Effect of phosphorus on ash fusion characteristics and mineral transformation during co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal
-
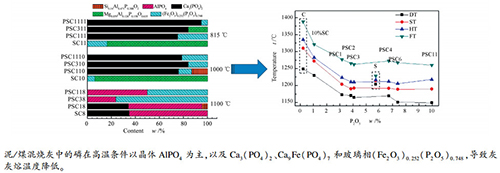
摘要: 采用灰熔点仪、X射线荧光仪(XRF)研究了无机非金属P2O5对城市污水污泥与烟煤的混烧灰熔融特性的影响,利用X射线衍射仪(XRD)、X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)研究在各混烧温度下灰中含磷矿物在晶体和非晶体间的演变。结果表明,对于Al2O3含量较多且熔点较高的灰样,磷含量的增加可显著降低其灰熔点,P2O5含量在0-4%时影响最大,使其灰熔点降低126℃;但对碱性含量高的灰样的影响较小。低温灰中主要以磷酸铝(AlPO4)晶体为主,温度升高后,与硬石膏(CaSO4)等含钙矿物和赤铁矿(Fe2O3)反应生成晶体Ca3(PO4)2和玻璃相(Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748,磷含量增加可使灰中玻璃相(Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748增加,是磷降低灰熔点的主要原因。Abstract: The influence of inorganic phosphorus on ash fusion characteristics of sewage sludge and coal were investigated by ash fusion temperature (AFT) detector and X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and the transformation of containing phosphate minerals of blended ashes with different temperatures between crystal and amorphous were explored using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). For the ash sample with high contents of Al2O3, which has higher AFT, raising content of phosphorus significantly results in a reduced ash fusion point, in particular it is lowered by 126℃ at 0-4% P2O5 content. But it has little effect on ash with high alkaline content. Aluminum phosphate (AlPO4) crystals is the major phosphor containing minerals in low temperature ashes, witch react with calcium minerals (CaSO4) and hematite (Fe2O3) to form Ca3(PO4)2 crystal and (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase along with increasing temperature. Meanwhile, (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 in glass phase increases with an increase in phosphorus content, which may be the primary cause of AFT decreasing.
-
Key words:
- ash fusion temperature /
- inorganic phosphorus /
- coal /
- sewage sludge
-
图 2 PSC样品的灰成分与文献数据的比较
Figure 2 Comparison of chemical composition of PSC ashes with those in literatures
(a): content of Al2O3, SiO2, Fe2O3; (b): content of CaO, MgO, Na2O, K2O, TiO2, SO3 (A): SC and SS, data from literatures; (B): PSC, data from literatures ---: trend line of mineral content change
图 3 添加磷的SC混合灰在各温度下的XRD谱图
A:硬石膏-Anhydrite (CaSO4); Ak:钙镁黄长石-Akermanite(Ca2MgSi2O7); B:钙长石-Anorthite, ordered (CaO ·Al2O3 ·2SiO2); C:磷酸钙-Calcium Phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2); F:铁橄榄石-Fayalite(2FeO ·SiO2); G:钙黄长石-Gehlenite (2CaO ·Al2O3 ·SiO2); H:赤铁矿-Hematite(Fe2O3); He:铁尖晶石-Hercynite, syn(FeO ·Al2O3); I:磷酸铁钙-Calcium Iron Phosphate(Ca9Fe(PO4)7); M:莫来石-Aluminum Silicate(2Al2O3 ·SiO2); Ma:磁铁矿-Magnetite (Fe3O4); P:磷酸铝-Aluminum Phosphate(AlPO4); Q:石英-Quartz (SiO2)
Figure 3 XRD patterns of ashes added with phosphorus at different temperatures
(a):SC(P2O5=1.04%); (b):PSC1(P2O5=3.15%); (c):PSC3(P2O5=4.06%); (d): PSC11(P2O5=9.96%)
表 1 污泥和煤的工业分析和灰成分分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis and ash composition analysis of coal and sludge
Sample Ultimate analysis wad /% Content of the chemical composition wd /% M A V FC Si Al Ti Fe Ca Mg K Na S P C 9.08 32.05 23.97 34.90 58.66 19.88 1.51 9.22 2.50 1.79 3.45 1.09 1.36 0.20 SS 4.87 49.79 43.89 1.45 32.16 10.22 0.97 10.03 23.14 3.61 2.23 0.68 9.80 5.80 表 2 实验工况表
Table 2 Conditions of experiments
Additive contents of P2O5 0 1% 2% 3% 4% 6% 9% 11% 815 ℃ SC8 PSC18 PSC28 PSC38 PSC48 PSC68 PSC98 PSC118 1000 ℃ SC10 PSC110 - PSC310 - - - PSC1110 1100 ℃ SC11 PSC111 - PSC311 - - - PSC1111 表 3 各样品815 ℃下灰的化学组成
Table 3 Chemical composition of ash samples
Sample Composition w/% SiO2 Al2O3 TiO2 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O SO3 P2O5 SC8 54.10 18.38 1.48 9.65 5.72 2.03 3.26 1.06 2.69 1.04 PSC18 53.85 18.23 1.44 9.20 5.59 1.96 3.14 0.78 1.88 3.15 PSC28 53.46 18.17 1.46 9.19 5.59 1.96 3.14 0.78 1.82 3.83 PSC38 53.40 17.84 1.45 9.22 5.70 2.05 3.12 0.79 1.81 4.06 PSC48 51.80 17.44 1.43 9.08 5.62 1.94 3.10 0.75 1.59 6.70 PSC68 51.37 17.22 1.43 9.18 5.72 1.99 3.05 0.69 1.42 7.38 PSC118 45.99 15.77 1.24 8.25 4.95 1.75 2.71 0.64 1.04 9.96 表 4 添加磷的SC混合灰各温度下的XRD晶相
Table 4 Minerals identified by XRD in ashes obtained at 815, 1000 and 1100 ℃
Sample 815 ℃ 1000 ℃ 1100 ℃ (a)SC Quartz,Hematite,Anhydrite,Anorthite,minute quantities of Aluminum Phosphate Quartz,Anorthite, Gehlenite, Akermanite, Hercynite Quartz, Anorthite, Gehlenite, Akermanite, Hercynite, Aluminum Silicate (b)PSC1 Quartz,Hematite,Anhydrite,Anorthite,Aluminum Phosphate,Calcium Phosphate Quartz, Anorthite, Gehlenite, Akermanite, Hercynite, Calcium Phosphate, Calcium Iron Phosphate Quartz, Anorthite, Gehlenite, Akermanite, Hercynite, Calcium Phosphate, Calcium Iron Phosphate (c)PSC3 Quartz,Hematite,Anhydrite,Anorthite,Aluminum Phosphate,Calcium Phosphate Quartz,Anorthite, Gehlenite, Akermanite, Hercynite, Calcium Phosphate, Calcium Iron Phosphate Quartz, Anorthite, Gehlenite, Fayalite, Akermanite, Calcium Phosphate, Calcium Iron Phosphate (d)PSC11 Quartz,Hematite,Anhydrite,Anorthite,Aluminum Phosphate,Calcium Phosphate,Calcium Iron Phosphate Quartz, Anorthite, Gehlenite, Akermanite, Hercynite, Calcium Phosphate, Calcium Iron Phosphate Quartz, Akermanite, Calcium Iron Phosphate 表 5 添加磷的泥/煤混烧灰的P 2p结合能峰位和半峰宽
Table 5 The binding energies and peak widths at half peak height for blended ashes
Sample 815 ℃ 1000 ℃ 1100 ℃ EB/eV FWHM EB/eV FWHM EB/eV FWHM SC 135.42 0.07 133.75 0.11 132.71 0.05 PSC1 133.72 0.24 133.71 0.12 133.22 0.44 PSC3 135.18 0.27 134.78 0.23 133.95 0.05 PSC11 134.22 2.28 133.83 1.45 133.53 0.05 表 6 添加磷的SC泥/煤混样中P 2p的XPS分峰参数
Table 6 Results of the curve fitting procedure with P 2p
Sample number Chemical formula Classification 2p binding energy E/eV Half-peak width (FWHM)E/eV Ratio of the peak area /% Atom content w/% (a) SC8 1. Ca3(PO4)2 alkaline earth 132.4 34.70 0.23 2. AlPO4 phosphates 2.3 phosphates 133.9 3.493 65.30 0.44 (b) SC10 1. (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 0.763 5.98 0.05 2. Mg0.059Al0.126P0.158O0.635 alkaline earth 133.9 2.5 94.02 0.73 phosphates (c) SC11 1. (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 1.54 16.33 0.07 2. Mg0.059Al0.126P0.158O0.635 alkaline earth 133.9 2.5 83.67 0.36 phosphates (d) PSC18 1.Si0.14Al0.471P0.388O2 aluminosilicophos phate 135.3 0.53 4.43 0.06 2.AlPO4 phosphates phosphates 133.9 3.32 61.43 0.85 3.Ca3(PO4)2 alkaline earth phosphates 133.4 2.28 34.14 0.47 (e) PSC110 1.Si0.14Al0.471P0.388O2 aluminosilicophos phate 135.1 1.41 12.99 0.05 2.Ca3(PO4)2 alkaline earth phosphates 133.4 2.30 75.78 0.31 3. (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 2.00 11.23 0.05 (f) PSC111 1.(Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 1.62 24.88 0.37 2.Ca3(PO4)2 alkaline earth phosphates 133.4 2.30 75.12 1.11 (g)PSC38 1. AlPO4 phosphates 133.9 2.64 23.61 0.55 2. (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 3.61 76.39 1.76 (h) PSC310 1. Ca3(PO4)2 alkaline earth phosphates 133.8 2.46 46.78 0.74 2. AlPO4 phosphates 133.9 1.28 29.45 0.47 3. (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 1.15 23.77 0.38 (i) PSC311 1. Ca3(PO4)2 phosphates 133.8 1.602 84.00 0.77 2. Mg0.059Al0.126P0.158O0.635 alkaline earth phosphates 133.9 2.5 16.00 0.15 (j)PSC118 1. (Fe2O3)0.372(P2O5)0.638 phosphates 134.7 2.18 50.33 4.31 2. AlPO4 phosphates 133.9 2.20 49.67 4.26 (k) PSC1110 1. (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 2.761 21.25 0.62 2. Ca3(PO4)2 alkaline earth phosphates 133.8 2.327 78.75 2.32 (l) PSC1111 1. (Fe2O3)0.252(P2O5)0.748 glass phase 135.3 0.66 5.04 0.14 2. Ca3(PO4)2 alkaline earth phosphates 133.8 2.38 94.96 2.73 -
[1] WANG K, ZHENG Y, ZHU X, BREWER C E, BROWN R C. Ex-situ catalytic pyrolysis of wastewater sewage sludge-a micro-pyrolysis study[J]. Biotechnol Technol, 2017, 232:229-234. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3f0519a32a7b61d888d0bb09d87928fe [2] ZHANG Q G, HU J J, LEE DUU-JONG, CHANG YINGJU, LEE YU-JEN. Sludge treatment:Current research trends[J]. Biotechnol Technol, 2017, 243:1159-1172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ027225986/ [3] 魏砾宏, 马婷婷, 杨天华, 李润东.污泥/煤混烧灰的结渣特性及矿物质演变规律研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(18):4697-4702. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGDC201518016.htmWEI Li-hong, MA Ting-ting, YANG Tian-hua, LI Run-dong. Slagging characteristics and minerals conversion of co-firing Ash of coal and sludge at high temperature[J]. Proc CSEE, 2015, 35(18):4697-4702. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGDC201518016.htm [4] ZHANG Q, LIU H F, QIAN Y P, XU M H, LI W F, XU J L. The influence of phosphorus on ash fusion temperature of sludge and coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 110(41):218-226. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=441e84ba85607837b27a7e76dd1f98bb [5] LI W D, LI M, LI W F, LIU H F. Study on the ash fusion temperatures of coal and sewage sludge mixtures[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(7):1566-1572. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.08.039 [6] 李明, 李伟东, 李伟锋, 刘海峰.污泥对神府煤灰熔点的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2009, 37(4):416-420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.04.006LI Ming, LI Wei-dong, LI Wei-feng, LIU Hai-feng. Influence of sewage sludge addition on Shenfu coal ash fusion temperatures[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2009, 37(4):416-420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.04.006 [7] XU H, ZHANG H, SHAO L, HE P. Fraction distributions of phosphorus in sewage sludge and sludge ash[J]. Waste Biomass Valor, 2012, 3(3):355-361. doi: 10.1007/s12649-011-9103-5 [8] FOLGUERAS M B, ALONSO M, FOLGUERAS J R. Modification of lignite ash fusion temperatures by the addition of different types of sewage sludge[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 137(131):348-355. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b242b25fb36470d66c986a9a9da45d4e [9] CUI H, NINOMIYA Y, MASUI M, MIZUKOSHI H, SAKANO T, KANAOKA C. Fundamental behaviors in combustion of raw sewage sludge[J]. Energy Fuels, 2005, 20(1):77-83. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036638813810_e4ab.html [10] ZHANG L, ITO M, SATO A, NINOMIYA Y, SAKANO T, KANAOKA C, MASUI M. Combustibility of dried sewage sludge and its mineral transformation at different oxygen content in drop tube furnace[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2004, 85(8/10):983-1011. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a81998d624b865e17c4d6ca1d01190c1 [11] OHBUCHI A, SAKAMOTO J, KITANO M, NAKAMURA T. X-ray fluorescence analysis of sludge ash from sewage disposal plant[J]. X-Ray Spectr, 2008, 37(5):544-550. doi: 10.1002/xrs.v37:5 [12] VAN DYK J C, BENSON S A, LAUMB M L, WAANDERS B. Coal and coal ash characteristics to understand mineral transformations and slag formation[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(6):1057-1063. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.11.034 [13] TOMASZ K, MARCO M, MICHAEL I, WEBER R. Investigation of ash deposit formation during co-firing of coal with sewage sludge, saw-dust and refuse derived fuel[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(12):2824-2837. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.01.024 [14] WANG L, SKJEVRAK G, HUSTAD J E, GRØNLI M G. Sintering characteristics of sewage sludge ashes at elevated temperatures[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2012, 96:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.12.022 [15] FOLGUERAS M, DÍAZ R, XIBERTA J, GARCÍA M, PIS J. Influence of sewage sludge addition on coal ash fusion temperatures[J]. Energy Fuels, 2005, 19(6):2562-2570. doi: 10.1021/ef058005a [16] 魏砾宏, 马婷婷, 李润东, 杨天华, 李延吉, 文丽娜.灰中酸性成分对灰熔融温度的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 10(24):1205-1211. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18504.shtmlWEI Li-hong, MA Ting-ting, LI Run-dong, YANG Tian-hua, LI Yan-ji, WEN Li-na. Effect of acidic compositions on ash fusion temperatures[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 10(24):1205-1211. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18504.shtml [17] CIESLIK B, KONIECZKA P. A review of phosphorus recovery methods at various steps of wastewater treatment and sewage sludge management. The concept of "no solid waste generation" and analytical methods[J]. J Clean Prod, 2017, 142:1728-1740. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.116 [18] FANG L, LI J, DONATELLO S, CHEESEMAN C R, WANG Q, POON C S, TSANG D C W. Recovery of phosphorus from incinerated sewage sludge ash by combined two-step extraction and selective precipitation[J]. Biochem Eng J, 2018, 348:74-83. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894718307757 [19] VILLEN GUZMAN M, GUEDES P, COUTO N, OTTOSEN L M, RIBEIRO A B, RODRIGUEZ MAROTO J M. Electrodialytic phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash under kinetic control[J]. Electrochim Acta, 2018, 287:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.08.032 [20] 孟详东, 黄群星, 严建华, 郜华萍.磷在污泥热解过程中的迁移转化[J].化工学报, 2018, 69(7):3208-3215. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201807046MENG Xiang-dong, HUANG Qun-xing, YAN Jian-hua, GAO Hua-ping. Migration and transformation of phosphorus during pyrolysis process of sewage sludge[J]. CIESC J, 2018, 69(7):3208-3215. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201807046 [21] NINOMIYA Y, ZHANG L, SAKANO T, KANAOKA C H, MASUI M. Transformation of mineral and emission of particulate matter during co-combustion of coal with sewage sludge[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(6):751-764. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.09.022 [22] 殷立宝, 邓昌亚, 张成, 方庆艳, 徐齐胜, 陈刚.工业、生活污泥与煤混合燃烧的灰熔特性研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(9):1068-1076. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2014.09.007YIN Li-bao, DENG Chang-ya, ZHANG Cheng, FANG Qing-yan, XU Qi-sheng, CHEN Gang. Fusion characteristics in co-combustion of coal with industrial and municipal sludge[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(9):1068-1076. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2014.09.007 -





 下载:
下载: