Effect of carbonization process on the strength and structure of Fe-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst
-
摘要: 以模型费托合成Fe基催化剂为研究对象, 在纯CO气氛中对催化剂进行不同时间的预处理, 采用多种手段对预处理后催化剂的物理化学性质和抗磨损能力进行了表征。结果表明, 在预处理初期, 随着预处理时间的延长, 催化剂的炭化程度显著提高, 伴随着催化剂比表面积的降低和颗粒粒径的减小, 而催化剂的抗磨损能力逐渐提高。当预处理时间超过72 h后, 继续延长预处理时间, 催化剂的炭化程度不再增加, 而积炭程度逐渐增加, 伴随着催化剂比表面积和颗粒粒径的增加, 催化剂的质量也同时增加, 并导致催化剂的抗磨损能力逐渐降低。Abstract: In order to gain an insight into the relationship between pretreatment condition and catalyst attrition resistance, an iron-based model catalyst for Fisher-Tropsch synthesis was carburized at 300℃ for different times and extensively characterized by multiple techniques; the effect of carburization and carbon deposition on the catalyst attrition resistance was then investigated.The results indicated that at the initial stage of pretreatment, the carbide content increases with the increase of carburization time, whereas the BET surface area and particle size are decreased, leading to an increase in the catalyst attrition resistance.With further increasing the carburization time above 72 h, the carbide content keeps almost constant, whereas the carbon deposition content, particle size and catalyst weight are increased, accompanying with a decrease in the attrition resistance.
-
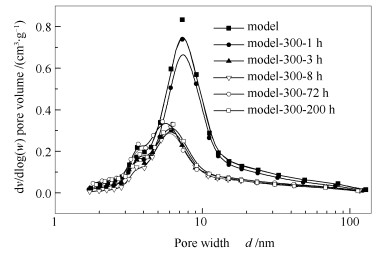
表 1 不同时间预处理后催化剂的织构性质
Table 1 Textural properties of catalysts after pretreatment for different time
Catalyst BET surface area A/(m2·g-1) Pore volume v/ (cm3·g-1) Pore size d/nm Mean vol.dia.d/μm Model 151 0.36 7.40 144.29 Model-300a-1 hb 121 0.31 7.55 139.82 Model-300-3 h 77 0.16 6.34 124.75 Model-300-8 h 63 0.15 7.16 128.88 Model-300-72 h 105 0.19 5.91 130.08 Model-300-200 h 97 0.17 6.15 141.42 note:for the catalyst sample Model-a-b, a represents pretreatment temperature in ℃ and b means the pretreatment time in h 表 2 不同时间预处理后催化剂的穆斯堡尔参数*
Table 2 Mössbauer parameters of the catalysts after pretreatment for different times
Catalyst Phase IS/(mm·s-1) QS/(mm·s-1) Hhf köe Area/% Sum/% Model-300-1 h Fe3O4(A) 0.27 -0.01 505 52.0 97.3 Fe3O4(B) 0.23 -0.13 467 45.3 χ-Fe5C2 0.30 0.22 255 2.7 2.7 Model-300-3 h Fe3O4(A) 0.25 0.11 505 11.0 41.8 Fe3O4(B) 0.48 -0.08 467 30.8 0.13 0.04 255 40.6 χ-Fe5C2 0.22 0.02 208 17.5 58.1 Model-300-8 h Fe3O4(A) 0.18 0.35 505 14.2 40.9 Fe3O4(B) 0.46 0.31 467 26.7 0.13 0.03 255 40.3 χ-Fe5C2 0.06 0.25 208 15.3 59.1 0.22 0.30 120 3.5 Model-300-72 h Fe3O4(A) 0.09 -0.04 505 4.1 12.2 Fe3O4(B) 0.66 -0.05 467 8.1 0.13 0.03 255 47.5 χ-Fe5C2 0.01 0.30 208 32.4 87.8 0.19 0.32 120 7.9 Model-300-200 h Fe3O4(A) 0.44 0.17 505 2.2 15.7 Fe3O4(B) 0.66 -0.07 467 13.5 0.16 0.03 255 46.6 χ-Fe5C2 0.12 0.16 208 34.3 84.3 0.20 0.12 120 3.4 a:the test temperature was 10 K 表 3 不同预处理时间催化剂的强度和质量变化
Table 3 Changes in strength and weight of the catalysts after pretreatment for different times
Catalyst Fine loss/% Attrition loss/% Recovery/% Weight c /% Model 6.47 43.64 87.05 100.0 Model-300-1 h 2.90 14.15 93.28 96.9 Model-300-3 h 0.00 1.34 93.44 86.7 Model-300-8 h 0.56 2.07 93.51 88.2 Model-300-72 h 0.75 5.62 95.57 94.2 Model-300-200 h 3.75 18.2 88.88 98.6 a:pretreatment temperature; b:pretreatment time; c:the weight of pretreated catalyst/the weight of fresh catalyst×100% -
[1] 李娟, 吴梁鹏, 邱勇, 定明月, 王铁军, 李新军, 马隆龙.费托合成催化剂的研究进展[J].化工进展, 2013, 32(s1):100-109. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/83c994575fbfc77da269b1bd-2.htmlLI Juan, WU Liang-peng, QIU Yong, DING Ming-yue, WANG Tie-jun, LI Xin-jun, MA Long-long.Research progress of catalysts for Fischer Tropsch synthesis[J].Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2013, 32(s1):100-109. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/83c994575fbfc77da269b1bd-2.html [2] DAVIS B H.Fischer-Tropsch synthesis:Reaction mechanisms for iron catalysts[J].Catal Today, 2009, 141(1):25-33. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222778912_Fischer-Tropsch_Synthesis_Reaction_mechanisms_for_iron_catalysts [3] DRY M E, HOOGENDOORN J C.Technology of the Fischer-Tropsch process[J].Cat Rev-Sci Eng, 1981, 23(1/2):265-278. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236566617_Technology_of_the_Fischer-Tropsch_Process [4] DRY M E.The Fischer-Tropsch process:1950-2000[J].Catal Today, 2002, 71(3):227-241. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920586101004539 [5] DRY M E.The Fischer-Tropsch process-commercial aspects[J].Catal Today, 1990, 6(3):183-206. doi: 10.1016/0920-5861(90)85002-6 [6] KROGH A.A review on coal-to-liquid fuels and its coal consumption[J].Int J Energy Res, 2010, 34(10):848-864. doi: 10.1002/er.v34:10 [7] SHROFF M D, KALAKKAD D S, COULTER K E, KOHLER S D, HARRINGTON M S, JACKSON N B.Activation of precipitated iron Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts[J].J Catal, 1995, 156(2):185-207. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1995.1247 [8] BUKUR D B, OKABE K, ROSYNEK M P, LI C P, WANG D J.Activation studies with a precipitated iron catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis.Ⅰ.Characterization studies[J].J Catal, 1995, 155(2):353-365. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1995.1217 [9] BUKUR D B.Activation studies with a precipitated iron catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis.Ⅱ.Reaction studies[J].J Catal, 1995, 155(2):366-375. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1995.1218 [10] AMELSE J A, BUTT J B, SCHWARTZ L H.Carburization of supported iron synthesis catalysts[J].J Phys Chem B, 1978, 82(5):558-563. doi: 10.1021/j100494a012 [11] REYMOND J P, MÉRIAUDEAU P, TEICHNER S J.Changes in the surface structure and composition of an iron catalyst of reduced or unreduced Fe2O3, during the reaction of carbon monoxide and hydrogen[J].J Catal, 1982, 75(1):39-48. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(82)90119-1 [12] KALAKKAD D S, SHROFF M D, KÖHLER S, JACKSON N, DATYE A K.Attrition of precipitated iron Fischer-Tropsch catalysts[J].Appl Catal A:Gen, 1995, 133(2):335-350. doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(95)00200-6 [13] ZHAO R, GOODWIN J G, JOTHIMURUGESAN, SANTOSH K, GANGWAL S K, SPIVEY J J.Spray-dried iron Fischer-Tropsch catalysts.1.Effect of structure on the attrition resistance of the catalysts in the calcined state[J].Ind Eng Chem Res, 2001, 40(4):1065-1075. doi: 10.1021/ie000644f [14] ZHAO R, SUDSAKORN K, GOODWIN J G, JOTHIMURUGESAN K, SANTOSH K, GANGWAL, SPIVEY J J.Attrition resistance of spray-dried iron F-T catalysts:Effect of activation conditions[J].Catal Today, 2002, 71(3):319-326. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920586101004588 [15] ZHAO R, GOODWIN J G, JOTHIMURUGESAN, SANTOSH K, GANGWAL S K, SPIVEY J J.Spray-dried Iron Fischer-Tropsch catalysts.2.Effect of carburization on catalyst attrition resistance[J].Ind Eng Chem Res, 2001, 40(5):1320-1328. doi: 10.1021/ie0006458 [16] 白亮. 铁催化剂浆态床费托合成的反应工程研究[D]. 太原: 中国科学院山西煤炭化学研究所, 2004.BAI Liang. Reaction engineering study on slurry fischer-tropsch synthesis over iron-based catalysts[D]. Taiyuan: Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2004. [17] YANG Y, XIANG H W, TIAN L, WANG H, ZHANG C H, TAO Z C.Structure and Fischer-Tropsch performance of iron-manganese catalyst incorporated with SiO2[J].Appl Catal A:Gen, 2005, 284(1):105-122. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X05000323 [18] 青明. Fe基F-T合成催化剂载体效应研究[D]. 太原: 中国科学院山西煤炭化学研究所, 2011.QING Ming. Support effects of the iron-based catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[D]. Taiyuan: Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011. [19] SUO H Y, WANG S, ZHANG C H, XU J, WU B S, YANG Y.Chemical and structural effects of silica in iron-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts[J].J Catal, 2012, 286(2):111-123. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021951711003599 [20] NING W, KOIZUMI N, CHANG H, MOCHIZUKI T, ITOH T, YAMADA M.Phase transformation of unpromoted and promoted Fe catalysts and the formation of carbonaceous compounds during Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction[J].Appl Catal A:Gen, 2006, 312(9):35-44. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X06004790 [21] XU J, BARTHOLOMEW C H.Temperature-programmed hydrogenation (TPH) and in situ Mössbauer spectroscopy studies of carbonaceous species on silica-supported iron Fischer-Tropsch catalysts[J].J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109(6):2392-2403. doi: 10.1021/jp048808j -





 下载:
下载: