Effect of alkali metal deposition on Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for NO reduction by NH3 at low temperature
-
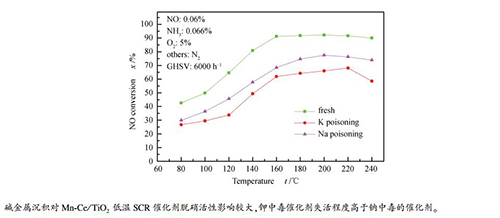
摘要: 采用溶胶凝胶法制备了Mn-Ce/TiO2低温SCR催化剂,考察了碱金属浓度与种类对催化剂活性的影响,探究了不同反应条件下钠盐沉积对活性保留分率的影响,利用SEM、BET、XRD和FT-IR对催化剂碱金属中毒原因进行了分析。结果表明,碱金属毒化后催化剂脱硝活性下降,钾中毒催化剂失活程度高于钠中毒的催化剂,2%钾中毒催化剂在160℃时NO去除率为62.0%,较新鲜催化剂下降29.2%。这主要因为碱金属毒化造成催化剂比表面积明显减小,且催化剂载体锐钛矿型TiO2部分转化为金红石型,BET和SEM表征均说明碱金属沉积堵塞了催化剂表面的微孔。碱金属对Mn-Ce/TiO2催化剂活性保留分率的影响表明,催化剂的颗粒粒径对其活性保留分率影响不大,碱金属含量减小、温度升高,Mn-Ce/TiO2催化剂的活性保留分率增加,Na2SO4和NaCl对Mn-Ce/TiO2催化剂的脱硝活性抑制作用大于KNO3。
-
关键词:
- 低温SCR /
- Mn-Ce/TiO2 /
- 碱金属中毒 /
- 活性保留分率
Abstract: A manganese and cerium oxide catalyst was prepared through sol-gel method. Effects of the concentration and type of alkali metals on performance of the Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalysts were investigated in selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. The cause of the alkali metal poisoning of the catalyst was studied and the influence of sodium salt deposition on the activity retention fraction under different reaction conditions was further studied. The catalysts were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), BET surface area, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), respectively. The results show that alkali metals exhibited an inhibiting effect on the selective catalytic reduction (SCR), and the deactivation rate of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst caused by potassium poisoning was higher than that by sodium poisoning. The NO conversion was decreased from 91.2% to 62.0% at a temperature of 160℃, when the potassium content was 2%. This is mainly because the presence of the alkali metal resulted in a reduction of the specific surface area of the catalyst, and the specific surface area of the potassium poisoning of the catalyst was reduced by 34.2%. The alkali metal poisoning could cause blockage of the micropores on the surface and the transfer from anatase to rutile phase of the catalyst. The effect of alkali metal on the retention fraction of the Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst indicates that the particle size of the catalyst had slight effect on its activity retention fraction. The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) activity of the Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst increased along with the temperature. While the content of alkali metal decreased, the retention rate of active metal increased. The inhibitory effect of Na2SO4 and NaCl on the denitrification activity of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst was more significant than that of NaNO3.-
Key words:
- low temperature SCR /
- Mn-Ce/TiO2 /
- alkali metal poisoning /
- activity retention fraction
-
表 1 催化剂的比表面积、平均孔径和总孔容
Table 1 Specific surface area, average pore size and total pore volume of the catalysts
Catalyst Specific surface area A/(m2·g-1) Average pore size d /nm Total pore volume v /(m3·g-1) Fresh 90.76 17.72 0.76 Na poisoning 65.29 21.05 0.58 K poisoning 59.69 21.78 0.55 -
[1] 郝吉明, 马广大, 王书肖.大气污染控制工程(第三版)[M].北京:高等教育出版社. 2010:378.HAO Ji-ming, MA Guang-da, WANG Shu-xiao. Air Pollution Control Engineering(Third Edition)[M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press, 2010:378. [2] DU X S, YANG G P, CHEN Y R, RAN JY, ZHANG L. The different poisoning behaviors of various alkali metal containing compounds on SCR catalyst[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 392:162-168. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.036 [3] CIMINO S, LISI L, TORTORLLI M. Low temperature SCR on supported MnOx catalysts for marine exhaust gas cleaning:Effect of KCl poisoning[J]. Chem Eng J, 2016, 283:223-230. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.07.033 [4] 陈巳樊.碱金属对钒钛催化剂脱硝行为的影响[D].北京: 北京化工大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10010-1013267106.htmCHEN Yi-fan. Effects of alkali metals on the denitration behavior of vanadium-titanium catalysts[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10010-1013267106.htm [5] 韩斌.碱金属对催化剂脱硝活性的影响及其本征动力学研究[D].北京: 北京化工大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10010-1013267157.htmHAN Bin. Effects of alkali metals on denitrification activity of catalysts and their intrinsic kinetics[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10010-1013267157.htm [6] KLING A, ANDERSSON C, MYRINGER A, ESKILSSON D, JÄRÃS S G. Alkali deactivation of high-dust SCR catalysts used for NOx reduction exposed to flue gas from 100 MW-scale biofuel and peat fired boilers:Influence of flue gas composition[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2007, 69(3/4):240-251. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337306001044 [7] ZHENG Y J, JENSEN A D, JOHNSSON J E. Deactivation of V2O5-WO3-TiO2 SCR catalyst at a biomass-fired combined heat and power plant[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2005, 60(3/4):253-264. [8] JIANG Y, ZHANG Y X, WU W H, GAO X. Kinetic study on potassium poisoning of V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO in flue gas[J]. Proc CSEE, 2014, 34(23):3899-3906. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdjgcxb201423010 [9] CHEN J P, YANG R T. Mechanism of poisoning of the V2O5/TiO2 catalyst for the reduction of NO by NH3[J]. J Catal, 1990, 125(2):411-420. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(90)90314-A [10] 沈伯雄, 熊丽仙, 刘亭, 王静, 田晓娟.纳米负载型V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂碱中毒及再生研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(1):85-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2010.01.016SHEN Bo-xiong, XIONG Li-xian, LIU Ting, WANG Jing, TIAN Xiao-juan. Alkali deactivation and regeneration of nano V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2010, 38(1):85-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2010.01.016 [11] 王舜.活性炭负载二氧化钛催化剂的制备及光电催化性能的研究[D].南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10287-1014006049.htmWANG Shun. Preparation and photoelectrocatalytic performance of activated carbon supported titania catalyst[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10287-1014006049.htm [12] 黄继辉, 童华, 童志权, 张俊峰, 黄妍. H2O和SO2对Mn-Fe/MPS催化剂用于NH3低温还原NO的影响[J].过程工程学报, 2008, 8(16):517-522. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgyj200803018HUANG Ji-hui, TONG Hua, TONG Zhi-quan, ZHANG Jun-feng, HUANG Yan. Effect of H2O and SO2 on Mn-Fe/MPS catalysts for NO reduction by NH3 at low temperature[J]. Chin J Process Eng, 2008, 8(16):517-522. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgyj200803018 [13] CENTENO M A, CARRZOSA I, ODRIOZOIA J A. NO-NH3 coad sorption on vanadia/titania catalysts:Determination of the reduction degree of vanadium[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2001, 29(4):307-314. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00214-9 [14] 郑足红. Mn-V-Ce/TiO2低温催化处理NOx活性及抗毒化性能研究[D].湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10530-2010012438.htmZHENG Zhu-hong. Low temperature catalytic treatment of NOx with Mn-V-Ce/TiO2 and its anti-toxicity performance[D]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10530-2010012438.htm [15] GASIOR M, HABER J, MACHEJ T, CZEPPE T. Mechanism of the reaction NO+NH3 on V5O2 catalysts[J]. J Mol Catal, 1988, 43(3):359-369. doi: 10.1016/0304-5102(88)85147-2 [16] TOPSØE N Y, TOPSØE H, DUMESIC J A. Vanadia/titania catalysts for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of nitric-oxide by ammonia:Ⅰ. Combined temperature-programmed in-situ, ftir and on-line mass-spectroscopy studies[J]. J Catal, 1995, 151(1):226-240. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1995.1024 [17] TOPSØE N Y. Characterization of the nature of surface sites on vanadia-titania catalysts by FTIR[J]. J Catal, 1991, 128(2):499-511. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(91)90307-P [18] ZHENG Y, JENSEN A D, JOHNSSON J E. Deactivation of V2O5-WO3-TiO2 SCR catalyst at a biomass-fired combined heat and power plant[J].Appl Catal B:Environ, 2005, 60(3/4):253-264. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=42d7a4e07ea28dd4a7cd809f85ca684d [19] KRÖCHER O, ELSENER M. Chemical deactivation of V2O5/WO3-TiO2 SCR catalysts by additives and impurities from fuels, lubrication oils and urea solution Ⅰ.Catalytic studies[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2008, 77(3/4):215-2227. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=41b830f008a174fb8cbb66f274c9e417 [20] CHEN L, LI J, GE M. The poisoning effect of alkali metals doping over nano V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Chem Eng J, 2011, 170(2/3):531-537. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=399fd63147e1906cfaa41d3df0ae8a45 [21] 姜烨.钛基SCR催化剂及其钾、铅中毒机理研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1011052213.htmJIANG Ye. Titanium-based SCR catalyst and its mechanism of potassium and lead poisoning[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1011052213.htm -





 下载:
下载: