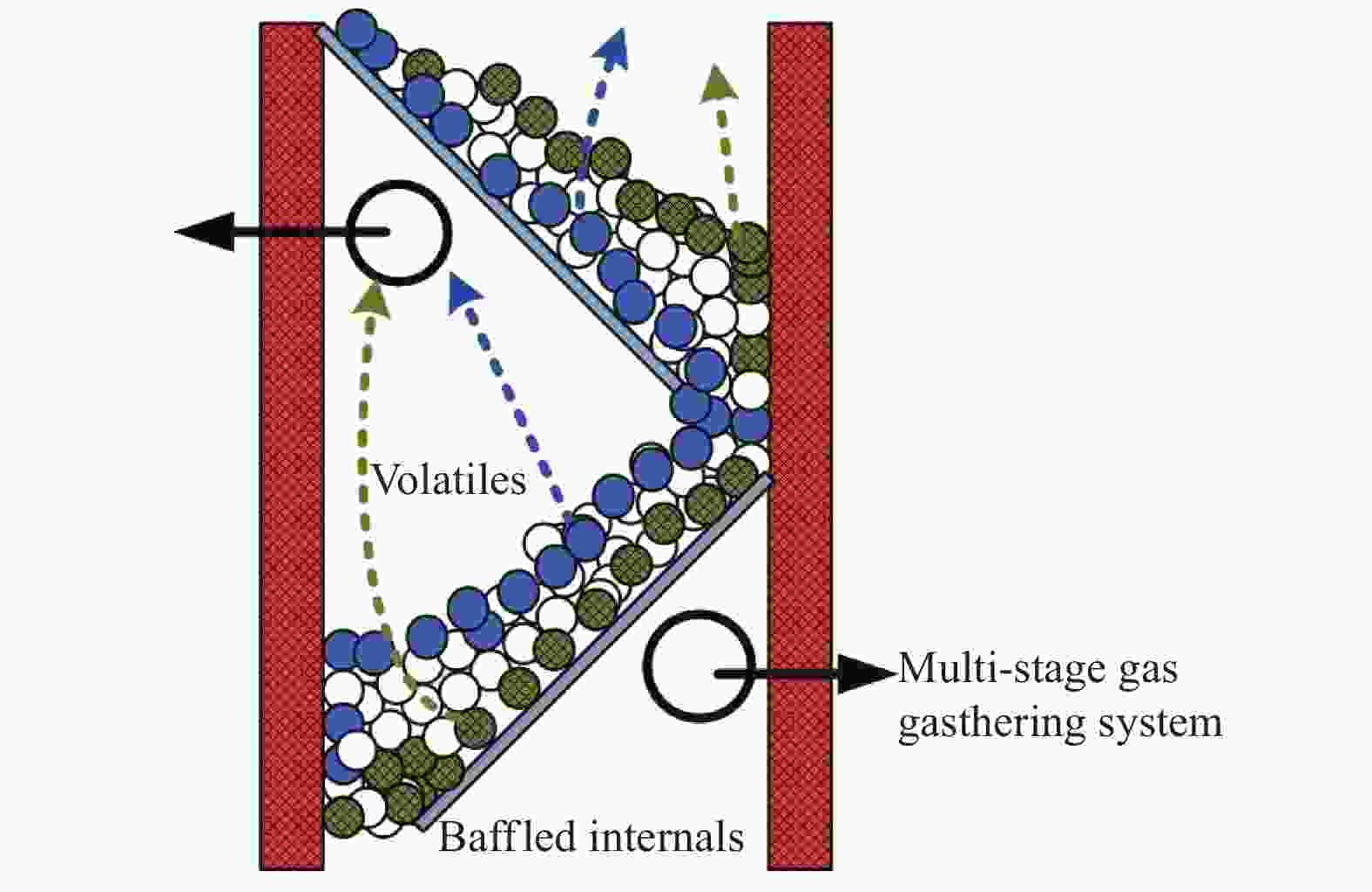
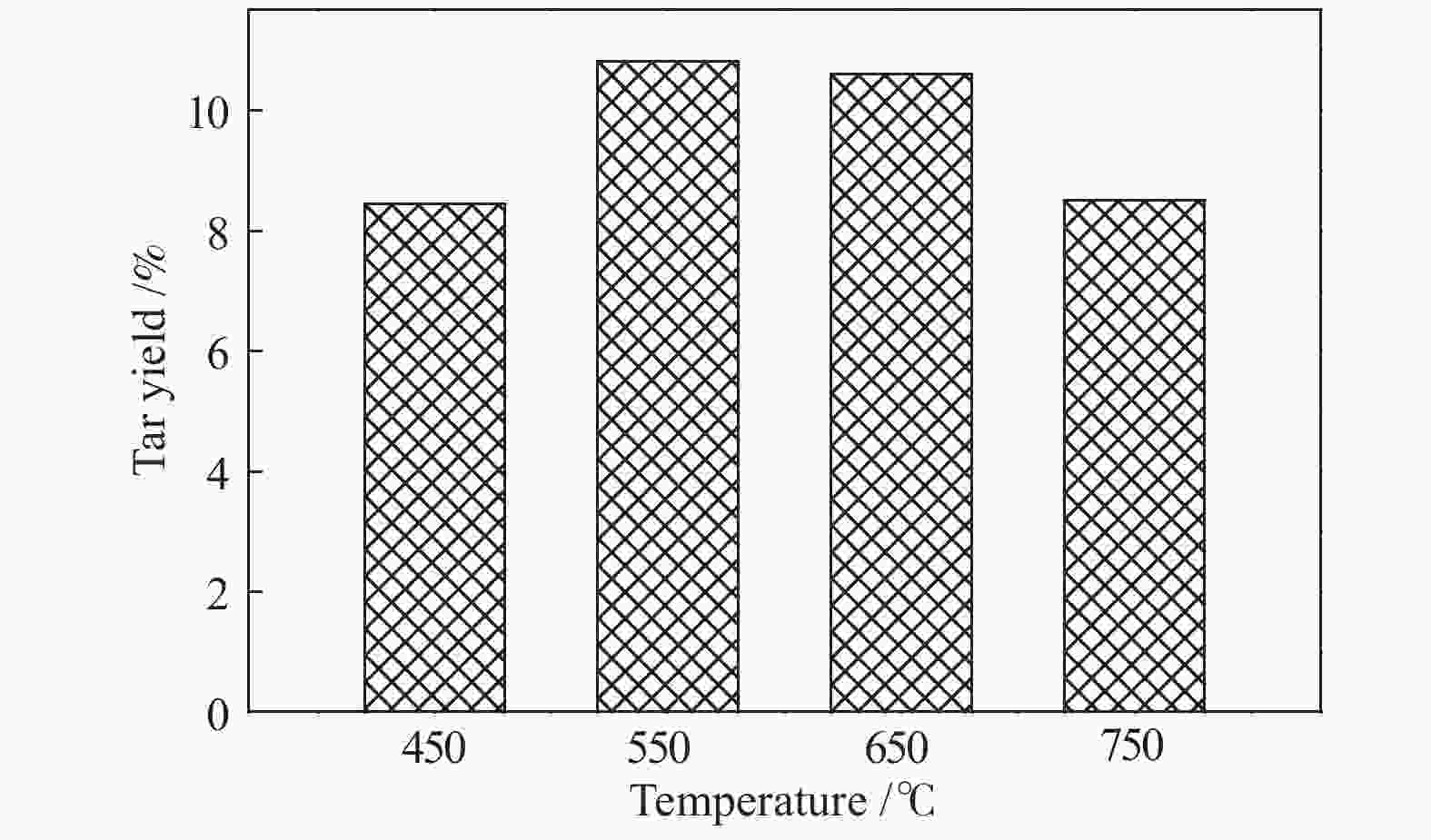
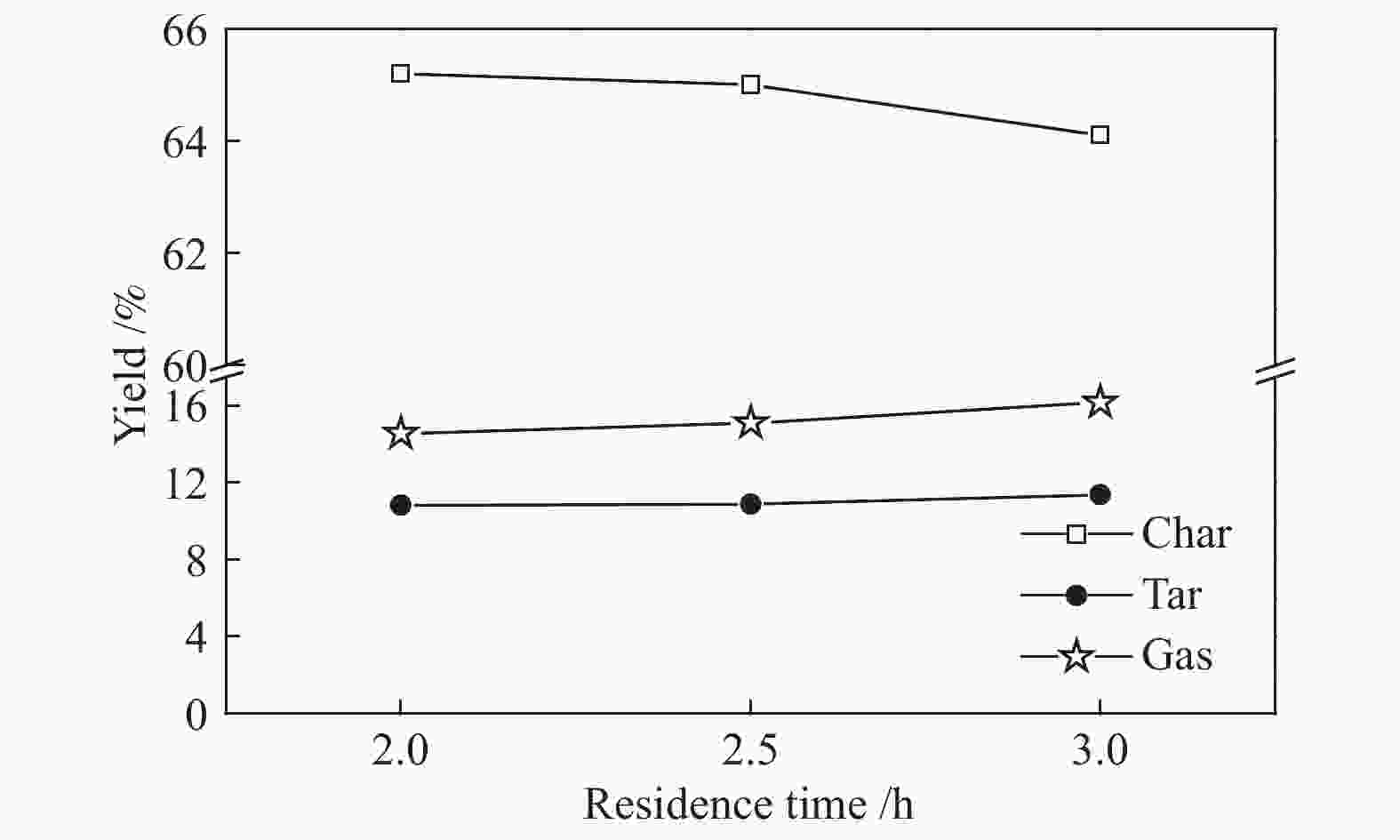
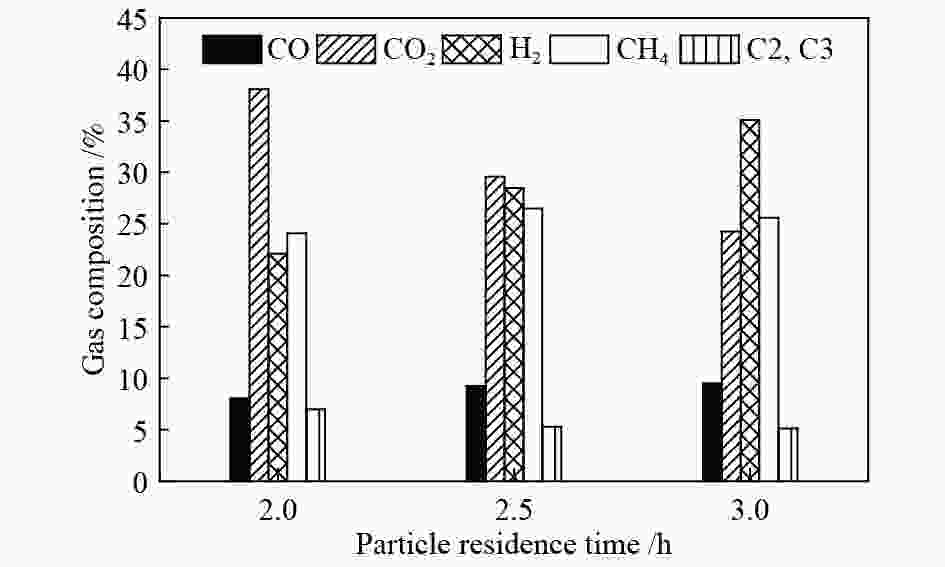
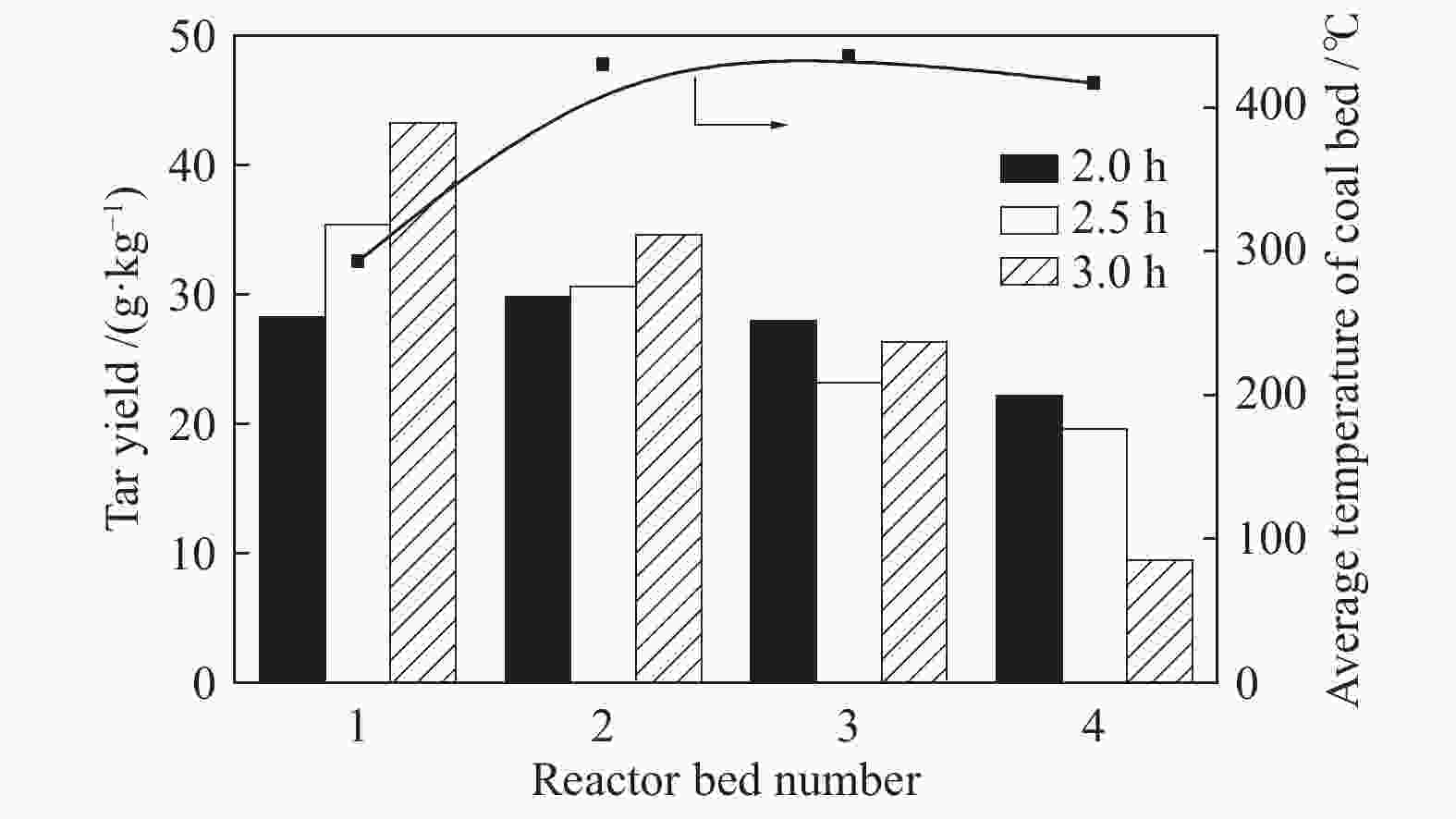
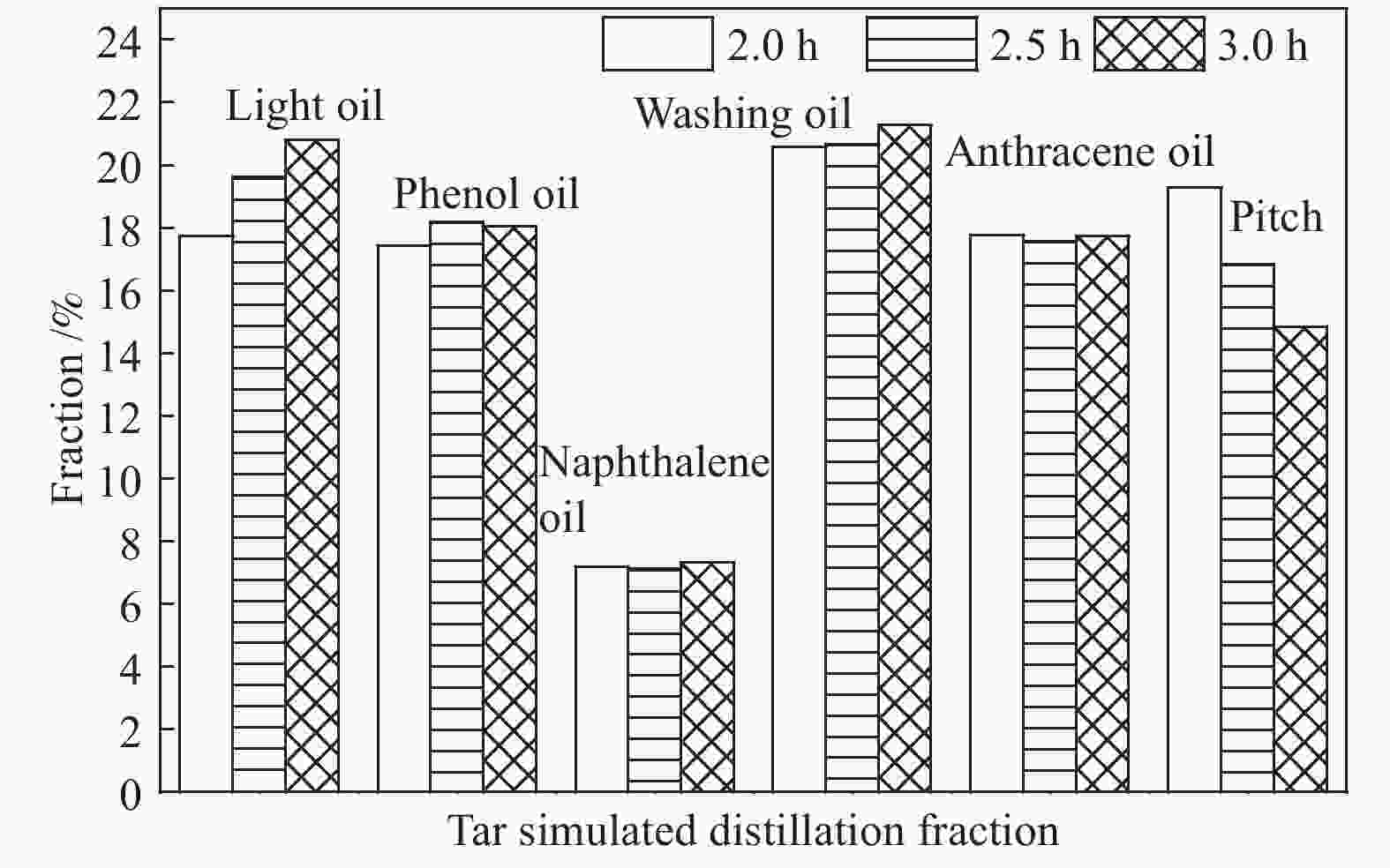
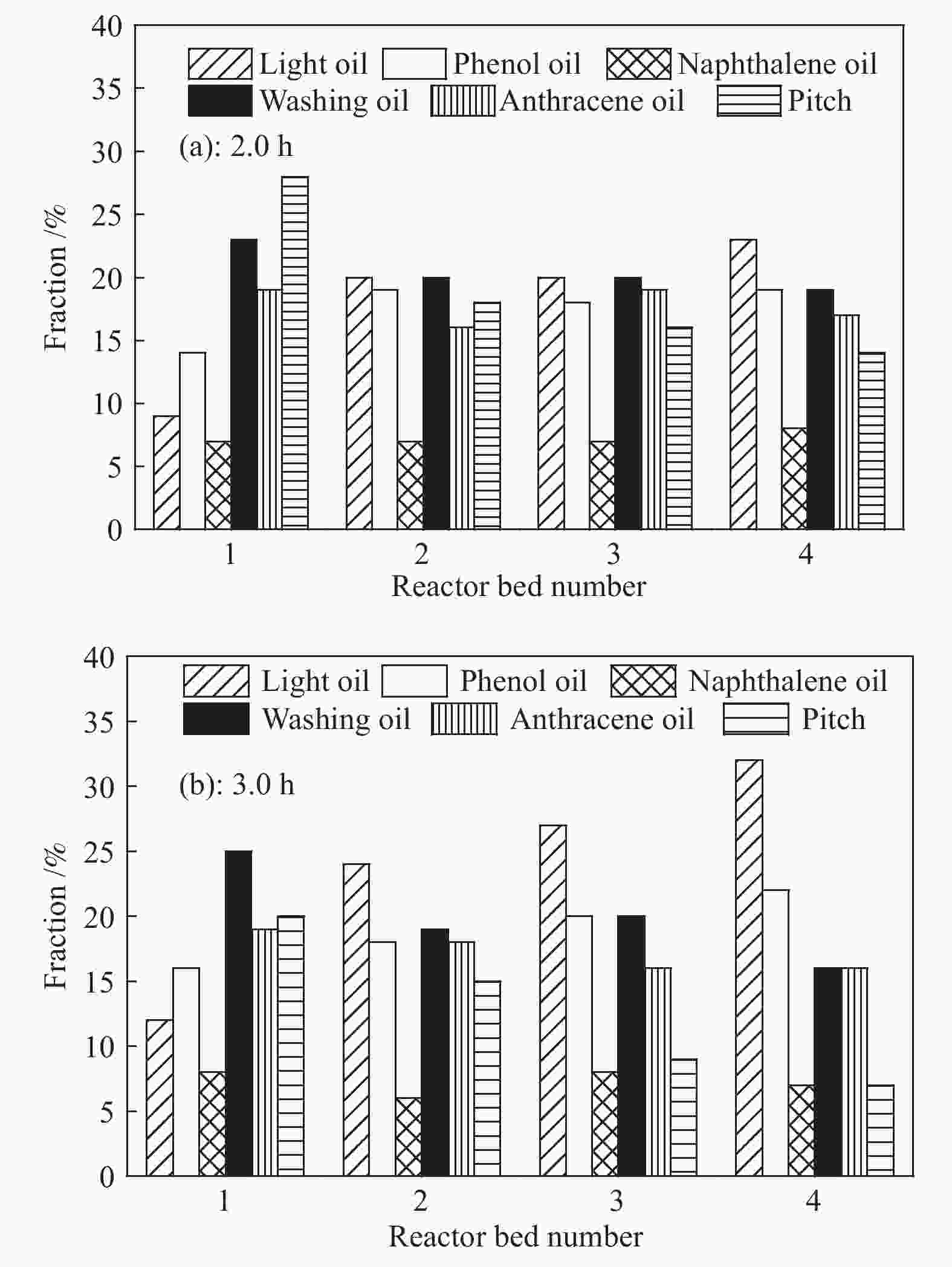
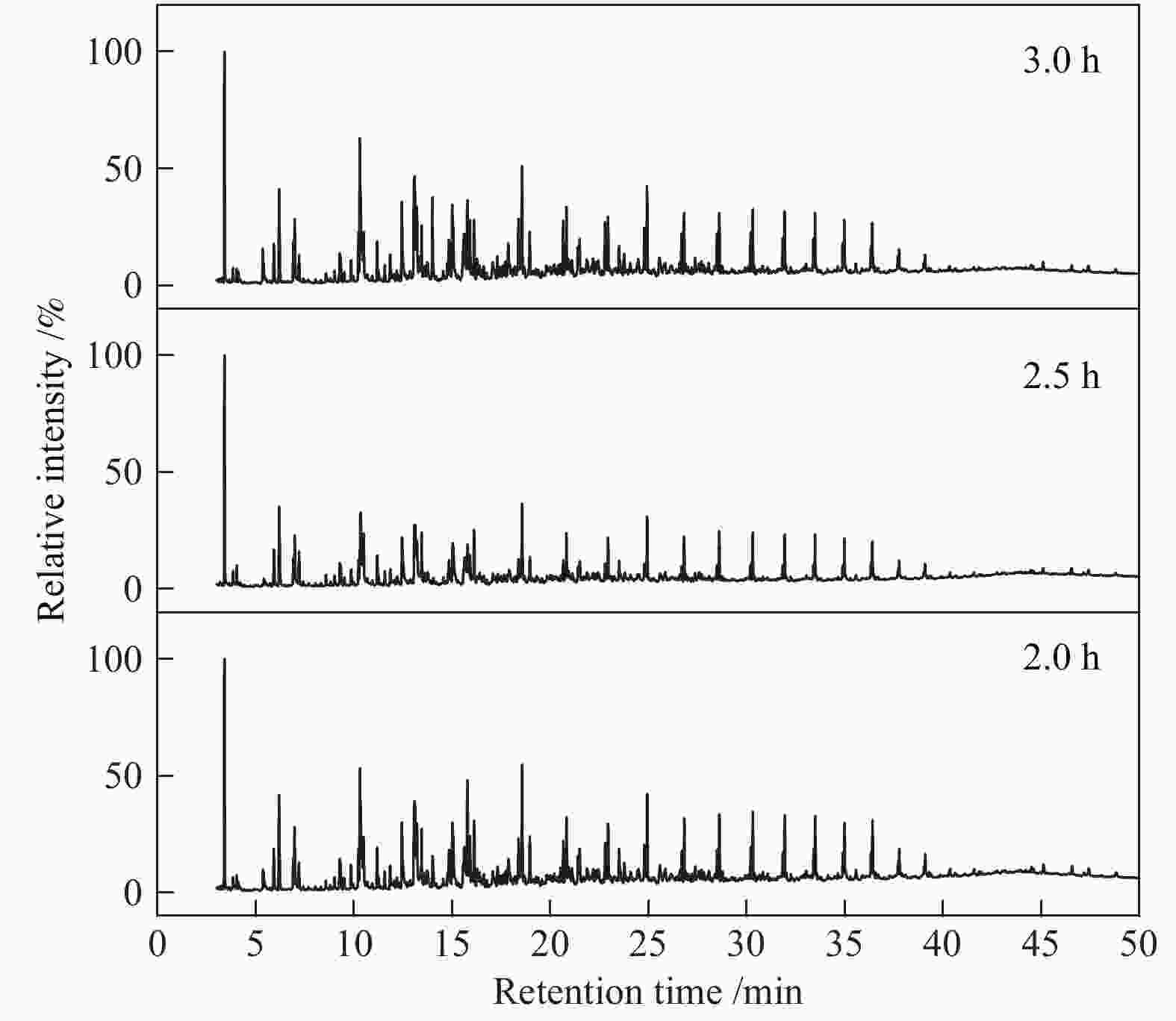
摘要: 针对常规移动床煤热解工艺所面临的无法处理粉煤,轻质焦油产率低、焦油品质差等问题,开发了折流内构件移动床热解工艺来调控气固两相的热质传递和热解反应过程。利用多段集气系统可及时地收集煤在不同热解阶段释放出的油气产物,研究了淖毛湖煤在不同温度和停留时间下的热解行为特性和产物品质。结果表明,折流内构件强化了颗粒间的热量和挥发分物质的传递,使其可处理0.4−6.0 mm的粉煤;在热解温度550 ℃,停留时间为3.0 h时,热解焦油产率达到最高为11.38%(占格金焦油产率的86.87%,质量分数),焦油馏分中低于360 ℃的轻质组分质量分数为85.0%;随着停留时间的延长,热解气中的H2体积分数从22.1%增加到了35.1%,CO体积分数从8.0%增加到了9.5%;在第一和第二层反应器中的焦油产率随停留时间的延长而增加,在第三和第四层反应器内当停留时间为2.0 h时焦油产率最大;随着床层数的增加,焦油模拟蒸馏馏分中的轻质组分含量增加,焦油脂肪烃化合物含量减小,而单环芳烃和二环芳烃的含量逐渐增加。Abstract: In view of the problems faced by the conventional moving bed coal pyrolysis process, such as the inability to deal with pulverized coal, low light tar yield, poor tar quality, etc., a moving bed pyrolysis process with baffled internals was developed to control the heat and mass transfer of the gas-solid two-phase and the pyrolysis reaction process. The multi-stage gas gathering system can collect the oil and gas products released in different pyrolysis stages of coal in time. The pyrolysis behavior and product quality of Naomaohu coal at different temperatures and residence times were investigated. The results show that the baffle internals enhance the heat and volatile matter transfer between particles, enabling it to process 0.4−6.0 mm pulverized coal. When the pyrolysis temperature is 550 ℃ and the residence time is 3 h, the pyrolysis tar yield reaches the highest 11.38%, which is 86.87% of the Gray-King assay yield, and the mass fraction of light components below 360 ℃ in the tar fraction is 85.0%. With the extension of the residence time, the H2 volume fraction in the pyrolysis gas increases from 22.1% to 35.1%, and the CO volume fraction increases from 8.0% to 9.5%. The tar yield in the first and second layer reactors increases with the extension of the residence time, and the maximum tar yield in the third and fourth layer reactors is obtained when the residence time is 2 h. As the number of beds increases, the content of light components in the tar simulated distillation fraction increases, the content of tar aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds decreases, and the content of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbons gradually increases. Based on the above research, it provides technical support for large-scale industrial processing of small particle size pulverized coal, and preparation of higher yield and quality tar.
-
Key words:
- moving bed /
- baffled internals /
- pyrolysis /
- residence time /
- tar quality
-
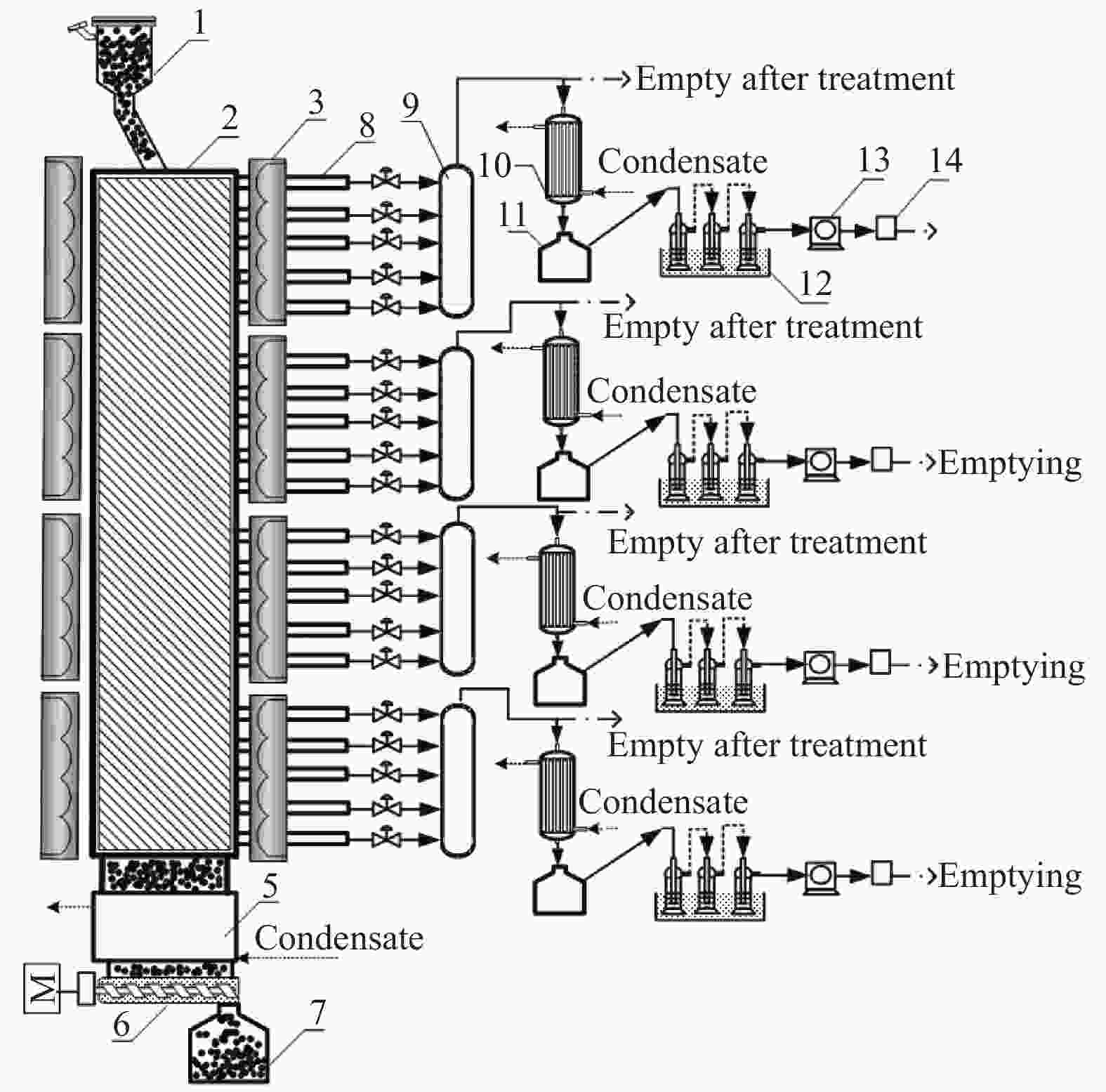
图 1 折流移动床热解工艺流程示意图
Figure 1 A schematic diagram of experimental system
1: Coal hopper; 2: Moving bed with baffled internals; 3: Electric furnaces; 4: Baffled internals; 5: Char condenser; 6: Screw discharger; 7: Char receiver; 8: Gas collector; 9: Gas buffer tank; 10: Multi-stage gas condenser; 11: Tar receiver; 12: Solvent absorption system; 13: Wet gas flow meter; 14: Gas bag
表 1 淖毛湖煤的工业分析及元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of NMH coal
Proximate analysis /% Ultimate analysis /%(daf) Gray-King /% Mad Ad Vdaf FCdaf C H N S O* tar(ad) 17.7 7.8 50.9 49.1 73.9 5.5 1.0 0.5 19.1 13.1 *:by difference 表 2 从GC-MS分析结果得到的各停留时间下所得焦油组分含量
Table 2 Tar composition content of different residence time obtained from GC-MS analysis results
Residence
time/hBed
numberAHs/% MAHs/% PC/% PAHs/% 2.0 1 48.44 17.35 23.15 8.72 2 38.65 18.99 26.49 13.68 3 35.69 22.84 24.16 14.12 4 32.39 24.01 13.61 17.55 2.5 1 48.89 21.70 20.06 6.55 2 38.63 23.07 22.37 12.33 3 32.60 19.01 27.01 18.06 4 28.26 31.54 17.16 19.44 3.0 1 44.92 21.98 22.00 9.32 2 37.54 24.12 24.20 13.17 3 28.30 25.76 19.78 18.24 4 25.12 33.28 14.89 19.33 -
[1] WU Z Q, MA C., JIANG Z, LUO Z Y. Structure evolution and gasification characteristic analysis on co-pyrolysis char from lignocellulosic biomass and two ranks of coal: Effect of wheat straw[J]. Fuel,2019,239:180−190. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.11.015 [2] ZHAO H Y, LI Y H, SONG Q, LIU S C, YAN J, MA Q X, MA L, SHU X Q. Investigation on the thermal behavior characteristics and products composition of four pulverized coals: its potential applications in coal cleaning[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2019,44(42):23620−23638. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.07.087 [3] REN X Y, CAO J P, ZHAO X Y, YANG Z, LIU T L, FAN X, ZHAO Y P, WEI X Y. Catalytic upgrading of pyrolysis vapors from lignite over mono/bimetal loaded mesoporous HZSM-5[J]. Fuel,2018,218:33−40. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.01.017 [4] LIU Z Y, GUO X J, SHI L, HE W J, WU J F, LIU Q Y, LIU J H. Reaction of volatiles–A crucial step in pyrolysis of coals[J]. Fuel, 2015, 154: 361−369. [5] ZHOU J, WU L, ZHOU J J, LIANG K, SONG Y H, TIAN Y H, ZHANG Q L, LAN X Z. Products optimization by FeS2 catalyst for low-rank coal microwave pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2019,255:115759. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115759 [6] CHEN Z H, SHI Y, LAI D G, GAO S Q, SHI Z, TIAN Y, XU G W. Coal rapid pyrolysis in a transport bed under steam-containing syngas atmosphere relevant to the integrated fluidized bed gasification[J]. Fuel,2016,176:200−208. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.082 [7] LI Q S, LIN Y K. Exergy analysis of the LFC process[J]. Energy Convers Manag,2016,108:348−354. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2015.11.024 [8] CORTEZ D H. Co-production of syncrude and power using the toscoal process[J]. J Jpn Petrol Inst,1982,4:3−19. [9] RAMMLER R W. The production of synthetic crude oil from oil sand by application of the Lurgi-Ruhrgas process[J]. Can J Chem Eng,1970,48:552−560. doi: 10.1002/cjce.5450480513 [10] ZHOU Q, ZOU T, ZHONG M, ZHANG Y M, WU R C, GAO S Q, XU G W. Lignite upgrading by multi-stage fluidized bed pyrolysis[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2013,116:35−43. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.04.022 [11] ZHANG C, WU R C, XU G W. Coal pyrolysis for high-quality tar in a fixed-bed pyrolyzer enhanced with internals[J]. Energy Fuels,2014,28(1):236−244. doi: 10.1021/ef401546n [12] QU X, LIANG P, WANG Z F, ZHANG R. Pilot development of polygeneration process of circulating fluidized bed combustion combined with coal pyrolysis[J]. Chem Eng Technol,2011,34:61−68. [13] CHEN Z H, LI Y J, LAI D G, GENG S L, ZHOU Q, GAO S Q, XU G W. Coupling coal pyrolysis with char gasification in a multi-stage fluidized bed to co-produce high-quality tar and syngas[J]. Appl Energy,2018,215:348−355. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.02.023 [14] 周琦. 低阶煤提质技术现状及完善途径[J]. 洁净煤技术,2016,22(2):23−30.ZHOU Qi. Status and improvement approach of low rank coal upgrading technologies[J]. Clean Coal Technol,2016,22(2):23−30. [15] 白效言, 裴贤丰, 张飏, 周琦, 王岩, 王之正. 小粒径低阶煤热解油尘分离问题分析[J]. 煤质技术,2015,30(6):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7677.2015.06.001BAI Xiao-yan, PEI Xian-feng, ZHANG Yang, ZHOU Qi, WANG Yan, WANG Zhi-zheng. Analysis on separation of tar and dust during pyrolysis of small-size low rank coal[J]. Coal Quality Technol,2015,30(6):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7677.2015.06.001 [16] HAN J Z, LIU X X, YUE J R, XI B F, GAO S Q, XU G W. Catalytic upgrading of in situ coal pyrolysis tar over Ni-char catalyst with different additives[J]. Energy Fuels,2014,28(8):4934−4941. doi: 10.1021/ef500927d [17] FURIMSKY E, VANCEA L, BELANGER R. Effect of coal rank on structure of tars from low-temperature pyrolysis of Canadian coals[J]. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev,1984,23(1):134−140. doi: 10.1021/i300013a027 [18] ZHU W K, SONG W L, LIN W G. Effect of the coal particle size on pyrolysis and char reactivity for two types of coal and demineralized coal[J]. Energy Fuels,2008,22(4):2482−2487. doi: 10.1021/ef800143h [19] CUI L J, LIN W G, YAO J Z. Influences of temperature and coal particle size on the flash pyrolysis of coal in a fast-entrained bed[J]. Chem Res Chin Univ,2006,22(1):103−110. doi: 10.1016/S1005-9040(06)60056-1 [20] VALDÉS C F, CHEJNE F. Effect of reaction atmosphere on the products of slow pyrolysis of coals[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2017,126:105−117. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2017.06.019 [21] GUEDEA I, PALLARÈS D, DÍEZ L I, JOHNSSON F. Conversion of large coal particles under O2/N2 and O2/CO2 atmospheres—Experiments and modeling[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2013,112:118−128. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.02.023 [22] JIANG Y, ZONG P J, TIAN B, XU F F, TIAN Y Y, QIAO Y Y, ZHANG J H. Pyrolysis behaviors and product distribution of Shenmu coal at high heating rate: A study using TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS[J]. Energy Convers Manag,2019,179:72−80. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2018.10.049 [23] ZHANG X Y, ZHOU B X, AN D H, CUI L, ZHENG Y, DONG Y. Effect of heating rate on pyrolysis characteristics and char structure of Zhundong lignite coal[J]. J China Coal Soc,2019,44(2):604−610. [24] SUELVES I, MOLINER R, LÁZARO M J. Synergetic effects in the co-pyrolysis of coal and petroleum residues: influences of coal mineral matter and petroleum residue mass ratio[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2000,55(1):29−41. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2370(99)00072-8 [25] ELLIS N, MASNADI M S, ROBERTS D G, KOCHANEK M A, LLYUSHECHKIN A Y. Mineral matter interactions during co-pyrolysis of coal and biomass and their impact on intrinsic char co-gasification reactivity[J]. Chem Eng J,2015,279:402−408. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.057 [26] 钟梅, 赵渊, 李显, 马凤云. K+、Ca2+和Fe3+对和丰煤热解产物分布、结构及品质的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2018,46(9):1044−1054. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.09.003ZHONG Mei, ZHAO Yuan, LI Xian, MA Feng-yun. Effects of K+, Ca2+ and Fe3+ on the distribution, structure and quality of the pyrolysis products of Hefeng coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2018,46(9):1044−1054. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.09.003 [27] WANG D M, CHEN Z H, LI C M, WANG D L, LI Y J, YANG H, LIU Z E, YU J, GAO S Q. High-quality tar production from coal in an integrated reactor: Rapid pyrolysis in a drop tube and downstream volatiles upgrading over char in a moving bed[J]. Fuel,2021,285:119156. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119156 [28] 王立坤. 国富炉低阶煤热解技术在兰炭行业的市场竞争力[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用,2020,246(1):53−56+4.WANG Li-kun. Market competitiveness of CGPS of Kunitomi furnace in semi coke industry[J]. Coal Process Comp Util,2020,246(1):53−56+4. [29] 崔童敏, 李超, 周志杰, 常清华, 高瑞, 于广锁, 王福臣. 神府烟煤快速热解特性研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2015,43(11):1287−1294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.11.002CUI Tong-min, LI Chao, ZHOU Zhi-jie, CHANG Qing-hua, GAO Rui, YU Guang-suo, WANG Fu-chen. Rapid pyrolysis characteristic of Shenfu bituminous coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2015,43(11):1287−1294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.11.002 [30] 张俊杰, 徐绍平, 王光永, 杨怀天. 停留时间对低阶煤快速热解产物分布、组成及结构的影响[J]. 化工进展,2019,38(3):1346−1352.ZHANG Jun-jie, XU Shao-ping, WANG Guang-yong, YANG Huai-tian. Effect of residence time on distribution, composition and structure of products derived from fast coal pyrolysis[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2019,38(3):1346−1352. [31] 周琦, 白立强, 陈兆辉, 高士秋, 许光文. 复合流化床低阶煤热解制备兰炭的工艺条件[J]. 过程工程学报,2019,38(3):1346−1352.ZHOU Qi, BAI Li-qiang, CHEN Zhao-hui, GAO Shi-qiu, XU Guang-wen. Preparation conditions of semi-coke via pyrolysis of low-rank coal in an integrated fluidization bed[J]. Chin J Process Eng,2019,38(3):1346−1352. [32] CUI L J, SONG W L, ZHANG J Y, YAO J Z, LIN W G. Influence of the gas and particle residence time on fast pyrolysis of lignite[J]. J Energy Resour Technol,2007,129(2):152−158. doi: 10.1115/1.2719208 [33] REICHEL D, SIEGL S, NEUBERT C, KRZACK S. Determination of pyrolysis behavior of brown coal in a pressurized drop tube reactor[J]. Fuel,2015,158:983−998. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.04.066 [34] 敦启孟, 陈兆辉, 皇甫林, 周杨, 余剑, 高士秋, 刘鸿雁. 温度和停留时间对煤热解挥发分二次反应的影响[J]. 过程工程学报,2018,18(1):140−147. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.217192DUN Qi-meng, CHEN Zhao-hui, HUANG Fu-lin, ZHOU Yang, YU Jian, GAO Shi-qiu, LIU Hong-yan. Influences of temperature and residence time on secondary reactions of volatiles from coal pyrolysis[J]. Chin J Process Eng,2018,18(1):140−147. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.217192 [35] 刘振宇. 煤快速热解制油技术问题的化学反应工程根源: 逆向传热与传质[J]. 化工学报,2016,67(1):1−5.LIU Zhen-yu. Origin of common problems in fast coal pyrolysis technologies for tar: The countercurrent flow of heat and volatiles[J]. CIESC J,2016,67(1):1−5. [36] 霍朝飞. 螺旋反应器中颗粒混合及煤热解特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2015.HUO Chao-fei. Mixing of particles and coal pyrolysis behaviors in screw reactors[D]. Beijing: UCAS, 2015. [37] 周琦. 折流内构件移动床新疆淖毛湖煤热解实验研究[J/OL]. 煤炭学报, 2021.DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2020.0603.ZHOU Qi. Experimental study on the pyrolysis of Xinjiang Naomaohu coal in a moving bed with baffled internals[J/OL]. J China Coal Soc, 2021.DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2020.0603. [38] ZHU J L, JIN L J, LUO Y W, HU H Q, XIONG Y K, WEI B Y, WANG D C. Fast co-pyrolysis of a massive Naomaohu coal and cedar mixture using rapid infrared heating[J]. Energy Convers Manag,2020,205:112442. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112442 -





 下载:
下载: