Preparation of ionic liquid supported metal-organic framework Py/MOF-199 and its adsorption desulfurization performance
-
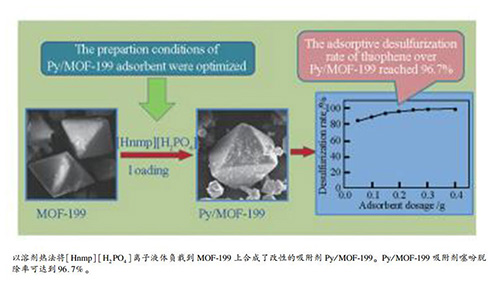
摘要: 制备了金属框架MOF-199(Cu-BTC),并将[Hnmp][H2PO4]离子液体负载到MOF-199上合成了离子液体负载的金属框架Py/MOF-199。对吸附剂进行了X射线衍射、红外光谱、扫描电镜、比表面积表征。考察了MOF-199预处理条件、离子液体负载方式、负载量、负载温度、负载时间对噻吩吸附脱除性能的影响,通过正交实验优化了吸附剂的制备条件和吸附脱硫条件。结果表明,离子液体改性得到的Py/MOF-199保持了MOF-199的规则的八面体结构。Py/MOF-199的适宜制备条件为:采用二氯甲烷索氏提取并真空干燥法进行预处理MOF-199后,再用溶剂热法负载[Hnmp][H2PO4],负载温度为50 ℃,负载时间为8 h,负载量为7%。各因素对吸附剂脱硫性能影响大小顺序为:负载温度>负载时间>离子液体负载量。适宜Py/MOF-199吸附脱硫条件为:模拟油为10 mL,吸附剂用量0.2 g,吸附温度70 ℃,吸附时间1 h。在此条件下,噻吩脱除率可达到96.7%。
-
关键词:
- 吸附脱硫 /
- 离子液体 /
- Py/MOF-199 /
- 噻吩(TP)
Abstract: MOF-199(Cu-BTC) was prepared and the ionic liquid supported MOF-199 adsorbents (Py/MOF-199) were successfully obtained via fixing ionic liquid[Hnmp] [H2PO4] onto the MOF-199. Adsorbents were characterized via XRD, FT-IR, SEM, and BET methods. The effects of pretreatment conditions of MOF-199, ionic liquid loading method, ionic liquid content, loading temperature and time on adsorptive removal performance of thiophene were studied. The preparation conditions of Py/MOF-199 adsorbent were optimized via orthogonal experiment, and the desulfurization conditions were also optimized. The results show that after the introduction of[Hnmp] [H2PO4] the regular octahedron structure of MOF-199 of Py/MOF-199 was maintained unchanged and the average pore diameter was increased. The optimal preparation conditions of Py/MOF-199 adsorbent are pretreating MOF-199 with Soxhlet extraction and drying in vacuum, then loading[Hnmp] [H2PO4] using solvothermal method, loading temperature of 50 ℃, loading time of 8 h, ionic liquid content of 7%. The influence of preparation factors on the desulfurization performance of adsorbent is in order:loading temperature > loading time > ionic liquid content. The optimal desulfurization conditions are model oil of 10 mL, Py/MOF-199 dosage of 0.2 g, adsorption under 70 ℃ for 1 h. Under these conditions, the thiophene desulfurization rate over Py/MOF-199 reached 96.7%.-
Key words:
- adsorptive desulfurization /
- ionic liquids /
- Py/MOF-199 /
- thiophene (TP)
-
表 1 MOF-199和Py/MOF-199吸附剂的BET比表面积、孔隙体积和孔径
Table 1 BET surface area pore volume and pore size of the adsorbents
Adsorbent BET area A/(m2·g-1) Pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) Pore size d/nm MOF-199 1362 0.71 2.13 7%Py/MOF-199 1074 0.62 2.35 表 2 正交试验因素水平
Table 2 Level of the factors of orthogonal test
Level Factor temperature t/℃ time t/h ionic liquid content w/% A B C 1 40 6 6 2 50 8 7 3 60 10 8 表 3 离子液体负载条件影响因素正交试验直观分析表
Table 3 Visual analysis table of orthogonal test for influencing factors of ionic liquid loading condition
Test Temperature t/℃ Time t/h Ionic liquid content Rate of thiophene removal A B C 1 40 6 6% 64.6% 2 40 8 7% 67.7% 3 40 10 8% 73.5% 4 50 6 7% 73.8% 5 50 8 8% 69.7% 6 50 10 6% 66.2% 7 60 6 8% 58.7% 8 60 8 6% 69.0% 9 60 10 7% 61.1% K1 205.9% 197.2% 199.8% K2 209.8% 206.5% 202.7% K3 188.8% 200.8% 202.0% Average k1 68.6% 65.7% 66.6% Average k2 69.9% 68.8% 67.6% Average k3 62.9% 66.9% 67.3% Range R 5.7% 3.1% 0.9% Primary order A>B>C Superior level A2 B2 C2 Superior combination A2B2C2 Kn is the comprehensive removal rate of thiophene at different levels of the same influence factor; kn is the average removal rate of thiophene at different levels of the same influence factor; R=kmax-kmin is the difference between the maximum removal rate and the minimum removal rate of thiophene for the same influence factor -
[1] CHEN X C, SONG D D, ASUMANA C, YU G R. Deep oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuels by lewis acidic ionic liquids based on 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium metal chloride[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2012, 359:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2012.03.014 [2] ULLAH R, BAI P, WU P, LIU B, SUBHAN F, YAN Z. Cation-anion double hydrolysis derived mesoporous mixed oxides for reactive adsorption desulfurization[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2017, 238:36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.02.037 [3] YANG C P, ZHAO K, CHEN Y, ZENG G M, ZHANG M M, SHAO J J, LU L. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of BT and DBT from n-octane using cyclohexanone peroxide and catalyst of molybdenum supported on 4A molecular sieve[J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2016, 163:153-161. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2016.02.050 [4] LEE K X, VALLA J A. Investigation of metal-exchanged mesoporous Y zeolites for the adsorptive desulfurization of liquid fuels[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2017, 201:359-369. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.018 [5] LENG K Y, SUN Y Y, ZHANG X, YU M, XU W. Ti-modified hierarchical mordenite as highly active catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene[J]. Fuel, 2016, 174:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.01.070 [6] YANG Q Y, LIU D H, ZHONG C L, LI J R. Development of computational methodologies for metal-organic frameworks and their application in gas separations[J]. Chem Rev, 2013, 113(10):8261-8323. doi: 10.1021/cr400005f [7] WU H H, GONG Q H, OLSON D H, LI J. Commensurate adsorption of hydrocarbons and alcohols in microporous metal organic frameworks[J]. Chem Rev, 2012, 112(2):836-868. doi: 10.1021/cr200216x [8] DECOSTE J B, PETERSON G W. Metal-organic frameworks for air purification of toxic chemicals[J]. Chem Rev, 2014, 114(11):5695-5727. doi: 10.1021/cr4006473 [9] SUN W, LIN L C, PENG X, SMIT B. Computational screening of porous metal-organic frameworks and zeolites for the removal of SO2 and NOx from flue gases[J]. AIChE J, 2014, 60(6):2314-2323. doi: 10.1002/aic.14467 [10] ACHMANN S, HAGEN G, HAMMERLE M, MALKOWSKY I, KIENER C, MOOS R. Sulfur removal from low-sulfur gasoline and diesel fuel by metal-organic frameworks[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2010, 33(2):275-280. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ecb53834c37cb01c6cf232d259e9c099&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] TAN P, XIE X Y, LIU X Q, PAN T, GU C, CHEN P F, ZHOU J Y, PAN Y C, SUN L B. Fabrication of magnetically responsive HKUST-1/Fe3O4 composites by dry gel conversion for deep desulfurization and denitrogenation[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2017, 321:344-352. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.026 [12] SZANYI J, DATURI M, CLET G, BAER D R, PEDEN C H F. Well-studied Cu-BTC still serves surprises:Evidence for facile Cu2+/Cu+ interchange[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2012, 14(13):4383-4390. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23708c [13] WU L M, XIAO J, WU Y, XIAN S K, MIAO G, WANG H H, LI Z. A combined experimental/computational study on the adsorption of organosulfur compounds over metal-organic frameworks from fuels[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(4):1080-1088. doi: 10.1021/la404540j [14] 王均凤, 张锁江, 陈慧萍, 李闲, 张密林.离子液体的性质及其在催化反应中的应用[J].过程工程学报, 2003, 3(2):177-185. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2003.02.016WANG Jun-feng, ZHANG Suo-jiang, CHEN Hui-ping, LI Xian, ZHANG Mi-lin. Properties of ionic liquids and its applications in catalytic reactions[J]. Chin J Process Eng, 2003, 3(2):177-185. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2003.02.016 [15] BABUCCI M, FANG C Y, HOFFMAN A S, BARE S R, GATES B C, UZUN A. Tuning the selectivity of single-site supported metal catalysts with ionic liquids[J]. ACS Catal, 2017, 7(10):6969-6972. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b02429 [16] KHAN N A, HASAN Z, JHUNG S H. Ionic liquids supported on metal-organic frameworks:Remarkable adsorbents for adsorptive desulfurization[J]. Chem Eur J, 2014, 20(2):376-380. doi: 10.1002/chem.v20.2 [17] BORFECCHIA E, MAURELLI S, GIANOLIIO D, GROPPO E, CHIESA M, BONINO F, LAMBERTI C. Insights into adsorption of NH3 on HKUST-1 metal-organic framework:A multitechnique approach[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2012, 116(37):19839-19850. doi: 10.1021/jp305756k -





 下载:
下载: