Low temperature catalytic oxidation of NO over sludge char under different pyrolysis activation conditions
-
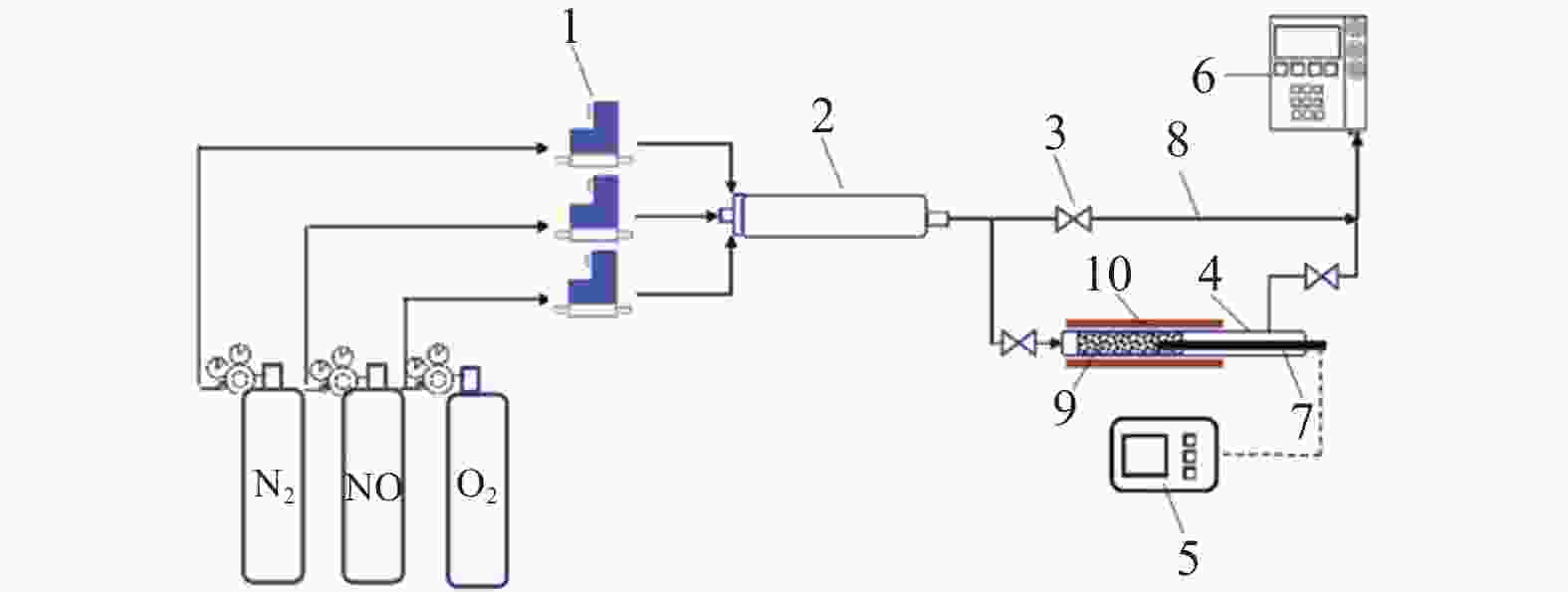
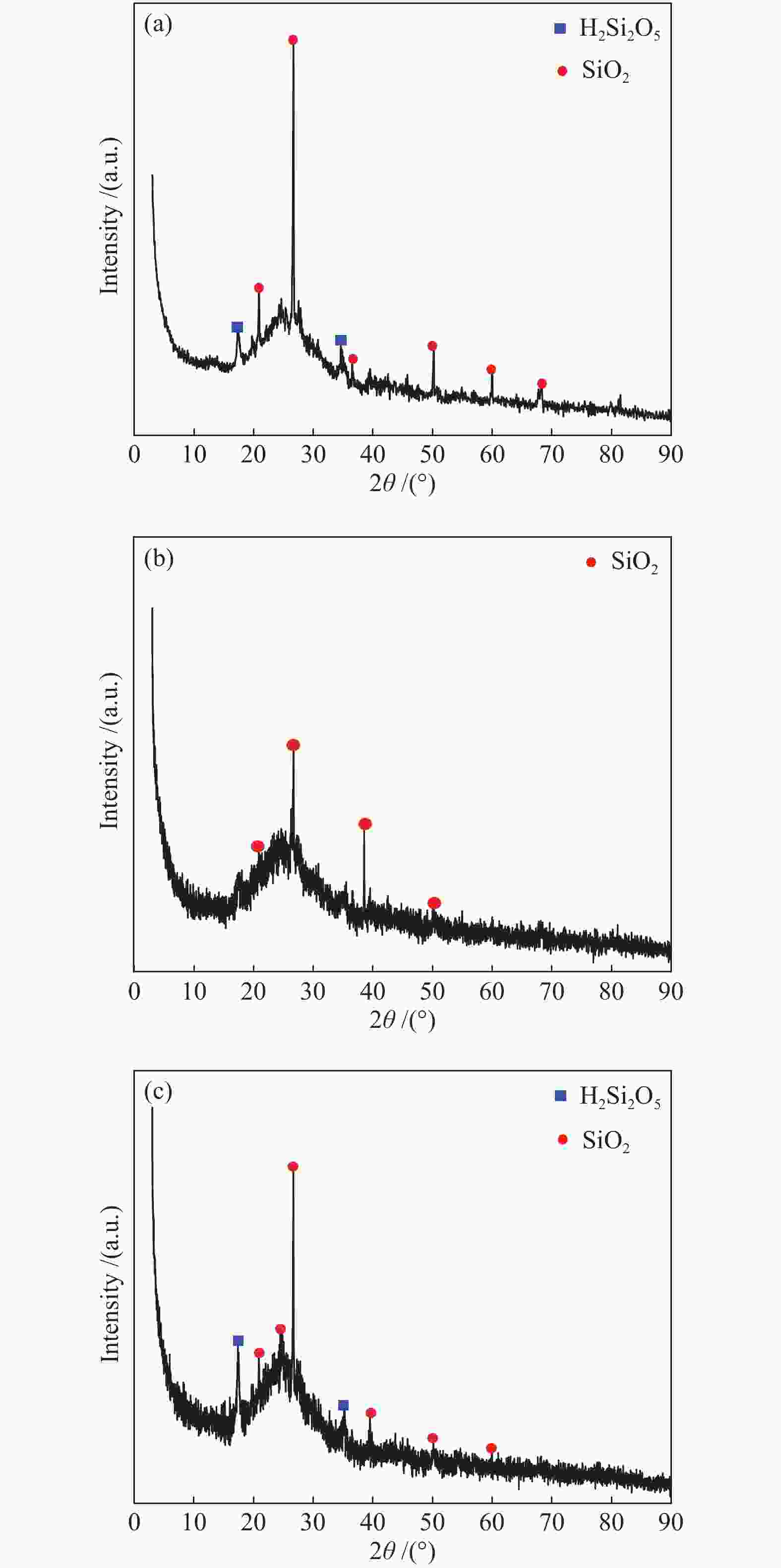
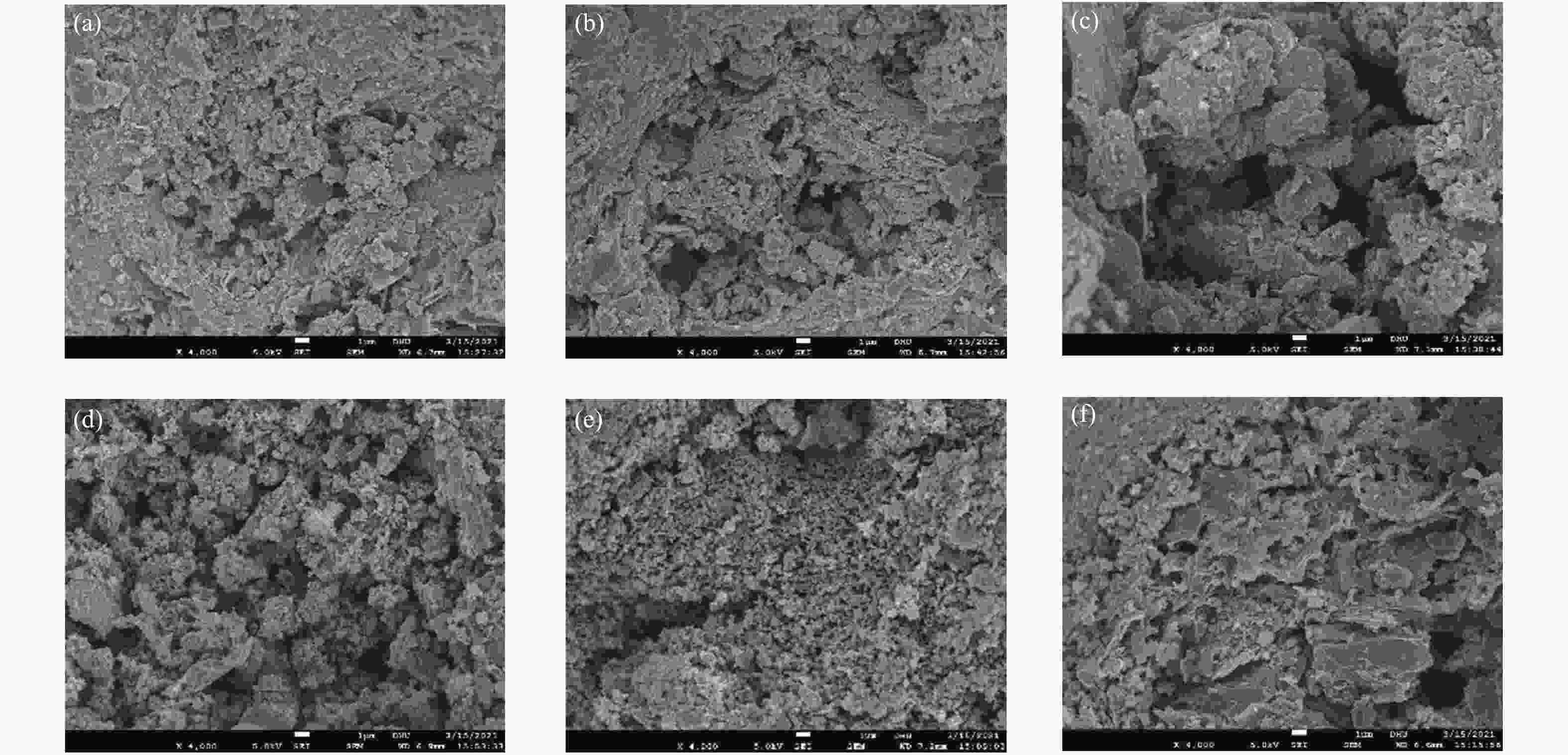
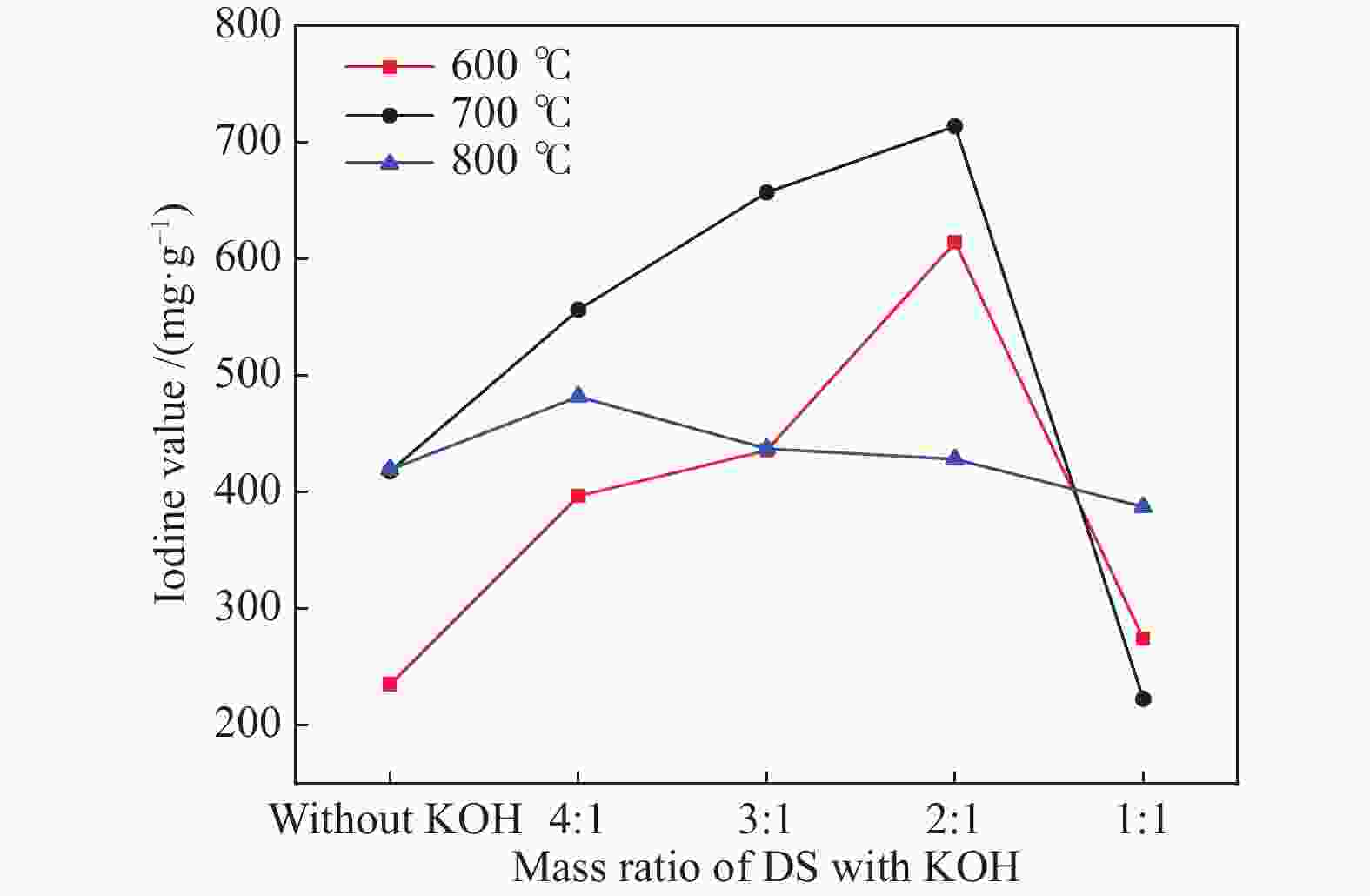
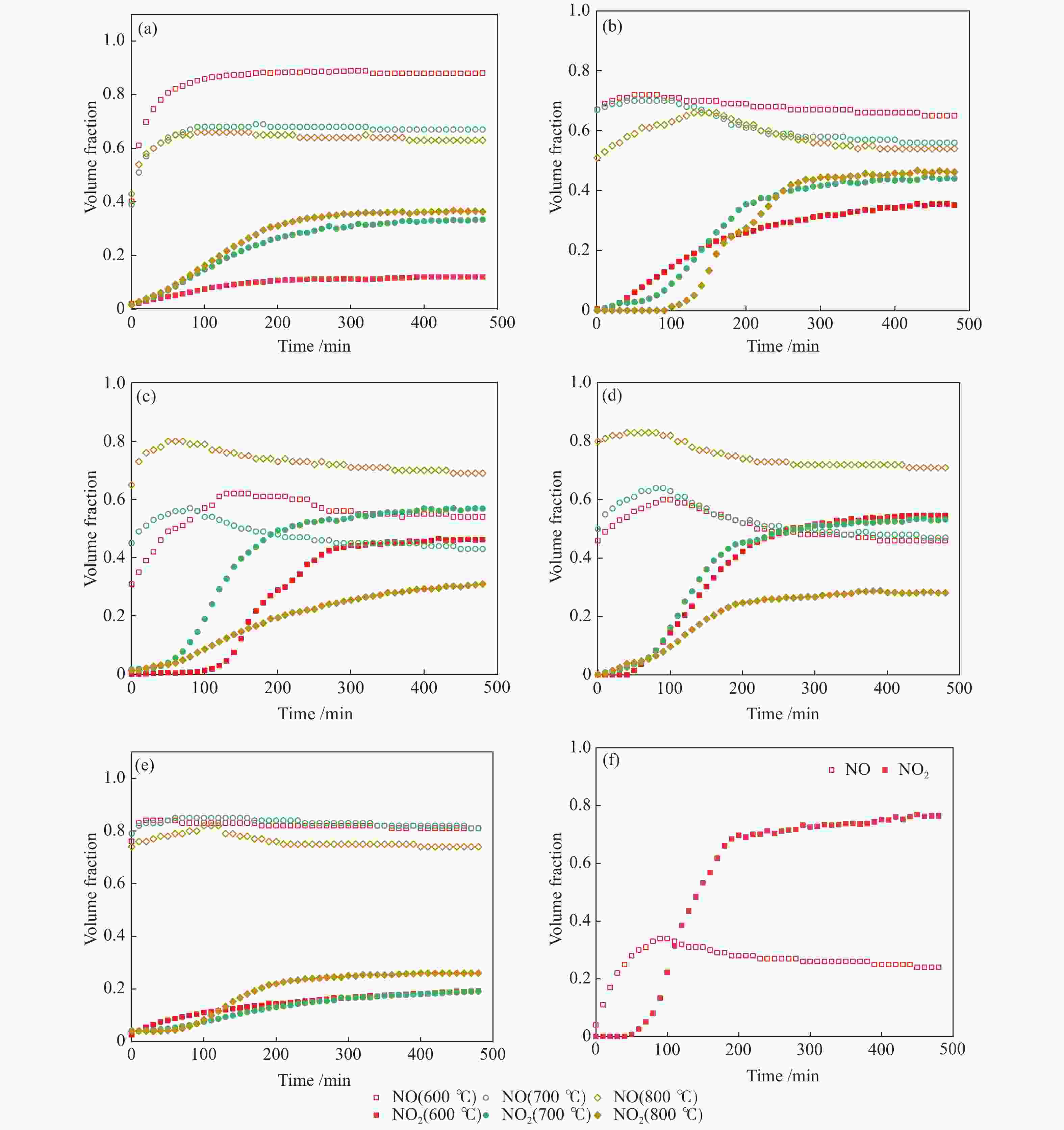
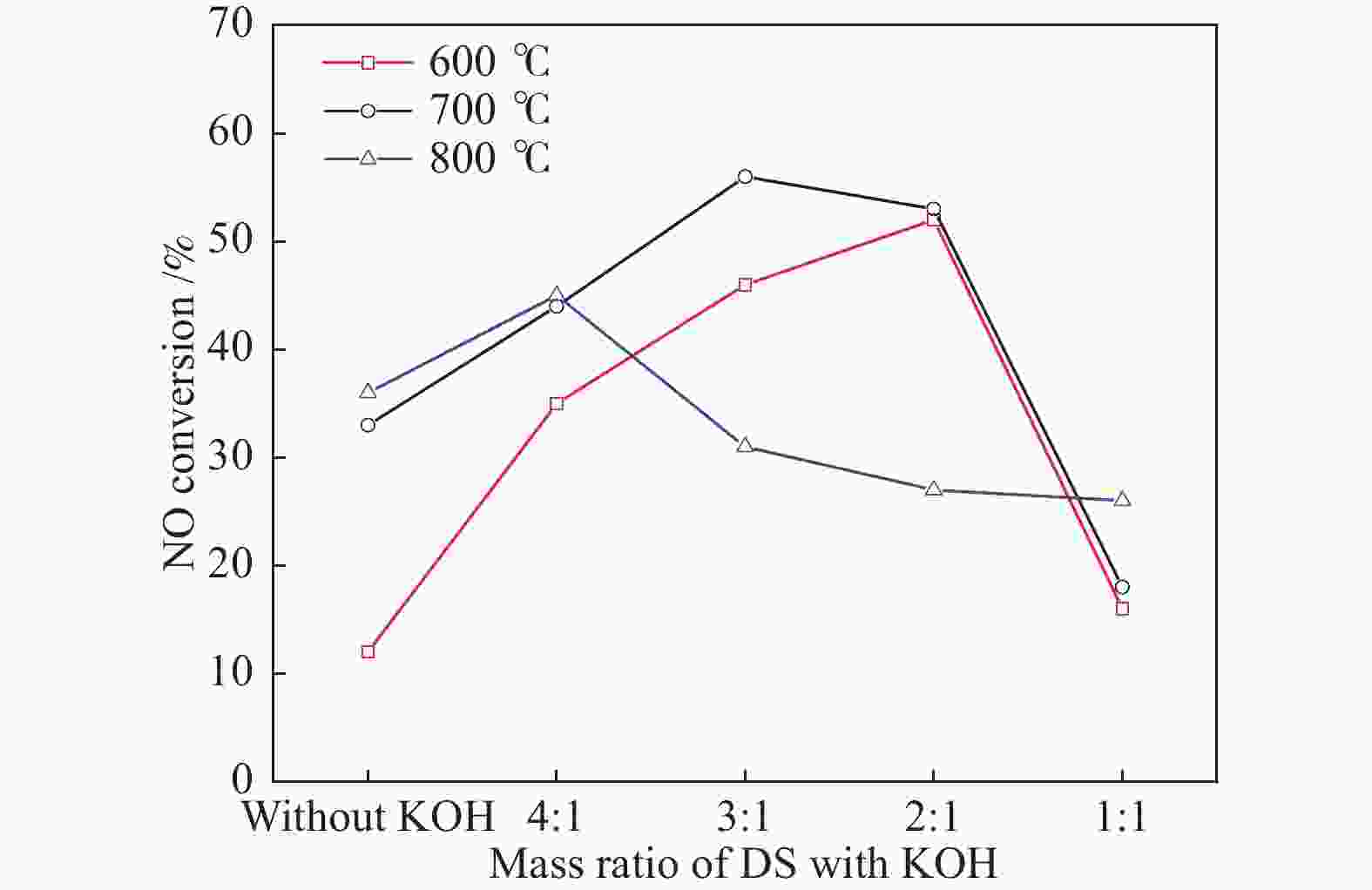
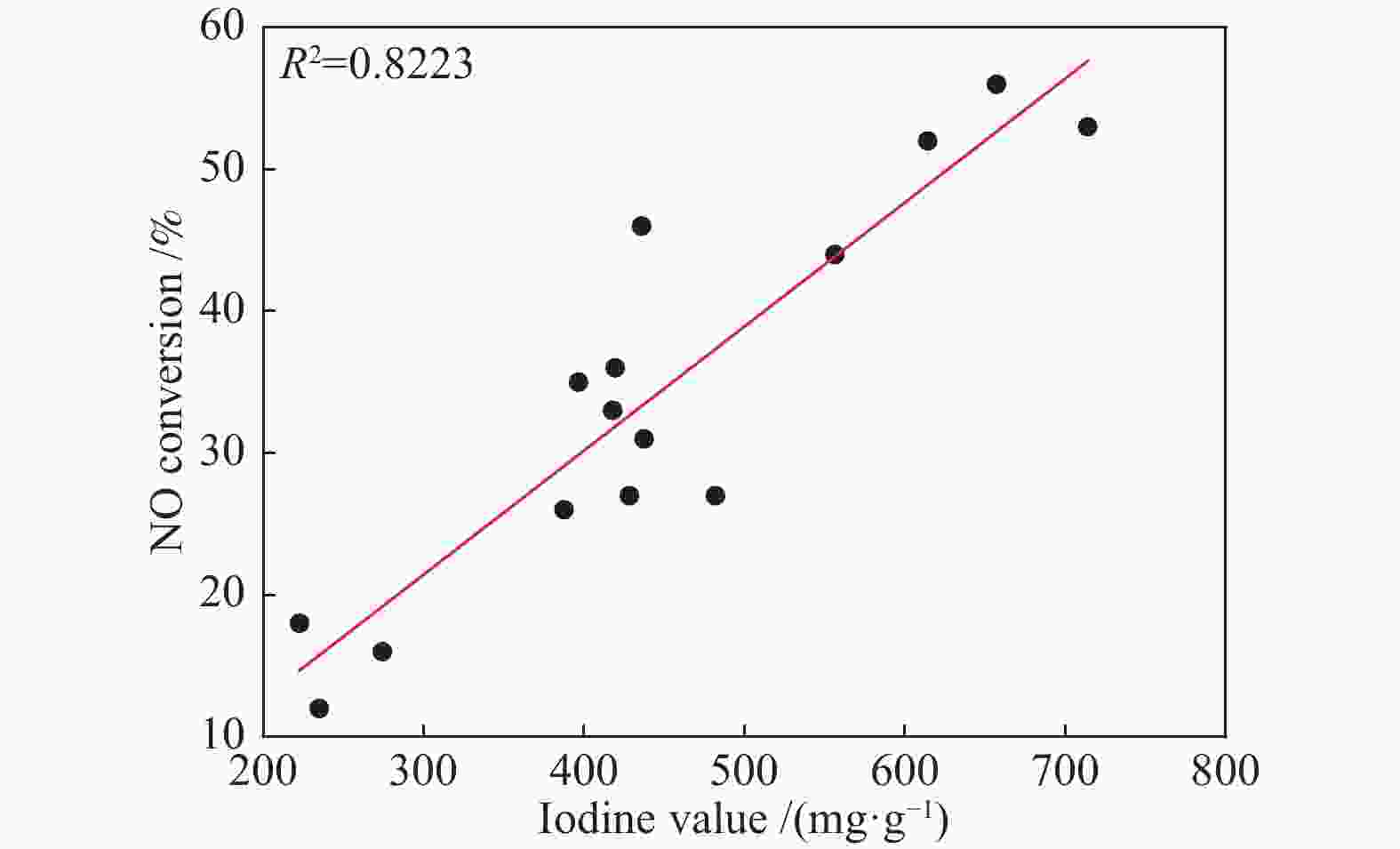
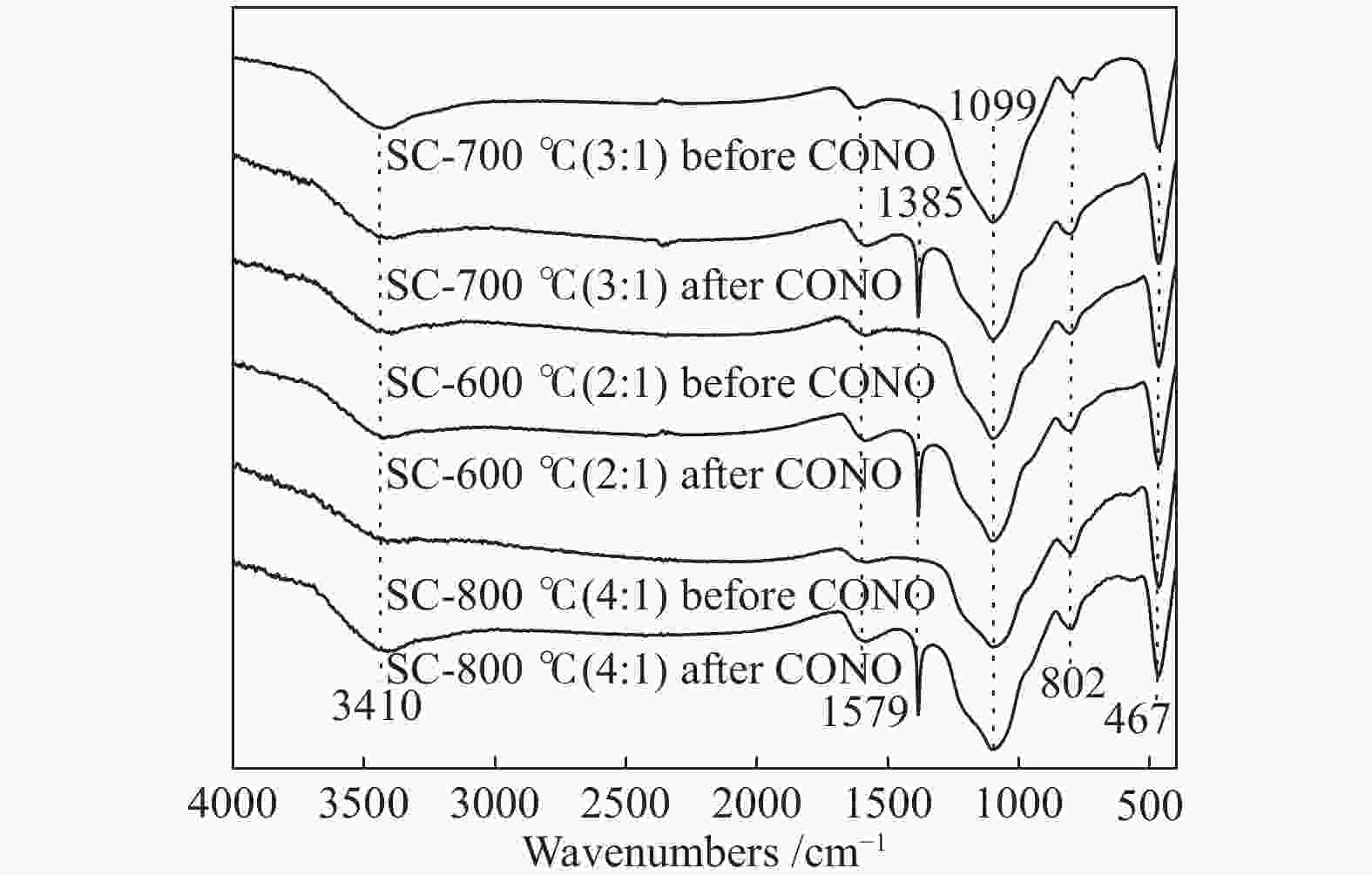
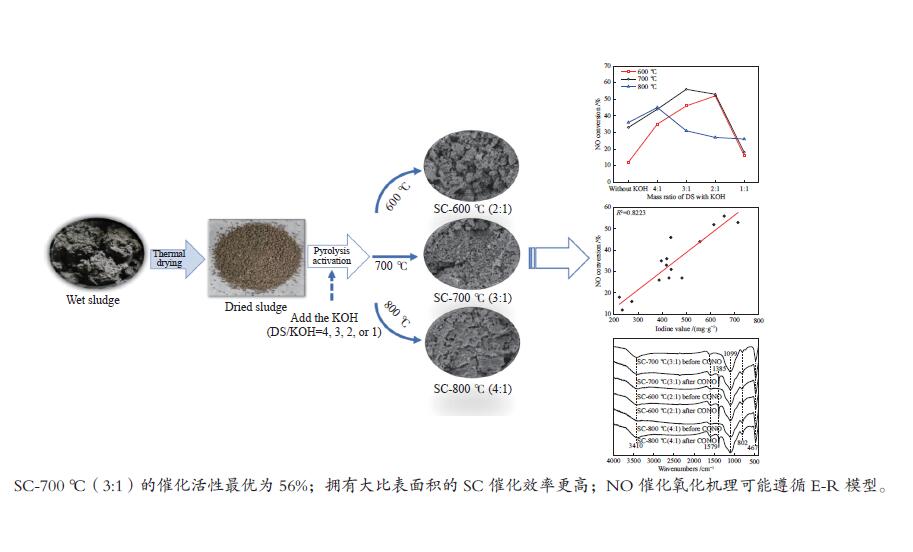
摘要: 以市政污泥为原料制备污泥炭(SC),开展了SC常温催化氧化NO的实验研究。通过对不同热解温度(600 、700 和800 ℃)和不同干基污泥(DS)/KOH混合质量比下(4∶1、3∶1、2∶1和1∶1)的NO脱除特性研究,探究了污泥裂解活化工艺对NO常温催化氧化的影响规律和作用机理。结果表明,热解温度和KOH活化均对SC的催化活性有显著影响,当热解温度由600 ℃升至800 ℃,裂解样的NO转化率由12%升至36%;不同热解温度下,SC的催化活性均随KOH用量增加呈先增大后减小趋势;当热解温度为700 ℃、DS/KOH = 3∶1时,SC的催化活性最优,达到56%;对该样品进一步进行氢气还原处理后,其脱硝效率进一步提升,达到76.5%。研究发现,SC的催化活性与其比表面积有强相关性,其反应机理遵循Eley-Rideal(E-R)模型。Abstract: Catalytic oxidation of NO (CONO) at ambient temperature over sludge char (SC) prepared from sewage sludge was studied in this paper. The influencing mechanism of sludge pyrolysis/activation parameters on the CONO were investigated for the SC prepared with different pyrolysis temperatures (600, 700, and 800 ℃) and different mass ratios of dried sludge (DS) to KOH (DS/KOH = 4∶1, 3∶1, 2∶1, and 1∶1). The results indicated that both pyrolysis temperature and KOH activation had great influence on the catalytic performance of SC. With the increase of temperature from 600 to 800 ℃, the NO conversion increased from 12% to 36%. However, the catalytic activity of KOH-activated SC increased and then decreased with the increase of KOH content. The SC prepared under the pyrolysis temperature of 700 ℃ and the DS/KOH mass ratio of 3∶1 showed the best catalytic performance with NO conversion of 56%. The NO conversion further increased to 76.5% when the SC was reduced by H2. It was also found that there was a strong correlation between the catalytic activity and the specific surface area of the SCs. The reaction might follow the Eley-Rideal (E-R) mechanism.
-
Key words:
- NO /
- catalytic oxidation /
- sludge char /
- KOH activation /
- pyrolysis
-
表 1 DS及不同工况样品的工业成分分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis of DS and SCs
Sample Proximate analysis w/% A V FC DS 43.24 49.64 7.12 SC-600 ℃ 67 22.69 10.31 SC-600 ℃(4∶1) 54.33 17.39 28.27 SC-600 ℃(3∶1) 53.12 20.93 25.95 SC-600 ℃(2∶1) 59.42 22.12 18.46 SC-600 ℃(1∶1) 64.26 24.96 10.78 SC-700 ℃ 73.22 14.08 12.7 SC-700 ℃(4∶1) 54.23 18.16 27.61 SC-700 ℃(3∶1) 53.74 20.22 26.04 SC-700 ℃(2∶1) 56.76 22.77 20.47 SC-700 ℃(1∶1) 73.87 16.23 9.9 SC-800 ℃ 75.09 10.89 14.02 SC-800 ℃(4∶1) 53.97 17.61 28.42 SC-800 ℃(3∶1) 55.83 18.94 25.23 SC-800 ℃(2∶1) 61.93 19.21 18.86 SC-800 ℃(1∶1) 69.82 19.23 10.95 表 2 DS的灰分分析
Table 2 Ash components in DS
Content w/% Fe2O3 SiO2 Al2O3 SO3 P2O5 TiO2 CaO K2O 36.64 ± 0.24 28.31 ± 0.23 10.61 ± 0.15 9.58 ± 0.15 7.29 ± 0.13 2.03 ± 0.07 1.82 ± 0.07 1.21 ± 0.05 -
[1] WOJCIECHOWSKA M, LOMNICKI S. Nitrogen oxides removal by catalytic methods[J]. Clean Technol Environ Policy,1999,1(4):237−247. doi: 10.1007/s100980050037 [2] BARMAN S, PHILIP L. Integrated system for the treatment of oxides of nitrogen from flue gases[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2005,40(3):1035−1041. [3] SKALSKA K, MILLER J S, LEDAKOWICZ S. Trends in NOx abatement: A review[J]. Sci Total Environ,2010,408(19):3976−3989. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.06.001 [4] TOPSOE N Y, TOPSOE H, DUMESIC J A. Vanadia/titania catalysts for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of nitric-oxide by ammonia[J]. J Catal,1995,151:226−240. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1995.1024 [5] 刘华彦. NO的常温催化氧化及碱液吸收脱除NOx过程研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011.LIU Hua-yan. Studies on NOx removal by catalytic oxidation and alkali solution absorption at ambient temperature[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011. [6] WANG G H, ZHANG R Y, GOMEZ M E, YANG L X, ZAMORA M L, HU M, LIN Y, PENG J F, GUO S, MENG J J. Persistent sulfate formation from London Fog to Chinese haze[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2016,113(48):13630−13635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616540113 [7] FU M, LI C, PEI L, LONG Q, ZHANG M, YANG Z, YU M, YANG F. A review on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by supported catalysts at 100−300 ℃ catalysts mechanism, kinetics[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2014,4(1):14−25. doi: 10.1039/C3CY00414G [8] LI Q, YANG H S, NIE A M, FAN X Y, ZHNAG X B. Catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over V2O5-MnOX/TiO2 carbon nanotube composites[J]. Catal Lett,2011,141(8):1237−1242. doi: 10.1007/s10562-011-0622-2 [9] XU Q, FANG Z L, CHEN Y Y, GUO Y L, GUO Y, WANG L, WANG Y S, ZHNG J S, ZHAN W C. Titania-samarium-manganese composite oxide for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2020,54:2530−2538. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b06701 [10] WANG J, ZHU J Z, ZHOU X X, DU Y Y, HANG W M, LIU J J, ZHANG W Q, SHI J L, CHEN H R. Nanoflower-like weak crystallization manganese oxide for efficient removal of low-concentration NO at room temperature[J]. J Mater Chem A,2015,3(14):7631−7638. doi: 10.1039/C5TA00468C [11] CHOI J, LEE K S, CHOI Y J, KIM Y J, KIM S S. Dry De-NOx process via gas-phase photochemical oxidation using an ultraviolet and aerosolized H2O/H2O2 hybrid system[J]. Energy Fuels,2014,28(8):5270−5276. doi: 10.1021/ef500645a [12] ELLMERS I, VELEZ R P, BENTRUP U, BRUCKNER A, GRUNERT W. Oxidation and selective reduction of NO over Fe-ZSM-5 How related are these reactions[J]. J Catal,2014,311:199−211. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.11.024 [13] VERMA A A, BATES S A, ANGGARA T, PAOLUCCI C, PAREKH A A, KAMASAMUDRAM A, YEZERETS A, YEZERETS A, MILLER J T, DELGASS W N, SCHNEIDER W F. NO oxidation: A probe reaction on Cu-SSZ-13[J]. J Catal,2014,312:179−190. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.01.017 [14] BODENSTEIN M. Die Ermittlung des Mechanismus chemischer Reaktionen[J]. Helv Chim Acta,1935,18(1):743−759. doi: 10.1002/hlca.193501801102 [15] WILLIAM S E, LARRY E C, ALEKSEY Y, NEALW C, JAMESE P. Overview of the fundamental reactions and degradation mechanisms of NOx storage/reduction catalysts[J]. Catal Rev,2004,46(2):163−245. doi: 10.1081/CR-200031932 [16] GUO Z C, XIE Y S, IKPYO H, KIM J Y. Catalytic oxidation of NO to NO2 on activated carbon[J]. Energy Convers Manage,2001,42(15/17):2005−2018. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(01)00058-9 [17] SOUSA J P S, PEREIRA M F R, FIGUEIREDO J L. Catalytic oxidation of NO to NO2 on N-doped activated carbons[J]. Catal Today,2011,176(1):383−387. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.11.040 [18] ESRAFILI M D, SAEIDI N. Si-embedded boron-nitride nanotubes as an efficient and metal-free catalyst for NO oxidation[J]. Superlattices Microstruct,2015,81:7−15. doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2015.01.014 [19] GORGULHO H F, GONCALVES F, PEREIRA M F R, FIGUEIREDO J L. Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels[J]. Carbon,2009,47(8):2032−2039. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2009.03.050 [20] MIYWAKI J, SHIMOHARA T, SHIRAHAMA N, YASUTAKE A, YOSHIKAWA M, MOCHIDA I, YOON S H. Removal of NOx from air through cooperation of the TiO2 photocatalyst and urea on activated carbon fiber at room temperature[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2011,110:273−278. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.09.012 [21] WANG W C, MCCOOL G, KAPUR N, YUAN G, SHAN B, NGUYEN M, GREHAM U M, DAVIS B H, JACOBS G, CHO K, HAO X H. Mixed-phase oxide catalyst based on Mn-mullite (Sm, Gd) Mn2O5 for NO oxidation in diesel exhaust[J]. Science,2012,337:832−835. doi: 10.1126/science.1225091 [22] MANOCHA L M, WARRIER A, MANOCHA S, EDIE D D, OGALE A A. Microstructure of carbon/carbon composites reinforced with pitch-based ribbon-shape carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2003,41(7):1425−1436. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00087-3 [23] SOUSA J P S, PEREIRA M F R, FIGUEIREDO J L. Carbon xerogel catalyst for NO oxidation[J]. Catalysis,2012,2(4):447−465. [24] 周易, 邓文义, 苏亚欣. 常温下碳基活性材料催化氧化NO的研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2021,40(2):857−867.ZHOU Yi, DENG Wen-yi, SU Ya-xin. Research progress in catalytic oxidation of NO by carbon-based active materials at room temperature[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2021,40(2):857−867. [25] DENG W Y, YAN J H, LI X D, WANG F, ZHU X W, LU S Y, CEN K F. Emission characteristics of volatile compounds during sludges drying process[J]. J Hazard Mater,2009,162(1):186−192. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.022 [26] 邓文义, 陶聪, 田诗娟, 印安东, 苏亚欣. 不同热解条件下制备的污泥炭低温还原NO[J]. 化工进展,2020,39(S1):263−269.DENG Wen-yi, TAO Cong, TIAN Shi-juan, YIN An-dong, SU Ya-xin. Low temperature reduction of NO over sludge char prepared under different pyrolysis conditions[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2020,39(S1):263−269. [27] DENG W Y, YIN A D, MA C J, SU Y X. Investigation of NO conversion by different types of sewage sludge chars under low temperature[J]. J Environ Manage,2018,209:236−244. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.065 [28] DENG W Y, HU M H, MA J C, SU Y X, RUAN S P, RONG S B. Structural and functional relationships of activated char briquettes from pyrolysis of sewage sludge for methylene blue removal[J]. J Cleaner Prod,2020,259:120907. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120907 [29] ZOU J L, DAI Y, WANG X, RE Z Y, TIAN G G, PAN K, LI S, ABUOBEIDAND M, FU H G. Structure and adsorption properties of sewage sludge-derived carbon with removal of inorganic impurities and high porosity[J]. Bioresour Technol,2013,142:209−217. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.064 [30] HADI P, XU M, NING C, LIN C S K, MCKAY G. A critical review on preparation, characterization and utilization of sludge-derived activated carbons for wastewater treatment[J]. Chem Eng J,2015,260:895−906. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.088 [31] MIAN M M, LIU G J, FU B, SONG Y. Facile synthesis of sludge-derived MnOx-N-biochar as an efficient catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2019,255:117765. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117765 [32] 陶聪. 常温下炭化污泥催化氧化脱除NO的实验研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2020.TAO Cong. Experimental study on catalytic oxidation of NO at ambient temperature over the chars from pyrolysis of sewage sludge[D], Shanghai: Master's degree thesis of Donghua University, 2020. [33] DENG W Y, TAO C, COBB K, ZHOU H F, RUAN R. Catalytic oxidation of NO at ambient temperature over the chars from pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere,2020,251:126429. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126429 [34] GB/T 12496.8—2015, 木质活性炭试验方法—碘吸附值的测定[S].GB/T 12496.8—2015, Test methods of wooden activated carbon—Determination of iodine number[S]. [35] TOSHIRO O, RITSUO T, MASAO I. Production and adsorption characteristics of MAXSORB: high-surface-area active carbon[J]. Gas Sep Purif,1993,7(4):241−245. doi: 10.1016/0950-4214(93)80024-Q [36] CHINGOMBE P, SAHA B, WAKEMAN R J. Surface modification and characteristics of a coal-based activated carbon[J]. Carbon,2005,43(15):3132−3243. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.06.021 [37] ZHANG H, TU Y J, DUAN Y P, LIN J, ZHI W D, TANG Y, XIAO L S, MENG L. Production of biochar from waste sludge/leaf for fast and efficient removal of diclofenac[J]. J Mol Liq,2020,299:112193. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112193 [38] ZHANG W J, RABIEA S, BAGREEV A, ZHUANG M S, RASOULI F. Study of NO adsorption on activated carbons[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2008,83(1/2):63−71. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.02.003 [39] SHEN W Z, FAN W B. Nitrogen-containing porous carbons: Synthesis and application[J]. J Mater Chem A,2013,1(4):999−1013. doi: 10.1039/C2TA00028H [40] SEYED A D, HAFIZ S, TINA L, JUSTIN M. NO oxidation by activated carbon catalysts: Impact of carbon characteristics, pressure, and the presence of water[J]. ACS Omega,2020,33:21172−21180. [41] CLAUDINO A, SOARES J L, MOREIRA R F P M, JOSE H J. Adsorption equilibrium and breakthrough analysis for NO adsorption on activated carbons at low temperatures[J]. Carbon,2004,42(8/9):1483−1490. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.01.048 [42] FIGUEIREDO J L, PEREIRA M F R, FREITAS M M A, ORFAO J J M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons[J]. Carbon,1999,37(9):1379−1389. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00333-9 [43] 李圆圆, 陈少华, 张召基, 石建稳, 汤凤霞. KOH活化丝瓜络制备高比表面积活性炭[J]. 化工进展,2012,31(6):1274−1279.LI Yuan-yuan, CHEN Shao-hua, ZHANG Zhao-ji, SHI Jian-wen, TANG Feng-xia. Preparation of high surface area activated carbons from Luffa cylindrical sponge by KOH activation[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2012,31(6):1274−1279. [44] ADAPA S, GAUR V, VERMA N. Catalytic oxidation of NO by activated carbon fiber (ACF)[J]. Chem Eng J,2006,116(1):25−37. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2005.10.007 [45] FAN H J, HE K J, ZHOU H, WANG J. Pyrolysis of municipal sewage in a slowly heating and gas sweeping fixed-bed reactor[J]. Energy Convers Manage,2014,88:1151−1158. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2014.05.043 [46] SANDOVAL S, KUMAR N, ORO-SOLE J. Tuning the nature of nitrogen atoms in N-containing reduced graphene oxide[J]. Carbon,2016,96:594−602. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.09.085 [47] LIU J, LI G Q, CHEN L, WANG Y, XU Y, QIAO X X, ZHANG Y F. Effects of atmospheric gas on pyrolysis characteristics of briquetted lignite and surface properties of semi-char[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2016,151:40−49. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.05.035 [48] YIN Y S, YIN J, ZHANG W, TIAN H, HU Z M, RUAN M, XU H F, LIU L, YAN X Z, CHEN D L. FT-IR and micro-Raman spectroscopic characterization of minerals in high-calcium coal ashes[J]. Energy Inst,2018,91(3):389−396. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2017.02.003 [49] ZHANG Z Q, ATKINSON J D, JIANG B Q, ROOD M J, YAN Z F. Nitric oxide oxidation catalyzed by microporous activated carbon fiber cloth: an updated reaction mechanism[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2014,148–149:573−581. [50] YANG H, LIU H, ZHOU K, YAN Z Q, ZHAO R, LIU Z H, LIU Z H, QIU J R. Oxidation path analysis of NO in the adsorption and removal process using activated carbon fibers[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2012,40(8):1002−1008. [51] ATKINSON J D, ZHANG Z Q, YAN Z F, ROOD M J. Evolution and impact of acidic oxygen functional groups on activated carbon fiber cloth during NO oxidation[J]. Carbon,2013,54:444−453. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.11.060 -




 下载:
下载: