Cu-Al spinel as a sustained release catalyst for H2 production from methanol steam reforming:Effects of different copper sources
-
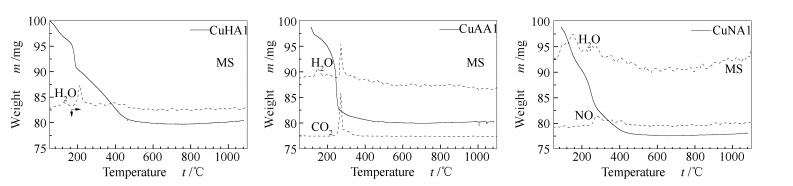
摘要: 以拟薄水铝石为铝源,氢氧化铜、乙酸铜和硝酸铜等为铜源,采用固相法合成Cu-Al尖晶石催化剂。采用TG-MS、XRD、H2-TPR、BET和XANES等表征技术,对合成过程、产物的物相、还原性质及表层结构进行研究,并考察了甲醇重整制氢的缓释催化性能。结果表明,三种铜源都得到尖晶石固溶体,其晶粒粒径相差不大,但其比表面积(25.4-65.9 m2/g)、孔容(0.213-0.434 cm3/g)、表面结构(Cu的分布)以及还原性能有明显的差别,从而导致不同的缓释催化行为。在甲醇重整反应过程中,铜铝缓释催化剂通过反应条件下还原释放活性铜物种而起催化作用。以氢氧化铜合成的催化剂活性高,反应稳定性好,反应后生成的Cu粒子最小(6.6 nm),其表现出优异的催化性能。Abstract: Cu-Al spinel catalysts were synthesized by the solid-state reaction method using pseudo-boehmite as the Al source and hydroxides, acetates and nitrates of copper as the Cu source. Several techniques such as TG-MS, XRD, H2-TPR, BET and XANES were employed for the exploration of the synthetic process, phase composition, reduction behaviors and surface structure of the catalysts. Moreover, the catalytic properties for methanol steam reforming (MSR) of these catalysts were evaluated. The obtained results showed that spinel solid solution can be successfully synthesized with the three different Cu sources. The synthesized spinels showed little difference in crystalline size, but their specific surface area (25.4-65.9 m2/g), pore volume (0.213-0.434 cm3/g), surface structure (distribution of Cu) and reduction properties were quite different, which led to different catalytic behavior and performance. During the methanol steam reforming reaction, active Cu species can be released from Cu-Al spinel structure. The catalyst synthesized from copper(Ⅱ) hydroxide shows excellent catalytic performance for MSR as it generates the smallest Cu particles (6.6 nm).
-
Key words:
- solid-state reaction method /
- solid solution /
- methanol steam reforming
-
表 1 催化剂的特征参数
Table 1 Characteristic parameter of fresh and tested catalysts
Fresh catalyst CuHAl-950 CuAAl-950 CuNAl-950 Cu source Cu(OH)2 Cu(CH3COO)2·H2O Cu(NO3)2·3H2O dspinel/ nm[a] 12.7 12.4 11.3 BET surface area A/ (m2·g-1) 65.9 33.8 25.4 Pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) 0.434 0.213 0.289 X spinel / %[b] 81.3 79.1 93.7 x in Cu1-3xVxAl2+2xO4 0.129 0.134 0.104 After MSR CuHAl-950-t CuAAl-950-t CuNAl-950-t dCu-after MSR / nm[c] 6.6 9.2 20.2 Cu0 surface area A/(m2 ·g-1)[d] 183.9 146.1 94.7 RD/%[e] 88.7 85.9 66.8 [a]: the crystallite size of spinel was calculated by the Scherrer equation with the XRD patterns (Figure 2);
[b]: the molar ratio of Cu in the Cu-Al spinel phase to total Cu as derived from H2-TPR (Figure 5);
[c]: Cu crystalline size of tested catalyst was calculated by the Scherrer equation with XRD patterns (Figure 8);
[d]: Cu surface area of tested catalyst was measured by N2O chemisorption method;
[e]: the releasing degree (RD) of Cu from spinel after catalytic testing was calculated by using H2-TPR data of tested samples -
[1] 李晓峰, 王晶, 张磊, 雷燕秋, 刘攀, 陈然, 陈何臻, 何素芳, 罗永明.铈和镨改性Ni/Al2O3催化剂对甲醇水蒸气重整制氢的影响[J].中国稀土学报, 2016, 34(4):403-410. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90301X/201604/669800762.htmlLI Xiao-feng, WANG Jing, ZHANG Lei, LEI Yan-qiu, LIU Pan, CHEN Ran, CHEN Ke-zheng, HE Su-fang, LUO Yong-ming. Effect of cerium and praseodymium addition on Ni/Al2O3 catalyst to produce H2 from methanaol steam reforming[J]. J Chin Soc Rare Earths, 2016, 34(4):403-410. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90301X/201604/669800762.html [2] 吝子东, 白松, 张晓辉.水电解制氢技术发展前景[J].舰船防化, 2014, (2):48-54. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jcfh201402014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLIN Zi-dong, BAI Song, ZHANG Xiao-hui. Dexelopment prospect of water electrolysis hydrogen production technology[J]. Chem Defe Ships, 2014, (2):48-54. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jcfh201402014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [3] WANG X, GORTE R J. A study of steam reforming of hydrocarbon fuels on Pd/ceria[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2002, 224(1):209-218. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X01007839 [4] ILINICH O, RUETTINGER W, LIU X, FARRAUTO R. Cu-Al2O3-CuAl2O4 water-gas shift catalyst for hydrogen production in fuel cell applications:Mechanism of deactivation under start-stop operating conditions[J]. J Catal, 2007, 247(1):112-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.01.014 [5] RARÓG-PILECKA W, SZMIGIEL D, KOWALCZYK Z, JODZIS S, ZIELINSKI J. Ammonia decomposition over the carbon-based ruthenium catalyst promoted with barium or cesium[J]. J Catal, 2003, 218(2):465-469. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9517(03)00058-7 [6] 王桂芝.甲醇制氢技术及在燃料电池中的应用[J].化学工业, 2008, 26(1):17-22. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=26526497WANG Gui-zhi. Technology for production hydrogen from methanol and its application in fuel cell system[J]. Chem Ind, 2008, 26(1):17-22. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=26526497 [7] SÁ S, SILVA H, BRANDÃO L, SOUSA J, MENDES A. Catalysts for methanol steam reforming-A review[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2010, 99(1/2):43-54. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337310002584 [8] MATSUMURA T, TANAKA K, TODE N, YAZAWA T, HARUTA M. Catalytic methanol decomposition to carbon monoxide and hydrogen over nickel supported on silica[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2000, 152(1/2):157-165. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1381116999002824 [9] SHEN G, FUJITA S, MATSUMOTO S, TAKEZAWA N. Steam reforming of methanol on binary Cu/ZnO catalysts:Effects of preparation condition upon precursors, surface structure and catalytic activity[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 1997, 124(2):123-136. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1381116997000782 [10] VELU S, SUZUKI K, OSAKI T. Selective production of hydrogen by partial oxidation of methanol over catalysts derived from CuZnAl-layered double hydroxides[J]. Catal lett, 1999, 62(2/4):159-167. doi: 10.1023/A:1019023811688 [11] VELU S, SUZUKI K. Selective production of hydrogen for fuel cells via oxidative steam reforming of methanol over CuZnAl oxide catalysts:effect of substitution of zirconium and cerium on the catalytic performance[J]. Top Catal, 2003, 22(3/4):235-244. doi: 10.1023/A:1023576020120 [12] 毛丽萍, 吕功煊.纳米Cu/Al2O3催化剂催化甲醇水蒸气重整制氢研究[J].甘肃科学学报, 2009, 21(1):77-80. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gskx200901025&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQMAO Li-ping, LV Gong-xuan. Hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming over nano-Cu/A12O3 catalyst[J]. J Gansu Sci, 2009, 21(1):77-80. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gskx200901025&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [13] PURNAMA H, GIRGSDIES F, RESSLER T, SCHATTKA J H, CARUSO R A, SCHOMÄCKER R, SCHLÖGL R. Activity and selectivity of a nanostructured CuO/ZrO2 catalyst in the steam reforming of methanol[J]. Catal Lett, 2004, 94(1/2):61-68. doi: 10.1023/B:CATL.0000019332.80287.6b [14] SHISHIDO T, YAMAMOTO Y, MORIOKA H, TAKAKI K, TAKEHIRA K. Active Cu/ZnO and Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts prepare by homogeneous precipitation method in steam reforming of methanol[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2004, 263(2):249-253. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2003.12.018 [15] OGUCHI H, NISHIGUCHI T, MATSUMOTO T, KANAI H, UTANI K, MATSUMURA Y, IMAMURA S. Steam reforming of methanol over Cu/CeO2/ZrO2 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2005, 281(1):69-73. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X04009184 [16] KAMEOKA S, TANABE T, TSAI A P. Spinel CuFe2O4:A precursor for copper catalyst with high thermal stability and activity[J]. Catal Lett, 2005, 100(1/2):89-93. doi: 10.1007/s10562-004-3091-z [17] MAITI S, LLORCA J, DOMINGUEZ M, COLUSSI S, TROVARELLI A, PRIOLKAR K, AQUILANTI G, GAYEN A. Combustion synthesized copper-ion substituted FeAl2O4 (Cu0.1Fe0.9Al2O4):A superior catalyst for methanol steam reforming compared to its impregnated analogue[J]. J Power Sources, 2016, 304:319-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.11.066 [18] YONG S, OOI C, CHAI S, WU X. Review of methanol reforming-Cu-based catalysts, surface reaction mechanisms, and reaction schemes[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(22):9541-9552. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.023 [19] MATSUKATA M, UEMIYA S, KIKUCHI E. Copper-alumina spinel catalysts for steam reforming of methanol[J]. Chem Lett, 1988, 5(5):761-764. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/244723471_Copper-Alumina_Spinel_Catalysts_for_Steam_Reforming_of_Methanol [20] FUKUNAGA T, RYUMON N, ICHIKUNI N, SHIMAZU S. Characterization of CuMn-spinel catalyst for methanol steam reforming[J]. Catal Commun, 2009, 10(14):1800-1803. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2009.06.001 [21] PUSSANA H, KAJORNSAK F. Cu-Cr, Cu-Mn, and Cu-Fe spinel-oxide-type catalysts for reforming of oxygenated hydrocarbons[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2013, 117(45):23757-23765. doi: 10.1021/jp407717c [22] 李光俊, 郗宏娟, 张素红, 谷传涛, 庆绍军, 侯晓宁, 高志贤.尖晶石CuM2O4(M=Al、Fe、Cr)催化甲醇重整反应的特性[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(12):1466-1471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.12.009LI Guang-jun, XI Hong-juan, ZHANG Su-hong, GU Chuan-tao, QING Shao-jun, HOU Xiao-ning, GAO Zhi-xian. Catalytic characteristics of spinel CuM2O4 (M=Al, Fe, Cr) for the steam reforming of methanol[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(12):1466-1471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.12.009 [23] HUANG Y H, WANG S F, TSAI A P, KAMEOKA S. Reduction behaviors and catalytic properties for methanol steam reforming of Cu-based spinel compounds CuX2O4 (X=Fe, Mn, Al, La)[J]. Cera Inter, 2014, 40(3):4541-4551. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.08.130 [24] 郗宏娟, 李光俊, 庆绍军, 侯晓宁, 赵金珍, 刘雅杰, 高志贤.固相法合成铜铝尖晶石催化甲醇重整反应[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(8):998-1002. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18242.shtmlXI Hong-juan, LI Guang-jun, QING Shao-jun, HOU Xiao-ning, ZHAO Jin-zhen, LIU Ya-jie, GAO Zhi-xian. Cu-Al spinel catalyst prepared by solid phase method for methanol steam reforming[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(8):998-1002. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18242.shtml [25] XI H, HOU X, LIU Y, QING S, GAO Z. Cu-Al spinel oxide as an efficient catalyst for methanol steam reforming[J]. Angew Chem, 2014, 53(44):11886-11889. doi: 10.1002/anie.201405213 [26] GRIONI M, GOEDKOOP J B, SCHOORL R, GROOT F M F, FUGGLR J C, SCHÄFERS F, KOCH E E, ROSSI G, ESTEVA J M, KARNATAK R C. Studies of copper valence states with Cu L3 X-ray-absorption spectroscopy[J]. Phys Rev B, 1989, 39(3):1541-1545. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.39.1541 [27] SHIMIZU K, MAESHIMA H, YOSHIDA H, SATSUMA A, HATTORI T. Spectroscopic characterisation of catalysts for selective Cu-Al2O3 catalytic reduction of NO with propene[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2000, 2(10):2435-2439. doi: 10.1039/b000943l [28] LUO M F, FANG P F, HE M, XIE Y L. In situ XRD, Raman, and TPR studies of CuO/Al2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2005, 239(1/2):243-248. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1381116905004164 -





 下载:
下载: