-
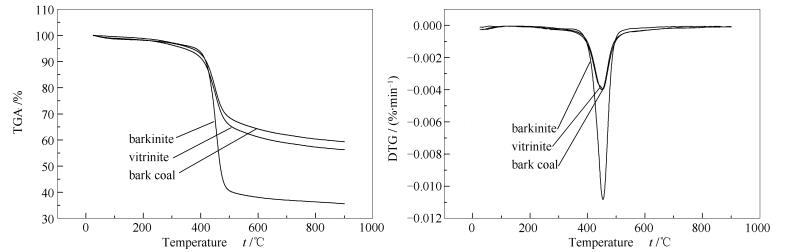
摘要: 以中国特殊显微组分树皮体作为研究对象,并与镜质体和树皮煤进行比较,通过热重实验分析了树皮体的热行为特性,并运用原位加热透射电镜(HRTEM)研究了树皮体在线受热后其化学结构变化特征,并进一步分析了树皮体热性质特性的原因。研究表明,相比于镜质体和树皮煤,树皮体在受热过程中的失重总量和热解最大速率均高,而三个样品的热解最大速率温度接近。在350 ℃之后,树皮体和镜质体的化学结构均具有定向性,且随着温度的升高,其定向性越明显。树皮体和镜质体分别在400和450 ℃时,呈现芳香层片堆积。同一温度条件下比较发现,树皮体和镜质体化学结构中以萘、2×2和3×3条纹为主;其次是4×4和5×5条纹。相比较而言,树皮体的萘含量高于镜质体,而镜质体中的3×3、4×4和5×5条纹的含量高于树皮体。在350-500 ℃,随着温度的逐渐升高,树皮体和镜质体中的萘含量增加,在450 ℃时,其萘的含量达到最高。树皮体的热解行为特性与其加热过程中化学结构特征变化有关,尤其是萘的含量变化。Abstract: Barkinite, one of Chinese special maceral, was chosen to study its peculiar thermal characteristics based on thermogravimetric analysis and Rock-eval analysis by comparing vitrinite with bark coal. The changes of chemical structure by heat-treatment of barkinite were discussed by HRTEM. The distribution of functional group of barkinite was studied by Micro-FTIR method. The results show that barkinite has the highest mass loss and the maximum rate of mass loss among these three samples. Barkinite and vitrinite have both orientated layers after temperature above 350℃. With the increasing of temperature, the orientation in aromatic layer is obviously improved and some layers in stacks increase. At the same temperature, for barkinite and vitrinite, three fringes show the greatest abundance, namely, naphthalene, 2×2, and 3×3 fringes, following by 4×4 and 5×5 fringes. Barkinite has a higher abundance of naphthalene than vitrinite and has lower abundances of larger aromatic fringes than vitrinite, for instance, 3×3, 4×4, and 5×5 fringes. With the increasing of temperature, the content of naphthalene in barkinite and vitrinite is increased. Their abundance reaches the highest at 450℃ that is also the temperature of the maximum mass loss rate of barkinite, which indicates that the thermal characteristics of barkinite is related to the abundance of naphthalene in the chemical structure of barkinite.
-
Key words:
- barkinite /
- thermogravimetric analysis /
- HRTEM /
- chemical structure
-
表 1 样品的基本性质
Table 1 Basic characteristics of coal samples used
Sample Ro
w/%Proximate analysis
w/%Ultimate analysis
wdaf/%H/C
atomic
ratioMaceral
φ/%Mad Ad Vdaf C H O* N St,d V Ba OL+I Bark coal 0.67 1.02 8.15 52.80 73.27 5.64 10.54 1.42 0.98 0.92 24 68 8 Barkinite - 0.84 0.39 69.93 - - - - 1.01 - 3 96 1 Vitrinite - 1.20 6.09 45.74 81.45 5.24 10.73 1.26 1.31 0.77 87 12 1 note: Ro: the mean maximum vitrinite reflectance; M: moisture; A: ash; V: volatile matter; ad: air-dry basis; d: dry basis; daf: dry-ash-free; V: vitrinite; Ba: barkinite; I: inertinite; OL: other liptinites; *: by difference; -: no determined 表 2 样品的热重参数和部分岩石热解
Table 2 TGA parameters analysis and Rock-Eval data of samples used
Sample Thermogravimetric analysis Rock-Eval[25] tmax/
℃MR/
(%·℃-1)S2/
(mg·g-1)S1+S2/
(mg·g-1)HI/
(mg·g-1)Bark coal 450 0.40 234 242 343 Vitrinite 453 0.40 237 244 296 Barkinite 454 1.08 461 472 611 note: tmax: temperature of maximum volatiles loss; MR: the maximum rate of mass loss; S1: amount of free hydrocarbons exposed before pyrolysis at 300 ℃ (mg (HC)/g (rock)); S2: amount of hydrocarbons exposed by the thermal cracking during programmed temperature increments above 300 ℃ in pyrolysis (mg (HC)/g (rock)); HI: hydrogen index 表 3 HRTEM晶格条纹归属分类
Table 3 Assignment of parallelogram-shaped aromatic fringes from the HRTEM fringe data
Aromatic sheet Minimum values
/nmMaximum values /nm Mean length
/nmGrouping
/nmNaphthalene 0.28 0.49 0.39 0.30-0.54 2×2 0.49 0.71 0.60 0.55-0.74 3×3 0.74 1.13 0.93 0.75-1.14 4×4 0.98 1.56 1.27 1.15-1.44 5×5 1.23 1.98 1.60 1.45-1.74 6×6 1.47 2.41 1.94 1.75-2.04 7×7 1.72 2.84 2.28 2.05-2.44 8×8 1.96 3.26 2.61 2.45-2.84 -
[1] HSIEH C Y. On lopinite, a new type of coal in China[J]. Bull Geol Soc China, 1933, 12(1/2):469-490. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229844350_On_Lopinite_a_New_Type_of_Coal_in_China [2] 韩德馨, 任德贻, 王延斌, 金奎励, 毛鹤龄, 秦勇.中国煤岩学[M].徐州:中国矿业大学出版社, 1996, 125-135.HAN De-xin, REN De-yi, WANG Yan-bing, JIN Kui-li, MAO He-ling, QIN Yong. Coal Petrology of China[M]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining & Technology Press, 1996. [3] GUO Y T, RENTON J J, PENN J H. FTIR microspectroscopy of particular liptinite-(lopinite-) rich, late permian coals from Southern China[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 1996, 29(1):187-197. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0166516295000240 [4] WANG S Q, TANG Y G, SCHOBERT H H, MITCHELL G D, LIAO Y F, LIU Z Z. A thermal behavior study of Chinese coals with high hydrogen content[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2010, 81:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2009.10.012 [5] WANG S Q, TANG Y G, SCHOBERT H H, JIANG D, SUN Y B, GUO Y N, SU Y F, YANG S P. Application and thermal properties of hydrogen-rich bark coal[J]. Fuel, 2015, 162:121-127. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.09.010 [6] 郭亚楠, 唐跃刚, 王绍清, 李薇薇, 贾龙.树皮残植煤显微组分分离及高分辨透射电镜图像分子结构[J].煤炭学报, 2013, 38(6):1019-1024. http://www.doc88.com/p-5945271006379.htmlGUO Yan-an, TANG Yue-gang, WANG Shao-qing, LI Wei-wei, JIA Long. Maceral separation of bark liptobiolite ande molecular structure study through high resolution TEM images[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2013, 38(6):1019-1024. http://www.doc88.com/p-5945271006379.html [7] GB/T 1558-2001. 烟煤显微组分分类[S].GB/T 1558-2001. Classification of macerals for bituminous coal[S]. [8] HOWER J C, SUǍREZ-RUIZ I, MASTALERZ M, COOK A C. The investigation of chemical structure of coal macerals via transmitted-light FT-IR microscopy by X. Sun[J]. Spectrochim Acta Part A, 2007, 67(5):1433-1437. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2006.11.034 [9] SUN X G. A study of chemical structure in "barkinite" using time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2001, 47(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/S0166-5162(01)00008-8 [10] 余海洋, 孙旭光, 焦宗福.华南晚二叠世"树皮体"显微傅里叶红外光谱(Micro-FTIR)特征及意义[J].北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 40(6):879-885. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHH201505047.htmYU Hai-yang, SUN Xug-uang, JIAO Zong-fu. Characterisistics and implications of micro-FT-IR spectroscopy of barkinite from upper permian coals, South China[J]. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekin, 2004, 40(6):879-885. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHH201505047.htm [11] SUN X G. The investigation of chemical structure of coal macerals via transmitted-light FT-IR microspectroscopy[J]. Spectrochim Acta Part A, 2005, 62(1):557-564. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1386142506006986 [12] 吴俊, 金奎励, 汪昆华, 顾世英.南方树皮煤红外光谱特征及成烃演化规律研究[J].煤田地质与勘探, 1990, (5):29-38. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94295X/199005/323930.htmlWU Jun, JIN Ku-li, WANG Kun-hua, GU Shi-ying. Infrared spectroscopy characteristics and forming-hydrocarbon evaluation rule for suberain coal in Southern China[J]. Coal Geol Explor, 1990, (5):29-38. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94295X/199005/323930.html [13] 余海洋, 孙旭光.江西乐平晚二叠世煤成烃机理红外光谱研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2007, 27(5):858-862. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx200705007YU Hai-yang, SUN Xu-guang. Research on hydrocarbon generation mechanism of upper permin coals from Leping, Jiangxi, based on ifrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectr Spectr Anal, 2007, 27(5):858-862. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx200705007 [14] WANG S Q, TANG Y G, SCHOBERT H H, JIANG D, GUO X, HUANG F, GUO Y N, SU Y F. Chemical compositional and structural characteristics of late permian bark coals from southern China[J]. Fuel, 2014, 126:116-121. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236114001598 [15] 郭绍辉, 李术元, 秦匡宗.用钌离子催化氧化法研究干酪根及其显微组分的化学结构[J].石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 24(3):54-57. http://www.doc88.com/p-58966651773.htmlGUO Shao-hui, LI Shu-yuan, QIN Kuang-zong. Structual characterization of kerogen and macerals by ruthenium ion catalyzed oxidation[J]. J Univ Pet, China, Ed Nat Sci, 2000, 24(3):54-57. http://www.doc88.com/p-58966651773.html [16] 焦堃, 姚素平, 张科, 胡文瑄.树皮煤的原子力显微镜研究[J].地质论评, 2012, 58(4):775-782. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201204018JIAO Kun, YAO Su-ping, ZHANG Ke, HU Wen-xuan. An atomic force microscopy study on "barkinite" liptobiolith[J]. Geol Rev, 2012, 58(4):775-782. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201204018 [17] WANG S Q, LIU S M, SUN Y B, JIANG D, ZHANG X M. Investigation of coal components of late permian different ranks bark coal using AFM and micro-FTIR[J]. Fuel, 2017, 187:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.09.049 [18] SHARAM A, KYOTANI T, TOMITA A. A new quantitative approach for microstructural analysis of coal char using HRTEM images[J]. Fuel, 1999; 78:1203-1212. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00046-0 [19] SHARAM A, KYOTANI T, TOMITA A. Direct observation of raw coals in lattice fringe mode using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy[J]. Energy Fuels, 2000, 14:1219-1225. doi: 10.1021/ef0000936 [20] SHARAM A, KYOTANI T, TOMITA A. Quantitive evaluation of structural transformation in raw coals on heat-treatment using HRTEM technique[J]. Fuel, 2001, 80:1467-1473. [21] MATHEWS J P, JONES A D, PAPPANO P J, HURT R, SCHOBERT H H. New insights into coal structure from the combination of HRTEM and laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry[C]//Proceedings of the 11th Int. Conf. on coal Sci: Exploring the horizons of coal. San Francisco, CA: 2001. [22] MATHEWS J P, FERNANDEZ-ALSO V, JONES A D, SCHOBERT H H. Determining the molecular weight distribution of pocahontas No. 3 low-volatile bituminous coal utilizing HRTEM and laser desorption ionization mass spectra data[J]. Fuel 2010, 89:1461-1469. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231426112_Molecular_Size_and_Shape_of_Some_Primary_Degradation_Products_of_a_Bituminous_Coal [23] MATHEWS J P, SHARAM A. The structure alignment of coal and the analogous case of argonne upper freeport coal[J]. Fuel, 2012, 95:19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.12.046 [24] VAN NIEKERK D, MATHEWS J P. Molecular representations of Permian-aged vitrinite-rich and inertinite-rich South African coals[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89:73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.07.020 [25] 黄帆. 乐平煤中树皮体的有机地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2015.HUANG Fan. Organic geochemical characteristics of barkinite in Leping coal[D]. Beijing: China university of Mining & Technology (Beijing), 2015. [26] STACH E, MACHKOWSKY M T H, TEICHMVLLER M, TAYLOR G H, CHANDRA D, TEICHMVLLER R. Stach's Textbook of Coal Petrology[M]. Berlin, Stuttgart:Gebrüder Borntraeger, 1982. [27] WANG S Q, TANG Y G, SCHOBERT H H, GUO Y N, GAO W C, LU X K. FTIR and simultaneous TG/MS/FTIR study of Late Permian coals from Southern China[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2013, 100:75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2012.11.021 -





 下载:
下载: