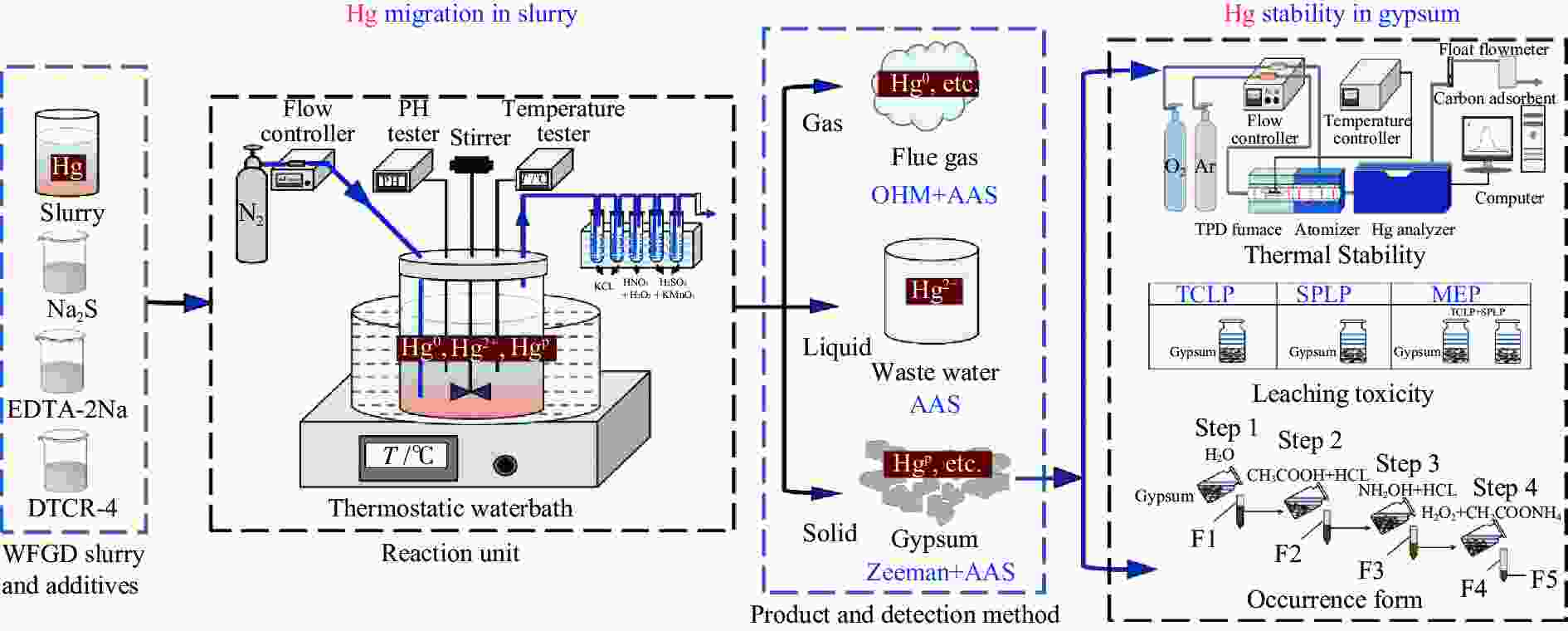
Migration and transformation of mercury in WFGD slurry from a coal-fired power unit and the effect of additive on mercury stability in gypsum
-
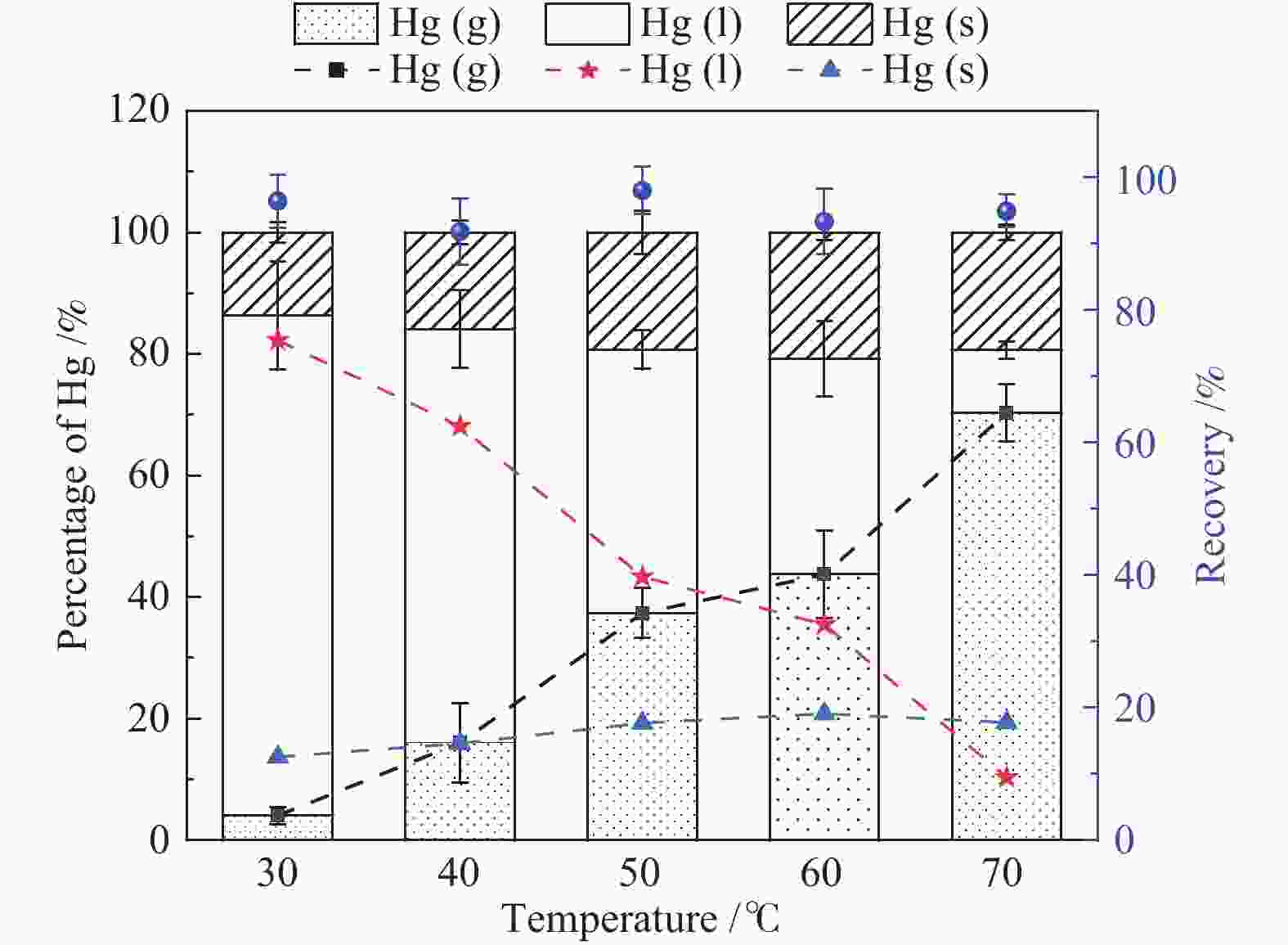
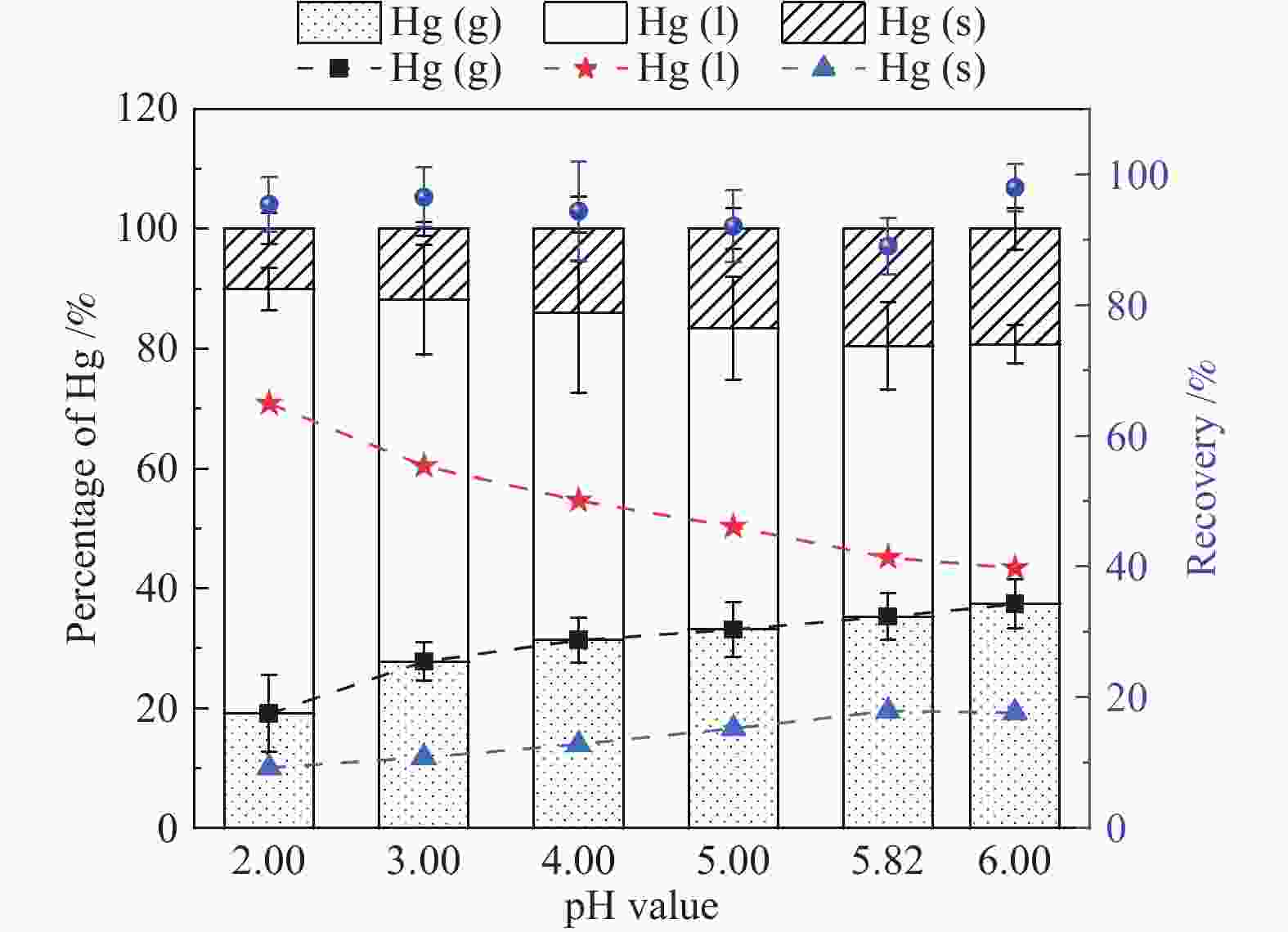
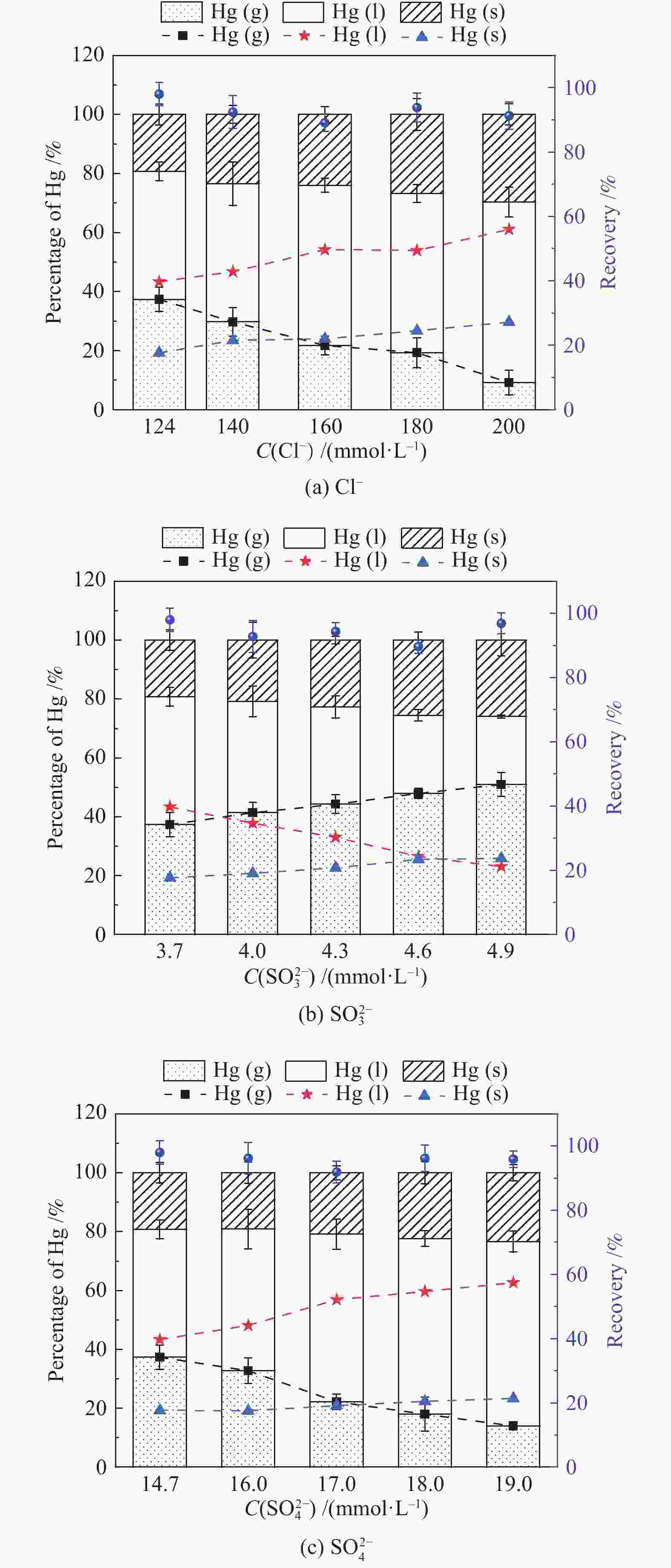
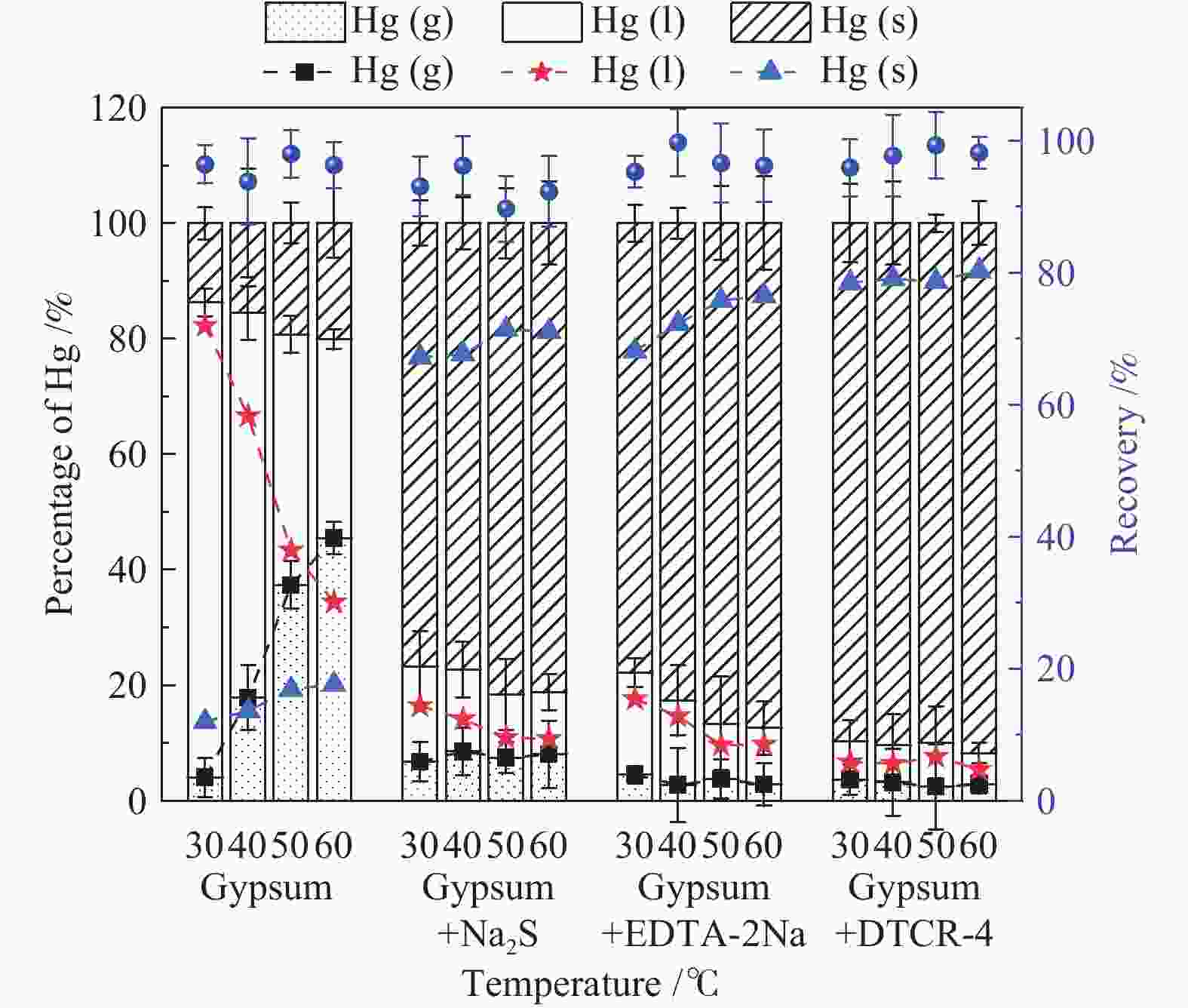
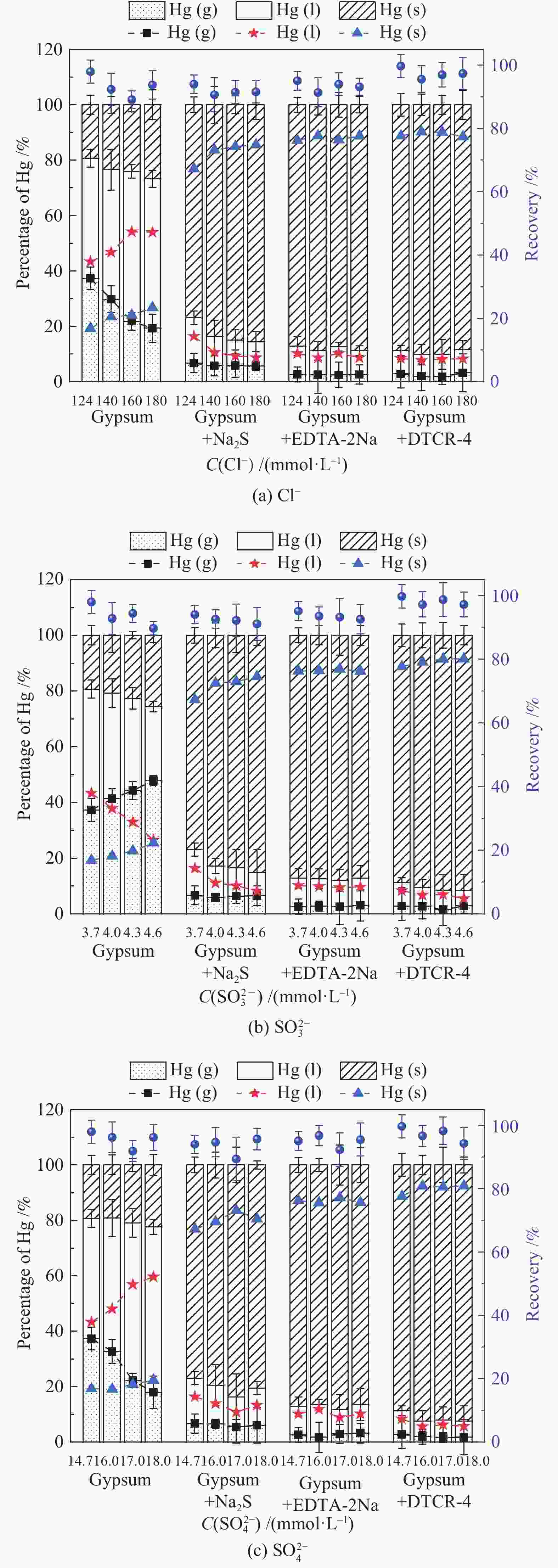
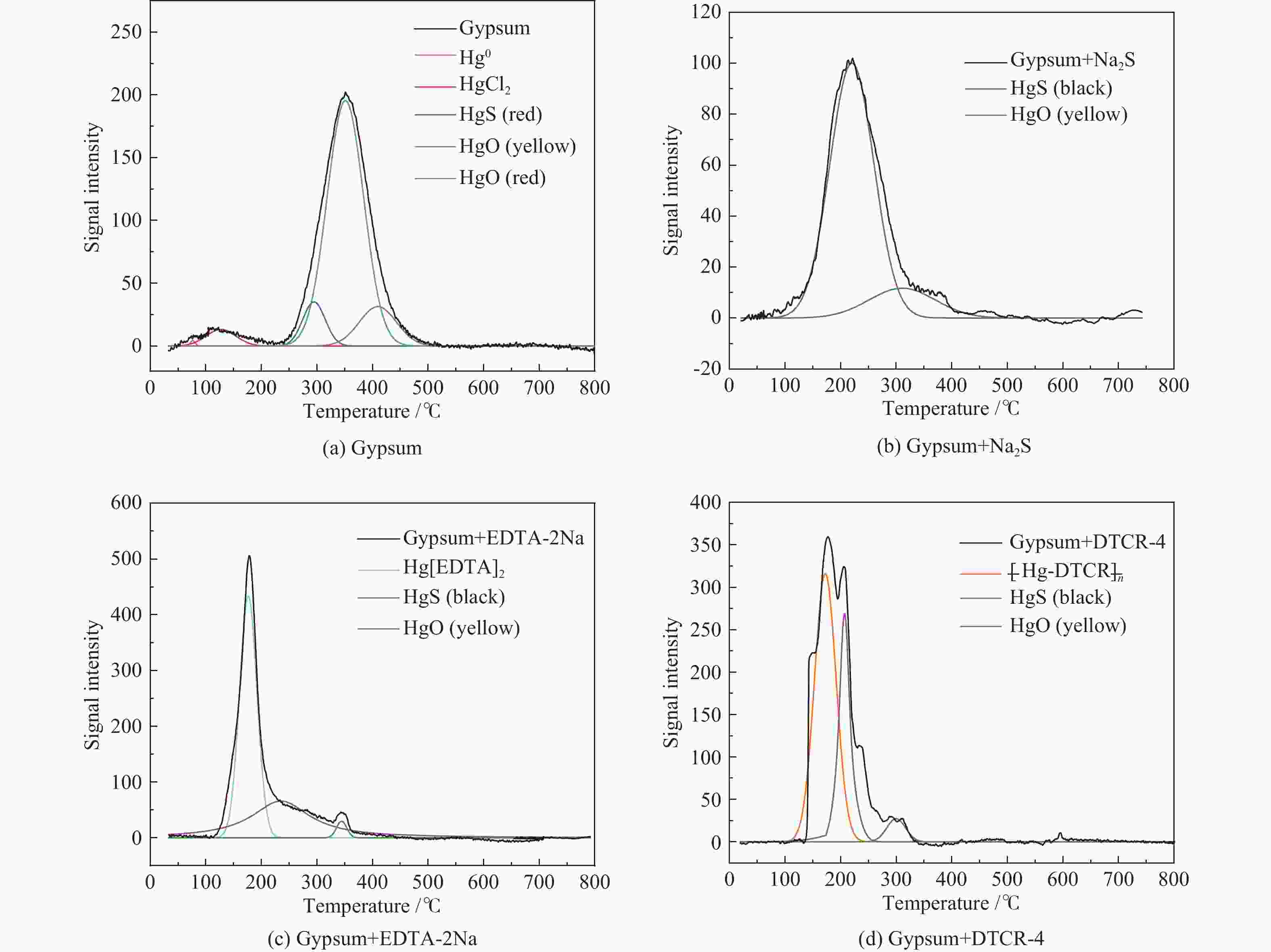
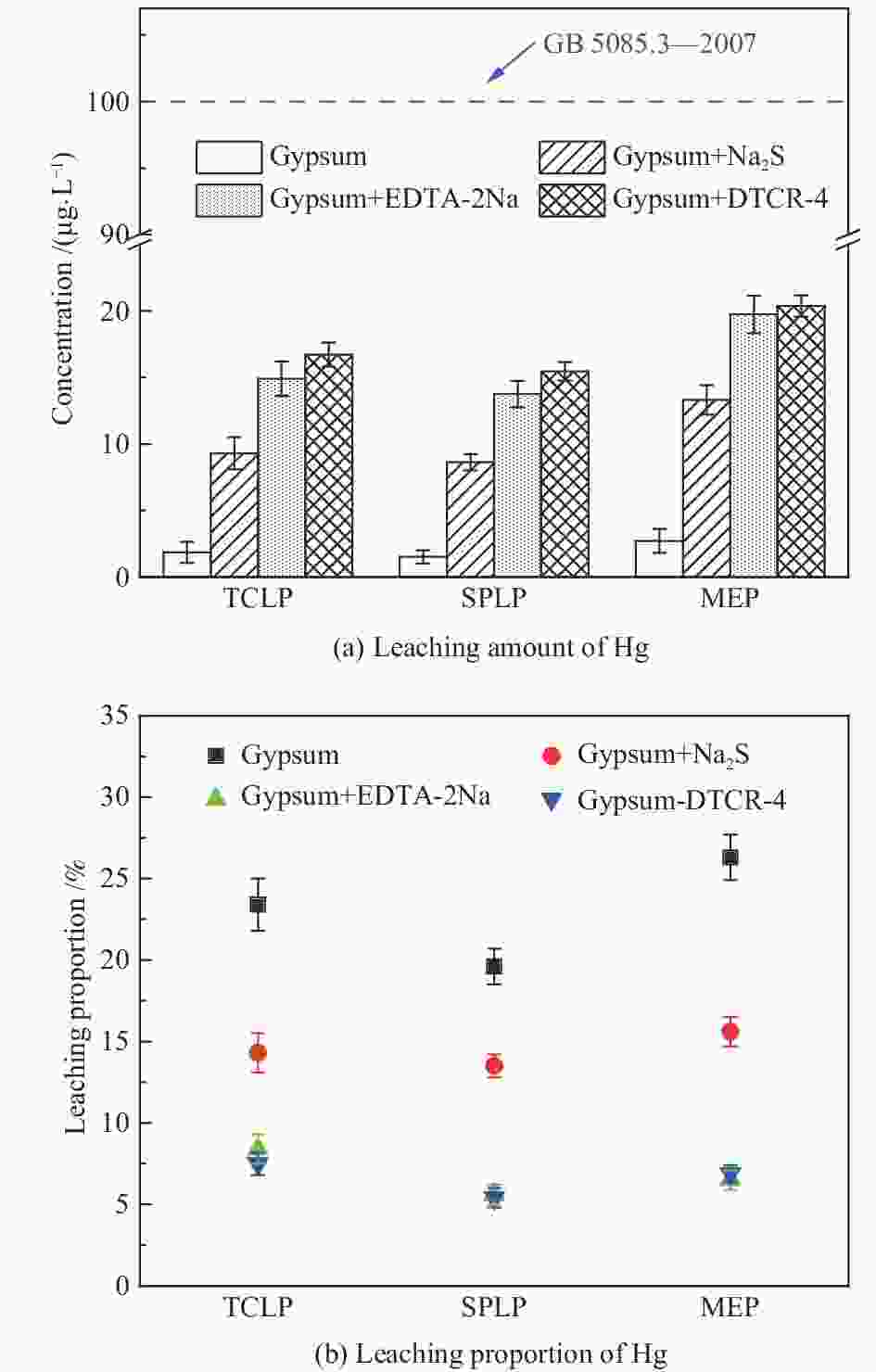
摘要: 以某300 MW超低排放燃煤机组现场脱硫浆液为研究对象,考察了浆液中汞迁移转化及添加剂对其影响行为,探讨了固相石膏中汞的热释放特性和环境风险。结果表明温度升高仅导致气相Hg0增加,而浆液pH升高会导致气相和固相中汞含量均有增加,Cl−或
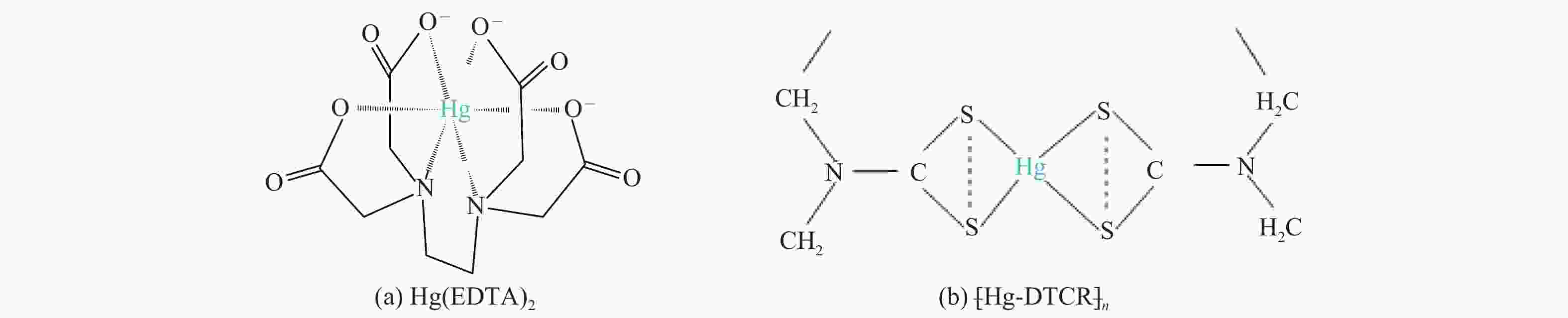
$ {\rm{SO}}^{2-}_{4} $ 浓度升高既可以抑制浆液中汞还原为Hg0也可以促进固相石膏中汞含量增加,而$ {\rm{SO}}^{2-}_{3} $ 浓度升高虽然有利于汞富集于固相但会引起Hg2+部分转化为Hg0。Na2S、EDTA-2Na或DTCR-4添加剂与Hg2+反应分别生成HgS、Hg(EDTA)2或[ −Hg-DTCR] −n,使浆液中75%以上汞转移至固相石膏中,并抑制了Hg2+还原为Hg0,其中DTCR-4对汞的固化效果最好,但热稳定性依次为Gypsum + EDTA-2Na < Gypsum + DTCR-4 < Gypsum + Na2S < Gypsum,主要原因是所生成Hg(EDTA)2、[ −Hg-DTCR] −n和HgS(black)的稳定性差异所致。进而采用TCLP、SPLP和MEP三种方法获得了样品中汞的化学稳定性为Gypsum < Gypsum + Na2S < Gypsum + EDTA-2Na < Gypsum + DTCR-4,其原因是石膏中水溶态汞、酸溶态汞和可氧化态汞含量的差异所致。Abstract: Slurry sample was collected from a 300 MW ultra-low emissions coal-fired power unit. The migration and transformation behaviors of mercury in the sample were investigated, and the effect of additive on the stability of mercury in solid gypsum was explored by considering the thermal release behavior and environmental risk. The results show that gaseous Hg0 is increased with the increase of slurry temperature, while Hg is increased in both gas phase and gypsum with the increase of slurry pH. The concentration of Cl− or$ {\rm{SO}}^{2-}_{4} $ increases in slurry could inhibit the reduction of Hg2+ to Hg0 and increase Hg proportion in gypsum. However, the increase of$ {\rm{SO}}^{2-}_{3} $ concentration is beneficial to the Hg enriched in gypsum and a part of Hg2+ reduced to Hg0. When Na2S, EDTA-2Na or DTCR-4 is added, Hg2+ is turned into HgS, Hg(EDTA)2 or [ −Hg-DTCR] −n, respectively among which more than 75% Hg is transferred to gypsum and Hg2+ is inhibited to reduce into Hg0. The thermal stability of Hg in gypsum can be ordered as Gypsum + EDTA-2Na < Gypsum + DTCR-4 < Gypsum + Na2S < Gypsum due to the stability difference among Hg(EDTA)2, [ −Hg-DTCR] −n and HgS(black). By using TCLP, SPLP and MEP, the chemical stability of Hg in gypsum can be ordered as Gypsum < Gypsum + Na2S < Gypsum + EDTA-2Na < Gypsum + DTCR-4 due to the concentration difference of water soluble mercury, acid soluble mercury and oxidizable mercury among gypsums.-
Key words:
- coal-fired power unit /
- WFGD slurry /
- mercury /
- migration and transformation /
- additive /
- gypsum /
- stability
-
表 1 入炉煤的工业分析以及氯和汞含量
Table 1 Proximate analysis, chlorine and mercury content of feed coal
Proximate analysis w/% S content/% Cl content/ (mg·kg−1) Hg content/ (mg·kg−1) M A V FC 2.57 14.84 30.09 52.50 0.37 0.078 0.0621 not: air drying base 表 2 本研究测量的脱硫浆液基本物性参数
Table 2 Main properties of WFGD slurry measured in this study
Sample Hg/ (μg·L−1) Temperature/ ℃ pH Cl−/ (mg·L−1) $ {\rm{SO}}^{2-}_{3} $/ (mg·L−1) $ {\rm{SO}}^{2-}_{4} $/ (mg·L−1) Slurry 157 50 5.82 4414 296 1413 表 4 含汞化合物的释放温度特征
Table 4 Release temperatures of Hg-containing compounds
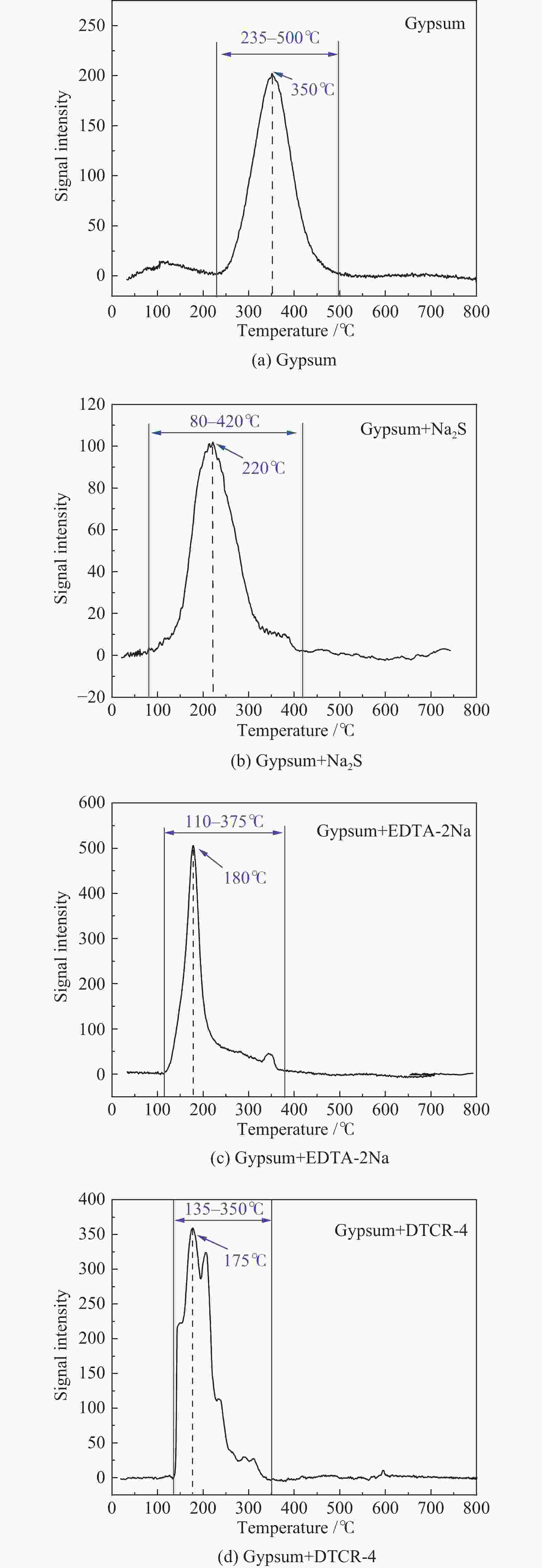
Hg-containing compounds Temperature range of Hg release/℃ Peak temperature of Hg release/℃ Hg2Cl2 110−220 119 ± 10 HgCl2 95−350 138 ± 4 HgS(black) 150−280 220 ± 11 HgS(red) 210−340 305 ± 12 HgO(yellow) 250−450 284 ± 7 HgO(red) 360−500 420 ± 10 HgSO4 495−600 560 ± 10 表 5 Hg2+与有机添加剂反应产物中汞的释放温度
Table 5 Release temperatures of mercury in the reaction products of Hg2+ and organic additives
Reaction product Temperature range of Hg release/℃ Peak temperature of Hg release/℃ Hg(EDTA)2 100−210 164 ± 4 [ −Hg-DTCR] −n 105−230 186 ± 4 -
[1] Minamata Convention on Mercury[S]. United Nations Environment Programme, 2017. [2] ZHAO W M, GENG X Z, LU J C, DUAN Y F, LIU S, HU P, XU Y F, HUANG Y J, TAO J, GU X B. Mercury removal performance of brominated biomass activated carbon injection in simulated and coal-fired flue gas[J]. Fuel,2021,285:119131. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119131 [3] 辛凤, 魏书洲, 张军峰, 马斯鸣, 赵永椿, 张军营. 燃煤烟气非碳基吸附剂脱汞研究进展[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(12):1409−1420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.12.002XIN Feng, WEI Shu-zhou, ZHANG Jun-feng, MA Si-ming, ZHAO Yong-chun, ZHANG Jun-yin. Research progress on the removal of mercury from coal-fired flue gas by using non-carbon-based adsorbents[J]. J Fuel Chem and Technol,2020,48(12):1409−1420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2020.12.002 [4] 岳光溪, 周大力, 田文龙, 麻林巍, 刘青, 章景皓, 王志轩, 龙辉, 廖海燕. 中国煤炭清洁燃烧技术路线图的初步探讨[J]. 中国工程科学,2018,20(3):74−79.YUE Guang-xi, ZHOU Da-li, TIAN Wen-long, MA Lin-wei, LIU Qin, ZHANG Jin-hao, WANG Zhi-xuan, LONG Hui, LIAO Hai-yan. Preliminary discussion on the technology roadmap of clean coal combustion in China[J]. Strategic Study CAE,2018,20(3):74−79. [5] 李晓航, 刘芸, 苏银皎, 滕阳, 关彦军, 张锴. 煤粉炉和循环流化床锅炉飞灰特性对其汞吸附能力的影响[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(3):1075−1082.LI Xiao-hang, LIU Xuan, SU Yin-jiao, TENG Yang, GUAN Yan-jun, ZHANG Kai. Difference of fly ash characteristics from PC and CFB boilers and its effect on mercury adsorption capability[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2019,70(3):1075−1082. [6] OTTEN B V, BUITRAGO P A, SENIOR C L, SILCOX G D. Gas-phase oxidation of mercury by bromine and chlorine in flue gas[J]. Energy Fuels,2011,25(8):3530−3536. [7] JENNIFER W, ERIK R, YING S C, LIM D H, NEGRIRA A S, KIRCHOFER A, FENG F, LEE K. Mercury adsorption and oxidation in coal combustion and gasification processes[J]. Int J Coal Geol,2012,90−91:4−20. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2011.12.003 [8] HAYNES W M E. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (Internet Version 2016) (96th)[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, 2016. [9] WU C L, CAO Y, DONG Z B, CHENG C M, LI H X, PAN W P. Evaluation of mercury speciation and removal through air pollution control devices of a 190 MW boiler[J]. J Environ Sci,2010,22(2):277−282. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60105-4 [10] SENIOR C L, HELBLE J J, SAROFIM A F. Emissions of mercury, trace elements, and fine particles from stationary combustion sources[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2002,65−66:263−288. [11] NARUHITO O, CARLOS E R, HIROFUMI K, WU S, SANDHYA E. Study of elemental mercury re-emission in a simulated wet scrubber[J]. Fuel,2012,91(1):93−101. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.06.018 [12] 毛琳, 张志越, 孙佳兴, 祁东旭, 陈逸鹏, 杨宏旻. 添加剂对抑制模拟脱硫浆液中汞再释放的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2018,46(10):1265−1271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.10.015MAO Lin, ZHANG Zhi-yue, SUN Jia-xing, QI Dong-xu, CHEN Yi-peng, YANG Hong-hao. Effects of additives on stabilization and inhibition of mercury re-emission in simulated wet gas desulphurization slurry[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2018,46(10):1265−1271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.10.015 [13] BARNA H, MELANIE H, GUNTER S. Impact of additives for enhanced sulfur dioxide removal on re-emissions of mercury in wet flue gas desulfurization[J]. Appl Energy,2014,114:485−491. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.09.059 [14] 蒋建国, 王伟, 甄晓月, 杜竹玮. 高分子螯合剂捕集重金属Pb2+的机理研究[J]. 环境科学学报,1997,18(2):31−31+95.JAING Jian-guo, WANG Wei, ZHEN Xiao-yue, DU Zhu-wei. Study on mechanism of polymer chelating agent for trapping heavy metal Pb2+[J]. Acta Sci Circum,1997,18(2):31−31+95. [15] KRZYZYNSKA R, HUTSON N D, ZHAO Y, SZELIGA Z, REGUCKI P. Mercury removal and its fate in oxidant enhanced wet flue gas desulphurization slurry[J]. Fuel,2018,211:876−882. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.10.004 [16] LIU S T, GAO Y, LIU Y C. Investigation on mercury reemission from Limestone-Gypsum wet flue gas desulfurization slurry[J]. The Scientific World J,2014,(3/4):581724. [17] SCHUETZE J, KUNTH D, WEISSBACH S, KOESER H. Mercury vapor pressure of flue gas desulfurization scrubber suspensions: effects of pH level, gypsum, and iron[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2012,46(5):3008−3013. doi: 10.1021/es203605h [18] OCHOA-GONZÁLEZ R, DIAZ-SOMOANO M, MARTINEZ-TARAZONA M R. Control of Hg0 re-emission from gypsum slurries by means of additives in typical wet scrubber conditions[J]. Fuel,2013,105:112−118. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.05.044 [19] 潘杰, 晏乃强, 瞿赞, 徐浩淼, 马永鹏, 陈万苗, 黄文君, 赵松建. 燃煤电厂脱硫石膏中汞的浸出特性研究[J]. 环境科学与技术,2015,38(7):88−92.PAN Jie, YAN Nai-qiang, QU Zan, XU Hao-miao, MA Yong-peng, CHEN Miao-wan, HUANG Wen-jun, ZHAO Song-jian. Leaching characteristics of mercury in WFGD gypsum[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2015,38(7):88−92. [20] CUI L M, WANG Y G, GAO L, HU L H, YAN L G, WEI Q, DU B. EDTA functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for removal of Pb(II), Hg(II) and Cu(II) in water treatment: Adsorption mechanism and separation property[J]. Chem Eng J,2015,281:1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.043 [21] SUN J, CHEN H, QI D, WU H, ZHOU C, YANG H. Enhanced immobilization of mercury (II) from desulphurization wastewater by EDTA functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles[J]. Environ Technol,2020,41(11):1366−1379. [22] 郭敏辉, 于洁, 官宝红. 电石渣脱硫废水中超标重金属的去除[J]. 水处理技术,2014,40(10):28−31.GUO Min-hui, YU Jie, GUAN Bao-hong. Heavy metals removal from the carbide slag desulfurization wastewater[J]. Technol Water Treatment,2014,40(10):28−31. [23] TANG T M, XU J, LU R J, WO J J. Enhanced Hg2+ removal and Hg0 re-emission control from wet fuel gas desulfurization liquors with additives[J]. Fuel,2010,89(12):3613−3617. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.07.045 [24] LE I R, HUANG C H, JEN Y S, YUAN C H, CHEN W H. Adsorption of vapor-phase elemental mercury (Hg0) and mercury chloride (HgCl2) with innovative composite activated carbons impregnated with Na2S and S0 in different sequences[J]. Chem Eng J,2013,229:469−476. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.059 [25] 付康丽, 姚明宇, 钦传光, 程广文, 聂剑平. 巯基聚苯乙烯树脂对FGD系统中Hg2+的脱除性能[J]. 化工学报,2016,67(6):2598−2604.FU Kang-li, YAO Ming-yu, QIN Chuan-guang, CHENG Wen-guang, NIE Jian-ping. Hg2+ removal from FGD system by thiol polystyrene resin[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2016,67(6):2598−2604. [26] 郝莹. 燃煤副产物脱硫石膏中重金属富集的地球化学特征及其环境风险[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2017.HAO Yin. Geochemical characteristics and potential risks of heavy metals in desulfurization gypsum from coal-fired power plants[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2017. [27] HJ 2053—2018. 燃煤电厂超低排放烟气治理工程技术规范[S].HJ 2053—2018. Technical specifications for flue gas ultra-low emission engineering of coal-fired power plant[S]. [28] Method 29, Determination of Metals Emissions from Stationary Sources[S]. [29] 苏银皎, 刘轩, 李丽锋, 李晓航, 姜平, 滕阳, 张锴. 三类煤阶煤中汞的赋存形态分布特征[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(4):1559−1566.SU Yin-jiao, LIU Xuan, LI Li-feng, LI Xiao-hang, JIANG Ping, TENG Yang, ZHANG Kai. The distribution characteristics of mercury speciation in coals with three different ranks[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2019,70(4):1559−1566. [30] RUMAVOR M, DIAZ S M, LOPEZ A M A, GONZALEZ R O, TARAZONA M R M. Temperature programmed desorption as a tool for the identification of mercury fate in wet-desulphurization systems[J]. Fuel,2015,148:98−103. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.01.101 [31] MARCZAK M, FAUSTYNA W, BURMISTRZ P, STRUGAA A, LECH S. Investigation of subbituminous coal and lignite combustion processes in terms of mercury and arsenic removal[J]. Fuel,2019,251:572−579. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.082 [32] YUDOVICH Y E, KETRIS M P. Mercury in coal: A review. part 1. geochemistry[J]. Int J Coal Geol,2005,62(3):107−134. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2004.11.002 [33] 管一明. 燃煤电厂烟气脱硫废水处理[J]. 电力环境保护,1998,14(1):38−44.GUAN Yi-ming. Treatment of flue gas desulfurization wastewater from coal-fired power plants[J]. Electric Power Technol Environ Protect,1998,14(1):38−44. [34] 禾志强, 田雁冰, 赵全中, 沈建军. 火力发电厂烟气脱硫废水处理工程实例[J]. 工业用水与废水,2008,39(5):83−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2008.05.023HE Zhi-qiang, TIAN Yan-bing, ZHAO Quan-zhong, SHEN Jian-jun. Examples of flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment project in thermal power plant[J]. Indust Water Wastewater,2008,39(5):83−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2008.05.023 [35] 吕松力, 斯琴, 李晓楠, 武鸿鹏. 燃煤电厂脱硫废水处理探讨[J]. 电站系统工程,2017,33(3):56−58.LV Song-li, SI Qin, LI Xiao-nan, WU Hong-peng. Discussion of FGD waste water treatment method on coal-fired power plant[J]. Power Sys Eng,2017,33(3):56−58. [36] LIU Y, WANG Y J, WU Z B, ZHOU S Y, WANG H Q. A mechanism study of chloride and sulfate effects on Hg2+ reduction in sulfite solution[J]. Fuel,2011,90(7):2501−2507. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.02.036 [37] CHANG L, ZHAO Y C, ZHANG Y, YU X H, LI Z H, GONG B G, LIU H, WEI S Z, WU H, ZHANG J Y. Mercury species and potential leaching in sludge from coal-fired power plants[J]. J Hazard Mater,2021,403:123927. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123927 [38] ZHANG Y S, ZHAO L L, GUO R T, WANG J W, CAO Y, ORNDORFF W, PAN W P. Influences of NO on mercury adsorption characteristics for HBr modified fly ash[J]. Int J Coal Geol,2017,170:77−83. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.10.002 [39] HAO Y, WU S M, PAN Y, LI Q, ZHOU J Z, XU Y B, QIAN G R. Characterization and leaching toxicities of mercury in flue gas desulfurization gypsum from coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Fuel,2016,177:157−163. [40] GB 5085.3—2007. 危险废物鉴别标准-浸出毒性鉴别[S].GB 5085.3—2007. Identification standards for hazardous wastes-Identification for extraction toxicity[S]. -









 下载:
下载: