Structural difference of gas coal separation components and its effect on sulfur transformation during pyrolysis of high sulfur coal
-
摘要: 利用ZnCl2溶液将两种气煤分别分选为不同镜质组含量的四种组分,通过核磁共振波谱(13C NMR)、煤岩分析仪、X射线荧光光谱(XRF)和基氏流动仪等表征分析了分选组分的炭结构、显微岩相组成、灰成分和胶质体行为,结合X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)探讨了不同气煤分选组分对高硫煤硫分热变迁行为及焦炭中形态硫分布的影响。结果表明,随着气煤中镜质组含量的增加,脂肪碳比例增大,热解过程中挥发分释放量增多,其中的氢自由基促进了形态硫的分解且及时稳定生成的硫自由基,形成含硫气体释放,使焦中硫含量降低;气煤中低密度组分的最大流动度最大、塑性区间最宽,与高硫煤共热解过程中胶质体稳定性最好;气煤中碱性矿物质主要富集在高密度组分中,导致共热解焦中硫化物硫和硫酸盐硫增加;共热解过程中,富集气煤中镜质组和选用碱性矿物质易脱除的煤种有利于焦中硫分的降低。Abstract: Two gas coals were respectively separated into four components with different vitrinite content using ZnCl2 solution. The carbon structure, composition of coal macerals and minerals, and plastic layer behavior of separating components were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (13C NMR), coal rock analyzer, X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) and Gieseler fluidity. Combining with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), effect of different gas coal separation components on sulfur transformation behavior during pyrolysis of high-sulfur coal and distribution of sulfur forms in coke was investigated. The results show that with increase of vitrinite content in gas coal, the relative ratio of aliphatic carbon in coal increases, and the release amount of volatiles increases during pyrolysis; hydrogen free radicals in volatiles promote decomposition of sulfur, stabilize sulfur free radicals in time and release as sulfur-containing gases, and thus sulfur content in coke is reduced. Low density components in gas coal have the largest maximum fluidity and widest plastic range, and stability of plastic layer is the best during co-pyrolysis with high sulfur coal. The basic minerals in gas coal are mainly enriched in high density components, which leads to increase of sulfide sulfur and sulfate sulfur in the coke. For utilization of gas coal in coal-blending pyrolysis, enrichment of vitrinite and selection of coals with easier removal of alkaline minerals are beneficial for reducing sulfur in coke.
-
Key words:
- gas coal /
- separation /
- high sulfur coal /
- sulfur transformation /
- plastic layer /
- alkaline minerals
-
表 1 煤样的工业分析、元素分析和形态硫分析
Table 1 Proximate, ultimate, and sulfur form analyses of coal samples
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis w/% Sulfur form wd/% Mad Ad Vdaf Cdaf Hdaf Ndaf St,d O* Ss Sp So HCG-R 1.55 8.88 40.52 83.98 5.70 2.05 0.52 7.70 0.01 0.14 0.37 LN-R 1.40 6.10 37.63 84.96 5.44 1.13 0.52 7.91 0.01 0.28 0.23 LL 0.20 9.94 19.90 88.49 4.69 1.42 1.94 3.25 0.02 0.26 1.66 note: ad: air dried basis; d: dry basis; daf: dry and ash-free basis; St: total sulfur; Ss: sulfate sulfur; Sp: pyritic sulfur; So: organic sulfur; O*: by difference 表 2 气煤分选组分的工业分析和元素分析
Table 2 Proximate and ultimate analyses of separation fractions from the two gas coals
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis w/% Mad Ad Vdaf Cdaf Hdaf Ndaf St,d O* HCG-D1 1.44 3.46 44.37 83.93 5.76 2.09 0.49 7.71 HCG -D2 1.47 8.85 37.29 84.19 5.56 1.96 0.48 7.76 HCG -D3 1.43 14.97 34.12 84.08 5.49 1.92 0.48 7.95 HCG -D4 1.29 23.84 31.57 82.88 5.55 1.88 0.50 9.03 LN-D1 1.20 3.14 39.47 84.65 5.57 1.15 0.29 8.33 LN-D2 1.24 5.64 33.66 85.35 5.15 1.08 0.38 8.01 LN-D3 1.20 9.62 31.86 84.63 5.04 1.08 0.57 8.61 LN-D4 1.14 17.48 30.41 83.51 4.95 1.05 0.92 9.37 note: ad: air dried basis; d: dry basis; daf: dry and ash-free basis; O*: by difference; St: total sulfur 表 3 13C NMR中不同类性质碳对应的化学位移
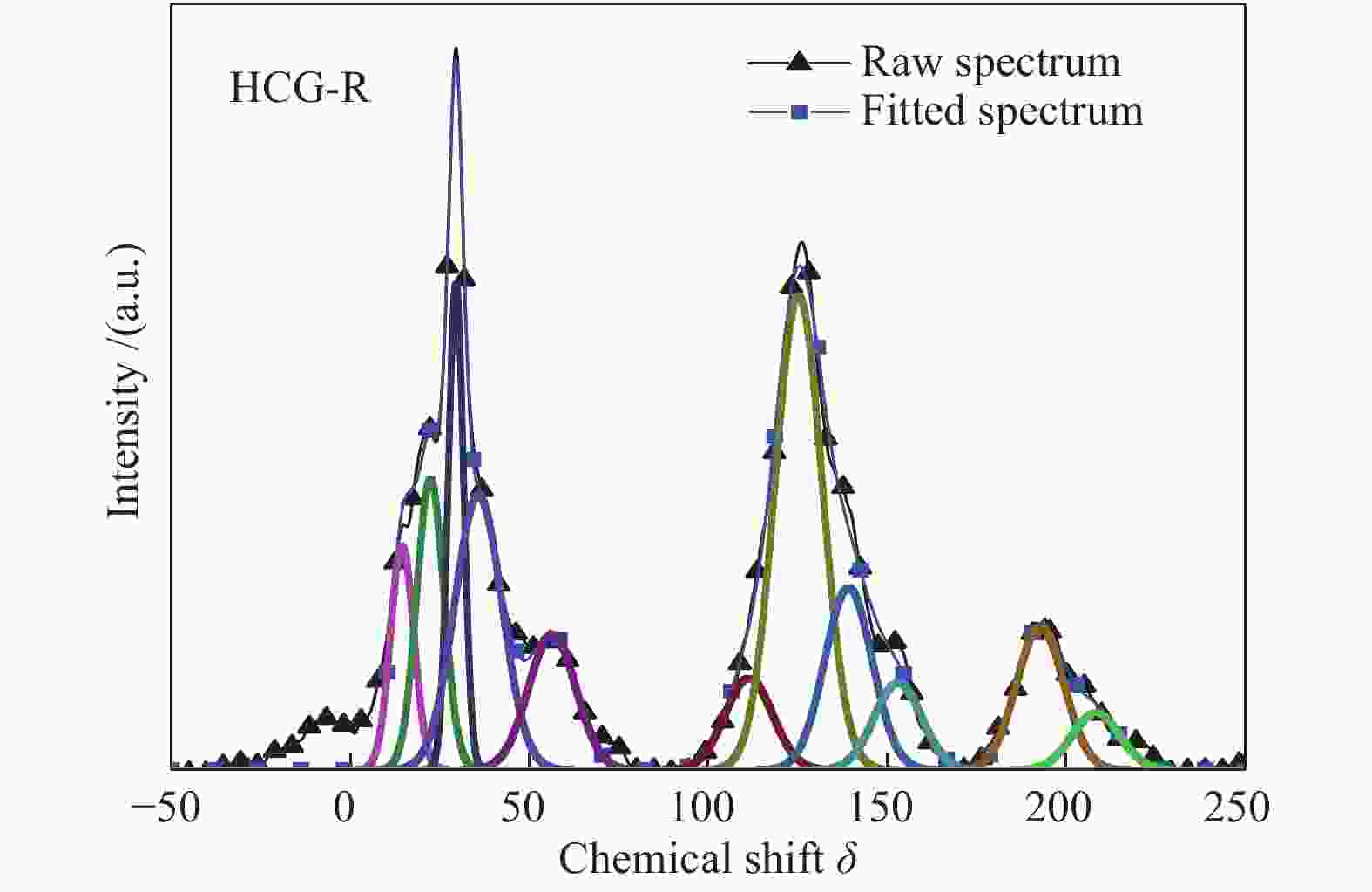
Table 3 Chemical shifts corresponding to different types of carbons in 13C NMR
Chemical shift δ Carbon type Carbon structure Symbol 14−22 aliphatic methyl 
fala 22−26 aromatic methyl −CH2−CH2−CH3 fal1 26−37 methylene −CH2−CH2−CH2− fal2 37−50 quaternary sp3 C 
fal3 50−95 oxygen aliphatic carbon −CH2−O−, −CH−O− falO 95−129 protonated aromatic carbon 
faH 129−137 aromatic bridgehead carbon 
faB 137−149 aliphatic substituted aromatic carbon 
faS 149−164 oxygen aromatic carbon 
faO 164−190 carboxyl −COOH/R faC1 190−220 quinone and carbonyl carbon 
faC2 表 4 不同煤样的灰成分分析
Table 4 Ash composition analyses of different coal samples
Sample Ash composition w/% MCI/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 TiO2 K2O Na2O P2O5 HCG-R 56.98 26.61 5.50 3.23 1.42 1.48 1.10 1.08 0.77 0.22 0.03 HCG-D1 53.05 23.88 7.25 4.91 1.92 2.31 1.79 1.00 0.78 0.50 0.02 HCG-D2 58.68 25.55 5.61 2.14 1.47 1.02 1.17 1.11 0.59 0.26 0.03 HCG-D3 61.13 25.98 4.24 1.59 1.19 0.98 0.96 1.05 0.57 0.15 0.03 HCG-D4 61.17 28.20 3.38 1.23 0.95 0.87 0.83 1.09 0.44 0.12 0.04 LN-R 37.82 20.60 14.48 11.92 3.43 5.95 0.75 0.27 0.78 0.04 0.08 LN-D1 34.48 23.14 10.97 11.63 4.33 10.06 0.94 0.19 1.06 0.05 0.04 LN-D2 43.50 25.92 9.93 6.60 2.42 6.62 0.73 0.30 1.29 0.03 0.04 LN-D3 43.93 24.79 10.23 7.58 2.50 7.02 0.64 0.30 1.08 0.02 0.07 LN-D4 43.04 21.45 11.56 11.12 3.38 5.91 0.66 0.28 0.73 0.03 0.15 表 5 气煤及其分选组分的煤岩分析和黏结指数
Table 5 Maceral analysis and caking index of gas coal and its separation components
Sample Maceral group/% Rmax/% G V I E M HCG-R 76.35 19.05 0.51 4.09 0.83 67.75 HCG-D1 86.96 10.70 0.49 1.85 0.80 83.14 HCG-D2 64.05 29.17 0.27 6.51 0.82 30.91 HCG-D3 53.09 33.72 0.17 13.02 0.82 18.24 HCG-D4 43.70 37.53 0.13 18.64 0.78 17.37 LN-R 61.22 34.65 0.83 3.30 0.71 46.88 LN-D1 69.37 29.09 0.84 0.70 0.71 66.29 LN-D2 45.51 51.72 0.26 2.51 0.76 17.47 LN-D3 41.33 55.73 0.40 2.54 0.79 15.95 LN-D4 39.02 56.78 0.27 3.93 0.82 15.14 note: V: vitrinite, I: inertinite, E: exinite, M is minerals, Rmax: average maximum vitrinite reflectance, G: caking index 表 6 气煤及分选组分的焦产率和脱硫率
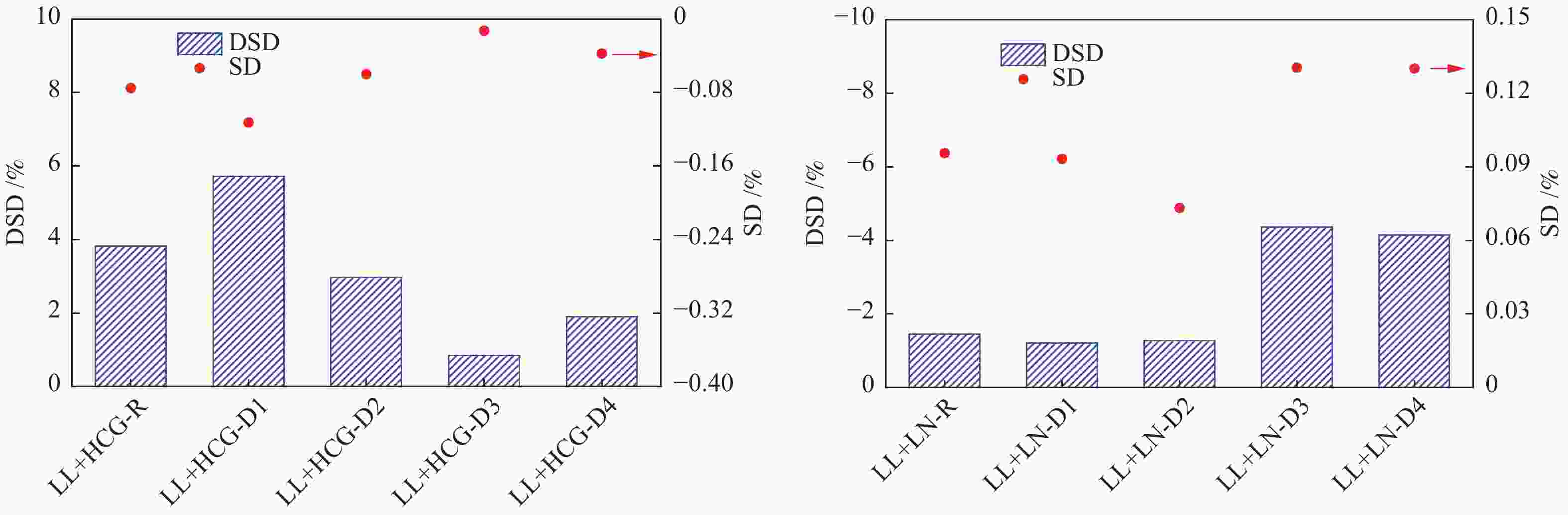
Table 6 Coke yield and sulfur removal rate of gas coal and separation components
Sample Coke yield/% Sulfur content in coke/% Total sulfur removal/% HCG-R 64.07 0.46 42.43 HCG-D1 61.58 0.41 47.72 HCG-D2 64.84 0.40 45.16 HCG-D3 67.37 0.37 47.31 HCG-D4 69.89 0.43 39.12 LN-R 64.95 0.53 32.90 LN-D1 63.10 0.38 17.03 LN-D2 67.98 0.42 23.66 LN-D3 69.89 0.51 37.14 LN-D4 71.11 0.99 22.30 表 7 不同煤样 13C NMR波谱图拟合结果
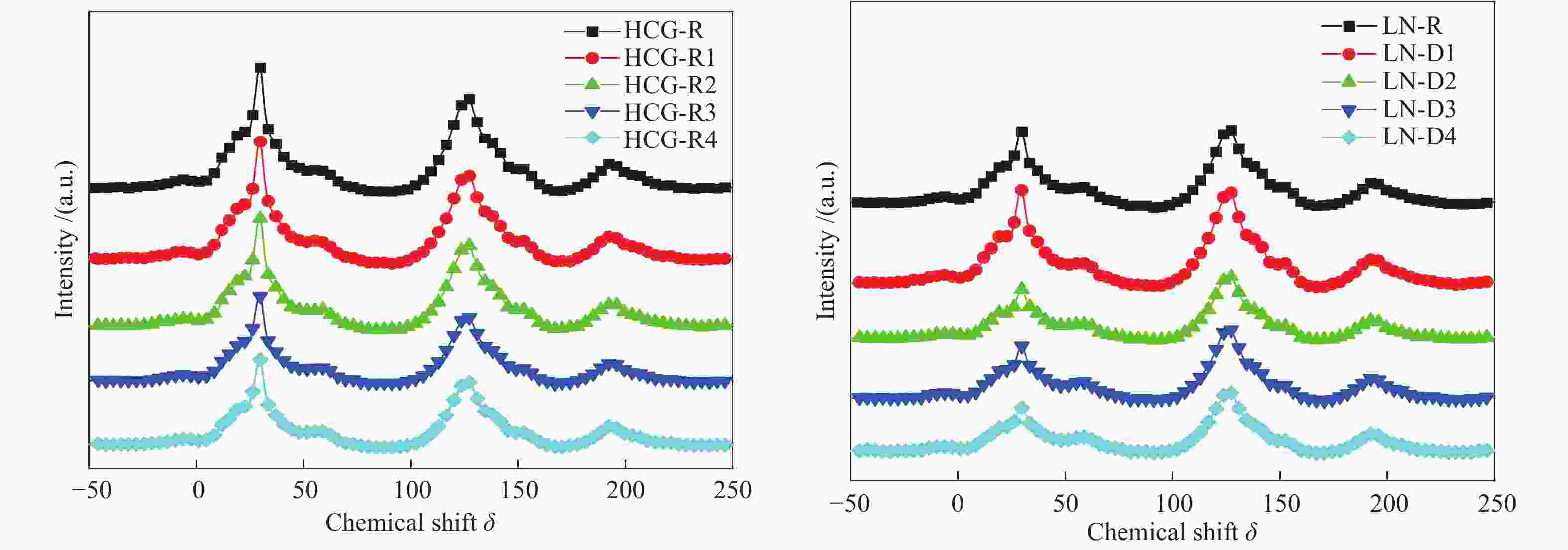
Table 7 Fitting results of 13C NMR spectra of different coal samples
Carbon type/% HCG-R HCG-D1 HCG-D2 HCG-D3 HCG-D4 LN-R LN-D1 LN-D2 LN-D3 LN-D4 fala 5.89 8.01 7.31 4.30 5.10 6.50 5.99 4.70 5.28 6.35 fal1 8.91 9.16 4.98 9.33 6.46 5.25 6.76 4.95 4.64 2.44 fal2 8.36 7.18 13.20 10.00 11.93 10.14 9.25 10.65 8.69 11.89 fal3 14.63 14.42 12.16 11.48 13.05 11.91 12.72 10.56 11.19 8.86 falO 7.21 7.18 7.10 8.90 6.54 7.62 7.46 8.11 8.53 8.10 faH 4.86 4.64 4.92 8.47 4.58 5.52 5.72 5.74 5.44 6.40 fa B 25.24 25.04 25.54 22.65 26.90 26.66 26.64 28.94 30.13 29.88 faS 9.68 9.39 9.64 9.97 9.57 10.01 9.53 9.94 9.47 9.56 faO 4.61 4.51 4.57 4.40 4.54 4.89 4.66 4.35 4.31 4.16 faC1 7.58 7.52 7.69 7.37 8.19 8.28 8.16 9.17 9.49 9.31 faC2 3.03 2.93 2.90 3.13 3.14 3.22 3.10 2.89 2.83 3.06 fal 44.99 45.96 44.75 44.02 43.09 41.42 42.19 38.97 38.34 37.64 fa 44.40 43.59 44.66 45.48 45.59 47.08 46.55 48.97 49.34 49.99 farN 39.53 38.94 39.75 37.01 41.00 41.56 40.84 43.23 43.91 43.59 表 8 不同单种煤的基氏流动度参数
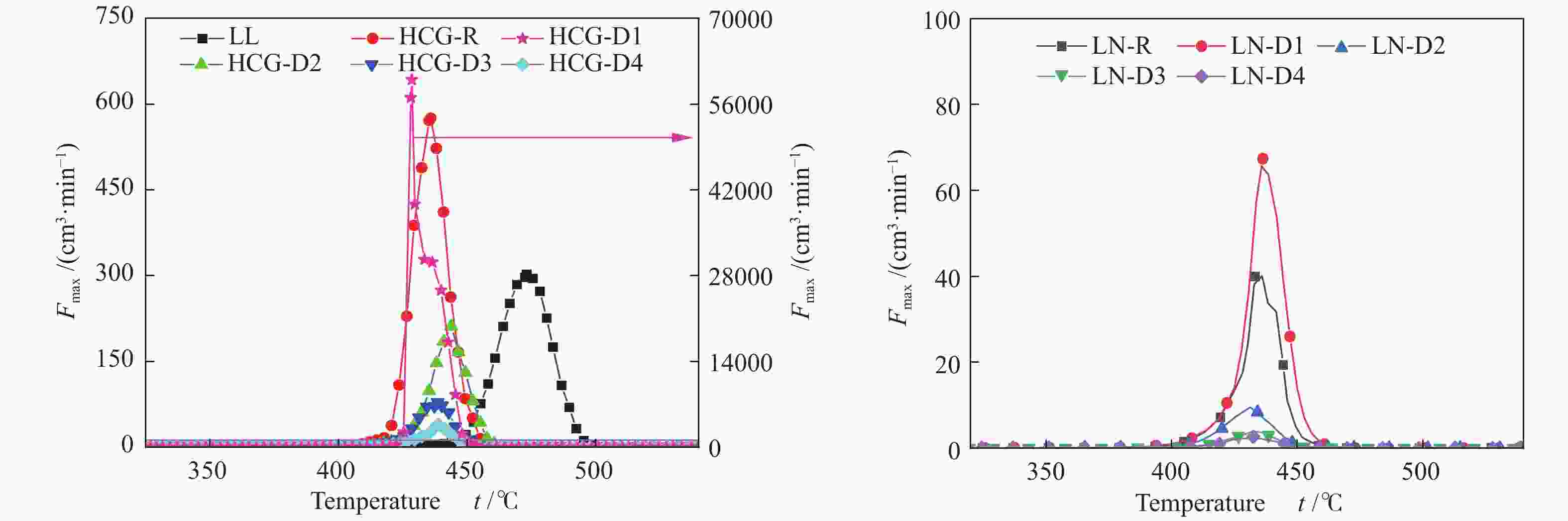
Table 8 Gieseler fluidity parameters of different coal samples
Sample t1/℃ t2/℃ t3/℃ △t Fmax / (cm3·min−1) Area LL 419.6 473.1 509.6 90.0 302.9 7722.54 HCG-R 394.0 435.8 469.6 75.6 575.3 9757.81 HCG-D1 390.8 428.5 486.7 95.9 59984.8 602428.14 HCG-D2 400.9 443.8 474.9 74.0 211.8 3570.21 HCG-D3 401.9 438.5 470.6 68.7 78.6 1446.70 HCG-D4 408.4 438.8 467.9 59.5 39.5 619.91 LN-R 401.4 434.4 469.6 68.2 43.3 772.88 LN-D1 399.7 437.2 473.2 73.5 68.7 1244.43 LN-D2 407.0 431.3 464.8 57.8 9.5 223.87 LN-D3 415.9 432.6 462.4 46.5 3.9 97.75 LN-D4 418.6 432.5 462.5 43.9 2.7 67.17 note: t1: softening temperature, t2: maximum fluidity temperature, t3: resolidification temperature, △t: plastic range, Fmax: maximum fluidity 表 9 不同配合煤的基氏流动度参数
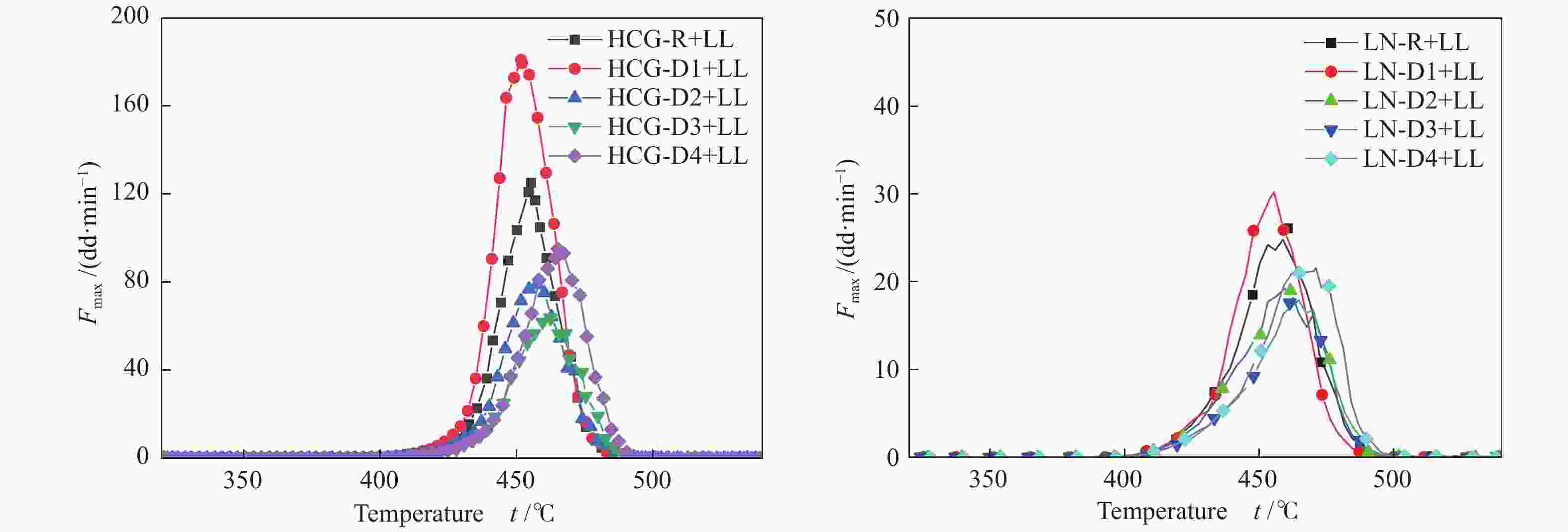
Table 9 Gieseler fluidity parameters of different coal blends
Sample t1/℃ t2/℃ t3/℃ △t Fmax / ( cm3·min−1) Area HCG-R+LL 407.3 455.2 500.3 93.0 125.2 3132.27 HCG-D1+LL 406.2 451.6 497.7 91.5 181.0 4733.20 HCG-D2+LL 410.3 457.4 500.9 90.6 79.1 2250.22 HCG-D3+LL 415.3 462.3 503.2 87.9 64.0 1915.75 HCG-D4+LL 413.0 465.1 505.3 92.3 95.1 2721.85 LN-R+LL 413.4 460.6 503.9 90.5 26.1 878.86 LN-D1+LL 412.2 455.5 499.8 87.6 30.2 916.18 LN-D2+LL 413.4 459.8 500.4 87.0 19.2 726.01 LN-D3+LL 415.9 462.5 503.7 87.8 18.5 627.16 LN-D4+LL 417.5 470.0 503.3 85.8 26.4 798.26 note: t1: softening temperature, t2: maximum fluidity temperature, t3: resolidification temperature, △t: plastic range, Fmax: maximum fluidity -
[1] 王健, 余诚桓, 吉武平. 配高硫煤炼焦的研究[J]. 燃料与化工,2011,42(5):26−27.WANG Jian, YU Cheng-heng, JI Wu-pin. Preparation of blending coking high sulfur coal[J]. Fuel Chem Process,2011,42(5):26−27. [2] 李丽英. 我国炼焦煤产业供需形势及发展对策研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2018,50(4):141−143.LI Li-ying. Study on supply and demand situation and development countermeasures of coking coal industry in China[J]. Coal Eng,2018,50(4):141−143. [3] 李丽英. 我国炼焦煤中长期供需预测研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2019,51(7):150−155.LI Li-ying. Research on forecast of supply and demand of coking coal in medium and long term in china[J]. Coal Eng,2019,51(7):150−155. [4] 段小宝. 高硫煤部分替代优质焦煤配煤炼焦的应用基础研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2018.DUAN Xiao-bao. Applied basic research on blending coking of partial replacing high quality coking coal by high sulfur coal[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018. [5] 王之正, 王利斌, 裴贤丰, 王岩, 白效言. 高硫煤热解脱硫技术研究现状[J]. 洁净煤技术,2014,20(2):76−79.WANG Zhi-zheng, WANG Li-bin, PEI Xian-feng, WANG Yan, BAI Xiao-yan. Desulfurization of high-sulfur coal through pyrolysis[J]. Clean Coal Technol,2014,20(2):76−79. [6] 王申祥, 付志新, 郭占成. 焦炭中硫的空间分布规律研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2006,34(2):142−145.WANG Shen-xiang, FU Zhi-xin, GUO Zhan-cheng. Study of sulfur dimensional distribution in coke[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2006,34(2):142−145. [7] GUO Z C, FU Z X, WANG S H. Sulfur distribution in coke and sulfur removal during pyrolysis[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2007,88(10):935−941. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.05.003 [8] SHEN Y F, WANG M J, HU Y F, KONG J, WANG J C, CHANG L P, BAO W R. Transformation and regulation of sulfur during pyrolysis of coal blend with high organic-sulfur fat coal[J]. Fuel,2019,249:427−433. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.03.066 [9] SHEN Y F, WANG M J, WU Y C, HU Y F, KONG J, DUAN X B, WANG J C, CHANG L P, BAO W R. Role of gas coal in directional regulation of sulfur during coal-blending coking of high organic-sulfur coking coal[J]. Energy Fuels,2020,34(3):2757−2764. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b03737 [10] 刘少林, 孔娇, 申岩峰, 李挺, 杨暖暖, 王美君, 常丽萍. 高有机硫炼焦煤分选组分中硫的赋存形态及其热变迁行为研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2019,47(8):915−924.LIU Shao-lin, KONG Jiao, SHEN Yan-feng, LI Ting, YANG Nuan-nuan, WANG Mei-jun, CHANG Li-pin. Sulfur occurrence and transformation during pyrolysis of the flotation fraction from coking coals with high organic sulfur[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2019,47(8):915−924. [11] 倪志强. 炼焦煤中镜质组的黏结性特征及其成焦行为[D]. 唐山: 河北联合大学, 2014.NI Zhi-qiang. The caking properties of the vitrinite in coking coals and its coking behavior[D]. Tangshan: Hebei United University, 2014. [12] 赵伟, 张晓欠, 周安宁, 杨志远. 神府煤煤岩显微组分的浮选分离及富集物的低温热解产物特性研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2014,42(5):527−533.ZHAO Wei, ZHANG Xiao-qian, ZHOUAn-ning, YANG Zhi-yuan. Flotation separation of Shenfu coal macerals and low temperature pyrolysis characteristics of different maceral concentrate[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2014,42(5):527−533. [13] GB/T478—2008, 煤沉浮试验方法[S].GB/T478—2008, Method for float and sink analysis of coal[S]. [14] 门东坡, 刘文礼, 张磊. 烟煤煤岩组分解离特性及分选研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2016,48(2):116−119.MEN Dong-po, LIU Wen-li, ZHANG Lei. Research on liberation characteristics and separation of macerals for bituminous coal[J]. Coal Eng,2016,48(2):116−119. [15] LIU P, LE J W, WANG L L, PAN T Y, LU X L. Relevance of carbon structure to formation of tar and liquid alkane during coal pyrolysis[J]. Appl Energy,2016,183:470−477. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.166 [16] 杨万庆, 李庆春, 张志刚. 不同变质程度煤碳结构差异对煤热解产物特性的影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(12):212−218.YANG Wan-qing, LI Qing-chun, ZHANG Zhi-gang. Effect of different carbon structure with different metamorphic degree on pyrolysis product characteristics[J]. Coal Sci Technol,2017,45(12):212−218. [17] YOSHIDA T, MAEKAWA Y. Characterization of coal structure by CP/MAS carbon-13 NMR spectrometry[J]. Fuel Process Technol,1987,15(15):385−395. [18] SUGGATE R P, DICHINSON W W. Carbon NMR of coals: the effects of coal type and rank[J]. Int J Coal Geol,2004,57(1):1−22. doi: 10.1016/S0166-5162(03)00116-2 [19] 梁建华, 史世庄, 张康华, 彭靖, 雷耀辉, 吴琼. 煤中灰成分催化指数的相关性[J]. 洁净煤技术,2011,17(1):33−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6772.2011.01.010LIANG Jian-hua, SHI Shi-zhuang, ZHANG Kang-hua, PENG Jing, LEI Yao-hui, WU Qiong. Interrelations of catalytic index of coal ash component[J]. Clean Coal Technol,2011,17(1):33−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6772.2011.01.010 [20] LIU F R, LI W, CHEN H K, LI B Q. Uneven distribution of sulfurs and their transformation during coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel,2007,86(3):360−366. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.07.021 [21] KOZLOWSKI M. XPS Study of reductively and non-reductively modified coals[J]. Fuel,2004,83(3):259−265. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.08.004 [22] 陈皓侃, 李保庆, 张碧江. 矿物质对煤热解和加氢热解含硫气体生成的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,1999,27(S1):6−11.CHEN Hao-kan, LI Bao-qing, ZHANG Bi-jiang. Effects of mineral matter on evolution of sulfur-containing gases in pyrolysis and hydropyrolysis[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,1999,27(S1):6−11. [23] JIN M L, CHENG J L, WANG L X, JIN S L, ZHANG R. Rheological properties of mesophase pitch investigated by the Giseeler fluidity method[J]. New Carbon Mater,2015,30(2):176−180. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(15)60183-4 [24] 李艳红, 赵文波, 常丽萍, 王美君, 王平艳, 杨荣. 炼焦机理和焦炭质量预测的研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2014,33(5):1142−1150.LI Yan-hong, ZHAO Wen-bo, CHANG Li-ping, WANG Mei-jun, WANG Ping-yan, YANG Rong. Progress of research on coking mechanism and coke quality prediction[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2014,33(5):1142−1150. [25] 申岩峰, 王美君, HU Yong-feng, 孔娇, 鲍卫仁, 常丽萍. 高硫炼焦煤化学结构及硫赋存形态对硫热变迁的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(2):144−153.SHEN Yan-feng, WANG Mei-jun, HU Yong-feng, KONG Jiao, BAO Wei-ren, CHANG Li-ping. Effect of chemical structure and sulfur speciation of high-sulfur coking coals on sulfur transformation during pyrolysis[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(2):144−153. [26] HU W J, WANG Q, ZHAO X F, ZHANG S, CHENG H. Relevance between various phenomena during coking coal carbonization. Part 2: Phenomenon occurring in the plastic layer formed during carbonization of a coking coal[J]. Fuel,2019,253:199−208. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.152 [27] WANG Q, CHENG H, ZHAO X F, ZHANG S, HU W J. Relevance between various phenomena during coking coal carbonization. Part 1: A new testing method developed on a sapozhnikov plastometer[J]. Energy Fuels,2018,32(7):7438−7443. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b01217 [28] HU W J, WANG Q, ZHAO X F, YANG S T, WU H L, ZHANG S, SUN J F. Relevance between various phenomena during coking coal carbonization. Part 3: Understanding the properties of the plastic layer during coal carbonization[J]. Fuel,2021,292(2):120371. -




 下载:
下载: