Study on the mineral transformation and heavy metal distribution during high-silicon coal combustion
-
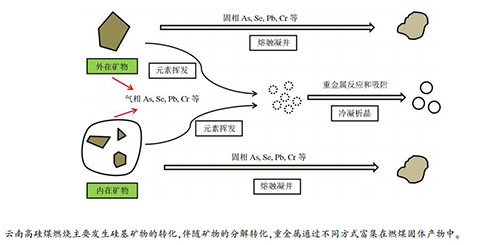
摘要: 选取云南宣威地区高硅煤,对其在燃烧过程中矿物转化特征及重金属分布富集规律进行了研究。高硅煤中的矿物主要由石英、高岭石、黄铁矿和锐钛矿组成。飞灰中莫来石可能来自煤中石英、高岭石的转变,而石英主要来自煤中原始石英组分或由SiO2-Al2O3系统转化形成。分析高硅煤和高硅飞灰中部分重金属的富集特性,发现高硅煤中富集的元素有Cr、Cu和As,电厂ESP各级电场中富集的重金属有Mo元素,而Se元素在高硅煤和飞灰中分别都低于世界煤和飞灰的平均值。放射性元素Th和U含量在细粒径的高硅飞灰中都高于世界煤灰平均值,在ESP的4电场飞灰中富集系数分别为1.51和1.59。Abstract: The high-silicon coal in Xuanwei area of Yunnan is selected to study the transformation behavior of minerals and the distribution and enrichment of heavy metals during the combustion process. The minerals in high-silicon coal are mainly composed of quartz, kaolinite, pyrite and anatase. The mullite in fly ash may come from the transformation of quartz and kaolinite in coal; the quartz in fly ash mainly comes from the original quartz component in coal or is formed by the conversion of SiO2-Al2O3 system. Analyzing the enrichment characteristics of several heavy metals in high-silicon coal and its fly ash, it can be found that Cr, Cu, and As are enriched in the high-silicon coal, and Mo is the heavy metal enriched in the electric fields of the ESP, while Se contents in high-silicon coal and fly ash in China are both lower than the world average level. The contents of radioactive elements of Th and U in the fine-particle high-silicon fly ash are higher than the average of world coal ash, and the enrichment factors in the fly ash in the four electric fields of the ESP are 1.51 and 1.59, respectively.
-
Key words:
- high-silicon coal /
- coal combustion /
- fly ash /
- mineral transformation /
- heavy metals
-
表 1 工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses
Proximate analysis wad/% Ultimate analysis wad/% N C S H M V A FC 1.07 62.44 1.42 2.70 1.70 12.17 28.70 57.43 ad: air-dry base; M: moisture; V: volatile matter; A: ash; FC: fixed carbon 表 2 高温灰的主要元素组成
Table 2 Major elemental composition of high temperature ash
Composition w/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO Na2O SO3 TiO2 P2O5 MnO 54.99 29.87 4.32 3.63 1.12 0.93 3.24 1.71 0.16 0.03 表 3 高硅煤及其高温灰中的矿物含量
Table 3 Mineral contents in the high-silicon coal and its high temperature ash
Sample Content w/% quartz kaolinite pyrite anatase hematite DD high-silicon coal 46 26 20 8 - High temperature ash 66.37 - - - 33.63 表 4 不同粒径的高硅粉煤灰中矿物质的定量
Table 4 Mineral contents of the high-silicon fly ash with different particle sizes
Sample Content w/% quartz mullite Fly ash (unsized) 70.45 29.55 Fly ash (38.5-74 μm) 68.31 31.69 Fly ash (< 30.8 μm) 79.78 20.22 表 5 高硅煤中的重金属含量和富集系数
Table 5 Heavy metal contents and enrichment factors (EF) of the high-silicon coal
Heavy metal Content/(μg·g-1) Average of world hard coal EF Cr 35.40 17 2.08 Cu 48.70 16 3.04 As 18 9 2 Se 0.56 1.60 0.35 Mo 2.97 2.10 1.41 Pb 14.60 9 1.62 Th 8.85 3.20 2.77 U 3.29 1.90 1.73 表 6 ESP各级电场飞灰中重金属含量(μg/g)及富集系数
Table 6 Heavy metal contents (μg/g) of each ESP electric field and enrichment factors (EF) of the high-silicon fly ash
1 electric field 2 electric field 3 electric field 4 electric field World average content EF content EF content EF content EF Cr 101 0.84 117 0.98 122 1.02 129 1.08 120 Cu 159 1.45 174 1.58 199 1.81 205 1.86 110 As 33.20 0.72 46.4 1.01 53.10 1.15 60.20 1.31 46 Se 2.45 0.25 3.38 0.34 6.90 0.69 8.69 0.87 10 Mo 20 1.43 30.50 2.18 35.90 2.56 42.40 3.03 14 Pb 53 0.96 66.70 1.22 81.90 1.49 89.60 1.63 55 Th 28.20 1.23 29.60 1.29 32.50 1.41 34.70 1.51 23 U 14.10 0.94 17.80 1.17 20.60 1.37 23.80 1.59 15 -
[1] LU S Y, ZHANG H M, SOJINU S O, LIU G H, ZHANG J Q, NI H G. Trace elements contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from Shenzhen, China[J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2015, 187(1): 4220. [2] MEHARG A A, RAHMAN M M. Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: Implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2003, 37(2): 229-234. [3] YANG P T, HASHIMOTO Y, WU W J, HUANG J H, CHIANG P N, WANG S L. Effects of long-term paddy rice cultivation on soil arsenic speciation[J]. J Environ Manage, 2020, 254: 109768. [4] CLARKE L B, SLOSS L L. Trace Elements Emissions from Coal Combustion and Gasification[M]. London: IEA Coal Research, 1992, 111. [5] YAO Z T, JI X S, SARKER P K, TANG J H, GE L Q, XIA M S, XI Y Q. A comprehensive review on the applications of coal fly ash[J]. EarthA-Sci Rev, 2015, 141: 105-121. [6] 刘桂建, 彭子成, 杨萍玥, 王桂梁, 宋超.煤中微量元素在燃烧过程中的变化[J].燃料化学学报, 2001, 29(2): 119-123.LIU Gui-jian, PENG Zi-cheng, YANG Ping-yue, WANG Gui-liang, SONG Chao. Changes of trace elemetns in coal during combustion[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2001, 29(2): 119-123. [7] FINKELMAN R B, OREM W, CASTRANOVA V, TATU C A, BELKIN H B, ZHENG B, LERCH H E, MAHARAJ S V, BATES A L. Health impacts of coal and coal use: Possible solutions[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2002, 50(1/4): 425-443. [8] SAIKIA B K, WARD C R, OLIVEIRA M L S, HOWER J C, LEAO F D, JOHNSTON M N, O'BRYAN A, SHARMA A, BARUAH B P, SILVA L F O. Geochemistry and nano-mineralogy of feed coals, mine overburden, and coal-derived fly ashes from Assam (North-east India): A multi-faceted analytical approach[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2015, 137: 19-37. [9] JONES K B, RUPPERT L F, SWANSON S M. Leaching of elements from bottom ash, economizer fly ash, and fly ash from two coal-fired power plants[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2012, 94: 337-348. [10] DUTTA B K, KHANRA S, MALLICK D. Leaching of elements from coal fly ash: Assessment of its potential for use in filling abandoned coal mines[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(7): 1314-1323. [11] AKAR G, POLAT M, GALECKI G, IPEKOGLU U. Leaching behavior of selected trace elements in coal fly ash samples from Yenikoy coal-fired power plants[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2012, 104: 50-56. [12] JEGADEESAN G, AL-ABED, S R, PINTO P. Influence of trace metal distribution on its leachability from coal fly ash[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(10/11): 1887-1893. [13] 董静兰, 耿晓, 高正阳, 刘彦丰.飞灰中的缺陷位SiO2对痕量元素As的吸附机理[J].燃料化学学报, 2018, 46(11): 1401-1408.DONG Jing-lan, GENG Xiao, GAO Zheng-yang, LIU Yan-feng. Adsorption mechanism of trace As on the defect sites of SiO2 in fly ash[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2018, 46(11): 1401-1408. [14] ZHAO S L, DUAN Y F, LIU M, WANG C P, ZHOU Q, LU J H. Effects on enrichment characteristics of trace elements in fly ash by adding halide salts into the coal during CFB combustion[J]. J Energy Inst, 2018, 91(2): 214-221. [15] LAN Q, HE X Z, COSTA D J, TIAN L W, ROTHMAN N, HU G, MUMFORD J L. Indoor coal combustion emissions, GSTM1 and GSTT1 genotypes, and lung canceer risk: A case-control study in Xun Wei, China[J]. Cancer Epidem Biomar, 2000, 9(6): 605-608. [16] DAI S F, TIAN L W, CHOU C L, ZHOU Y P, ZHANG M Q, ZHAO L, WANG J M, YANG Z, CAO H Z, REN D Y. Mineralogical and compositional characteristics of Late Permian coals from an area of high lung cancer rate in Xuan Wei, Yunnan, China: Occurrence and origin of quartz and chamosite[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2008, 76(4): 318-327. [17] 雍其润, 龚本根, 赵永椿, 张军营.高硅煤中Si-Al-Fe-Ca四元体系碳热反应研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(11): 1296-1302.YONG Qi-run, GONG Ben-gen, ZHAO Yong-chun, ZHANG Jun-ying. Carbothermal reduction of Si-Al-Fe-Ca quaternary system in a high-silica coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(11): 1296-1302. [18] 周林, 邵龙义, 刘君霞, 宋晓焱.宣威肺癌高发区室内PM10对肺泡上皮细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国环境科学, 2010, 30(7): 1004-1008.ZHOU Lin, SHAO Long-yi, LIU Jun-xia, SONG Xiao-yan. Affects of indoor PM10 in Xuanwei on lung cell apoptosis[J]. China Environ Sci, 2010, 30(7): 1004-1008. [19] 樊景森, 邵龙义, 王静, 王建英, 李泽熙.云南宣威燃煤室内可吸入颗粒物质量浓度变化特征[J].中国环境科学, 2012, 32(8): 1379-1383.FAN Jing-sen, SHAO Long-yi, WANG Jing, WANG Jian-ying, LI Ze-xi. Variations in mass concentrations of indoor inhalable particulates in the coal-burning indoor air in Xuanwei County, Yunnan province[J]. China Environ Sci, 2012, 32(8): 1379-1383. [20] ZHAO Y C, ZHANG J Y, ZHENG C G. Transformation of aluminum-rich minerals during combustion of a bauxite-bearing Chinese coal[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2012, 94: 182-190. [21] 于敦喜, 徐明厚, 易帆, 黄建辉, 李庚.燃煤过程中颗粒物的形成机理研究进展[J].煤炭转化, 2004, 27(4): 7-12.YU Dun-xi, XU Ming-hou, YI Fan, HUANG Jian-hui, LI Geng. A review on particle formation mechanisms during coal combstion[J]. Coal Convers, 2004, 27(4): 7-12. [22] KETRIS M P, YUDOVICH Y E. Estimations of clarkes for carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2009, 78(2): 135-148. [23] MARTINEZ-TARAZONA M R, SPEARS D A. The fate of trace elements and bulk minerals in pulverized coal combustion in a power station[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1996, 47(1): 79-92. [24] BUHRE B J P, HINKEY J T, GUPTA R P, NELSON P F, WALL T F. Fine ash formation during combustion of pulverised coal-coal property impacts[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(2): 185-193. [25] MCLENNAN A R, BRYANT G W, STANMORE B R, WALL T F. Ash formation mechanisms during pf combustion in reducing conditions[J]. Energy Fuels, 2000, 14(1): 150-159. [26] SENIOR C L, BOOL Ⅲ L E, SRINIVASACHAR S, PEASE B R, PORLE K. Pilot scale study of trace element vaporization and condensation during combustion of a pulverized sub-bituminous coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 63: 149-165. -





 下载:
下载: