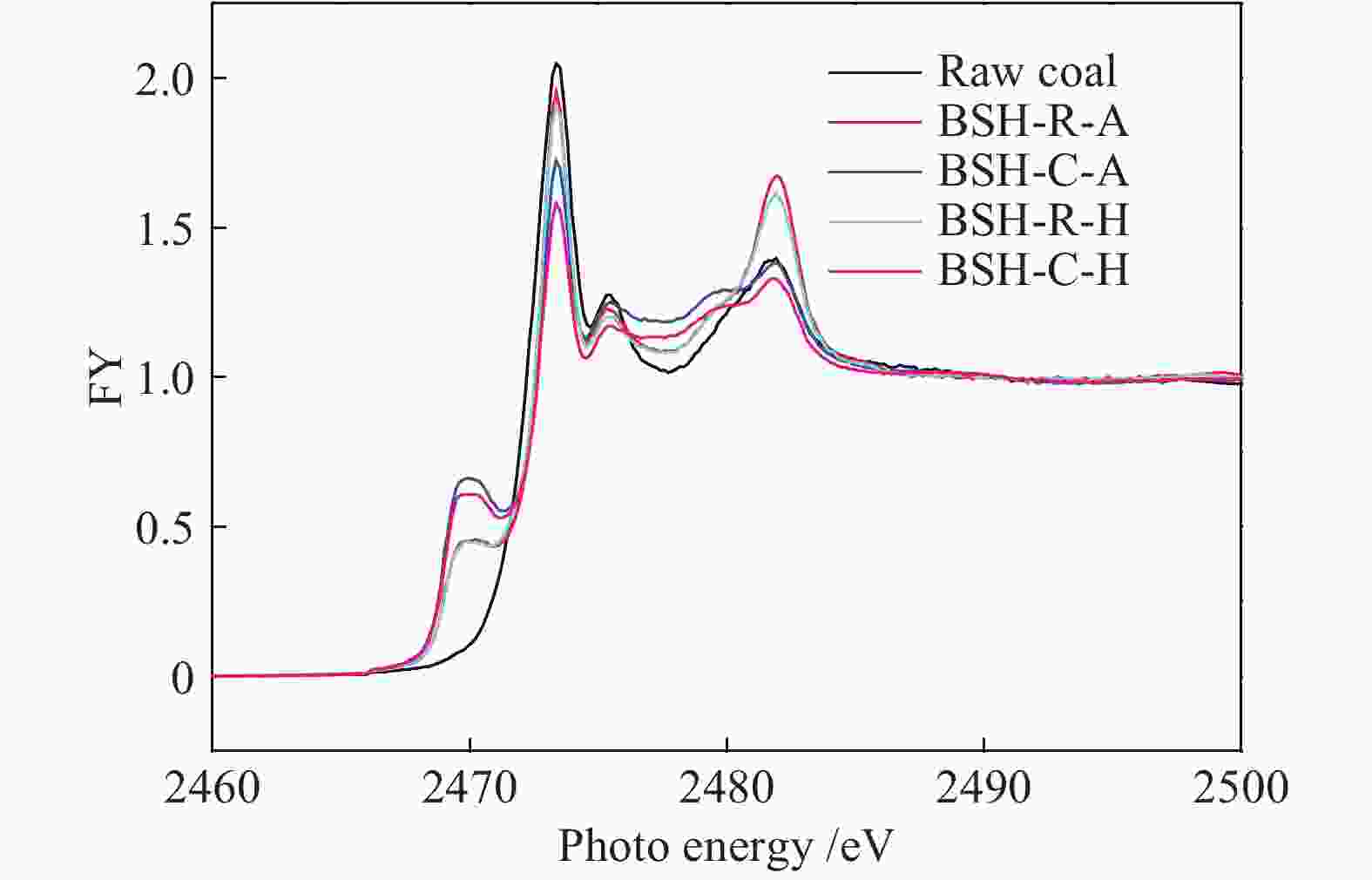
Effects of iron catalyst and atmosphere on sulfur transformation during pressurized low-temperature pyrolysis of Baishihu coal
-
摘要: 选取镜质组含量高的白石湖煤为研究对象,考察了高分散铁催化剂及热解气氛对煤加压低温热解过程中硫元素迁移影响。采用GC-SCD和FT-ICR MS研究了热解焦油中含硫化合物分子组成,采用XANES研究了热解半焦中硫分子结构。结果表明,白石湖煤中的硫化物主要是煤主体结构中侧链的S1类。催化剂中的单质硫助剂在热解过程中部分会进入焦油中形成硫醇或硫醚化合物。高分散铁系催化剂能活化煤中的氢原子,促进焦油中芳香硫化物的氢化饱和及裂解。该催化剂优先捕获硫化氢,增加了焦炭中黄铁矿的含量,抑制了半焦中硫酸盐的生成。在H2气氛和高分散铁系催化剂的作用下,噻吩类化合物明显减少,亚砜类化合物减少。Abstract: A vitrinite-rich low rank coal, Baishihu (BSH) coal with moderate sulfur content was treated by dehydration and crushing. The treated samples were pyrolyzed in an alloy tubular reactor under 2 MPa. Influence of iron catalyst and atmosphere on sulfur transformation during pressurized low-temperature coal pyrolysis was investigated. Molecular composition of sulfur compounds in tar was characterized by gas chromatography with sulfur chemiluminescence detector (GC-SCD) combined with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS). Sulfur K-edge XANES was used to study sulfur molecular structure after pyrolysis. Sulfur compounds in BSH coal are predominantly S1 class species in branch chain of the coal. Elemental sulfur in catalyst enters the tar and forms mercaptan or thioether compounds during pyrolysis. Iron catalyst promotes activation of hydrogen atoms in coal and contributes to hydrogenation saturation and cracking of aromatic sulfide in tar. The catalyst preferentially captures H2S to increase content of pyrite in char and inhibits formation of sulfate. Under H2 atmosphere, significant decrease of thiophene compounds is observed with catalyst coupled with decrease of sulfoxide compounds.
-
Key words:
- sulfur transformation /
- FT-ICR MS /
- XANES /
- coal pyrolysis /
- iron catalyst
-
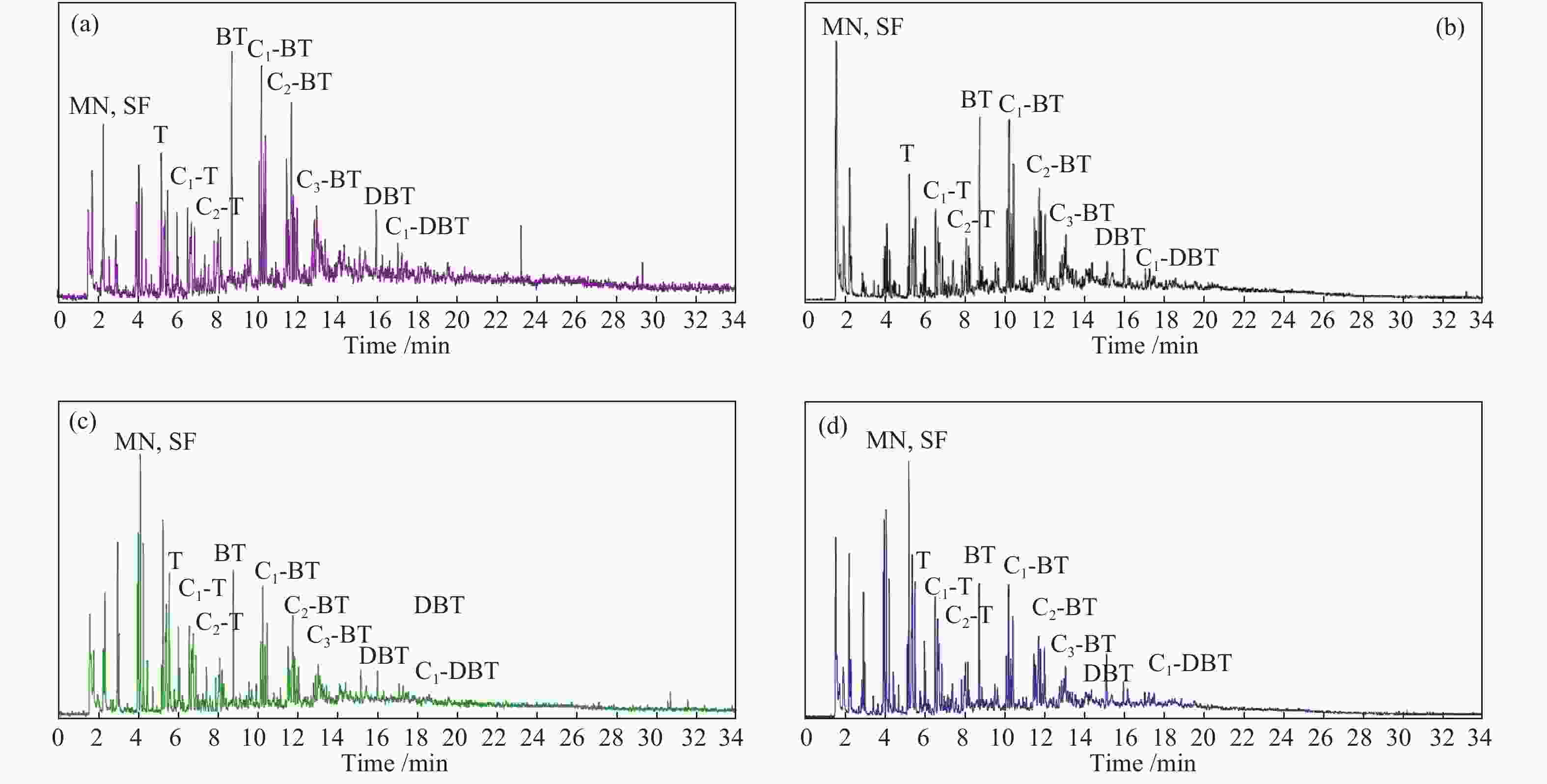
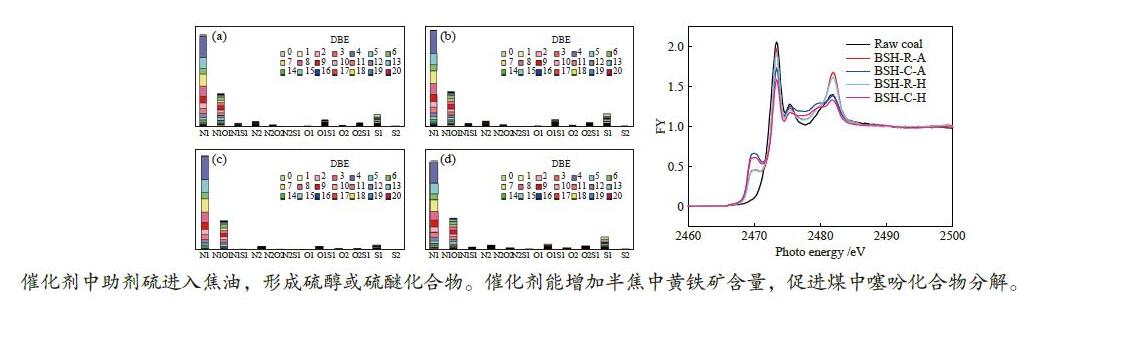
Figure 2 GC-SCD analysis of tar by pyrolysis of (a)BSH-R-A, (b)BSH-C-A, (c)BSH-R-H, (d)BSH-C-H
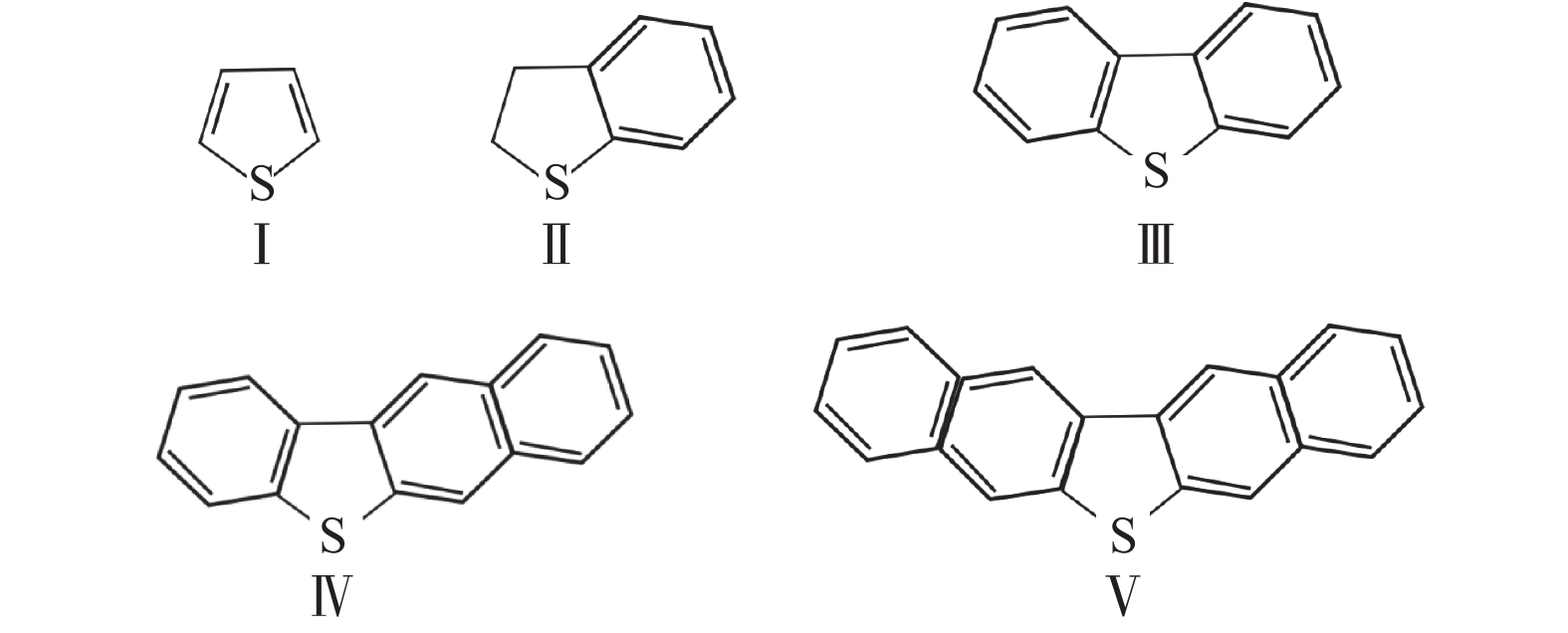
sulfur-containing compounds are denoted by the following letters: mercaptan (MN), sulfoether (SF), thiophene (T), thiophene derived compounds (Ts), benzothiophene (BT), benzothiophene derived compounds (BTs), dibenzothiophene (DBT), dibenzothiophene derived compounds (DBTs)
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of coal samples
Ultimate analyses wdaf/% Proximate analyses w/% C H N S O Mad Ad Vdaf FCdaf 75.01 4.82 0.96 1.16 18.05 16.67 6.37 50.60 49.4 note: ad is air-dried basis; daf is dried and ash-free basis Table 2 Sulfur forms analysis of coal samples
Sulfur forms in coal w/% Sulfur form ratio in total S w/% St Ss Sp So Ss Sp So 1.16 0.07 0.04 1.05 6.17 3.17 90.66 note: St is total sulfur; Ss is sulfate sulfur; Sp is pyrite; So is organic sulfur Table 3 Effect of iron catalysts and atmosphere on pyrolysis
Sample# Tar yield w/% Char yield w/% BSH-R-A 8.21 63.57 BSH-C-A 8.37 63.50 BSH-R-H 8.24 63.47 BSH-C-H 8.54 63.11 #: sample code A-B-C means that the sample was obtained by pyrolysis of coal A (BSH = Baishihu coal) with the addition of B (R = raw coal, C = iron catalyst) in atmosphere C (H = H2, A = Ar) Table 4 Sulfur distribution in different phases
BSH-R-A w/% BSH-C-A w/% BSH-R-H w/% BSH-C-H w/% gas tar char gas tar char gas tar char gas tar char 5.22 57.97 36.81 9.28 43.46 47.26 5.51 63.85 30.64 10.26 40.76 48.98 Table 5 GC-SCD analysis result of tar by pyrolysis of (a)BSH-R-A, (b)BSH-C-A, (c)BSH-R-H, (d)BSH-C-H
Sample MN&SF/% T&Ts/% BT&BTs/% DBT&DBTs/% BSH-R-A 45.66 19.28 32.41 2.65 BSH-C-A 49.43 16.37 31.75 2.45 BSH-R-H 41.39 31.81 24.35 2.45 BSH-C-H 42.16 30.73 25.02 2.09 -
[1] CHEN Z H, GAO S Q, XU G W. Analysis and control methods of coal pyrolysis process[J]. J CIESC,2017,68(10):3693−3707. (in Chinese) [2] WANG J G, ZHAO X H. Demonstration of key technologies for clean and efficient utilization of low-rank coal[J]. Bull Chin Acad of Sci,2012,27(3):382−388. [3] WANG X L, GUO H Q, LIU F R, HU R S, WANG M J. Effects of CO2 on sulfur removal and its release behavior during coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2016,165:484−489. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.10.047 [4] GARCIA R, MOINELO S R, LAFFERTY C J, SNAPE C E. Pyrolytic desulphurisation of some high-sulphur coals[J]. Energy Fuels,1991,5(4):582−586. doi: 10.1021/ef00028a009 [5] CHEN H K, LI B Q, YANG J L, ZHANG B J. Transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis and hydropyrolysis of coal[J]. Fuel,1998,77(6):487−493. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(97)00275-5 [6] WILLIAM H, CALKINS. Investigation of organic sulfur-containing structures in coal by flash pyrolysis experiments[J]. Energy Fuels,1987,1(1):59−64. doi: 10.1021/ef00001a011 [7] JORJANI E, YPERMAN J, CARLEER R, REZAI B. Reductive pyrolysis study of sulfur compounds in different Tabas coal samples (Iran)[J]. Fuel,2006,85(1):114−120. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2005.05.007 [8] HUANG F, ZHANG L Q, YI B J, XIA Y Z, ZHENG C J. Effect of H2O on pyrite transformation behavior during oxy-fuel combustion[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2015,131:458−465. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.12.027 [9] LEVY J H, WHITE T J. The reaction of pyrite with water vapor[J]. Fuel,1988,67(10):1336−1339. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(88)90114-7 [10] SUGAWARA K, ABE K, SUGAWARA T, NISHIYAMA Y, SHOLES M. Dynamic behaviour of sulfur forms in rapid pyrolysis of coals with alkali treatment[J]. Fuel,1995,74(12):1823−1829. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)80014-9 [11] GARCÍA-LABIANO F, HAMPARTSOUMIAN E, WILLIAMS A. Determination of sulfur release and its kinetics in rapid pyrolysis of coal[J]. Fuel,1995,74(7):1072−1079. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)00049-B [12] BAI Y, WANG Y, ZHU S, LI F, XIE K C. Structural features and gasification reactivity of coal chars formed in Ar and CO2 atmospheres at elevated pressures[J]. Energy,2014,74:464−470. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.07.012 [13] WANG M, TIAN J, DANIEL G R, CHANG L, XIE K C. Interactions between corncob and lignite during temperature-programmed co-pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2015,142(1):102. [14] HE H, XIA J L, HUANG G H, JIANG H C, TAO X X, ZHAO Y D, HE W. Analysis of the elemental sulfur bio-oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans with sulfur K-edge XANES[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol,2011,27(8):1927−1931. doi: 10.1007/s11274-010-0629-7 [15] WANG M J, HU Y F, WANG J C, CHANG L P, WANG H. Transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis of inertinite-rich coals andcorrelation with their characteristics[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2013,104:585−592. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.05.010 [16] YANG N N, GUO H Q, LIU F R, ZHANG H, HU Y F, HU R S. Effects of atmospheres on sulfur release and its transformation behavior during coal thermolysis[J]. Fuel,2018,215:446−453. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.11.099 [17] WU Z, RODGERS R P, MARSHALL A G. Compositional determination of acidic species in Illinois No. 6 coal extracts by electrospray ionization fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy Fuels,2004,18(5):1424−1428. doi: 10.1021/ef049933x [18] WU Z, RODGERS R P, MARSHALL A G. Two-and three-dimensional van krevelen diagrams: A graphical analysis complementary to the kendrick mass plot for sorting elemental compositions of complex organic mixtures based on ultrahigh-resolution broadband fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass measurements[J]. Anal Chem,2004,76(9):2511−2516. doi: 10.1021/ac0355449 [19] SHI Q, PAN N, LONG H Y, CUI D C, GUO X F, LONG Y H, CHUNG K H, ZHAO S Q. Characterization of middle-temperature gasification coal tar. part 3: Molecular composition of acidic compounds[J]. Energy Fuels,2013,27(1):108−117. doi: 10.1021/ef301431y [20] KONG J, WEI X Y, YA H L, LI Z K, ZHAO M X, LI Y, ZONG Z M. Analysis of extractable basic nitrogen compounds in buliangou subbituminous coal by positive-ion ESI FT-ICR MS[J]. Fuel,2015,159:385−391. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.06.091 [21] SHI Q, HOU D J, CHUNG K H, XU C M, ZHAO S Q, ZHANG Y H. Characterization of heteroatom compounds in a crude oil and its saturates, aromatics, resins and asphaltenes (SARA) and non-basic nitrogen fractions analyzed by negative-ion electrospray ionization fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy Fuels,2010,24(4):2545−2553. doi: 10.1021/ef901564e [22] LIU M, WANG Y G, ZHAO P, QU S J, CHEN G F. Molecular characterization of sulfur and nitrogen compounds in THF extract of Baishihu lignite[J]. J Chem Technol,2019,47(3):257−262. [23] ZHAO P, MAO X F, ZHAO Y, LI J F, CHANG Q L, LI W B, HU F T. Study on moderate hydrogenation liquefaction of lignite in Eastern area of Xinjiang[J]. Coal Conver,2019,42(5):47−53. [24] SHI Q, XU C M, ZHAO S Q, CHUNG K H, ZHANG Y H, GAO W. Characterization of basic nitrogen species in coker gas oils by positive-ion electrospray ionization fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy Fuels,2009,24(1):563−569. [25] LIU P, SHI Q, CHUNG K H, ZHANG Y H, PAN N, ZHAO S Q, XU C M. Molecular characterization of sulfur compounds in venezuela crude oil and its SARA fractions by electrospray ionization fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy Fuels,2010,24(9):5089−5096. doi: 10.1021/ef100904k [26] YAMASHITA H, OHTSUKA Y, YOSHIDA S. Change of local structure of iron compounds on brown coal during devolatilization and gasification[J]. Energy Fuels,1989,3(5):686−690. [27] RUTKOWSKI P, MULLENS S, YPERMAN J, GRYGLEWICZ G. AP-TPR investigation of the effect of pyrite removal on the sulfur characterization of different rank coals[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2002,76(2):121−138. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3820(02)00019-X [28] MONTANO P A, BOMMANNAVAR A S, SHAH V. Mössbauer study of transformations of pyrite under conditions of coal liquefaction[J]. Fuel,1981,60(8):703−711. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(81)90223-4 [29] MONTANO P A, VAISHNAVA P P, KING J A. Mössbäuer study of decomposition of pyrite in hydrogen[J]. Fuel,1981,60(8):712−716. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(81)90224-6 -





 下载:
下载: