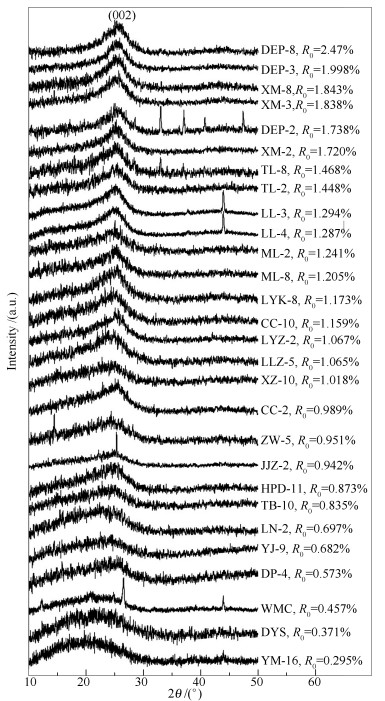
-
摘要: 通过对28个最大镜质组反射率0.30%-2.05%镜煤样品的X射线衍射(XRD) 分析, 获得XRD结构参数, 得到这些参数随反射率增大呈现的阶段性规律。在镜质组反射率小于1.0%阶段, La和Lc急剧增加, d002迅速减小, 含氧官能团的脱落和脂肪长度支链化程度减小占主导; 在1.0%-1.6%阶段, La持续增加, d002先增加后减小, Lc先减小然后趋于平稳, 芳香体系脱氢和调整空间位阻同时进行; 在1.6%-2.0%阶段, d002持续减小, Lc和La的增大, 煤结构演化以芳构化为主。XRD结构参数演化与第一、二次煤化作用跃变关系密切。Abstract: The structural parameters including La, Lc and d002 of 28 coal samples with the maximum vitrinite reflectance Ro, max varying from 0.30% to 2.05% were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD). The change in the XRD parameters associated with increasing vitrinite reflectance was obtained. The results indicate that, for the test coals with Ro, max less than 1.0%, the values of La and Lc sharply increase while d002 shows a reverse trend, and the decrease of oxygen-containing functional group and the length of branching aliphatic side chains are dominated. For those with Ro, max from 1.0% to 1.6%, the value of La continuously increases, d002 increases first and then decreases, and Lc decreases first and then remains steady. Moreover, dehydrogenation and adjusting the space steric hindrance are simultaneous. The value of d002 continues to decrease while La and Lc increases, and the variation of coal structure is dominated by aromatization process during the Ro, max range of 1.6% to 2.0%. The variation of XRD parameters presents close relation with the first and the second coalification jump phase.
-
Key words:
- low-middle rank coals /
- X-ray diffraction /
- structural evolution
-
表 1 样品的化学和光学参数
Table 1 Chemical and optical parameters for studied samples
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ro/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Mad Aad Vdaf C H O* N S YM-16 14.22 4.27 45.17 0.30 75.01 3.84 19.63 1.21 0.31 DYS 18.99 10.89 58.03 0.37 68.74 3.76 25.61 1.48 0.57 WMC 5.14 16.15 42.12 0.46 77.79 4.47 16.02 1.13 0.43 DP-4 1.50 14.27 40.35 0.57 77.89 4.39 13.51 1.16 2.86 YJ-9 2.59 8.97 30.91 0.68 82.10 4.43 9.94 1.24 2.19 LN-2 0.73 3.65 38.12 0.70 83.46 4.08 10.47 1.23 0.73 TB-10 0.45 5.15 39.30 0.84 83.50 4.45 8.09 1.21 2.69 HPD-11 0.78 10.72 36.28 0.87 81.22 4.31 12.5 1.19 0.66 JJZ-2 0.75 22.33 37.09 0.94 81.23 4.71 12.09 0.95 0.75 ZW-5 0.79 16.11 36.27 0.95 78.69 4.49 13.02 1.08 2.53 CC-2 0.59 8.56 34.46 0.99 81.51 4.28 12.44 1.13 0.54 XZ-10 0.53 15.39 27.21 1.02 86.76 4.01 7.59 1.02 0.44 JJZ-5 0.48 18.86 27.98 1.07 82.83 4.57 9.21 0.95 2.22 LYZ-2 0.56 5.02 28.11 1.07 86.35 4.01 7.95 1.10 0.53 CC-10 0.68 10.31 29.15 1.16 84.86 4.09 9.20 1.15 0.70 LYK-8 0.49 10.91 23.62 1.17 86.64 4.03 6.64 1.15 1.41 ML-8 0.48 9.00 27.96 1.21 86.32 4.04 6.76 1.11 1.66 ML-2 0.45 7.90 28.11 1.24 85.46 4.02 7.59 1.10 1.75 LL-4 0.49 6.21 26.29 1.29 83.46 4.03 10.75 1.09 0.60 LL-3 1.00 4.60 25.49 1.29 88.18 3.99 6.11 1.15 0.52 TL-2 0.39 6.70 24.01 1.45 87.17 3.94 7.07 1.10 0.65 TL-8 0.45 7.46 21.36 1.47 86.09 3.91 6.12 1.08 2.71 XM-2 0.61 9.52 17.25 1.72 89.80 3.88 4.58 1.05 0.58 DEP-2 0.62 8.56 17.04 1.74 90.13 4.56 3.32 1.44 0.46 XM-3 0.70 8.18 15.18 1.84 90.43 3.73 3.95 1.08 0.72 XM-8 0.96 6.52 15.13 1.84 88.10 3.83 4.76 1.12 2.13 DEP-3 0.53 14.36 16.67 2.00 89.50 3.94 4.37 1.03 1.00 DEP-8 0.57 2.37 12.22 2.05 88.41 3.49 5.22 1.15 1.70 * : by difference 表 2 XRD结构参数
Table 2 XRD structural parameters for studied samples
Sample Ro/% d002/nm Lc/nm La/ nm N(layers) YM 0.30 0.393 5 0.983 4 0.937 7 3.50 DYS 0.37 0.392 8 1.063 6 0.903 3 3.71 WMC 0.46 0.392 8 1.149 7 1.025 3 3.93 DP-4 0.57 0.373 2 1.238 6 1.011 9 4.32 YJ-9 0.68 0.376 8 1.433 9 1.009 5 4.81 LN-2 0.70 0.370 1 1.570 5 1.014 5 5.24 TB-10 0.84 0.354 2 1.582 1 1.158 6 5.47 HPD-11 0.87 0.358 6 1.624 5 1.157 0 5.53 JJZ-2 0.94 0.357 4 1.685 9 1.137 0 5.72 ZW-5 0.95 0.356 7 1.653 4 1.145 5 5.64 CC-2 0.99 0.352 3 1.646 7 1.191 1 5.67 XZ-10 1.02 0.350 3 1.725 7 1.224 5 5.93 JJZ-5 1.07 0.355 4 1.733 8 1.279 7 5.88 LYZ-2 1.07 0.349 6 1.813 7 1.305 0 6.19 CC-10 1.16 0.353 9 1.794 4 1.323 9 6.07 LYK-8 1.17 0.352 1 1.755 8 1.319 6 5.99 ML-8 1.21 0.354 6 1.749 1 1.232 4 5.93 ML-2 1.24 0.363 1.695 8 1.250 6 5.67 LL-4 1.29 0.356 7 1.738 6 1.304 1 5.87 LL-3 1.29 0.357 4 1.744 6 1.374 1 5.88 TL-2 1.45 0.352 3 1.712 2 1.375 3 5.86 TL-8 1.47 0.354 1 1.761 9 1.317 5 5.98 XM-2 1.72 0.353 1 1.998 4 1.361 4 6.66 DEP-2 1.74 0.347 6 1.918 4 1.420 7 6.52 XM-3 1.84 0.349 5 1.952 1 1.419 1 6.59 XM-8 1.84 0.347 3 1.941 2 1.515 5 6.59 DEP-3 2.00 0.349 5 1.931 8 1.527 0 6.53 DEP-8 2.05 0.344 6 2.132 9 1.579 0 7.19 note: N=Lc/d002+1 -
[1] LARSEN J W, GUREVICH I, GLASS A S, STEVENSON D S. A method for counting the hydrogen-bond cross-links in coal[J]. Energy Fuels, 1996, 10(6): 1269-1272. doi: 10.1021/ef960004i [2] WATANABE, I, SAKANISHI K, MOCHIDA I. Changes in coal aggregate structure by heat treatment and their coal rank dependency[J]. Energy Fuels, 2002, 16(1): 18-22. doi: 10.1021/ef010144e [3] LU L, SAHAJWALLA V, KONG C, HARRIS D. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis and its application to various coals[J].Carbon, 2001, 39(12): 1821-1833. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(00)00318-3 [4] 王丽, 张蓬洲.煤的XRD的结构分析[J].煤炭转化, 1997, 20(1): 50-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTZH199701008.htmWANG Li, ZHANG Peng-zhou. XRD study of coal structure[J]. Coal Convers, 1997, 20(1): 50-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTZH199701008.htm [5] 罗陨飞, 李文华.中低变质程度煤显微组分大分子结构的XRD研究[J].煤炭学报, 2004, 29(3): 338-341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB200403018.htmLUO Yun-fei, LI Wen-hua. X-ray diffraction analysis on the different macerals of several low-to-medium metamorpic grade coals[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2004, 29(3): 338 -341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB200403018.htm [6] 李小明, 曹代勇, 张守仁, 邢秀云.不同变质类型煤的XRD结构演化特征[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2003, 31(3): 5-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200303001.htmLI Xiao-ming, CAO Dai-yong, ZHANG Shou-ren, XING Xiu-yun. Study of the XRD parameter evolution of coal of different metamorphism types[J].Coal Geol Explor, 2003, 31(3): 5-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200303001.htm [7] 姜波, 秦勇, 宋党育, 王超.高煤级构造煤的XRD结构及其构造地质意义[J].中国矿业大学学报, 1998, 27(2): 115-118. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD802.001.htmJIANG Bo, QIN Yong, SONG Dang-yu, WANG Chao. XRD structure of high rank tectonic coals and its implication to structural geology[J]. J China Univ Min Technol, 1998, 27(2): 115-118. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD802.001.htm [8] 吴晓英.烟煤高温焦炭微晶结构的X衍射研究[J].西安矿业学院学报, 1999, 19(2): 158-160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB902.014.htmWU Xiao-ying. Study of XRD on the crystallite structure characteristics of high temperature coke of coals[J]. J Xi'an Min Inst, 1999, 19(2): 158-160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB902.014.htm [9] 张小东, 张鹏.不同煤级煤分级萃取后的XRD结构特征及其演化机理[J].煤炭学报, 2014, 39(5): 941-946. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201405024.htmZHANG Xiao-dong, ZHANG Peng. Characteristics of XRD parameter for different ranks of coals under fractional extraction and its evolution mechanism[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2014, 39(5): 941-946. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201405024.htm [10] WATANABE I, SAKANISHI K, MOCHIDA I.Changes in coal aggregate structure by heat treatment and their coal rank dependency[J]. Energy Fuels, 2002, 16(1): 18-22. doi: 10.1021/ef010144e [11] TAKAGI H, MARUYAMA K, YOSHIZAWA N, YAMADA Y, SATO Y. XRD analysis of carbon stacking structure in coal during heat treatment[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(17/18): 2427-2433. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=16147961 [12] WU S, GU J, ZHANG X, WU Y, GAO J. Variation of carbon crystalline structures and CO2 gasification reactivity of Shenfu coal chars at elevated temperatures[J]. Energy Fuels, 2008, 22(1): 199-206. doi: 10.1021/ef700371r [13] FENG B, BHATIA S K, BARRY J C. Variation of the crystalline structure of coal char during gasification[J]. Energy Fuels, 2003, 17(3): 744-54. doi: 10.1021/ef0202541 [14] LIN Q, GUET J M. Characterization of coals and macerais by X-ray diffraction[J].Fuel, 1990, 69(7): 821-825. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(90)90224-E [15] WU S, GU J, ZHANG X, WU Y, GAO J. Variation of carbon crystalline structures and CO2 gasification reactivity of Shenfu coal chars at elevated temperatures[J]. Energy Fuels, 2008, 22(1): 199-206. doi: 10.1021/ef700371r [16] PETERSEN H I, ROSENBERG P, NYTOFT H P. Oxygen groups in coals and alginite-rich kerogen revisited[J]. Int J of Coal Geol, 2008, 74(2): 93-113. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2007.11.007 [17] BODOEV N V, GUET J M, GRUBER R, DOLGOPOLOV N I, WILHELM J C, BAZAROVA O. FT-IR and XRD analysis of sapropelitic coals[J]. Fuel, 1996, 75(7): 839-842. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(96)00022-1 [18] SENNECA O, SALATINO P, MASI S. Microstructural changes and loss of gasification reactivity of chars upon heat treatment[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(13): 1483-1493. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00056-8 [19] STRYDOM CA, BUNT J R, SCHOBERT H H, RAGHOO M. Changes to the functional groups of an inertinite rich medium rank coal during acid treatment processes[J].Fuel Process Technol, 2011, 92(4): 764-770. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.09.008 [20] 李霞, 曾凡桂, 王威, 董夔, 程丽媛.低中煤级煤结构演化的FT-IR表征[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(12): 2900-2908. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201512021.htmLI Xia, ZENG Fan-gui, WANG Wei, DONG Kui, CHENG Li-yuan. FT-IR characterization of structural evolution in the low-middle rank coals[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2015, 40(12): 2900-2908. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201512021.htm [21] 翁成敏, 潘治贵.峰峰煤田煤的X射线衍射分析[J].地球科学, 1981, (1): 214-221. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX198101017.htmWENG Cheng-min, PAN Zhi-gui. X-ray diffraction analysis of coal in Fengfeng coalfield[J]. Earth Sci, 1981, (1): 214-221. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX198101017.htm [22] 韩德馨.中国煤岩学[M].徐州:中国矿业大学出版社, 1996: 260.HAN De-xin. Coal Ketrology in China[M]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 1996: 260. [23] MOCHIDA I, SAKANISHI K. Catalysts for coal conversions of the next generation[J]. Fuel, 2000, 79(3/4): 221-228. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222221996_Catalysts_for_coal_conversions_of_the_next_generation [24] ARENILLAS A, RUBIERA F, PIS J J, CUESTA M J, IGLESIAS M J, JIMÉNEZ A, SUÁREZ-RUIZ I. Thermal behaviour during the pyrolysis of low rank perhydrous coals[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2003, 68-69: 371-385. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2370(03)00031-7 [25] 张玉波.中低煤化作用阶级煤化作用机理的13C-NMR研究[D].太原:太原理工大学, 2006. http://www.oalib.com/references/19418312ZHANG Yu-bo. 13C-NMR research of coalfication mechanism for low-medium rank coal[D].Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technolgy, 2006. http://www.oalib.com/references/19418312 -





 下载:
下载: