Effect of acidity on the catalytic performance of ZSM-5 zeolites in the synthesis of trioxane from formaldehyde
-
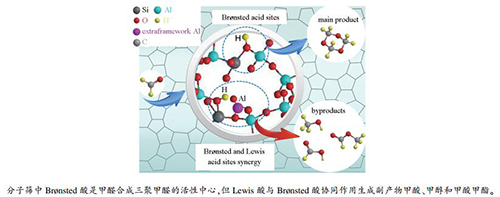
摘要: ZSM-5分子筛是合成三聚甲醛的有效催化剂。本工作通过XRF、XRD、SEM、NH3-TPD、Py-FTIR和27Al MAS NMR等手段对一系列不同SiO2/Al2O3物质的量比的ZSM-5分子筛催化剂进行了表征,研究了ZSM-5分子筛中Brønsted酸中心和Lewis酸中心对其甲醛合成三聚甲醛催化性能的影响。结果表明,SiO2/Al2O3物质的量比为250的ZSM-5分子筛具有合适的Brønsted酸中心用于催化甲醛缩聚为三聚甲醛的反应,同时其Lewis酸中心量极少,可有效抑制Cannizzaro或Tishchenko等副反应,提高三聚甲醛的选择性,因而具有最佳的合成三聚甲醛催化性能。寿命实验评价结果显示,SiO2/Al2O3物质的量比为250的ZSM-5分子筛具有良好的催化稳定性,单程寿命长达114 h,并且可通过550℃焙烧再生恢复其催化活性。Abstract: ZSM-5 zeolite is considered as an effective catalyst in the synthesis of trioxane from formaldehyde. In this work, a series of ZSM-5 zeolites with different SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratios were used in the synthesis of trioxane from formaldehyde; through characterization by XRF, XRD, SEM, NH3-TPD, Py-FTIR and 27Al MAS NMR, the effect of acidity including the Brønsted and Lewis acid sites on the catalytic performance of ZSM-5 zeolites in the trioxane synthesis was investigated. The results indicate that the ZSM-5-250 zeolite with a SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratio of 250 exhibits excellent catalytic performance in the synthesis of trioxane. The ZSM-5-250 zeolite owns sufficient amount of Brønsted acid sites which are active for the synthesis of formaldehyde to trioxane; meanwhile, it has few Lewis acid sites and can then effectively inhibit various side-reactions like the Cannizzaro or Tishchenko reactions. Moreover, the ZSM-5-250 zeolite displays high stability with a single-pass lifetime of 114 h and can be regenerated easily through calcination at 550℃.
-
Key words:
- trioxane /
- ZSM-5 zeolite /
- formaldehyde /
- acidity /
- Brønsted acid /
- Lewis acid
-
Table 1 Al content and textural properties of various ZSM-5 zeolites and γ-Al2O3 and resin
Catalyst Al content /(mmol·g-1) ABET /(m2·g-1) vtotal /(cm3·g-1) d /nm Resin - 13 0.130 19.27 γ-Al2O3 - 206 0.540 5.23 ZSM-5-30 0.870 332 0.233 0.569 ZSM-5-100 0.295 351 0.244 0.558 ZSM-5-180 0.168 339 0.227 0.525 ZSM-5-250 0.126 339 0.230 0.559 ZSM-5-400 0.084 342 0.238 0.560 0.1Al-ZSM-5-100 0.306 347 0.241 0.553 0.3Al-ZSM-5-100 0.314 340 0.238 0.550 0.5Al-ZSM-5-100 0.323 338 0.237 0.551 note: Al content was measured by XRF, the surface area (ABET) was determined from nitrogen sorption isotherms by BET method; the total pore volume (vtotal) was obtained at a relative pressure of 0.99; the average pore diameter (D) was derived by using BJH method for resin and γ-Al2O3 and using t-plot method for the ZSM-5 zeolites Table 2 Acidity and Al content of various ZSM-5 zeolites and γ-Al2O3 and resin
Catalyst Acidity by NH3-TPD
/(mmol·g-1)Acidity by Py-FTIR /(mmol·g-1) Al content /% Brønsted Lewis AlF AlEF Resin 1.320 - - - - γ-Al2O3 0.165 0.000 0.027 - ZSM-5-30 0.784 0.492 0.038 93.1 6.9 ZSM-5-100 0.296 0.178 0.034 96.2 3.8 ZSM-5-180 0.187 0.092 0.016 97.5 2.5 ZSM-5-250 0.161 0.049 0.009 97.7 2.3 ZSM-5-400 0.126 0.027 0.005 97.8 2.2 0.1Al-ZSM-5-100 0.286 0.174 0.042 93.0 7.0 0.3Al-ZSM-5-100 0.278 0.163 0.048 92.4 7.6 0.5Al-ZSM-5-100 0.251 0.150 0.057 91.9 8.2 note: the acidity of resin was determined by the acid-base titration method, the contents of framework Al (AlF) and extra-framework (AlEF) were determined by 27Al MAS NMR Table 3 Textural properties of the ZSM-5-250 catalyst before and after reaction test
Catalyst ABET /
(m2·g-1)vtotal /
(cm3·g-1)d /nm ZSM-5-250, fresh 339 0.230 0.559 ZSM-5-250-D, used 310 0.201 0.509 ZSM-5-250-R, regenerated 342 0.238 0.560 note: the surface area (ABET) was determined from nitrogen sorption isotherms by BET method; the total pore volume (vtotal) was obtained at a relative pressure of 0.99; the average pore diameter (d) was derived by using the t-plot method Table 4 Acidity of the ZSM-5-250 catalyst before and after reaction test
Catalyst Acidity by NH3-TPD /
(mmol·g-1)Acidity Py-FTIR
/(mmol·g-1)Brønsted Lewis ZSM-5-250, fresh 0.161 0.049 0.009 ZSM-5-250-D, used 0.105 0.021 0.003 ZSM-5-250-R, regenerated 0.159 0.050 0.008 -
[1] MU Y B, JIA M C, JIANG W, WAN X B. A novel branched polyoxymethylene synthesized by cationic copolymerization of 1, 3, 5-Trioxane with 3-(Alkoxymethyl)-3-ethyloxetane[J]. Macromol Chem Phys, 2013, 214(23):2752-2760. doi: 10.1002/macp.201300473 [2] HOFFMANN M, BIZZARRI C, LEITNER W, MULLER T E. Reaction pathways at the initial steps of trioxane polymerisation[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2018, 8(21):5594-5603. doi: 10.1039/C8CY01691G [3] WU Q, LI W, WANG M, HAO Y, CHU T, SHANG J, LI H, ZHAO Y, JIAO Q. Synthesis of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers from methylal and trioxane catalyzed by bronsted acid ionic liquids with different alkyl groups[J]. Rsc Adv, 2015, 5(71):57968-57974. doi: 10.1039/C5RA08360E [4] BARANOWSKI C J, BAHMANPOUR A M, KROCHER O. Catalytic synthesis of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (OME):A review[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2017, 217:407-420. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.06.007 [5] ROESSLER D G-U S-S V. Procédé de préparation du trioxanne: FR1374872[P]. 1964-10-09. [6] BALASHOV A L, KRASNOV V L, DANOV S M, CHERNOV A Y, SULIMOV A V. Formation of cyclic oligomers in concentrated aqueous solutions of formaldehyde[J]. J Struct Chem, 2001, 42(3):398-403. doi: 10.1023/A:1012408904389 [7] GRUTZNER T, HASSE H. Solubility of formaldehyde and trioxane in aqueous solutions[J]. J Chem Eng Data, 2004, 49(3):642-646. doi: 10.1021/je030243h [8] MAIWALD M, GRUTZNER T, STROFER E, HASSE H. Quantitative NMR spectroscopy of complex technical mixtures using a virtual reference:Chemical equilibria and reaction kinetics of formaldehyde-water-1, 3, 5-trioxane[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2006, 385(5):910-917. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0477-3 [9] GRUTZNER T, HASSE H, LANG N, SIEGERT M, STROFER E. Development of a new industrial process for trioxane production[J]. Chem Eng Sci, 2007, 62(18/20):5613-5620. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c8116edc13beb3c962f260091caa44b2 [10] MASAMOTO J, HAMANAKA K, YOSHIDA K, NAGAHARA H, KAGAWA K, IWAISAKO T, KOMAKI H. Synthesis of trioxane using heteropolyacids as catalyst[J]. Angew Chem-Int Ed, 2000, 39(12):2102-2104. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20000616)39:12<2102::AID-ANIE2102>3.0.CO;2-E [11] XIA C, TANG Z, CHEN J, ZHANG X, LI Z, GUO E. Method of synthesizing trioxymethylene from formaldehyde by the catalytic action of an ionic liquid: US7244854B2[P]. 2007-07-17. [12] ZHAO Y M, HU Y F, QI J G, MA W T. Bronsted-acidic ionic liquids as catalysts for synthesizing trioxane[J]. Chin J Chem Eng, 2016, 24(10):1392-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2016.05.001 [13] ARIAS-UGARTE R, WEKESA F S, FINDLATER M. Selective aldol condensation or cyclotrimerization reactions catalyzed by FeCl3[J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 2015, 56(19):2406-2411. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.03.040 [14] KIEDIK M, KRUEGER A. Synthesis of trioxane in presence of sulfuric acid and ion-exchange resins as catalyst-comparisons of methods[J]. Przem Chem, 1990, 69(12):539-540. [15] DINTZNER M R, MONDJINOU Y A, PILEGGI D J. Montmorillonite clay-catalyzed cyclotrimerization and oxidation of aliphatic aldehydes[J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 2010, 51(5):826-827. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.12.009 [16] LEE S O, KITCHIN S J, HARRIS K D M, SANKAR G, DUGAL M, THOMAS J M. Acid-catalyzed trimerization of acetaldehyde:A highly selective and reversible transformation at ambient temperature in a zeolitic solid[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2002, 106(6):1322-1326. doi: 10.1021/jp012440y [17] MORI H, YAMAZAKI T, OZAWA S, OGINO Y. Liquid-phase reaction of acetaldehyde over various ZSM-5 zeolites[J]. Bull Chem Soc Jpn, 1993, 66(9):2498-2504. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.66.2498 [18] YE Y, YAO M, CHEN H X Z. Influence of silanol defects of ZSM-5 zeolites on trioxane synthesis from formaldehyde[J]. Catal Lett, 2020, 150(5):1445-1453. doi: 10.1007/s10562-019-03040-x [19] ISHIDA H, AKAGISHI K. The synthetic reaction of trioxane from formalin on the zeolite catalysts[J]. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi, 1996, (3):290-297. doi: 10.1246/nikkashi.1996.290 [20] FU M, YE Y, LEI Q, CHEN H, ZHANG X. Research on the synthetic 1, 3, 5-trioxane over ZSM-5 zeolite[J]. Chin J Synthetic Chem, 2020. [21] RODRIGUEZ-GONZALEZ L, SIMON U. NH3-TPD measurements using a zeolite-based sensor[J]. Meas Sci Technol, 2010, 21(2):7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7d75fb6d8163b3d5a966dc39356c3248 [22] DIEZ V K, APESTEGUIA C R, DI COSIMO J I. Synthesis of ionones on solid Bronsted acid catalysts:Effect of acid site strength on ionone isomer selectivity[J]. Catal Today, 2010, 149(3/4):267-274. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2a11d96941d8d53a28a121efa8e30947&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [23] WU W Q, WEITZ E. Modification of acid sites in ZSM-5 by ion-exchange:An in-situ FT-IR study[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 316:405-415. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.07.194 [24] JIN F, LI Y D. A FT-IR and TPD examination of the distributive properties of acid sites on ZSM-5 zeolite with pyridine as a probe molecule[J]. Catal Today, 2009, 145(1/2):101-107. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092058610800271X [25] ISERNIA L F. FT-IR study of the relation, between extra-framework aluminum species and the adsorbed molecular water, and its effect on the acidity in ZSM-5 steamed zeolite[J]. Mater Res-Ibero-Am J, 2013, 16(4):792-802. [26] RODRIGUEZ-GONZALEZ L, HERMES F, BERTMER M, RODRIGUEZ-CASTELLON E, JIMENEZ-LOPEZ A, SIMON U. The acid properties of H-ZSM-5 as studied by NH3-TPD and 27Al-MAS-NMR spectroscopy[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2007, 328(2):174-182. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2007.06.003 [27] WOOLERY G L, KUEHL G H, TIMKEN H C, CHESTER A W, VARTULI J C. On the nature of framework bronsted and lewis acid sites in ZSM-5[J]. Zeolites, 1997, 19(4):288-296. doi: 10.1016/S0144-2449(97)00086-9 [28] LI S H, HUANG S J, SHEN W L, ZHANG H L, FANG H J, ZHENG A M, LIU S B, DENG F. Probing the spatial proximities among acid sites in dealuminated H-Y zeolite by solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112(37):14486-14494. doi: 10.1021/jp803494n [29] GELBARD G. Organic synthesis by catalysis with ion-exchange resins[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2005, 44(23):8468-8498. doi: 10.1021/ie0580405 [30] BIRDJA Y Y, KOPER M T M. The importance of cannizzaro-type reactions during electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139(5):2030-2034. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b12008 [31] RUSSELL A E, MILLER S P, MORKEN J P. Efficient Lewis acid catalyzed intramolecular cannizzaro reaction[J]. J Org Chem, 2000, 65(24):8381-8383. doi: 10.1021/jo0010734 [32] OESTREICH D, LAUTENSCHUTZ L, ARNOLD U, SAUER J. Reaction kinetics and equilibrium parameters for the production of oxymethylene dimethyl ethers (OME) from methanol and formaldehyde[J]. Chem Eng Sci, 2017, 163:92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2016.12.037 [33] INDU B, ERNST W R, GELBAUM L T. Methanol formic acid esterfication equilibrium in sulfuric acid solutions-influence of sodium salts[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 1993, 32(5):981-985. doi: 10.1021/ie00017a031 [34] MORRIS S A, GUSEV D G. Rethinking the claisen-tishchenko reaction[J]. Angew Chem-Int Ed, 2017, 56(22):6228-6231. doi: 10.1002/anie.201611186 [35] WU J B, ZHU H Q, WU Z W, QIN Z F, YAN L, DU B L, FAN W B, WANG J G. High Si/Al ratio HZSM-5 zeolite:An efficient catalyst for the synthesis of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers from dimethoxymethane and trioxymethylene[J]. Green Chem, 2015, 17(4):2353-2357. doi: 10.1039/C4GC02510E [36] ARROYO S T, GARCIA A H, ALVERO M M, MARTIN J A S. Theoretical study of the neutral hydrolysis of methyl formate via a concerted and stepwise water-assisted mechanism using free-energy curves and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Struct Chem, 2011, 22(4):909-915. doi: 10.1007/s11224-011-9777-0 [37] GLARBORG P, ALZUETA M U, KJAERGAARD K, DAM-JOHANSEN K. Oxidation of formaldehyde and its interaction with nitric oxide in a flow reactor[J]. Combust Flame, 2003, 132(4):629-638. doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(02)00535-7 [38] HOCHGREB S, DRYER F L. A comprehensive study on CH2O oxidation kinetics[J]. Combust Flame, 1992, 91(3/4):257-284. [39] OLM C, VARGA T, VALKO E, CURRAN H J, TURANYI T. Uncertainty quantification of a newly optimized methanol and formaldehyde combustion mechanism[J]. Combust Flame, 2017, 186:45-64. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.07.029 -





 下载:
下载: