Steam gasification characteristics of Zhundong coal with additive CaO at medium temperature
-
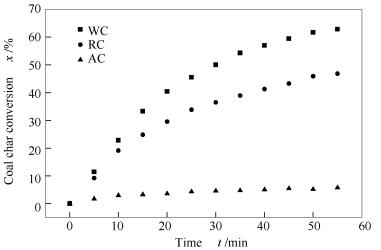
摘要: 以内在碳捕集气化为背景,利用加压热重分析仪开展CaO对准东煤中温(700-750 ℃)水蒸气气化反应动力学特性的影响研究,采用氮气吸附仪对准东煤焦的比表面积进行测定,并对煤中不同赋存形态碱金属含量采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES)进行测定。结果表明,准东煤中的可溶性碱金属元素能有效催化气化反应,引入的二氧化碳吸收剂CaO与碱金属间表现出协同催化作用。水洗后的准东煤焦活性最高,添加CaO后的气化活性最好。Ca/C物质的量比对准东煤气化特性的影响研究表明,CaO的添加存在饱和量,Ca/C物质的量比为1.0较为合适。利用均相模型(HM)、缩核模型(SCM)以及修正体积模型(MVM)对反应动力学实验数据进行拟合,结果表明,修正体积模型可以较好地体现添加CaO的准东煤中温水蒸气气化反应动力学特性,由此获得反应活化能为160.90 kJ/mol。Abstract: The steam gasification characteristics of Zhundong coal with additive CaO at medium temperature of 700-750℃ were investigated by Thermal Gravimetric Analyzer (TGA). The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) specific surface area of the coal char was tested by N2 adsorption, and the different occurrence modes of alkali metals in the coal were analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer (ICP-OES). The results show that the soluble sodium could catalyze the gasification reaction effectively and the water-washed coal has the highest activity. The additive CaO and the inherent sodium have a synergistic effect during the gasification, and the optimal Ca/C molar ratio is 1.0. The kinetic parameters were calculated using the homogeneous model (HM), the shrinking core model (SCM) and the modified volumetric model (MVM), respectively. The results indicate that the MVM is better to represent the char steam gasification reaction, and its activation energy calculated by the MVM is 160.90 kJ/mol.
-
Key words:
- Zhundong coal /
- alkali metal /
- CaO /
- steam gasification /
- kinetics
-
表 1 准东煤的工业分析与元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of Zhundong coal
Proximate analysis wad /% Ultimate analysis wad /% M A V FC C H O N S 15.69 5.74 33.90 44.67 54.65 1.70 21.14 0.65 0.43 表 2 准东煤、水洗煤和酸洗煤的灰成分分析
Table 2 Ash composition analysis of RC, WC and AC
Sample Composition of ash w/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O SO3 others RC 8.795 10.370 5.940 32.759 5.882 0.228 4.670 28.971 2.4 WC 17.248 16.798 9.073 40.681 4.360 0.163 0.497 8.068 2.33 AC 78.921 4.821 5.773 2.164 0.615 0.461 0.874 4.181 2.23 表 3 准东煤中不同赋存形态碱金属含量
Table 3 Different occurrence modes of alkali metals in Zhundong coal
Occurrence mode Content w/% Na K Water soluble 1970.1 69.7 Hydrochloric acid soluble 698.4 42.5 Insoluble 213.5 216.4 Total 2882 328.6 表 4 原煤、水洗煤、酸洗煤焦的碱金属钠含量
Table 4 Different amount of sodium in the char of RC, WC and AC
Sample Na content w/(μg·g-1) RC char 4390 WC char 1232 AC char 356 表 5 原煤、水洗煤、酸洗煤热解焦的比表面积
Table 5 Specific surface area of chars from pyrolysis of RC, WC and AC
Sample Surface area A/(m2·g-1) RC char 90.27 WC char 139.14 AC char 276.24 表 6 采用收缩核模型拟合的相关系数及动力学常数
Table 6 Linear correlation coefficients and the reaction rate constants fitted by SCM
Temperature t/℃ R2 k/min-1 700 0.95543 0.00643 720 0.95024 0.00871 735 0.94544 0.0125 750 0.94001 0.01597 表 7 采用均相模型拟合的相关系数及动力学常数
Table 7 Linear correlation coefficients and the reaction rate constants fitted by HM
Temperature t/ ℃ R2 k/min-1 700 0.9749 0.0075 720 0.9687 0.0103 735 0.9671 0.015 750 0.9591 0.0197 表 8 采用修正体积模型拟合的相关系数及动力学常数
Table 8 Linear correlation coefficients and the reaction rate constants fitted by MVM
Temperature t/℃ R2 A B k/min-1 700 0.99901 0.01642 0.80468 0.00590 720 0.99896 0.02246 0.74876 0.00803 735 0.99966 0.03381 0.79886 0.01161 750 0.99866 0.04341 0.74543 0.01531 表 9 采用不同模型拟合获得的煤焦水蒸气气化反应的动力学参数
Table 9 Kinetic parameters of char steam gasification based on the SCM, HM and MVM
Kinetic model Ea/(kJ·mol-1) lnk0/min-1 SCM 154.12 13.981 HM 163.11 15.241 MVM 160.90 14.726 -
[1] 付子文, 王长安, 翁青松, 车得福.水洗对准东煤煤质特性影响的实验研究[J].西安交通大学学报, 2014, 48(3):54-60. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/5ba393d4cc22bcd126ff0ca1.htmlFU Zi-wen, WANG Chang-an, WENG Qing-song, CHE De-fu. Experimental investigation for effect of water washing on Zhundong coal properties[J]. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ, 2014, 48(3):54-60. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/5ba393d4cc22bcd126ff0ca1.html [2] 丁浩然, 郑瑛, 刘旭辉, 罗聪, 郑楚光.准东煤水蒸气/氢气常压混合气化研究[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(11):2674-2682. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/a6a2c09c804d2b160a4ec04b-2.htmlDING Hao-ran, ZHENG Ying, LIU Xu-hui, LUO Cong, ZHENG Chu-guang. Study on characteristics of H2/H2O gasfication of Zhundong Coal[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2015, 40(11):2674-2682. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/a6a2c09c804d2b160a4ec04b-2.html [3] ZHANG H X, GUO X W, ZHU Z P. Effect of temperature on gasification performance and sodium transformation of Zhundong coal[J]. Fuel, 2017, 189:301-311. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.097 [4] 宋国良, 齐晓宾, 宋维健, 吕清刚.新疆准东高碱煤流态化气化过程中碱金属的迁移特性[J].过程工程学报, 2015, 15(4):541-547. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.215210SONG Guo-liang, QI Xiao-bin, SONG Wei-jian, LV Qing-gang. Migration characteristics of alkali metals in Zhundong high-alkali coal from Xingjiang during fluidized gasification process[J]. Chin J Process Eng, 2015, 15(4):541-547. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.215210 [5] MCCULLOUGH D P, EYK, P J V, ASHMAN P J, MULLINGER P J. Investigation of agglomeration and defluidization during spouted-bed gasification of high-sodium, high-sulfur south Australian lignite[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(7):2772-2781. doi: 10.1021/ef2002537 [6] 董倩. 准东煤热解及气化反应特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院工程热物理研究所, 2015. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2957929DONG Qian. Characteristics study on pyrolysis and gasification of Zhundong coal[D]. Beijing: Institute of Engineering Thermophysics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2957929 [7] LIN S Y, SUZUKI Y, HATANO H, HARADA M. Hydrogen production from hydrocarbon by integration of water-carbon reaction and carbon dioxide removal (HyPr-RING method)[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(2):339-1440. doi: 10.1021/ef000089u [8] JOSE C, TOLEDO J, GREGORIA M. Steam gasification of coal at low-medium (6002 capture in fluidized bed at atmospheric pressure:The effect of inorganic species. 1. literature review and comments[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2006, 45:6137-6146. doi: 10.1021/ie0602658 [9] GE H J, SHEN L H, GU H M, SONG T, JIANG S X. Combustion performance and sodium absorption of ZhunDong coal in a CLC process with hematite oxygen carrier[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2016, 94:40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.10.043 [10] 刘敬, 王智化, 项飞鹏, 黄镇宇, 刘建忠, 周俊虎, 岑可法.准东煤中碱金属的赋存形式及其在燃烧过程中的迁移规律实验研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(3):316-322. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18373.shtmlLIU Jing, WANF Zhi-hua, XIANF Fei-peng, HUANF Zhen-yu, LIU Jian-zhong, ZHOU Jun-hu, CEN Ke-fa. Modes of occurrence and transformation of alkali metals in Zhundong coal during combustion[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(3):316-322. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18373.shtml [11] ZHU C, QU S J, ZHANG J, WANG Y, ZHANG Y H, Distribution, occurrence and leaching dynamic behavior of sodium in Zhundong coal[J]. Fuel, 2016, 190:189-197. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236116311334 [12] 陈川, 张守玉, 刘大海, 郭熙, 董爱霞, 熊绍武, 施大钟, 吕俊复.新疆高钠煤中钠的赋存形态及其对燃烧过程的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(7):832-838. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18218.shtmlCHEN Chuan, ZHANG Shou-yu, LIU Da-hai, GUO Xi, DONG Ai-xia, XIONG Shao-wu, SHI Da-Zhong, LÜ Jun-fu. Existence form of sodium in high sodium coals from Xinjiang and its effect on combustion process[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(7):832-838. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18218.shtml [13] JIN H, CHEN Y N, GE Z W, LIU S K, REN C S, GUO L J. Hydrogen production by Zhundong coal gasification in supercritical water[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(46):16096-16103. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.09.003 [14] LIU H P, CHEN T P, LI Y, SONG Z Y, WANG S W, WU S H. Temperature rise characteristics of ZhunDong coal during microwave pyrolysis[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2016, 148:317-323. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.03.017 [15] ZHANG K, LI Y, WANG Z H, LI Q, WHIDDON R, HE Y, CEN K F. Pyrolysis behavior of a typical Chinese sub-bituminous Zhundong coal from moderate to high temperatures[J]. Fuel, 2016, 185:701-708. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.08.038 [16] WANG X B, XU Z X, WEI B, ZHANG L, TAN H Z, YANG T, MIKULČIĆ H, DUIĆ N. The ash deposition mechanism in boilers burning Zhundong coal with high contents of sodium and calcium:A study from ash evaporating to condensing[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2015, 80:150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.01.051 [17] 宋维建, 宋国良, 齐晓宾, 吕清刚.不同预处理方法对准东高碱煤中碱金属含量测定的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(2):162-167. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18775.shtmlSONG Wei-jian, SONG Guo-liang, QI Xiao-bin, LÜ Qing-gang, Effect of pretreatment methods on the determination of alkali metal content in high alkaili metal Zhundong coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2016, 44(2):162-167. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18775.shtml [18] 卫小芳, 刘铁峰, 黄戒介, 房倚天, 王洋.高钠煤及其洗煤的气化反应研究[J].煤炭转化, 2008, 31(3):10-13. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical_mtzh200803003.aspxWEI Xiao-fang, LIU Tie-feng, HUANF Jie-jie, FANG Yi-tian, WANG Yang. Study of the gasification reactivity of high-sodium coal and washed coals[J]. Coal Convers, 2008, 31(3):10-13. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical_mtzh200803003.aspx [19] QUYN D M, WU H, HAYASHI JI, LI CZ. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal (Ⅳ):Catalytic effects of NaCl and ion-exchangeable Na in coal on char reactivity[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(5):587-593. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00323-X [20] 王贤华, 陈汉平, 王静, 辛芬, 杨海平.无机矿物质盐对生物质热解特性的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2008, 36(6):679-683. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200806007WANG Xian-hua, CHEN Han-ping, WANG Jing, XIN Fen, YANG Hai-ping. Influence of mineral matters on biomass pyrolysis characteristics[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2008, 36(6):679-683. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200806007 [21] 赵冰, 王嘉瑞, 陈凡敏, 王小悦, 李小江.高钠煤水热脱钠处理及其对燃烧特性的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(12):1416-1422. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18533.shtmlZHAO Bing, WANG Jia-rui, CHEN Fan-min, WANG Xiao-yue, LI Xiao-jiang. Hydrothermal treatment to remove sodium from high sodium coal and its influence on combustion characteristics[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(12):1416-1422. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18533.shtml [22] MIMS C A, PABST J K. Alkali-catalyzed carbon gasification kinetics:Unification of H2O, D2O and CO2 reactivities[J]. J Catal, 1987, 107(1):209-220. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(87)90286-7 [23] WANG J, JIANG M Q, YAO Y H, ZHANG Y M, CAO J Q. Steam gasification of coal char catalyzed by K2CO3 for enhanced production of hydrogen without formation of methane[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(9):1572-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.12.017 [24] MIURA K, HASHIMOTO K, SILVESTON P L. Factors affecting the reactivity of coal chars during gasification and indices representing reactivity[J]. Fuel, 1989, 68(11):1461-1475. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(89)90046-X [25] ZHANG Z G, KYOTANI T, TOMITA A. Dynamic behavior of surface oxygen complexes during oxygen-chemisorption and subsequent temperature-programmed desorption of calcium-loaded coal chars[J]. Energy Fuels, 1989, 3(5):556-571. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231269664_Dynamic_behavior_of_surface_oxygen_complexes_during_O2_chemisorption_and_subsequent_temperature-programmed_desorption_of_calcium-loaded_coal_chars [26] OHTSUKA Y, ASAMI K. Highly active catalysts from inexpensive raw materials for coal gasification[J]. Catal Today, 1997, 39(1/2):111-125. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092058619700093X [27] LEVENSPIEL O. Chemical Reaction Engineering[M]. New York:Jonh Wiley and Sons, 1999. [28] MOLINA A, MONDRAGON F. Reactivity of coal gasification with steam and CO2[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(15):1831-1839. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00123-9 [29] KASAOKA S, SAKATA Y, TONG C. Kinetic evaluation of the reactivity of various coal chars for gasification with carbon dioxide in comparison with steam[J]. Int Chem Eng, 1985, 25(1):160-175. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/236534330_Kinetic_evaluation_of_the_reactivity_of_various_coal_chars_for_gasification_with_carbon_dioxide_in_comparison_with_steam [30] 程秀秀, 黄瀛华, 任德庆.煤焦的孔隙结构及其与气化的关系[J].燃料化学学报, 1987, 15(8):261-267. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=rlhx198703010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHENG Xiu-xiu, HUANG Ying-hua, REN De-qing. The relationship between pore structure of coal chars and gasification activities[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1987, 15(8):261-267. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=rlhx198703010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ -





 下载:
下载: