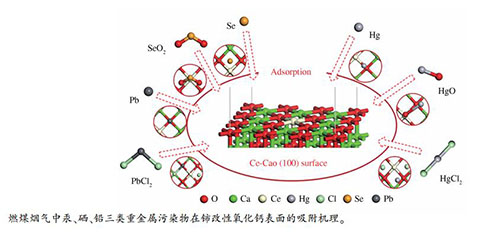
Interaction mechanism between heavy metals and Ce-doped CaO in flue gas of coal combustion
-
摘要: 氧化钙(CaO)作为一种吸附剂广泛应用于燃煤烟气重金属的净化,但其吸附效率有限,需要进一步改性提升。金属铈(Ce)改性可调整其表面电子分布,增强化学活性。基于此,本研究建立了Ce-CaO (100)周期性模型,研究了燃煤烟气中汞、硒、铅三类重金属污染物的吸附机理。结果表明,除Hg0在Ce-CaO (100)表面上的吸附为物理吸附外,其余重金属污染物均为化学吸附,Ce位点和O位点为重金属污染物的主要活性吸附位点,吸附分子与Ce-CaO (100)表面之间存在明显的电荷转移与强烈的相互作用。Ce掺杂改性提升了CaO (100)表面对重金属污染物的吸附能力,尤其对Se0、SeO2和HgCl2的捕集能力显著提高。Abstract: Calcium oxide (CaO) has been widely used as an adsorbent in the purification of heavy metals in coal-fired flue gas. However, the adsorption efficiency is limited and a further modification is needed. The cerium (Ce) modification can redistribute the surface electrons and enhance the chemical activity of CaO. Therefore, the Ce-CaO (100) periodic model was established to study the adsorption mechanism of mercury, selenium, and lead pollutants in the coal-fired flue gas. The results show that, except for the physical adsorption of Hg0 on the Ce-CaO (100) surface, the other heavy metal pollutants are chemically adsorbed on the surface. The Ce-site and O-site are the main active adsorption sites of heavy metal pollutants. Intense charge transfer and strong interaction are observed between adsorption molecules and Ce-CaO (100). Moreover, the adsorption capacity of Ce-doped CaO (100) surface for heavy metal pollutants has been improved, especially the significantly increased capture capacity on Se0, SeO2 and HgCl2.
-
Key words:
- coal-fired flue gas /
- heavy metals /
- modified CaO /
- adsorption mechanism /
- density functional theory
-
表 1 Hg0、HgCl2和HgO在Ce-CaO (100)表面吸附构型的几何参数和吸附能
Table 1 Geometry parameters and adsorption energies of Hg0, HgCl2 and HgO on Ce-CaO (100) surface
RHg-surface1 /Å RHg-Cl2 /Å RHg-O3 /Å Ead /(kJ·mol-1) Hg0-Ce-CaO (100) 1A 3.315 - - -17.16 1B 3.048 - - -26.85 1C 3.433 - - -26.24 1D 3.378 - - -19.52 1E 3.497 - - -21.28 1F 3.161 - - -28.03 HgCl2-Ce-CaO (100) 1G 4.986 3.812 - -461.50 1H 3.448 3.535 - -452.30 1I 3.456 4.049 - -447.78 1J 4.835 3.596 - -441.30 HgO-Ce-CaO (100) 1K 3.286 - 2.799 -650.84 1L 3.548 - 2.778 -652.15 1M 3.257 - 2.82 -648.98 1N 4.646 - 4.646 -647.92 1: RHg-surface represents the distance between Hg atom and Ce-CaO surface; 2: RHg-Cl is the furthest distance between Hg atom and Cl atom in HgCl2 molecule; 3: RHg-O symbolizes the distance of Hg atom and O atom in HgO molecule 表 2 Se0和SeO2在Ce-CaO (100)表面吸附构型的几何参数和吸附能
Table 2 Geometry parameters and adsorption energies of Se0 and SeO2 on Ce-CaO (100) surface
RSe-surface5 /Å Ead /(kJ·mol-1) Se0-Ce-CaO (100) 2A 2.634 -525.91 2B 2.774 -529.18 2C 2.896 -515.84 2D 2.876 -465.89 2E 2.716 -429.69 SeO2-Ce-CaO (100) 2F 2.910 -437.93 2G 3.168 -392.45 2H 2.851 -398.34 2I 3.185 -437.81 5: RSe-surface represents the distance between Se atom and Ce-CaO surface 表 3 Pb0和PbCl2在Ce-CaO (100)表面吸附构型的几何参数和吸附能
Table 3 Geometry parameters and adsorption energies of Pb0 and PbCl2 on Ce-CaO (100) surface
RPb-surface7 /Å Ead /(kJ·mol-1) Pb0-Ce-CaO (100) 3A 2.500 -276.73 3B 3.339 -194.76 3C 3.412 -199.82 PbCl2-Ce-CaO (100) 3D 3.669 -282.08 3E 2.396 -263.13 7: RPb-surface represents the distance between Pb atom and Ce-CaO surface -
[1] DENG S, SHI Y, LIU Y, CHEN Z, WANG X F, CAO Q, LI S G, ZHANG F. Emission characteristics of Cd, Pb and Mn from coal combustion: Field study at coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 126: 469-475. [2] 郭胜利.燃煤重金属迁移转化特征及其污染控制研究[D].重庆: 重庆大学, 2014.GUO Sheng-li. Study on migration and transformation characteristics of heavy metals in coal combustion and its pollution control[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2014. [3] 乔岗杰, 刘轩, 赵元财, 刘红刚, 孔凡荣, 张锴.燃煤电厂典型重金属排放与控制进展[J].电站系统工程, 2020, 36(2): 1-4+8.QIAO Gang-jie, LIU Xuan, ZHAO Yuan-cai, LIU Hong-gang, KONG Fan-rong, ZHANG Kai. Progress in emission and control of typical heavy metals in coal-fired power plants[J]. Power Plant Syst Eng, 2020, 36(2): 1-4+8. [4] ZHANG Y L, ZHAO Y C, YANG Y J, LIU P F, LIU J, ZHANG J Y. DFT study on Hg0 adsorption over graphene oxide decorated by transition metals (Zn, Cu and Ni)[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2020, 525: 146519. [5] YOO J M, KIM B S, LEE J C, KIM M S, NAM C W. Kinetics of the volatilization removal of lead in electric arc furnace dust[J]. Mater Trans, 2005, 46(2): 323-328. [6] YANG Y J, LIU J, WANG Z, MIAO S, DING J Y, YU Y N, ZHANG J C. A complete catalytic reaction scheme for Hg0 oxidation by HCl over RuO2/TiO2 catalyst[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2019, 373: 660-670. [7] MCNUTT M. Mercury and health[J]. Sci, 2013, 341: 1430-1430. [8] YANG J P, ZHAO Y C, MA S M, ZHU B B, ZHANG J Y, ZHENG C G. Mercury removal by magnetic biochar derived from simultaneous activation and magnetization of sawdust[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2016, 50(21): 12040-12047. [9] HOU W H, ZHOU J S, QI P, GAO X, LUO Z Y. Effect of H2S/HCl on the removal of elemental mercury in syngas over CeO2-TiO2[J]. Chem Eng J, 2014, 241: 131-137. [10] FAN Y M, ZHOU Y Q, ZHU Z W, DU W, LI L L. Zerovalent selenium adsorption mechanisms on CaO surface: DFT calculation and experimental study[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2017, 121(39): 7385-7392. [11] FAN Y M, ZHUO Y Q, LOU Y, ZHU Z W, LI L L. SeO2 adsorption on CaO surface: DFT study on the adsorption of a single SeO2 molecule[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 413: 366-371. [12] XING J Y, WANG C B, ZOU C, ZHANG Y. DFT study of Se and SeO2 adsorbed on CaO (0 0 1) surface: Role of oxygen[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2020, 510: 145488. [13] CHENG J F, ZENG H C, ZHANG Z H, XU M H. The effects of solid absorbents on the emission of trace elements, SO2, and NOx during coal combustion[J]. Int J Energy Res, 2001, 25(12): 1043-1052. [14] CLARKE L B. The fate of trace elements during coal combustion and gasification: An overview[J]. Fuel, 1993, 72(6): 731-736. [15] GHOSHDASTIDAR A, MAHULI S K, AGNIHOTRI R, FAN L. Selenium capture using sorbent powders: mechanism of sorption by hydrated lime[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1996, 30(2): 447-452. [16] WANG K S, CHIANG K Y, LIN S M, TSAI C C, SUN C J. Effects of chlorides on emissions of toxic compounds in waste incineration: study on partitioning characteristics of heavy metal[J]. Chemosphere, 1999, 38(8): 1833-1849. [17] WANG J, XIA S, YU L. Adsorption of Pb (Ⅱ) on the kaolinite (001) surface in aqueous system: A DFT approach[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2015, 339: 28-35. [18] LOEF M, MENDOZA L F, WALACH H. Lead (Pb) and the risk of Alzheimer's disease or cognitive decline: A systematic review[J]. Toxin Rev, 2011, 30(4): 103-114. [19] NAVASACIEN A, GUALLAR E, SILBERGELD E K, ROTHENBERG S J. Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease-A systematic review[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2007, 115(3): 472-482. [20] MARKUS J, MCBRATNEY A B. A review of the contamination of soil with lead: Ⅱ. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of soil lead[J]. Environ Int, 2001, 27(5): 399-411. [21] 马晓文, 李建军.燃煤电厂重金属污染与控制技术研究进展[J].四川化工, 2019, 22(1): 5-8.MA Xiao-wen, LI Jian-jun. Research progress of heavy metal pollution and control technology in coal-fired power plants[J]. Sichuan Chem Eng, 2019, 22(1): 5-8. [22] 郭胜利, 李东伟, 耿伟乐, 张建.调制碳酸钙对燃煤重金属As, Cd, Zn的排放控制[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(12): 2967-2973.GUO Sheng-li, LI Wei-dong, GENG Wei-le, ZHANG Jian. Emission control of heavy metals As, Cd, and Zn from coal combustion by calcined calcium carbonate[J]. Acta Coal Sin, 2015, 40(12): 2967-2973. [23] 刘晶, 郑楚光, 曾汉才, 张军营, 陆晓华.固体吸附剂控制燃煤重金属排放的实验研究[J].环境科学, 2003, 24(5): 23-27.LIU Jing, ZHENG Chu-guang, ZENG Han-cai, ZHANG Jun-ying, LU Xiao-hua. Experimental study on controlling heavy metal emission from coal combustion with solid adsorbents[J]. Environ Sci, 2003, 24(5): 23-27. [24] 李明晖.飞灰中未燃尽碳及氧化钙表面吸附砷的机理研究[D].北京: 华北电力大学, 2019.LI Ming-hui. Mechanism of arsenic adsorption on unburned carbon and calcium oxide in fly ash[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2019. [25] 孙晓, 钱枫, 魏新鲜, 严军.添加CaO对燃煤重金属元素富集效果的影响[J].化工环保, 2016, 36(2): 205-210.SUN Xiao, QIAN Feng, WEI Xin-xian, YAN Jun. Effect of CaO addition on enrichment of heavy metals in coal combustion[J]. Chem Environ Prot, 2016, 36(2): 205-210. [26] 吴晗.氧化钙基CO2吸附剂的改性研究[D].上海: 华东理工大学, 2013.WU Han. Modification of CaO based CO2 adsorbent[D]. Shanghai: East China University of science and technology, 2013. [27] LANG J H, HAN Q, YANG J H, LI C S, YANG L L, ZHANG Y J, GAO M, WANG D D, CAO J. Fabrication and optical properties of Ce-doped ZnO nanorods[J]. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107: 074302. [28] DONG X, LIN Y C, MA Y Q, ZHAO L. Ce-doped UiO-67 nanocrystals with improved adsorption property for removal of organic dyes[J]. R Soc Chem, 2019, 9: 27674. [29] LU H, KHAN A, PRATSINIS S E, SMINRNIOTIS P G. Flame-made durable doped-CaO nanosorbents for CO2 capture[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 23(2): 1093-1100. [30] 张秀霞, 谢苗, 伍慧喜, 吕晓雪, 林日亿, 周志军.钙对焦炭非均相还原NO的微观作用机理: DFT研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2020, 48(2): 163-171.ZHANG Xiu-xia, XIE Miao, WU Hui-xi, LV Xiao-xue, LIN Ri-yi, ZHOU Zhi-jun. Micro mechanism of calcium on heterogeneous reduction of no by coke: DFT study[J]. Acta Fuel Chem, 2020, 48(2): 163-171. [31] 袁淑萍, 王建国, 李永旺, 彭少逸. Fe在丝光沸石骨架中取代位置的DFT研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2001, 29(S1): 252-254.YUAN Shu-ping, WANG Jian-guo, LI Yong-wang, PENG Shao-yi. DFT Study on the substitution sites of Fe in mordenite framework[J]. Acta Fuel Chem, 2001, 29(S1): 252-254. [32] LIU L, HONG D, GUO X. A study of metals promoted CaO-based CO2 sorbents for high temperature application by combining experimental and DFT calculations[J]. J CO2 Util, 2017, 22: 155-163. [33] FAN Y M, ZHUO Y Q, LI L L. SeO2 adsorption on CaO surface: DFT and experimental study on the adsorption of multiple SeO2 molecules[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 420: 465-471. [34] FAN Y M, YAO J G, ZHANG Z L, SCEATS M, ZHUO Y Q, LI L L, MAITLAND G C, FENNELL P S. Pressurized calcium looping in the presence of steam in a spout-fluidized-bed reactor with DFT analysis[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2018, 169: 24-41. [35] LI Z P, NIU S L, ZHAO G J, HAN K H, LI Y J, LU C M, CHENG S. Molecular simulation study of strontium doping on the adsorption of methanol on CaO (100) surface[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2020, 48(2): 172-178. [36] ESRAFILI M D, NEMATOLLAHI P, ABDOLLAHPOUR H. A comparative DFT study on the CO oxidation reaction over Al-and Ge-embedded graphene as efficient metal-free catalysts[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2016, 378: 418-425. [37] RAHMATHULLA S S, SIRAJUDDEEN M M S. Nitrogen induced half metallic ferromagnetism in oxides of calcium and cadmium: A DFT perspective[J]. Mater Chem Phys, 2020, 243: 122336. [38] DAI W, SHUI Z H, LI K. First-principle investigations of CaO (100) surface and adsorption of H2O on CaO (100)[J]. Comput Theor Chem, 2011, 967(1): 185-190. [39] GALLOWAY B, PADAK B. Effect of flue gas components on the adsorption of sulfur oxides on CaO (100)[J]. Fuel, 2017, 197: 541-550. [40] CHAKRADHAR A, LIU Y, SCHMIDT J, KADOSSOV E, BURGHAUS U. Adsorption and dissociation kinetics of alkanes on CaO (100)[J]. Surf Sci, 2011, 605(15/16): 1537-1543. [41] WANG W J, FAN L L, WANG G P, LI Y H. CO2 and SO2 sorption on the alkali metals doped CaO (100) surface: A DFT-D study[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 425: 972-977. [42] 闫广精, 王春波, 张月, 陈亮. H2O对SO2在CaO表面上吸附的影响理论研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(10): 1163-1172.YAN Guang-jing, WANG Chun-bo, ZHANG Yue, CHENG Liang. Theoretical study on the effect of H2O on SO2 adsorption on CaO surface[J]. Acta Fuel Chem, 2019, 47(10): 1163-1172. [43] 徐沁, 陈大志.本征O空位缺陷对ZnO表面甲醛吸附性质影响的密度泛函理论研究[J].应用物理, 2020, 10(6): 8.XU Qing, CHENG Da-zhi. Density functional theory study on the effect of intrinsic O vacancy defects on formaldehyde adsorption on ZnO surface[J]. Appl Phys, 2020, 10(6): 8. [44] MILMAN V, REFSON K, CLARK S J, PICKARD C J, YATES J R, GAO S P, HASNIP P J, PROBERT M I J, PERLOV A, SEGALL M D. Electron and vibrational spectroscopies using DFT, plane waves and pseudopotentials: CASTEP implementation[J]. J Mol Struct: THEOCHEM, 2010, 954(1/3): 22-35. [45] CHEN H, CHOI Y, LIU M L, LIN M C. A theoretical study of surface reduction mechanisms of CeO2 (111) and (110) by H2[J]. Chem Phys Chem, 2007, 8(6): 849-855. [46] LOSCHEN C, CARRASCO J, NEYMAN K M, ILLAS F. First-principles LDA+U and GGA+ U study of cerium oxides: Dependence on the effective U parameter[J]. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75(3): 035115. [47] WANG K S, CHIANG K Y, LIN S M, TSAI C C, SUN C J. Effects of chlorides on emissions of toxic compounds in waste incineration: Study on partitioning characteristics of heavy metal[J]. Chemosphere, 1999, 38(8), 1833-1849. [48] XIN G, ZHAO P, ZHENG C. Theoretical study of different speciation of mercury adsorption on CaO (001) surface[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2009, 32(2): 2693-2699. [49] FAN Y M, ZHUO Y Q, LOU Y, ZHU Z W, LI L L. SeO2 adsorption on CaO surface: DFT study on the adsorption of a single SeO2 molecule[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 413: 366-371. -





 下载:
下载: