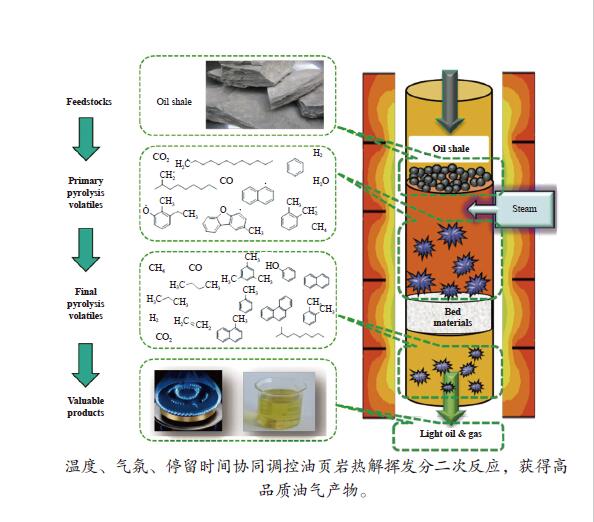
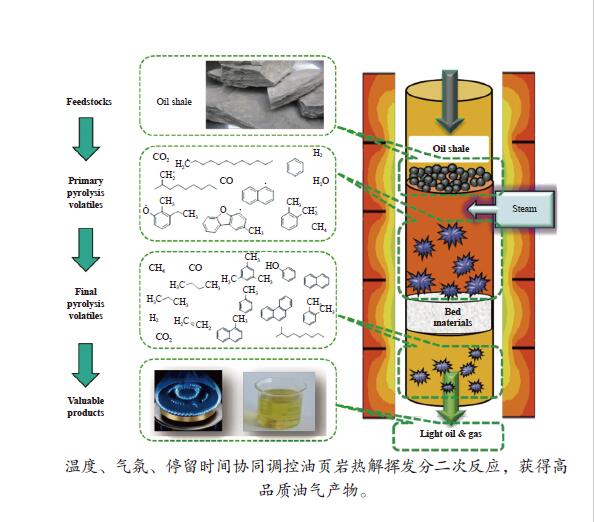
Effects of secondary reaction of primary volatiles on oil/gas yield and quality in oil shale pyrolysis
-
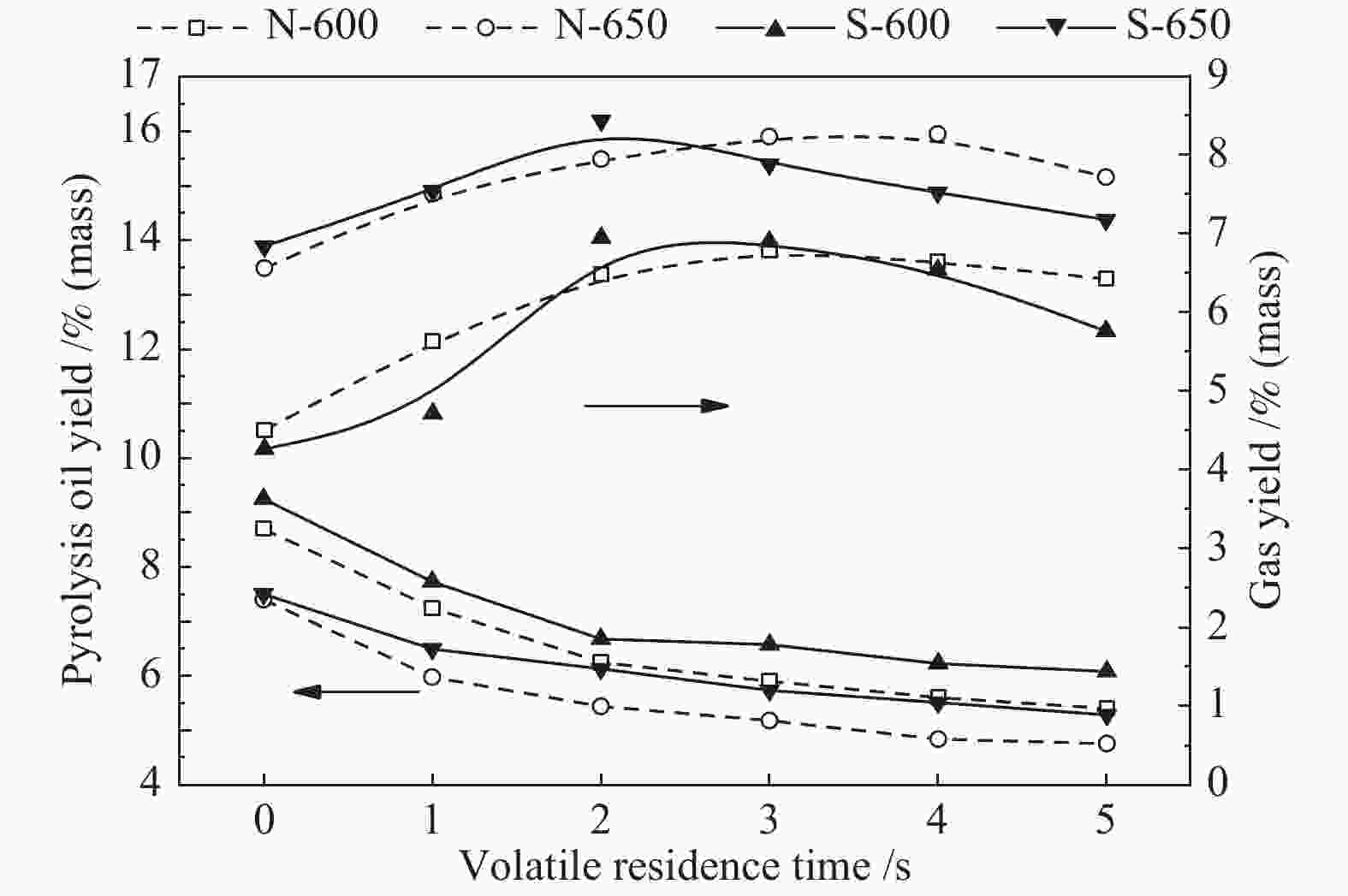
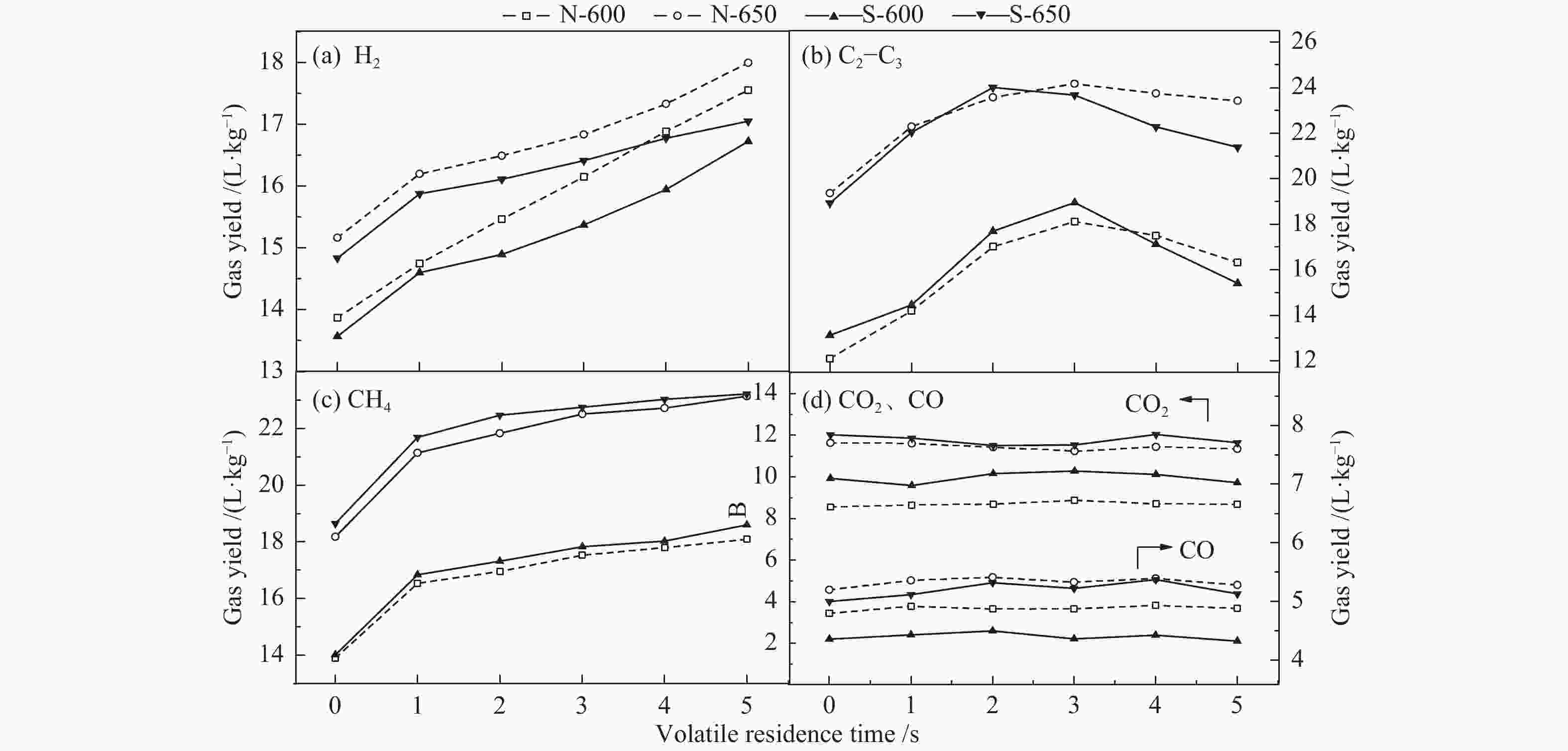
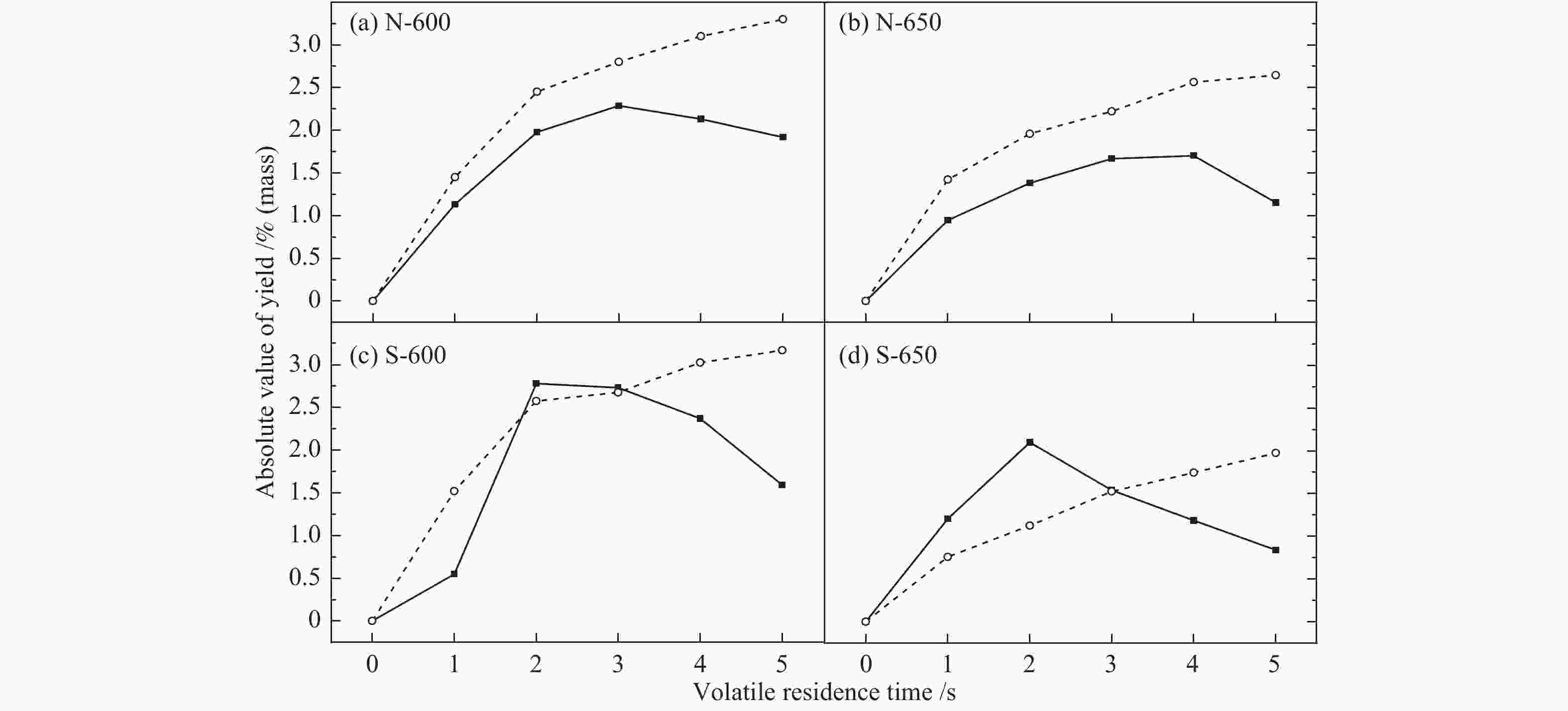
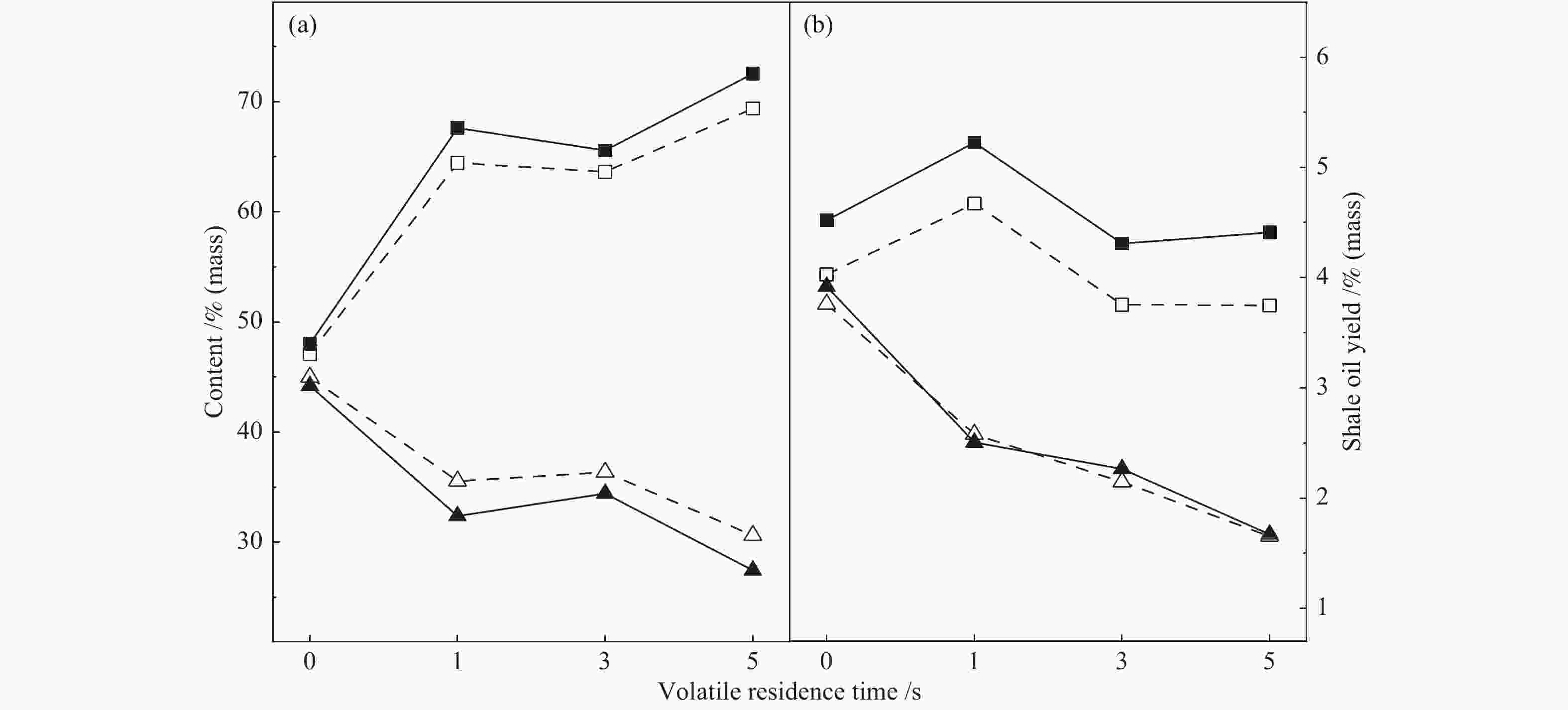
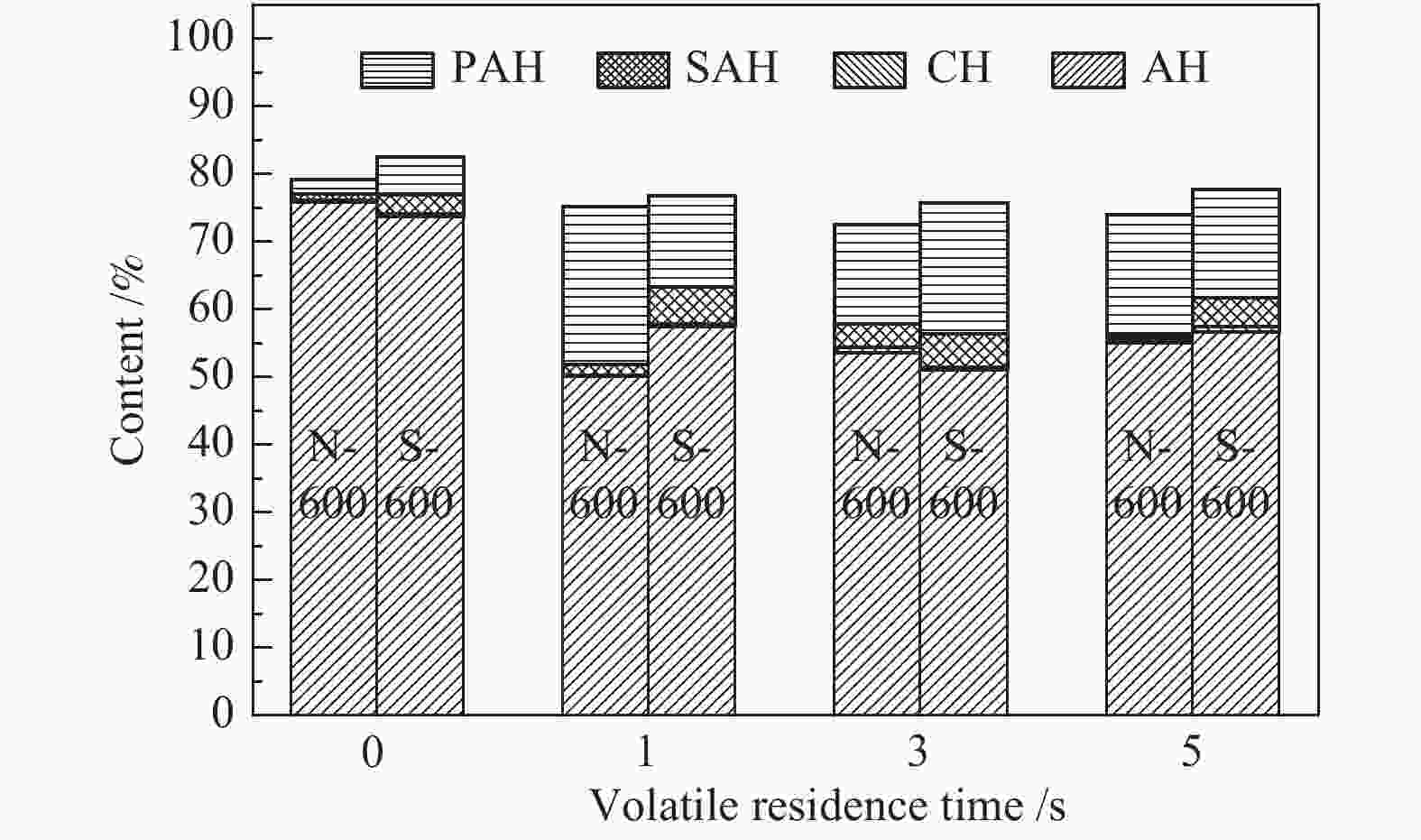
摘要: 采用两段反应器对油页岩热解释放的一次挥发分产物进行不同热态条件下的二次反应特性研究,考察第二段温度、气氛与停留时间对油气收率及品质的影响。研究结果表明,转化温度对油气产率的影响最明显,在优化第一段热解反应条件的基础上,当反应器第二段温度由600 ℃提高到650 ℃时,油页岩热解油产率下降15%(质量分数,下同),气体产率增加约20%。与氮气气氛相比,水蒸气作为第二段反应气氛能够提高液体油品收率约5%,并且热解油主要集中在馏程 < 350 ℃的汽柴油馏分。结合GC-MS分析表明,停留时间0−3 s二次反应主要为裂解过程,水蒸气能够提高油品中芳烃含量,同时抑制芳烃缩聚;3−5 s二次反应主要为缩聚过程,焦炭生成量增加,汽柴油馏分收率保持稳定,VGO馏分油收率下降约30%。Abstract: The reaction behaviors of primary volatiles from oil shale pyrolysis were investigated using a two-stage reactor under different in-situ thermal reaction conditions. The reaction parameters of secondary reactor, such as, reactor temperature, atmosphere and residence time, were studied for their effects on the pyrolysis oil/gas yield and quality. The results showed that the reaction temperature had profound influence on the oil and gas yield. The pyrolyzed shale oil and gas yield reduced by 15% and increased by 20% (mass) respectively, with the temperature of 2nd stage reactor increasing from 600 to 650 °C under optimized reaction condition of 1st stage. Comparing with nitrogen atmosphere, the liquid oil yield could be enhanced by 5% when steam was added as the reaction atmosphere in the second stage, and the corresponding oil was mainly concentrated in the gasoline and diesel distillations (that is, boiling point < 350 °C). The GC-MS analysis illustrated that the secondary reaction at the residence time of 0−3 s was mainly pyrolysis while the presence of steam could increase the content of aromatics in the oil and meanwhile suppress the condensation of aromatics. When the residence time was greater than 3−5 s, the secondary reaction was mainly condensation of poly-aromatics, which led to the increase of coke. Meanwhile, the gasoline and diesel oil yield remained stable, and the VGO fractions decreased by about 30%.
-
Key words:
- oil shale /
- pyrolysis volatiles /
- steam reforming /
- secondary reaction
-
表 1 桦甸油页岩的工业分析、元素分析和铝甑分析
Table 1 Proximate, ultimate and Fischer assay analyses of Huadian oil shale
Proximate analysis wd/% Ultimate analysis wad/% Fischer assay wad/% A V FC C H O* N S oil gas water coke 49.94 33.14 16.92 34.32 3.56 11.02 0.89 0.78 11.30 9.62 3.92 75.16 d: dry basis; ad: air-dried basis; *: calculated by difference -
[1] Statistical review of world energy[Z]. London: British Petroleum, 2020. [2] 石剑, 李术元, 马跃. 爱沙尼亚油页岩及其热解产物的电子顺磁共振研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2018,46(1):1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.01.001SHI Jian, LI Shu-yuan, MA Yue. Electron paramagnetic resonance study of Estonia oil shale and its pyrolysis products[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2018,46(1):1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.01.001 [3] ZHOU H R, LI H W, DUAN R H, YANG Q C. An integrated scheme of coal-assisted oil shale efficient pyrolysis and high-value conversion of pyrolysis oil[J]. Energy,2020,196:117106. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117106 [4] 于海龙, 姜秀民, 赵翔, 周俊虎, 岑可法. 油页岩与煤的混烧特性研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2004,32(3):274−277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2004.03.004YU Hai-long, JIANG Xiu-min, ZHAO Xiang, ZHOU Jun-hu, CEN Ke-fa. Study on mixed burning characteristics of oil shale and coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2004,32(3):274−277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2004.03.004 [5] DAI M, YU Z, Fang S, MA X. Behaviors, product characteristics and kinetics of catalytic co-pyrolysis spirulina and oil shale[J]. Energy Convers Manage,2019,192:1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.04.032 [6] 高子翔. 纤维素与半纤维素在固定床反应器中的热解特性研究[D]. 淄博: 山东理工大学, 2019.GAO Zi-xiang. Study on the pyrolysis characteristics of cellulose and hemicellulose in a fixed bed reactor[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology, 2019. [7] CHEN Z H, TIAN Y, LAI D G, ZHAN J H, GAO S Q. Oil shale pyrolysis in a moving bed with internals enhanced by rapid preheating in a heated drop tube[J]. Energ Convers Manage,2020,224:113358. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113358 [8] LAI D G, CHEN Z H, LIN L X, ZHANG Y M, GAO S Q, XU G W. Secondary cracking and upgrading of shale oil from pyrolyzing oil shale over shale ash[J]. Energy Fuels,2015,29(4):2219−2226. doi: 10.1021/ef502821c [9] HU C S, LIU C, LIU Q Y, ZHANG H Y, WU S L, XIAO R. Effects of steam to enhance the production of light olefins from ex-situ catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2020,210:106562. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2020.106562 [10] EFTHYMIOS K, YANG W H, WLODZIMIERZ B. Production of liquid feedstock from biomass via steam pyrolysis in a fluidized bed reactor[J]. Energy Fuels,2013,27(8):4748−4759. doi: 10.1021/ef400580x [11] 秦梓雅. 污水污泥流化床水蒸气气化焦油特性的研究[D]. 天津: 天津工业大学, 2018.QIN Zi-ya. Study on characteristics of tar in fluidized bed steam gasification of sewage sludge[D]. Tianjin: Tiangong University, 2018. [12] WANG H, WANG L, ZHANG J P, JING Y F, CAO Y B. Effects of pyrolysis temperature and reaction time on the performance of swine-manure-derived bio-binder[J]. Transport Res Part D: Trans Environ,2020,89:102608. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2020.102608 [13] 黄雷, 张玉明, 张亮, 张晓晨, 孙国刚. 页岩灰和FCC催化剂调控油页岩热解产物二次反应特性[J]. 化工学报,2017,68(10):3770−3778.HUANG Lei, ZHANG Yu-ming, ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Xiao-chen, SUN Guo-gang. Effects of shale ash and FCC catalyst on adjusting secondary reaction of volatiles in oil shale pyrolysis[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2017,68(10):3770−3778. [14] 吴仕生, 曾玺, 任明威, 汪印, 徐绍平, 许光文. 含氧/蒸汽气氛中煤高温分解产物分布及反应性[J]. 燃料化学学报,2012,40(6):660−665. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.06.004WU Shi-sheng, ZENG Xi, REN Ming-wei, WANG Yin, XU Shao-ping, XU Guang-wen. Distribution and reactivity of decomposition products of coal at high temperature in oxygen/steam atmosphere[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2012,40(6):660−665. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.06.004 [15] HAYASHI J I, IWATSUKI M, MORISHITA K, TSUTSUMI A, CHIBA T. Roles of inherent metallic species in secondary reactions of tar and char during rapid pyrolysis of brown coals in a drop-tube reactor[J]. Fuel,2002,81(15):1977−1987. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00128-X [16] XU W C, TOMITA A. Effect of temperature on the flash pyrolysis of various coals[J]. Fuel,1987,66(5):632−636. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(87)90271-7 [17] CHEN Y Q, LIU B, YANG H P, WANG X H, ZHANG X, CHEN H P. Generalized two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy to reveal the mechanisms of lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis[J]. Proc Combust Inst,2018,37(3):3013−3021. [18] 畅志兵, 初茉, 张超, 王文娟, 曲洋. 颗粒粒径对油页岩热解产油率的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2015,43(6):663−668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.06.004CHANG Zhi-bing, CHU Mo, ZHANG Chao, WANG Wen-juan, QU Yang. Influence of particle size on oil yield from pyrolysis of oil shale[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2015,43(6):663−668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.06.004 [19] XIONG R, DONG L, YU J, ZHANG X F, JIN L, XU G W. Fundamentals of coal topping gasification: characterization of pyrolysis topping in a fluidized bed reactor[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2010,91(8):810−817. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.07.005 [20] YAN J W, JIANG X M, HAN X X. Study on the characteristics of the oil shale and shale char mixture pyrolysis[J]. Energy Fuels,2009,23(12):5792−5797. doi: 10.1021/ef9008345 [21] 林炳丞. 高含油污泥的定向催化热解研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020.LIN Bing-cheng. Study on directional catalytic pyrolysis of high oily Sludge[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020. [22] NAZZAL J M. Influence of heating rate of the pyrolysis of Jordan oil shale[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2002,62(2):225−238. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2370(01)00119-X [23] YAN F, LUO S Y, Hu Z Q, XIAO B, CHENG G. Hydrogen-rich gas production by steam gasification of char from biomass fast pyrolysis in a fixed-bed reactor: Influence of temperature and steam on hydrogen yield and syngas composition[J]. Bioresour Pyrolysis Technol,2010,101(14):5633−5637. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.025 [24] SONG Y, WANG Y, HU X, HU S, XIANG J, ZHANG L, ZHANG S, MIN Z H, LI C Z. Effects of volatile–char interactions on in situ destruction of nascent tar during the pyrolysis and gasification of biomass. Part I. Roles of nascent char[J]. Fuel,2014,122(122):60−66. [25] 王擎, 王锐, 贾春霞, 任立国, 王浩添, 闫宇赫. 油页岩热解的FG-DVC模型[J]. 化工学报,2014,65(6):2309−2315.WANG Qing, WANG Rui, JIA Chun-xia, REN Li-guo, WANG Hao-tian, YAN Yu-he. FG-DVC model for oil shale pyrolysis[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2014,65(6):2309−2315. [26] DIEGO F, CANO A G, BAREA S N, PEDRO O. The influence of temperature and steam on the yields of tar and light hydrocarbon compounds during devolatilization of dried sewage sludge in a fluidized bed[J]. Fuel,2013,108:341−350. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.01.022 [27] PARTHASARATHY P, NARAYANAN K S. Hydrogen production from steam gasification of biomass: Influence of process parameters on hydrogen yield-A review[J]. Renewable Energy,2014,66:570−579. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2013.12.025 [28] LI Q Y, HAN X X, LIU Q Q, JIANG X M. Thermal decomposition of Huadian oil shale. Part 1. Critical organic intermediates[J]. Fuel,2014,121:109−116. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.12.046 [29] CHEN B, HAN X X, LI Q Y, JIANG X M. Study of the thermal conversions of organic carbon of Huadian oil shale during pyrolysis[J]. Energy Convers Manage,2016,127:284−292. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2016.09.019 [30] LAI D G, SHI Y, GENG S L, CHEN Z H, GAO S Q, ZHAN J H, XU G W. Secondary reactions in oil shale pyrolysis by solid heat carrier in a moving bed with internals[J]. Fuel,2016,173:138−145. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.01.052 -




 下载:
下载: