Distribution and enrichment characteristics of arsenic in feed-coal and by-products of coal-fired power plants
-
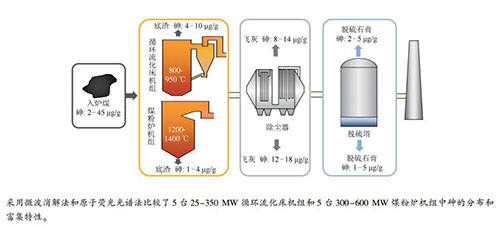
摘要: 采用微波消解法和氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法,考察并比较了五台容量25-350 MW循环流化床(CFB)机组和五台容量300-600 MW煤粉炉(PC)机组中砷的分布和富集特性。通过比较常规湿法消解和三种混酸微波消解体系,确定了适宜消解方案为体积比6:2:2的HNO3-HCl-HF混酸溶液微波消解法。煤中砷燃烧后绝大部分挥发出来被飞灰捕获,底渣中砷含量仅为1.95-9.75 μg/g,烟气中砷主要被飞灰吸附后依次被除尘器和脱硫塔捕集,其中,飞灰砷含量为8.68-17.63 μg/g,脱硫石膏砷含量为1.71-4.0 μg/g。燃烧温度是决定砷迁移与富集的主要因素,PC机组更高的炉膛燃烧温度使得较多砷从煤中释放出来,导致残留在底渣中砷含量低于CFB机组,同时PC机组飞灰在高温下更易形成硅铝酸盐类型的玻璃质从而捕获烟气中挥发态砷,其飞灰中砷含量为12.08-17.63 μg/g,普遍高于CFB机组飞灰中砷含量8.68-13.84 μg/g;随着锅炉负荷增大,炉膛内温度升高,飞灰与入炉煤中砷含量比值呈增长趋势。CFB机组燃用煤中灰分含量为33.96%-59.63%,显著高于PC机组15.05%-41.67%,故其相对富集系数高于PC机组,同时CFB机组有更多除尘器尚未捕获的细颗粒进入脱硫系统,使其脱硫石膏中砷含量也高于PC机组。Abstract: The distribution and enrichment characteristics of arsenic in five circulating fluidized bed (CFB) units with capacity between 25 to 350 MW and five pulverized coal furnace (PC) units with capacity between 300 to 600 MW were investigated using microwave digestion and hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry. By comparing the conventional wet digestion method and three kinds of mixed-acid microwave digestion systems, the appropriate digestion method was determined to be HNO3-HCl-HF acid solution mixed in a volume ratio of 6:2:2 with microwave digestion. The majority of the arsenic in coal evaporates during combustion and captured by the fly ash, the arsenic content in the bottom slag is only 1.95-9.75 μg/g. Most arsenic in the flue gas is adsorbed by the fly ash, most of the adsorbed arsenic is successively captured by the dust collector and desulfurization system. The arsenic contents in the fly ash and gypsum is 8.68-17.63 μg/g and 1.71-4.0 μg/g, respectively. Combustion temperature is the key factor affecting the release of arsenic. PC has a higher furnace temperature than CFB and makes more arsenic volatilize from coal and less arsenic remain in bottom slag. Meanwhile, a higher combustion temperature in PC unit produces more glassiness as aluminosilicate in the fly ash, which can capture the arsenic from the flue gas. Therefore, the arsenic content in the fly ash from PC unit is 12.08-17.63 μg/g, which is significantly higher than that from CFB, 8.68-13.84 μg/g. Moreover, the furnace temperature increases with the boiler load, which makes the ratio of arsenic content in the fly ash to the feed coal show an increasing trend. The ash content of the coal used for CFB and PC units is 33.96%-59.63% and 15.05%-41.67%, which makes the relative enrichment factor of arsenic in CFB higher than that in PC. Furthermore, more fine particles escaped from the dust collector should be captured by the desulfurization system, resulting that the arsenic concentration in the desulfurization gypsum of CFB unit is higher than that in PC unit.
-
表 1 所选燃煤机组容量、类型及取样点
Table 1 Capacity, boiler type and sampling points of the coal-fired power units
Capacity /MW Boiler type Sample Plant1(TS) 25 CFB feed coal + bottom slag + fly ash Plant2(GRT) 135 CFB feed coal + bottom slag + fly ash Plant3(WP) 200 CFB feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum Plant4(PS) 300 CFB feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum Plant5(YG) 300 CFB feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum Plant6(CZ) 300 PC feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum Plant7(HF) 330 PC feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum Plant8(SH) 600 PC feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum Plant9(DZ) 600 PC feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum Plant10(ST) 600 PC feed coal + fly ash + bottom slag + gypsum 表 2 所选燃煤机组入炉煤的工业分析
Table 2 Proximate analysis of the feed coals from the coal-fired power units
Plant Proximate analysis wad/% M A V FC TS 1.94 59.63 15.81 22.62 GRT 2.23 41.50 29.72 26.55 WP 1.24 61.20 18.62 18.94 YG 2.36 33.96 24.94 38.74 PS 2.38 39.76 24.74 33.12 CZ 0.90 41.67 12.26 45.17 HF 1.25 29.32 10.67 58.76 SH 2.67 15.05 29.95 52.33 DZ 3.98 16.42 25.57 54.03 ST 2.83 29.67 27.32 40.18 表 3 微波消解混酸体系配比表
Table 3 Composition of the acid solutions for the microwave digestion systems
Microwave digestion system Acid solution Ratio Mixed acid solution 1 HNO3-HCl-H2O2 6:2:2 Mixed acid solution 2 HNO3-HCl-H2SO4 6:2:2 Mixed acid solution 3 HNO3-HCl-HF 6:2:2 表 4 混酸体系定性消解对比
Table 4 Qualitative comparison of digestion results among the four mixed-acid digestion systems
Digestion method Solution Residue HNO3-HCl-HF microwave digestion clear almost no residue HNO3-HCl-H2O2 microwave digestion clear almost no residue except the gypsum HNO3-HCl-H2SO4 microwave digestion clear and yellow almost no residue HNO3-HCl-HF wet digestion clear grey residue 表 5 WP机组所采样品加标回收实验
Table 5 Recovery percentage and accuracy test of the samples from the WP unit
Sample Measuring result As content(μg/g,n=7) RSD /% recovery /% Feed coal 3.50±0.05 1.40 Feed coal + 2.0×10-8 As standard solution 22.54±0.85 3.76 95.20 Fly ash 10.78±0.35 3.21 Fly ash + 2.0×10-8 As standard solution 31.36±1.07 3.42 102.90 Bottom slag 3.79±0.14 3.77 Bottom slag + 2.0×10-8 As standard solution 24.68±1.30 5.29 104.45 Gypsum 3.99±0.20 4.91 Gypsum+ 2.0×10-8 As standard solution 22.22±0.34 1.54 94.40 -
[1] FINKELMAN R B. Trace elements in coal: Environmental and health significance[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 1999, 67: 2-9. [2] NRIAGU J O, PACYNA J M. Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals[J]. Nature, 1988, 333(6169): 134-139. [3] LIEVE H. Sampling technologies and air pollution control devices for gaseous and particulate arsenic: A review[J]. Environ Pollut, 2005, 137(2): 305-315. [4] 魏绍青, 滕阳, 李晓航, 苏银皎, 杨玮, 张锴. 300MW等级燃煤机组煤粉炉与循环流化床锅炉汞排放特性比较[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(8): 1009-1016.WEI Shao-qing, TENG Yang, LI Xiao-hang, SU Yin-jiao, YANG Wei, ZHANG Kai. Comparison of mercury emission from around 300 MW coal-fired power generation units between pulverized boiler and circulating fluidized-bed boiler[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(8): 1009-1016. [5] SENIOR C L, BOOL L E, MORENCY J R. Laboratory study of trace element vaporization from combustion of pulverized coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 63: 109-124. [6] ZHAO Y C, ZHANG J Y, HUANG W C, WANG Z H, LI Y, SONG D Y, ZHAO F H, ZHENG C G. Arsenic emission during combustion of high arsenic coals from Southwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Energy Convers Manage, 2008, 49: 615-624. [7] 邹潺, 王春波, 邢佳颖.煤燃烧过程中砷与氮氧化物的反应机理[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(2): 139-144.ZOU Chan, WANG Chun-bo, XING Jia-ying. Reaction mechanism of arsenic and nitrous oxide s during coal combustion[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2019, 47(2): 139-144. [8] AKIRA O, TSUNENORI N, YUKA S, AKIRA I, HIROKAZU T. Analysis of arsenic and some other elements in coal fly ash by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2005, 119(1/3): 213-217. [9] LOPEZ-ANTON M A, DIAZ-SOMOANO M, SPEARS D A, MARTINEZ-TARAZONA M R. Arsenic and selenium capture by fly ashes at low temperature[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2006, 40: 3947-3951. [10] ZHENG C H, WANG L, ZHANG Y X, ZHANG J, ZHAO H T, ZHOU J S, GAO X, CEN K F. Partitioning of hazardous trace elements among air pollution control devices in ultra-low-emission coal-fired power plants[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(6): 6334-6344. [11] ZHAO Y, ZHONG W Q, SUN H. Removal of arsenic from flue gas using NaClO/NaClO2 complex absorbent[J]. Chem Eng Res Des, 2019, 144: 505-511. [12] TIAN H Z, WANG Y, XUE Z G, QU Y P, CHAI F H, HAO J M. Atmospheric emissions estimation of Hg, As, and Se from coal-fired power plants in China, 2007[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2011, 409(16): 3078-3081. [13] DUAN L B, CUI J, JIANG Y, ZHAO C S, EDWARD J A. Partitioning behavior of Arsenic in circulating fluidized bed boilers co-firing petroleum coke and coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2017, 166: 107-114. [14] GENG W H, FURUZONO T, NAKAJIMA T, TAKANASHI H, OHKI A. Determination of total arsenic in coal and wood using oxygen flask combustion method followed by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2010, 176: 356-360. [15] ZHANG N, SUN G L, MA H R. Determination of ultra-trace selenium in mineral samples by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry with pressurized-PTFE-vessel acid digestion[J]. Miner Eng, 2007, 20(15): 1397-1400. [16] WANG J, NAKAZATO T, SAKANISHI K, YAMADA O, TAO H, SAITO I. Microwave digestion with HNO3/H2O2 mixture at high temperatures for determination of trace elements in coal by ICP-OES and ICP-MS[J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2004, 514(1): 115-124. [17] AKIRA I, TSUNENORI N, HIROKAZU T, AKIRA O, YOSHIO F, TORU Y. Effect of pretreatment conditions on the determination of major and trace elements in coal fly ash using ICP-AES[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(2): 257-263. [18] HATANPAA E, KAJANDER K, LAITINEN T, PIEPPONEN S, REVITZER H. A study of trace element behavior in two modern coal-fired power plants I. Development and optimization of trace element analysis using reference materials[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1997, 51(3): 205-217. [19] 朱振武, 禚玉群.不同酸体系对微波消解法测量燃煤副产物中痕量元素的影响[J].清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 56(10): 1072-1078.ZHU Zhen-wu, ZHUO Yu-qun. Effect of acid systems for determination of trace elements in coal combustion byproducts using microwave digestion method[J]. J Tsinghua Univ (Sci & Technol), 2016, 56(10): 1072-1078. [20] GÓMEZ-ARIZA J L, SÁNCHEZ-RODAS D, GIRÁLDEZ I, MORALES E. A comparison between ICP-MS and AFS detection for arsenic speciation in environmental samples[J]. Talanta, 2000, 51(2): 257-268. [21] 刘晶, 郑楚光, 贾小红, 徐杰英.微波消解和电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法同时测定煤灰中的14种元素[J].分析化学, 2003, 31(11): 1360-1363.LIU Jing, ZHNEG Chu-guang, JIA Xiao-hong, XU Jie-ying. Determination of 14 elements in coal ash by microwave digestion and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Anal Chem, 2003, 31(11): 1360-1363. [22] 王学涛, 金保升, 仲兆平, 屈成锐.气氛对焚烧飞灰熔融过程中重金属行为的影响[J].中国电机工程学报, 2006, 26(7): 47-52.WANG Xue-tao, JIN Bao-sheng, ZHONG Zhao-ping, QU Cheng-rui. Influence of atmospheres on behavior of heavy metals during melting process of fly ashes from municipal solid waste incinerator[J]. Proc CSEE, 2006, 26(7): 47-52. [23] 赵峰华, 任德贻, 彭苏萍, 王运泉, 张军营, 丁振华, 丛志远.煤中砷的赋存状态[J].地球科学进展, 2003, 18(2): 214-220.ZHAO Feng-hua, REN De-yi, PENG Su-ping, WANG Yun-quan, ZHANG Jun-ying, DING Zhen-hua, CONG Zhi-yuan. The modes of occurrence of arsenic in coal[J]. Adv Earth Sci, 2003, 18(2): 214-220. [24] 刘慧敏, 王春波, 张月, 孙喆, 邵欢.温度和赋存形态对燃煤过程中砷迁移和释放的影响[J].化工学报, 2015, 66(11): 4643-4651.LIU Hui-min, WANG Chun-bo, ZHANG Yue, SUN Zhe, SHAO Huan. Effect of temperature and occurrence form of arsenic on its migration and volatilization during coal combustion[J]. J Chem Ind Eng, 2015, 66(11): 4643-4651. [25] CHEN C, LI Q, TAO D J, ZHAI J P, TAO C L. Physical and chemical prosperities difference between pulverized coal boiler fly ash and circulating fluidized bed combustion ash[J]. Asian J Chem, 2012, 24(10): 4538-4540. [26] 李杨, 陈伟, 赵永椿, 李海龙, 张军营, 李杰, 胡浩权. Fe/Al-SiO2复合金属氧化物用于燃煤烟气中汞的脱除[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(12): 1409-1416.LI Yang, CHEN Wei, ZHAO Yong-chun, LI Hai-long, ZHANG Jun-ying, LI Jie, HU Hao-quan. Removal of elemental mercury from flue gas by Fe/Al-SiO2 complex[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2019, 47(12): 1409-1416. [27] 朱永清.硅酸盐熔体结构学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990.ZHU Yong-qing. Silicate Melt Structure[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990. [28] 赵峰华, 任德贻, 许德伟, 尹金双, 李亚男, 王秀琴.燃煤产物中砷的物相研究[J].中国矿业大学学报, 1999, 28(4): 366-367.ZHAO Feng-hua, REN De-yi, XU De-wei, YIN Jin-shuang, LI Ya-nan, WANG Xiu-qin. Research on the phase of arsenic in coal-burning residue[J]. J China Univ Min Technol, 1999, 28(4): 366-367. [29] MEIJ R, VERDENBREGT L H J, WINKEL H T. The fate and behavior of mercury in coal-fired power plants[J]. J Air Waste Manage, 2002, 52(8): 912-917. [30] BHATTACHARYYA S, DONAHOE J, DAN P. Experimental study of chemical treatment of coal fly ash to reduce the mobility of priority trace elements[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(7): 1173-1184. [31] RODELLA N, BOSIOA, ZACCO A, BORGESE L, PASQUALI M, DALIPI R, DEPERO L E, PATEL V, BINGHAM P A, BONTEMPI E. Arsenic stabilization in coal fly ash through the employment of waste materials[J]. J Environ Chem Eng, 2014, 2(3): 1352-1357. [32] YUDOVICH Y E, KETRIS M P. Arsenic in coal: A review[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2005, 61: 141-196. -





 下载:
下载: