Methanol to propylene reaction performance and trapped carbonaceous species over zeolites with different topologies
-
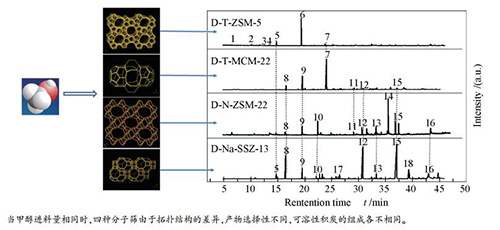
摘要: 采用TEAOH溶液处理MFI结构ZSM-5分子筛、MWW结构MCM-22分子筛,NaOH溶液处理TON结构ZSM-22分子筛、CHA结构SSZ-13分子筛得到四种结构的扩孔分子筛。在反应温度480℃、反应压力0.1 MPa、甲醇与水质量比1:1、甲醇质量空速1.5 h-1的条件下,考察了四种扩孔分子筛的甲醇制丙烯(MTP)催化性能,并采用XRD、N2吸附-脱附、NH3-TPD、TG、UV-Raman和GC-MS等方法表征催化剂的物化性质及MTP反应2 h后的分子筛积炭性质。结果表明,四种分子筛扩孔改性后均出现介孔,其中,T-ZSM-5分子筛在MTP反应中寿命最长;T-MCM-22分子筛寿命次之且失活速率慢;而一维孔道结构N-ZSM-22分子筛和八元环尺寸较小的N-SSZ-13分子筛均失活迅速。受拓扑结构和孔道扩散的影响,MTP反应2 h后,分子筛积炭量增加的顺序为T-ZSM-5<N-ZSM-22<T-MCM-22<N-SSZ-13且可溶焦分子质量随积炭量增加而增重,即从五甲基苯增重到菲、芘等多环芳烃。Abstract: Mesoporous ZSM-5 (MFI), MCM-22 (MWW), ZSM-22 (TON) and SSZ-13 (CHA) zeolites were obtained by TEAOH and NaOH solution treatment. Under the following operating conditions:t=480℃, p=0.1 MPa, m(methanol):m(H2O)=1:1 and WHSV (methanol)=1.5 h-1, the catalytic properties of four mesoporous zeolites with different topologies were investigated in the methanol to propylene (MTP) reaction. The fresh and spent samples after 2 h were characterized with XRD, nitrogen adsorption experiments, NH3-TPD, TG, UV-Rama and GC-MS techniques. It demonstrated that both zeolites exist mesopores after treated by alkali. The mesoporous T-ZSM-5 zeolite had the highest lifetime; the lifetime of T-MCM-22 zeolite with was secondary and deactivation rate was slow; The N-ZSM-22 with one-dimensional channel structure and N-SSZ-13 zeolite with 8-member ring channels both deactivated rapidly. Due to the difference of topology structure and diffusion performance, their coke contents after 2 h increased in the order:T-ZSM-5 < N-ZSM-22 < T-MCM-22 < N-SSZ-13. Moreover, the molecular weight of soluble coke increased with the increasing of coke contents, changed from pentamethylbenzene to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, such as phenanthrene and pyrene.
-
Key words:
- methanol to propylene (MTP) /
- mesoporous /
- zeolite topology /
- deactivation behavior
-
表 1 不同拓扑结构分子筛的比表面积和孔结构
Table 1 Specific surface areas and pore properties of zeolites with different topologies
Sample SBET a/(m2·g-1) Sext/(m2·g-1) Smicrob/(m2·g-1) vtotalc/(cm3·g-1) vmicrob/(cm3·g-1) vmesod/(cm3·g-1) T-ZSM-5 375 27 348 0.204 0.160 0.044 T-MCM-22 458 71 387 0.582 0.182 0.400 N-ZSM-22 225 45 181 0.420 0.060 0.320 N-SSZ-13 516 46 470 0.313 0.217 0.096 SBET: specific surface area; Sext: external surface area; Smicro=micropore specific area, a: BET method; b: t-plot method; c: volume adsorbed at p/p0 =0.99; d: mesopore volumes were calculated by vtotal-vmicro 表 2 不同拓扑结构分子筛反应2 h的产物分布
Table 2 Products yields of zeolites with different topologies measured at 2 h
Sample Gaseous product yields w/% x/%(methanol) P/E ratio C3 HTI C1 C2= C2 C3= C3 C4= C4 C5+ T-ZSM-5 4.56 8.59 1.49 9.74 16.43 4.45 16.39 38.35 100 1.13 1.695 T-MCM-22 1.04 11.36 0.80 15.98 6.34 6.53 19.45 38.50 100 1.41 0.397 N-ZSM-22 3.67 12.54 0.47 26.63 4.83 15.53 1.83 34.50 79 2.12 0.181 N-SSZ-13 0.76 42.63 0.78 21.85 0.96 6.80 0.14 26.08 84 0.51 0.044 reaction conditions: t=480 ℃, WHSV=1.5 h-1, p=0.1 MPa, m(H2O):m(CH3OH) = 1:1,2 h, C3 HTI = C3 alkanes/ C3 alkenes 表 3 不同拓扑结构分子筛反应2 h的比表面积和孔结构
Table 3 Specific surface areas and pore properties of zeolites with different topologies after 2 h
Sample SBETa
/(m2·g-1)Sext
/(m2·g-1)Smicrob
/(m2·g-1)vtotalc
/(cm3·g-1)vmicrob
/(cm3·g-1)vmesod
/(cm3·g-1)D-T-ZSM-5 320 31 288 0.182 0.134 0.048 D-T-MCM-22 196 52 144 0.470 0.070 0.400 D-N-ZSM-22 81 44 37 0.379 0.084 0.295 D-N-SSZ-13 161 4 156 0.088 0.073 0.015 SBET: specific surface area; Sext: external surface area; Smicro= micropore specific area, a: BET method; b: t-plot method; c: volume adsorbed at p/p0 =0.99; d: mesopore volumes were calculated by vtotal-vmicro 表 4 不同拓扑结构分子筛反应2 h对应可溶性积炭组成及相对含量
Table 4 Contents of soluble coke species on partial deactivated zeolites with different topologies after 2 h
Species Sample Relative content w/% D-T-ZSM-5 D-T-MCM-22 D-N-ZSM-22 D-N-SSZ-13 1 
0.02 - - - 2 
0.04 - - - 3 
0.05 - - - 4 
0.02 - - - 5 
12.86 - - 2.33 6 
81.27 - - - 7 
5.73 69.44 - - 8 
- 5.55 5.36 9.88 9 
- 17.10 8.14 7.10 10 
- - 12.35 6.07 11 
- 2.43 3.34 - 12 
- 1.40 6.68 22.92 13 
- - 8.02 1.41 14 
- - 30.06 - 15 
- 4.08 22.12 36.89 16 
- - 3.93 - 17 
- - - 7.21 18 
- - - 6.18 -
[1] STOCKER M. Methanol-to-hydrocarbons:Catalytic materials and their behavior[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 1999, 29(1):3-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb201205011 [2] CHEN J Q, BOZZANO A, GLOVER B, FUGLERUD T, KVISLE S. Recent advancements in ethylene and propylene production using the UOP/Hydro MTO process[J]. Catal today, 2005, 106(1):103-107. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ab2e8c6aab97bd946516d8db695f5673&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] MEI C, WEN P, LIU Z, LIU H, WANG Y, YANG W, XIE Z, HUA W, GAO Z. Selective production of propylene from methanol:Mesoporosity development in high silica HZSM-5[J]. J Catal, 2008, 258(1):243-249. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2008.06.019 [4] CUI T L, LV L B, ZHANG W B, LI X H, CHEN J S. Programmable synthesis of mesoporous ZSM-5 nanocrystals as selective and stable catalysts for the methanol-to-propylene process[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2016, 6(14):5262-5266. doi: 10.1039/C6CY00379F [5] SUN C, DU J, LIU J, YANG Y, REN N, SHEN W, XU H, TANG Y. A facile route to synthesize endurable mesopore containing ZSM-5 catalyst for methanol to propylene reaction[J]. Chem Commun, 2010, 46(15):2671-2673. doi: 10.1039/b925850g [6] LI H, WANG Y, FAN C, SUN C, WANG X, WANG C, ZHANG X, WANG S. Facile synthesis of a superior MTP catalyst:Hierarchical micro-meso-macroporous ZSM-5 zeolites[J]. App Catal A:Gen, 2018, 551:34-48. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.12.007 [7] DAI C, ZHANG A, LI L, HOU K, DING F, LI J, MU D, SONG C, LIU M, GUO X. Synthesis of hollow nanocubes and macroporous monoliths of silicalite-1 by alkaline treatment[J]. Chem Mater, 2013, 25(21):4197-4205. doi: 10.1021/cm401739e [8] HE Y, LIU M, DAI C, XU S, WEI Y, LIU Z, GUO X. Modification of nanocrystalline HZSM-5 zeolite with tetrapropylammonium hydroxide and its catalytic performance in methanol to gasoline reaction[J]. Chin J Catal, 2013, 34(6):1148-1158. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60579-8 [9] SHI Y, XING E, XIE W, ZHANG F, MU X, SHU X. Enhancing activity without loss of selectivity-Liquid-phase alkylation of benzene with ethylene over MCM-49 zeolites by TEAOH post-synthesis[J]. App Catal A:Gen, 2015, 497(1):135-144. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0234833093 [10] CAMPO P D, BEATO P, REY F, NVARRO M T, OLSBYE U, LILLERUD K P, SVELLE S. Influence of post-synthetic modifications on the composition, acidity and textural properties of ZSM-22 zeolite[J]. Catal Today, 2017, 299:120-134. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f5b3cdcc3164cf53383ae7320e7eceff&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] CAMPO P D, OLSBYE U, LILLERUD K P, SVELLE S, BEATO P. Impact of post-synthetic treatments on unidirectional H-ZSM-22 zeolite catalyst:Towards improved clean MTG catalytic process[J]. Catal Today, 2017. 299:135-145. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2bb79cc129bff74f8d2856c9e3a198d7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [12] SOMMER L, MORES D, SVELLE S, STOCKER M, WECKHUYSEN B M, OLSBYE U. Mesopore formation in zeolite H-SSZ-13 by desilication with NaOH[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2013, 132(3):384-394. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d70d3df6e5cebb99fd6314813cd8ecfc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] JI W P, LEE J Y, KIM K S, HONG S B, SEO G. Effects of cage shape and size of 8-membered ring molecular sieves on their deactivation in methanol-to-olefin (MTO) reactions[J]. App Catal A:Gen, 2008, 339(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2008.01.005 [14] BLEKEN F, SKISRAD W, BARBERA K, KUSTOVA M, BORDIGA S, BEATO P, LILLERUD K P, SVELLE S, OLSBYE U. Conversion of methanol over 10-ring zeolites with differing volumes at channel intersections:comparison of TNU-9, IM-5, ZSM-11 and ZSM-5[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2011, 13(7):2539-2549. doi: 10.1039/C0CP01982H [15] OLSBYE U, SVELLE S, BJORGEN M, BEATO P, JANSSENS T V W, JOENSEN F, BORDIGA S, LILLERUD K P. Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons:How zeolite cavity and pore size controls product selectivity[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2012, 51(24):5810-5831. doi: 10.1002/anie.201103657 [16] 胡思, 巩雁军, 张卿, 张军亮, 张亚飞, 杨飞鹰, 窦涛.不同结构分子筛的甲醇制丙烯催化性能[J].化工学报, 2012, 63(12):3889-3896. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.12.022HU Si, GONG Yan-jun, ZHANG qin, ZHANG Jun-liang, ZHANG Ya-fei, YANG Fei-ying, DOU Tao. Methanol to propylene reaction over zeolite catalysts with different topologies[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 63(12):3889-3896. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.12.022 [17] MAPNOUX P, ROGER P, CANFF C, FOUCHE V, GNEP N S, GUISNET M. New technique for the characterization of carboNceous compounds responsible for zeolite deactivation[J]. Stud Surf Sci Catal, 1987, 34:317-330. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2991(09)60370-0 [18] ILIAS S, KHARE R, MALEK A, BHAN A. A descriptor for the relative propagation of the aromatic-and olefin-based cycles in methanol-to-hydrocarbons conversion on H-ZSM-5[J]. J Catal, 2013, 303:135-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.03.021 [19] KHARE R, MILLAR D, BHAN A. A mechanistic basis for the effects of crystallite size on light olefin selectivity in methanol-to-hydrocarbons conversion on MFI[J]. J Catal, 2015, 321:23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.10.016 [20] WANG P, HUANG L, LI J, DONG M, WANG J, TATSUMIC T, FAN W. Catalytic properties and deactivation behavior of H-MCM-22 in the conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons[J]. RSC Adv, 2015, 5(36):28794-28802. doi: 10.1039/C5RA00048C [21] ZHANG L, WANG H, LIU G, GAO K, WU J. Methanol-to-olefin conversion over H-MCM-22 catalyst[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2016, 411(1):311-316. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2cf18d7c16fd7fc63f1058a625da4af9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [22] 耿蕊, 董梅, 王浩, 牛宪军, 樊卫斌, 王建国, 秦张峰.十元环分子筛在甲醇芳构化反应中催化性能的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(9):1119-1127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2014.09.013GENG Rui, DONG Mei, WANG Hao, NIU Xian-jun, FAN Wei-bin, WANG Jian-guo, QIN Zhang-feng. An investigation on the catalytic performance of 10 MR zeolites in methanol aromatization reaction[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(9):1119-1127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2014.09.013 [23] BJORGEN M, AKYALCIN S, OLSBYE U, BENRD S, KOLBOE S, SVELLE S. Methanol to hydrocarbons over large cavity zeolites:Toward a unified description of catalyst deactivation and the reaction mechanism[J]. J Catal, 2010, 275(1):170-180. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.08.001 [24] LEE K, LEE S, JUN Y, CHOI M. Cooperative effects of zeolite mesoporosity and defect sites on the amount and location of coke formation and its consequence in deactivation[J]. J Catal, 2017, 347:222-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.01.018 [25] WAN Z, LI G, WANG C, YANG H, ZHANG D. Relating coke formation and characteristics to deactivation of ZSM-5 Zeolite in methanol to gasoline conversion[J]. App Catal A:Gen, 2018, 549:141-151. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.09.035 [26] FERRARI A C, ROBERTSON J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon[J]. Phys Rev B, 2008, 61(20):14095-14107. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6654d102b84ac04b880882d407f8b391&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [27] IGLESIAS-JUEZ A, BEALE A M, MAAIJENK, WENG T, GLATZEL P, WECKHUYSEN B M. A combined in situ time-resolved UV-Vis, Raman and high-energy resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy study on the deactivation behavior of Pt and PtSn propane dehydrogenation catalysts under industrial reaction conditions[J]. J Catal, 2010, 276(2):268-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.09.018 [28] LI J, XIONG G, Feng Z, LIU Z, XIN Q, LI C. Coke formation during the methanol conversion to olefins in zeolites studied by UV Raman spectroscopy[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2000, 39(1/2):275-280. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0214892602 [29] LI K, CHANG Q, YIN J, ZHAO C, HUANG L, TAO Z, YUN Y, ZHANG C, XIANG H, YANG Y, LI Y. Deactivation of Pt/KL catalyst during n-heptane aromatization reaction[J]. J Catal, 2018, 361:193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.001 [30] 王森, 陈艳艳, 卫智虹, 秦张峰, 李俊汾, 董梅, 樊卫斌, 王建国.分子筛骨架结构和酸性对其甲醇制烯烃(MTO)催化性能影响研究进展[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(10):1202-1214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.10.008WANG Sen, CHEN Yan-yan, WEI Zhi-hong, QIN Zhang-feng, LI Jun-fen, DONG Mei, FAN Wei-bin, WANG Jian-guo. Recent research progresses in the effect of framework structure and acidity of zeolites on their catalytic performance in methanol to olefins(MTO)[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(10):1202-1214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.10.008 [31] WANG S, CHEN Y, WEI Z, QIN Z, LIANG T, DONG M, LI J, FAN W, WANG J. Evolution of aromatic species in supercages and its effect on the conversion of methanol to olefins over H-MCM-22 Zeolite:A density functional theory study[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2016, 120(49):27964-27979. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b08154 [32] LI J, WEI Y, QI Y, TIAN P, LI B, HE Y, CHANG F, SUN X, LIU Z. Conversion of methanol over H-ZSM-22:The reaction mechanism and deactivation[J]. Catal Today, 2011, 164(1):288-292. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.10.095 -





 下载:
下载: