Sulfur occurrence and transformation during pyrolysis of the flotation fraction from coking coals with high organic sulfur
-
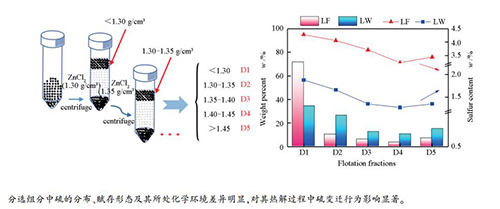
摘要: 利用重介质分选法分别将两种高有机硫炼焦煤分选为密度范围不同的五个组分。采用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)、核磁共振波谱仪(13C NMR)和热解质谱联用技术(Py-MS)探究不同分选组分中硫的赋存形态及其热变迁行为。结果表明,不同分选组分中硫的分布、赋存形态及其所处化学环境存在显著差异。有机硫主要分布在低密度组分(D1)中,且以噻吩硫的形式存在;无机硫作为矿物质组分主要分布于高密度组分(D5)中。随着分选组分密度的增大,其脂肪碳的比例降低,芳香碳的比例增加,D1中硫醇、硫醚等硫化物的含量明显增加。热解过程中脂肪碳结构裂解生成的挥发分促进含硫气体的释放,进而提高了D1的脱硫效率,D5中硫的热变迁行为则主要受煤中矿物质的影响。Abstract: Two coking coals with high organic sulfur were separated into five fractions with different density ranges by heavy medium separation. The occurrences and transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis of different fractions were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), solid state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (13C NMR) and pyrolysis mass spectrometry (Py-MS). The results show that different fractions have significant differences in distribution, occurrence, and chemical environment of sulfur. Organic sulfur is mainly distributed in the low density fraction (D1) and exists in the form of thiophene. Inorganic sulfur such as mineral component is mainly distributed in the high density fraction (D5). As the increase of density of coal fraction, the proportion of aliphatic carbon decreases, and aromatic carbon increases, as well as content of mercaptan and thioether in D1 increases greatly. The volatiles are greatly released since decomposition of aliphatic carbon structure during pyrolysis, which promotes the release of sulfur containing gases, and then improves desulfurization efficiency of D1. However, transformation of sulfur is mainly affected by minerals during D5 pyrolysis.
-
Key words:
- heavy medium separation /
- high sulfur coal /
- occurrence /
- pyrolysis /
- sulfur transformation
-
表 1 煤样的工业分析、元素分析和硫形态分析
Table 1 Proximate, ultimate, and sulfur form analyses of coal samples
Sample Proximate analysis wad /% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Sulfur form wd/% M A V FC C H N S Oa Ss Sp So St LW-RC 1.03 10.27 22.48 66.31 89.19 4.89 1.51 1.94 2.47 0.18 0.16 1.40 1.74 LW-D1 1.01 2.37 25.26 71.36 90.17 5.06 1.57 1.93 1.27 0.04 0.05 1.79 1.88 LW-D2 0.67 5.48 23.52 70.33 90.32 4.88 1.50 1.76 1.54 0.02 0.11 1.53 1.66 LW-D3 0.68 8.99 20.74 69.59 89.71 4.61 1.45 1.48 2.75 0.02 0.14 1.19 1.35 LW-D4 1.04 12.50 19.10 67.36 89.64 4.66 1.43 1.46 2.81 0.07 0.11 1.09 1.27 LW-D5 1.09 30.18 16.09 52.64 84.75 4.82 1.37 1.95 7.11 0.14 0.45 0.76 1.35 LF-RC 0.51 7.34 30.18 61.97 85.60 5.07 1.35 4.53 3.45 0.04 0.28 3.87 4.19 LF-D1 0.67 3.53 30.97 64.83 88.12 3.53 1.32 4.44 2.59 0.03 0.12 4.13 4.28 LF-D2 0.41 6.52 30.04 63.03 87.61 3.92 1.34 4.34 2.79 0.04 0.25 3.77 4.06 LF-D3 0.44 10.65 26.34 62.57 87.93 4.33 1.29 4.05 2.40 0.01 0.34 3.36 3.71 LF-D4 0.48 14.56 22.35 62.61 88.10 4.51 1.32 3.79 2.28 0.04 0.42 2.77 3.23 LF-D5 0.61 33.93 18.66 46.80 85.79 4.98 1.37 5.22 2.64 0.02 1.61 1.81 3.44 note: ad: air dried basis; d: dried basis; daf: dried and ash-free basis; Ss: sulfate sulfur; Sp: pyritic sulfur; So: organic sulfur; St: total sulfur; a: by difference 表 2 13C NMR中不同类型碳对应的化学位移
Table 2 Chemical shift for different structural carbons in solid-state 13C NMR spectra
Assignment Chemical shift δ Characters Aliphatic methyl 14-22 fal3 Aromatic methyl 22-26 fala Methylene 26-37 fal2 Quaternery sp3 C 37-50 fal1, fal* Oxygen aliphatic carbon 50-95 falO Protonated aromatic carbon 95-129 faH Aromatic bridgehead carbon 129-137 faB Aliphatic substituted aromatic carbon 137-149 faS Oxygen aromatic carbon 149-164 faO Carboxyl 164-190 Quinone and carbonyl carbon 190-220 faCC 表 3 13C NMR波谱图拟合
Table 3 Curves-fitting results of 13C NMR spectra of raw coal and flotation fractions
Sample /% CH2/CH3 f3al faal f2al f1al+f*al fOal fHa fBa fSa fOa fCC1a fal fa LW-RC 5.54 5.20 8.43 1.31 6.65 1.25 56.04 7.70 4.19 3.34 20.48 69.18 0.79 LW-D1 2.12 5.54 10.83 3.06 4.57 0.92 55.82 8.54 4.67 3.94 21.54 69.94 1.41 LW-D4 5.20 4.73 7.99 2.87 3.13 1.85 59.15 8.26 4.47 3.34 20.79 72.74 0.80 LW-D5 1.59 4.21 4.88 1.03 12.63 0.83 61.27 7.06 5.27 1.23 11.71 74.43 0.84 LF-RC 4.09 3.29 1.10 16.11 3.26 8.44 36.24 13.48 1.99 12.00 24.59 60.15 0.15 LF-D1 3.74 3.98 1.91 18.62 2.82 8.68 36.77 16.01 1.15 6.33 28.25 62.61 0.38 LF-D4 1.76 8.21 1.94 14.18 3.33 12.2 40.41 14.20 0.89 2.89 26.09 67.70 0.19 LF-D5 4.67 3.20 0.93 13.32 3.61 9.87 43.49 15.87 0.59 4.42 22.12 69.82 0.12 表 4 原煤与分选组分的半焦产率及脱硫率
Table 4 Char yield and desulfurization rate of raw coal and flotation fractions
Sample Char yield wd/% Desulfurization rate η/% LW-RC 77.44 32.33 LW-D1 75.51 36.28 LW-D2 77.45 36.07 LW-D3 80.00 34.71 LW-D4 81.40 29.84 LW-D5 82.33 10.85 LF-RC 71.79 40.12 LF-D1 70.82 41.59 LF-D2 72.42 40.84 LF-D3 75.40 39.88 LF-D4 77.69 39.67 LF-D5 80.62 42.38 -
[1] 武晨晓.东庞煤矿高硫煤配煤炼焦的研究与应用[J].洁净煤技术, 2013, 19(1):61-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jjmjs201301016WU Chen-xiao. Preparation of blended raw high-sulphur coal in Dongpang coal mine[J]. Clean Coal Technol, 2013, 19(1):61-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jjmjs201301016 [2] 王健, 余诚桓, 吉武平.配高硫煤炼焦的研究[J].燃料与化工, 2011, 42(5):26-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2011.05.010WANG Jian, YU Cheng-heng, JI Wu-pin. Preparation of blending coking high sulfur coal[J]. Fuel Chem Process, 2011, 42(5):26-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2011.05.010 [3] IBARRA J V, PALACIOS J M, MOLINER R, BONET A J. Evidence of reciprocal organic matter-pyrite interactions affecting sulfur removal during coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 1994, 73(7):1046-1050. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(94)90235-6 [4] CALKINS W H. The chemical forms of sulfur in coal:A review[J]. Fuel, 1994, 73(4):475-484. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(94)90028-0 [5] GRYGLEWICA G, WILK P, YPERMAN J, FRANCO D V, MAES I I, MUILENS J, POUCKE L C V. Interaction of the organic matrix with pyrite during pyrolysis of a high-sulfur bituminous coal[J]. Fuel, 1996, 75(13):1499-1504. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(96)00141-X [6] ZHANG D K, YANI S. Sulphur transformation during pyrolysis of an Australian lignite[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2011, 33(2):1747-1753. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2010.07.074 [7] CHEN H K, LI B Q, YANG J L, ZHANG B J. Transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis and hydroprolysis of coal[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77:487-493. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(97)00275-5 [8] WANG M J, LIU L J, WANG J C, CHANG L P, WANG H, HU Y F. Sulfur K-edge XANES study of sulfur transformation during pyrolysis of four coals with different ranks[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 131:262-269. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.10.038 [9] WANG M J, JIA T H, WANG J C, HU Y F, LIU F R, WANG H, CHANG L P. Changes of sulfur forms in coal after tetrachloroethylene extraction and theirs transformations during pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2016, 186:726-733. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.09.007 [10] 陈皓侃, 李保庆, 张碧江.矿物质对煤热解和加氢热解含硫气体生成的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 1999, 27(S1):5-10. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10141-2006021579.htmCHEN Hao-kan, LI Bao-qing, ZHANG Bi-jiang. effects of mineral matter on evolution of sulfur - containing gases in pyrolysis and hydropyrolysis[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1999, 27(S1):5-10. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10141-2006021579.htm [11] 周仕学, 聂西文, 王荣春, 刘泽常.高硫强粘结性煤与生物质共热解的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2000, 28(4):294-297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2000.04.002ZHOU Shi-xue, NIE Xi-wen, WANG Ron-chun, LIU Ze-chang. Study on co-pyrolysis of high sulfur and strongly caking coal with biomass[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2000, 28(4):294-297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2000.04.002 [12] 康西栋, 胡善亭, 潘治贵, 潘银苗, 王凌志.煤的显微煤岩学特征与焦炭强度的关系[J].现代地质, 1997, 11(2):164-169. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ702.005.htmKANG Xi-dong, HU Shan-ting, PANG Zhi-gui, PAN Yin-miao, WANG Ling-zhi. Study on relationship between microscopic coal petrology and coke intensity[J]. Geosci, 1997, 11(2):164-169. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ702.005.htm [13] 周师庸, 赵俊国.炼焦煤性质与高炉焦炭质量[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2005.ZHOU Shi-yon, ZHAO Jun-guo. Properties of Coking Coal and Quality of Coke for the Blast Furnace[M]. Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005. [14] ZHANG L, LIU W L, MEN D P. Preparation and coking properties of coal maceral concentrates[J]. Int J Min Sci Technol, 2014, 24(1):93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2013.12.016 [15] TSENG B H, BUCKENTIN M, HSIEH K C. Organic sulphur in coal macerals[J]. Fuel, 1986, 5(3):385-389. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5d78ea62ef9053cfd863459c5ef4a910&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [16] DEMIR I, HARVEY R D. Variation of organic sulfur in macerals of selected Illinois Basin coals[J]. Org Geochem, 1991, 7(4):525-533. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=04019c85b2feee1ef734fac46929a549&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] 雷加锦, 任德贻, 韩德馨, 唐修义.不同沉积环境成因煤显微组分的有机硫分布[J].煤田地质与勘探, 1995, 3(5):14-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500724050LEI Jia-jin, REN De-yi, HAN De-xin, TANG Xiu-yi. The distribution of organic sulfur in macerals of coals accumulated in different environments[J]. Coal Geol Explor, 1995, 3(5):14-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500724050 [18] 孙庆雷, 李文, 陈皓侃, 李宝庆.煤显微组分热解过程中含硫气体逸出特性[J].中国矿业大学学报, 2005, 4(4):518-522. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2005.04.024SUN Qing-lei, LI Wen, CHEN Hao-kan, LI Bao-qing. Characteristic of sulfur-containing gases released from the pyrolysis of coal macerals[J]. J China Univ Min Technol, 2005, 4(4):518-522. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2005.04.024 [19] 陈鹏.用XPS研究兖州煤各显微组分中有机硫存在形态[J].燃料化学学报, 1997, 5(3):238-241. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLHX703.008.htmCHEN Peng. Application of XPS in study forms of organic sulfur in macerals of Yanzhou coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1997, 5(3):238-241. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLHX703.008.htm [20] LI C L, YANG S S, CHEN X J, LIN X C, WANG Y G. The characteristic of Shengli brown coal fractions from heavy medium separation and its influence on CO2 gasification[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2017, 155:232-237. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.06.041 [21] LIN X C, LUO M, LI S Y, YANG Y P, CHEN X J, B, WANG Y G. The evolutionary route of coal matrix during integrated cascade pyrolysis of a typical low-rank coal[J]. Appl Energy, 2017, 199:335-346. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.05.040 [22] QUEROL X, CABRERA L, PICKEL W, LÓPEZ-SOLER A, HAGEMANN H W, FERNÁNDEZ-TURIEL J L. Geological controls on the coal quality of the Mequinenza subbituminous coal deposit, northeast Spain[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 1996, 29(1):67-91. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=595ef45a79633ac092326ba898393744&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [23] 葛涛, 蔡川川.不同密度炼焦煤中有机硫的XPS研究[J].安徽理工大学学报, 2015, 35(3):14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1098.2015.03.005GE Tao, CAI Chuan-chuan. The XPS analysis of different density level organic sulfur in coking coal[J]. J Anhui Univ Sci Technol, 2015, 35(3):14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1098.2015.03.005 [24] 么秋香, 杜美利, 王水利, 刘静, 杨建利.高硫煤中硫的赋存形态及其可选性评价[J].煤炭转化, 2013, 36(1):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2013.01.006YAO Qiu-xiang, DU Mei-li, WANG Shui-li, LIU Jing, YANG Jian-li. Modes of occurrence and washability evaluation of sulfur in high sulfur coal[J]. Coal Convers, 2013, 36(1):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2013.01.006 [25] LIU F R, LI W, CHEN H K, LI B Q. Uneven distribution of sulfurs and their transformation during coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(3):360-366. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.07.021 [26] KOZLOWSKI M. XPS Study of reductively and non-reductively modified coals[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(3):259-265. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.08.004 [27] 马玲玲, 秦志宏, 张露, 刘旭, 陈航.煤有机硫分析中XPS分峰拟合方法及参数设置[J].燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(3):277-283. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18367.shtmlMA Ling-ling, QIN Zhi-hong, ZHANG Lu, LIU Xu, CHEN Hang. Peak fitting methods and parameter settings in XPS analysis for organic sulfur in coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(3):277-283. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18367.shtml [28] HOU J L, MA Y, LI S Y, SHI J, HE L, LI J. Transformation of sulfur and nitrogen during Shenmu coal pyrolysis[J] Fuel, 2018, 231:134-144. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.05.046 [29] LIU P, LE J W, WANG L L, PAN T Y, LU X L, ZHANG D X. Relevance of carbon structure to formation of tar and liquid alkane during coal pyrolysis[J]. Appl Energy, 2016, 183:470-477. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.166 [30] WANG M J, HU Y F, WANG J C, CHANG L P, WANG H. Transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis of inertinite-rich coals and correlation with their characteristics[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2013, 104:585-592. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.05.010 -





 下载:
下载: