Recent advances in integrated carbon dioxide capture and methanation technology
-
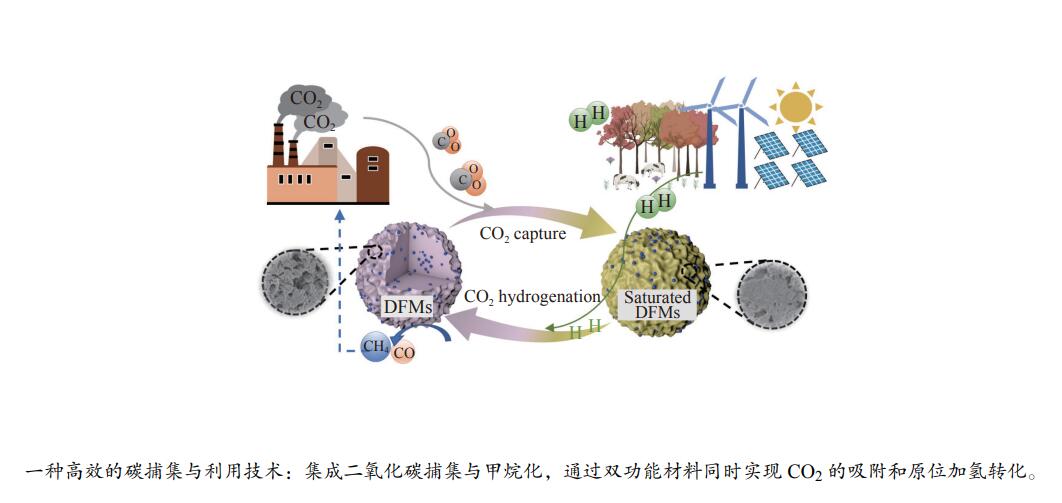
摘要: 开发新型高效的二氧化碳捕集或利用技术对于减少化石能源利用过程的二氧化碳排放、缓解全球变暖等具有重要意义。集成二氧化碳捕集与利用技术(ICCU)因其能耗低和效率高等优势获得了广泛关注。该技术利用一种双功能材料通过集成二氧化碳吸附和原位转化两个主要过程,实现CO2的高效转化并获得含碳燃料。本工作综述了ICCU中主要技术之一集成二氧化碳捕集与甲烷化转化。首先对实现该过程的双功能材料的组成和特性进行概述,重点从反应温度、反应时间、反应气体成分等角度探讨了影响ICCU甲烷化反应的因素,并对该技术未来的机遇和挑战进行总结和展望,以期为中国“双碳”目标下致力于二氧化碳捕集和利用的相关研究提供一定的借鉴。Abstract: The development of novel carbon dioxide capture or utilization technology is of great significance to reduce carbon dioxide emissions from fossil energy utilization, as well as to alleviate global warming. The integrated carbon dioxide capture and utilization (ICCU) technology, which integrate carbon dioxide adsorption and in-situ conversion to realize efficient conversion of carbon dioxide to carbon containing fuels over dual function material, has attracted extensive attentions due to its advantages of low energy consumption and high efficiency. In this paper, the composition and characteristics of the dual function materials for CO2 capture and methanation were summarized. The factors which affected the methanation process were discussed from the perspectives of reaction temperature, reaction time, feed gas compositions. The challenges and opportunities in the near future were also proposed.
-
Key words:
- carbon dioxide /
- capture and utilization /
- methanation /
- dual function materials
-
表 1 CO2的捕集和利用
Table 1 Summary of CO2 capture and utilization technology
Technology Description Advantages Disadvantages Ref. CO2 capture technology pre-combustion capture separate other combustibles from CO2 before carbon based fuel combustion high CO2 concentration
and easy separationneed upgrade current power plant which is difficult and high-cost [8,9] oxy-fuel combustion capture burning fuel using pure oxygen, or a mixture of oxygen, capture CO2 in
tail gasproducts can be stored directly high cost of oxygen production, sensitive to air leakage [10] post-combustion capture adsorption separation the different binding force between porous materials and gases is used to realize the separation of gas mixtures flexible operation, safe and low cost poor selectivity, unstable performance of some inorganic adsorbents [11,12] absorption separation separation of gas mixtures using different solubility high CO2 concentration and high yield high energy consumption, high equipment investment [13] membrane separation capture using differences in solubility and diffusivity high selectivity, low
energy consumptionnarrow application, poor stability [14,15] CO2 utilization technology electrochemical conversion the reduction of CO2 into chemicals is driven by the potential difference between the two electrodes flexible operation, mild reaction conditions low stability of electrocatalyst, high energy consumption [16] solar thermochemical conversion technology solar radiation is used to drive CO2 and H2O to produce strong endothermic reaction for utilization low energy consumption low conversion efficiency [17] photochemical
conversionCO2 conversion reaction is promoted by absorbing heat energy and overcoming activation energy mild reaction conditions, strong oxidation ability low efficiency in light energy utilization rate, difficulty in control [18] catalytic conversion catalysts are used to promote the formation and fracture of chemical bonds low cost and good safety stability and conversion efficiency need improvement [19,20] -
[1] 朱东波, 张相伟. 中国数字金融发展的环境效应及其作用机制研究[J]. 财经论丛,2022,(3):37−46.ZHU Dong-bo, ZHANG Xiang-wei. Research on the environmental effect of digital finance development in China[J]. Coll Essays Financ Econ,2022,(3):37−46. [2] 高鸣, 张哲晰. 碳达峰、碳中和目标下我国农业绿色发展的定位和政策建议[J]. 华中农业大学学报(社会科学版),2022,(1):24−31.GAO Ming, ZHANG Zhe-xi. Positioning and policy suggestions of China’s agricultural green development under the targets of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[J]. Huazhong Agri Univ(Soc Sci),2022,(1):24−31. [3] 张贤, 李阳, 马乔, 刘玲娜. 我国碳捕集利用与封存技术发展研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2021,23(6):70−80.ZHANG Xian, LI Yang, MA Qiao, LIU Ling-na. Development of carbon capture, utilization and storage technology in China[J]. Str Study CAE,2021,23(6):70−80. [4] LIANG J, WU Q, HUANG Y, CAO R. Reticular frameworks and their derived materials for CO2 conversion by thermo−catalysis[J]. Energy Chem,2021,3(6):100064. doi: 10.1016/j.enchem.2021.100064 [5] JOUNY M, LV J, CHENG T, KO B H, ZHU J, JIAO F. Formation of carbon-nitrogen bonds in carbon monoxide electrolysis[J]. Nat Chem,2019,11(9):846−851. doi: 10.1038/s41557-019-0312-z [6] LOW J, CHENG B, YU J. Surface modification and enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of TiO2: A review[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2017,392:658−686. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.093 [7] MOSS M, REED D G, ALLEN R W K, STYRING P. Integrated CO2 capture and utilization using non-thermal plasmolysis[J]. Front Energy Res,2017,5. [8] MARTÍN C F, GARCÍA S, PIS J J, RUBIERA F, PEVIDA C. Doped phenol-formaldehyde resins as precursors for precombustion CO2 capture adsorbents[J]. Energy Procedia,2011,4:1222−1227. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2011.01.177 [9] ZHONG D, WANG J, LU Y, LI Z, YAN J. Precombustion CO2 capture using a hybrid process of adsorption and gas hydrate formation[J]. Energy,2016,102:621−629. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.02.135 [10] 连晶红. 生物质富氧燃烧烟气中CO2捕集联合制取硫酸硝酸的研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2015: 41–48.LIAN Jing-hong. Research on CO2 capture with combined production of H2SO4 and HNO3 from oxy-biomass combustion flue gas[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2015: 41–48. [11] 聂千. 活性炭孔结构对CO2和CH4吸附分离性能的影响[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021: 31–71.NIE Qian. Effect of pore structure of activated carbon on adsorption and separation performance of CO2 and CH4[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021: 31–71. [12] 唐进京, 鲁军辉, 李俊明, 王随林. CO2/H2O吸附分离特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2022,42(6):2216−2227.TANG Jin-jing, LU Jun-hui, LI Jun-ming, WANG Sui-lin. Study on adsorption characteristics of CO2/H2O[J]. Proc CSEE,2022,42(6):2216−2227. [13] 操洁瑛. 两类季铵盐型交联聚离子液体及其对CO2的变压吸收分离研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2018: 46–52.CAO Jie-ying. Two kinds of quaternary ammonium-based crosslinked polymeric ionic liquids and their applications in separating CO2 by pressure swing absorption[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2018: 46–52. [14] 晏水平, 陈竞翱, 艾平, 王媛媛, 张衍林. 利用膜吸收技术分离沼气中CO2[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(11):196−204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.11.032YAN Shui-ping, CHEN Jing-ao, AI Ping, WANG Yuan-yuan, ZHANG Yan-lin. CO2 removal from biogas by using membrane absorption technology[J]. Trans CSAE,2012,28(11):196−204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.11.032 [15] CHEN K, NI L, ZHANG H, XIE J, YAN X, CHEN S, QI J, WANG C, SUN X, LI J. Veiled metal organic frameworks nanofillers for mixed matrix membranes with enhanced CO2/CH4 separation performance[J]. Sep Purif Technol,2021,279:119707. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119707 [16] 孟怡辰, 况思宇, 刘海, 范群, 马新宾, 张生. 面向CO2电化学转化的铜基催化剂研究进展[J]. 物理化学学报,2021,37(5):47−63.MENG Yi-chen, KUANG Si-yu, LIU Hai, MA Xin-bin, ZHANG Sheng. Recent advances in electrochemical CO2 reduction using copper-based catalysts[J]. Acta Phys-Chim Sin,2021,37(5):47−63. [17] ISHAQ H, SIDDIQUI O, CHEHADE G, DINCER I. A solar and wind driven energy system for hydrogen and urea production with CO2 capturing[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(6):4749−4760. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.01.208 [18] 张中伟, 郭瑞堂, 秦阳, 郭德宇, 潘卫国. 金属有机框架材料在光催化还原CO2中的应用[J]. 材料导报,2021,35(21):21058−21070.ZHANG Zhong-wei, GUO Rui-tang, QIN Yang, GUO De-yu, PAN Wei-guo. Application of metal-organic framework in CO2 photocatalytic reduction[J]. Mater Rep,2021,35(21):21058−21070. [19] 刘慧敏, 王美慧, 于戈文, 丁健, 王亚雄. Cu基催化材料在CO2转化中的应用[J]. 应用化工,2021,50(9):2525−2528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.09.041LIU Hui-min, WANG Mei-hui, YU Ge-wen, DING Jian, WANG Ya-xiong. Application of Cu-based catalytic materials in CO2 conversion[J]. Appl Chem Ind,2021,50(9):2525−2528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.09.041 [20] 乔哲. 修饰HZSM-5催化LPG临CO2转化制烯烃研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2021: 16–48.QIAO Zhe. Study on transformation of LPG in the presence of CO2 to olefins on modified HZSM-5 catalysts[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2021. [21] BREWER P J, BROWN R J C, MILLER M N, MINARRO M D, MURUGAN A, MILTON M J T, RHODERICK G C. Preparation and validation of fully synthetic standard gas mixtures with atmospheric isotopic composition for global CO2 and CH4 monitoring[J]. Anal Chem,2014,16−48. [22] SUN S Z, SUN H M, WILLIAMS P T, WU C F. Recent advances in integrated CO2 capture and utilization: A review[J]. Sustainable Energy Fuels,2021,5(18):4546−4559. doi: 10.1039/D1SE00797A [23] BERMEJO-LÓPEZ A, PEREDA-AYO B, ONRUBIA-CALVO J A, GONZÁLEZ-MARCOS J A, GONZÁLEZ-VELASCO J R. Tuning basicity of dual function materials widens operation temperature window for efficient CO2 adsorption and hydrogenation to CH4[J]. J CO2 Util,2022,58:101922. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.101922 [24] SUN H, ZHANG Y, GUAN S, HUANG J, WU C F. Direct and highly selective conversion of captured CO2 into methane through integrated carbon capture and utilization over dual functional materials[J]. J CO2 Util,2020,38:262−272. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2020.02.001 [25] HU J, HONGMANOROM P, CHIRAWATKUL P, KAWI S. Efficient integration of CO2 capture and conversion over a Ni supported CeO2-modified CaO microsphere at moderate temperature[J]. Chem Eng J,2021,426:130864. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130864 [26] VALVERDE J M, SANCHEZ-JIMENEZ P E, PEREZ-MAQUEDA L A. Calcium-looping for post-combustion CO2 capture. On the adverse effect of sorbent regeneration under CO2[J]. Appl Energy,2014,126:161−171. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.081 [27] 康东芮. 基于新型双功能催化剂的二氧化碳捕集和利用研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2020: 13−30.KANG Dong-rui. Research on carbon dioxide capture and utilization based on new dual-function catalyst[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of technology, 2020: 13−30. [28] JO S B, WOO J H, LEE J H, KIM T Y, KANG H I, LEE S C, KIM J C. A novel integrated CO2 capture and direct methanation process using Ni/CaO catal-sorbents[J]. Sustainable Energy Fuels,2020,4(9):4679−4687. doi: 10.1039/D0SE00760A [29] BERMEJO-LÓPEZ A, PEREDA-AYO B, GONZÁLEZ-MARCOS J A, GONZÁLEZ-VELASCO J R. Ni loading effects on dual function materials for capture and in-situ conversion of CO2 to CH4 using CaO or Na2CO3[J]. J CO2 Util,2019,34:576−587. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2019.08.011 [30] HE Z, LIBBY M C, FARRAUTO R J. Catalysts and adsorbents for CO2 capture and conversion with dual function materials: Limitations of Ni-containing DFMs for flue gas applications[J]. J CO2 Util, 2022, 428: 1312. [31] CIMINO S, RUSSO R, LISI L. Insights into the cyclic CO2 capture and catalytic methanation over highly performing Li-Ru/Al2O3 dual function materials[J]. Chem Eng J,2022,428:131275. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131275 [32] DUYAR M S, WANG S, ARELLANO-TREVIñO M A, FARRAUTO R J. CO2 utilization with a novel dual function material (DFM) for capture and catalytic conversion to synthetic natural gas: An update[J]. J CO2 Util,2016,15:65−71. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2016.05.003 [33] BERMEJO-LÓPEZ A, PEREDA-AYO B, GONZÁLEZ-MARCOS J A, GONZÁLEZ-VELASCO J R. Mechanism of the CO2 storage and in situ hydrogenation to CH4. Temperature and adsorbent loading effects over Ru-CaO/Al2O3 and Ru-Na2CO3/Al2O3 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2019,256:117845. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117845 [34] EFREMOVA A, RAJKUMAR T, SZAMOSVÖLGYI Á, SÁPI A, BAÁN K, SZENTI I, GÓMEZ-PÉREZ J, VARGA G, KISS J, HALASI G, KUKOVECZ A, KÓNYA Z. Complexity of a Co3O4 system under ambient-pressure CO2 methanation: Influence of bulk and surface properties on the catalytic performance[J]. J Phys Chem C,2021,125(13):7130−7141. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c09717 [35] EFREMOVA A, SZENTI I, KISS J, SZAMOSVöLGYI A, SÁPI A, BAÁN K, OLIVI L, VARGA G, FOGARASSY Z, PÉCZ B, KUKOVECZ A, KÓNYA Z. Nature of the Pt-cobalt-oxide surface interaction and its role in the CO2 methanation[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2022,571:151326. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151326 [36] LEE C H, CHOI S W, YOON H J, KWON H J, LEE H C, JEON S G, LEE K. Na2CO3-doped CaO-based high-temperature CO2 sorbent and its sorption kinetics[J]. Chem Eng J,2018,352:103−109. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.141 [37] AL-MAMOORI A, THAKKAR H, LI X, ROWNAGHI A A, REZAEI F. Development of potassium- and sodium-promoted CaO adsorbents for CO2 capture at high temperatures[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2017,56(29):8292−8300. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b01587 [38] SUN H, PARLETT C M A, ISAACS M A, LIU X T, ADWEK G, WANG J Q, SHEN B X, HUANG J, WU C F. Development of Ca/KIT-6 adsorbents for high temperature CO2 capture[J]. Fuel,2019,235:1070−1076. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.07.044 [39] GAO F, HUANG J, SUN H, HU J, WANG M, MI J, WU C F. CO2 capture using mesocellular siliceous foam (MCF)-supported CaO[J]. J Energy Inst,2019,92(5):1591−1598. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2018.07.015 [40] 高峰, 李存梅, 王媛, 孙国华, 李开喜. 树脂基球状活性炭的制备及对二氧化碳吸附性能的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2014,42(1):116−120.GAO Feng, LI Cun-mei, WANG Yuan, SUN Guo-hua, LI Kai-xi. Preparation of resin-base spherical activated carbon and study on adsorption properties towards CO2[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2014,42(1):116−120. [41] 胡苏阳, 刘鑫博, 唐建峰, 李光岩, 孙永彪, 花亦怀, 李秋英. 13X沸石分子筛对低浓度CO2动态吸附[J]. 化工进展,2022,41(1):153−160.HU Su-yang, LIU Xin-bo, TANG Jian-feng, LI Guang-yan, SUN Yong-biao, HUA Yi-huai, LI Qiu-ying. Dynamic adsorption of low concentration CO2 over 13X zeolite[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2022,41(1):153−160. [42] 周程, 南永永, 查飞, 田海峰, 唐小华, 常玥. 金属有机骨架材料在二氧化碳加氢中的应用[J]. 燃料化学学报,2021,49(10):1444−1457. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60097-XZHOU Cheng, NAN Yong-yong, CHA Fei, TIAN Hai-feng, TANG Xiao-hua, CHANG Yue. Application of metal-organic frameworks in CO2 hydrogenation[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2021,49(10):1444−1457. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60097-X [43] SANG Y, CAO Y, WANG L, YAN W, CHEN T, HUANG J, LIU Y N. N-rich porous organic polymers based on Schiff base reaction for CO2 capture and mercury(II) adsorption[J]. J Colloid Interf Sci,2021,587:121−130. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.12.002 [44] SUN H, WANG Y, XU S, OSMAN A I, STENNING G, HAN J, SUN S, ROONEY D, WILLIAMS P T, WANG F, WU C F. Understanding the interaction between active sites and sorbents during the integrated carbon capture and utilization process[J]. Fuel,2021,286:119308. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119308 [45] MA X, LI X, CUI H, ZHANG W, CHENG Z, ZHOU Z. Metal oxide-doped Ni/CaO dual-function materials for integrated CO2 capture and conversion: Performance and mechanism[J]. AIChE J, 2023, 69(1): e17520. [46] LIU Q, DONG H. In Situ Immobilizing Ni nanoparticles to FDU-12 via trehalose with fine size and location control for CO2 methanation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2020,8(4):2093−2105. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07004 [47] HU F, YE R, LU Z H, ZHANG R B, FENG G. Structure-activity relationship of Ni-based catalysts toward CO2 methanation: recent advances and future perspectives[J]. Energy Fuels,2021,36(1):156−169. [48] ARELLANO-TREVIÑO M A, KANANI N, JEONG-POTTER C W, FARRAUTO R J. Bimetallic catalysts for CO2 capture and hydrogenation at simulated flue gas conditions[J]. Chem Eng J,2019,375:121953. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.121953 [49] JEONG-POTTER C, FARRAUTO R. Feasibility study of combining direct air capture of CO2 and methanation at isothermal Conditions with dual function materials[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2021,282:119416. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119416 [50] JEONG-POTTER C, ABDALLAH M, SANDERSON C, GOLDMAN M, GUPTA R, FARRAUTO R. Dual function materials (Ru + Na2O/Al2O3) for direct air capture of CO2 and in situ catalytic methanation: the impact of realistic ambient conditions[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2021,307:120990. [51] WANG S, FARRAUTO R J, KARP S, JEOM J H, SCHRUNK E T. Parametric, cyclic aging and characterization studies for CO2 capture from flue gas and catalytic conversion to synthetic natural gas using a dual functional material (DFM)[J]. J CO2 Util,2018,27:390−397. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.08.012 [52] PROAñO L, ARELLANO-TREVIñO M A, FARRAUTO R J, FIGUEREDO M, JEONG-POTTER C, COBO M. Mechanistic assessment of dual function materials, composed of Ru-Ni, Na2O/Al2O3 and Pt-Ni, Na2O/Al2O3, for CO2 capture and methanation by in-situ DRIFTS[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2020,533:147469. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147469 [53] PORTA A, VISCONTI C G, CASTOLDI L, MATARRESE R, JEONG-POTTER C, FARRAUTO R, LIETTI L. Ru-Ba synergistic effect in dual functioning materials for cyclic CO2 capture and methanation[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2021,283:119654. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119654 [54] DUYAR M S, TREVIÑO M A A, FARRAUTO R J. Dual function materials for CO2 capture and conversion using renewable H2[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2015,168−169:370−376. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.12.025 [55] 张锦川, 杨应举, 刘晶, 华芷萱. Ni/SSZ-13催化剂的CO2甲烷化反应性能研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2021,49(7):960−966.ZHANG Jin-chuan, YANG Ying-ju, LIU Jing, HUA Zhi-xuan. Catalytic activity of Ni/SSZ-13 catalyst for CO2 methanation[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2021,49(7):960−966. [56] 刘华平, 叶素芳, 王呈呈, 孔丽萍, 叶向荣, 钟依均, 朱伟东, 陈刚, 王树华. ZrO2负载金属对CO2甲烷化的催化作用[J]. 低温与特气,2016,34(2):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7804.2016.02.001LIU Hua-ping, YE Su-fang, WANG Cheng-cheng, KONG Li-ping, YE Xiang-rong, ZHONG Yi-jun, ZHU Wei-dong, CHEN Gang, WANG Shu-hua. Catalytic performance of zirconia supported metal catalysts on CO2 methanation -a review[J]. LTSG,2016,34(2):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7804.2016.02.001 [57] 高美琦, 宋华. 载体类型对Ni基催化剂CO2甲烷化性能的影响[J]. 能源化工,2021,42(5):1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7906.2021.05.001GAO Mei-qi, SONG Hua. The influence of support types of nickel-based catalysts on CO2 methanation performance[J]. Energ Chem Ind,2021,42(5):1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7906.2021.05.001 [58] 张荣斌, 仝塞, 杨金美, 唐纤秾, 黄传庆, 王学文, 冯刚, 蔡建信. 石墨烯负载镍催化CO2加氢甲烷化[J]. 高等学校化学学报,2017,38(12):2255−2261. doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170348ZHANG Rong-bin, TONG Sai, YANG Jin-mei, TANG Xian-nong, HUANG Chuan-qing, WANG Xue-wen, FENG Gang, CAI Jian-xin. Graphene supported nickel catalyst for methanation of carbon dioxide[J]. Chem J Chin Univ,2017,38(12):2255−2261. doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170348 [59] ZHENG Q, FARRAUTO R, CHAU NGUYEN A. Adsorption and methanation of flue gas CO2 with dual functional catalytic materials: A parametric study[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2016,55(24):6768−6776. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b01275 [60] 顾碧娇. 改性Mg-MOF碳化衍生材料的制备及其CO2吸附性能研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2021: 38–44.GU Bi-jiao. Preparation of modified Mg-MOF carbonation derived materials and their CO2 adsorption properties[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021: 38–44. [61] 周郁文, 苏通明, 蒋月秀, 秦祖赠, 纪红兵. Co负载量对Co/TiO2催化CO2甲烷化性能影响[J]. 精细化工,2018,35(1):72−80.ZHOU Yu-wen, SU Tong-ming, JIANG Yue-xiu, QIN Zu-zeng, JI Hong-bing. Effect of Co loading amount on catalytic performance of Co /TiO2 catalysts for CO2 methanation[J]. Fine Chem,2018,35(1):72−80. [62] SASAYAMA T, KOSAKA F, LIU Y, YAMAGUCHI T, CHEN S, MOCHIZUKI T, URAKAWA A, KURAMOTO K. Integrated CO2 capture and selective conversion to syngas using transition-metal-free Na/Al2O3 dual-function material[J]. J CO2 Util,2022,60:102049. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102049 [63] BERMEJO-LÓPEZ A, PEREDA-AYO B, GONZÁLEZ-MARCOS J A, GONZÁLEZ-VELASCO J R. Simulation-based optimization of cycle timing for CO2 capture and hydrogenation with dual function catalyst[J]. Catal Today, 2021, 394−396: 314−324 [64] JEONG-POTTER C, PORTA A, MATARRESE R, VISCONTI C G, LIETTI L, FARRAUTO R. Aging study of low Ru loading dual function materials (DFM) for combined power plant effluent CO2 capture and methanation[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2022,310:121294. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121294 -





 下载:
下载: