Review on the fate of antimony and its emission control technologies during coal combustion
-
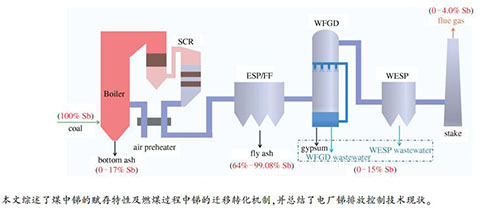
摘要: 锑是一种潜在有毒痕量元素,燃煤电厂是中国大气锑污染的重要来源。本研究通过对世界各国文献综述,详细介绍了煤中锑的含量及赋存形态,并从煤燃烧过程中锑的挥发行为、迁移特性和产物分布等角度阐释了燃煤过程中锑的迁移转化机制。此外,总结了电厂在燃烧前、燃烧中和燃烧后等不同阶段锑的排放控制技术现状。旨在为全面认知燃煤过程中锑的迁移转化及污染控制提供理论参考和技术指导。Abstract: Antimony is a trace element with potential toxicity. As a major source of atmospheric antimony pollution in China, the fate of antimony released during coal combustion has been attracting increasing concern. In this study, the contents and occurrence modes of antimony in coals were summarized, with subsequent discussions on the vaporization and transformation behavior of antimony in the coal combustion process. The partitioning of antimony in bottom ash, size-segregated fly ash particles as well as flue gas were also presented. Regarding the potential control methods for antimony emission, technologies facing pre-combustion, combustion and post-combustion stages were proposed respectively. It aims to provide a guideline for understanding the behavior of antimony migration and emission control during coal combustion.
-
Key words:
- antimony /
- coal combustion /
- vaporization behavior /
- migration characteristic /
- emission control
-
表 1 世界煤中锑含量
Table 1 Concents of antimony in coal around the world
Country Content of Sb/(μg·g-1) Number of sample Reference range average China 0.05-120 2.56 133 Ren et al. 1999[10] 0.1-10 2 446 Zhao et al.2002[11] - 0.71 1123 Bai et al.2007[12] - 0.84 527 Dai et al. 2008[13] 0.02-348 7.06 1058 Qi et al. 2008[9] 0-3.97 1.48 1612 Tian et al. 2011[5] Malaysia 2-96 76 39 Sia et al. 2012[14] Australia 0.01-1.2 0.5 - Swaine 1990[8] Japan 0.05-1.5 0.54 - Dale et al. 1993[15] - 0.874 33 Ito et al. 2006[16] USA -35 1.2 7473 Finkelman 1993[17] Word 0.005-10 0.92 - Ketris et al. 2009[18] Swain 1990[8] -: not provided Speciation Chemical formula Melting points /℃ Boiling points /℃ Metal Sb 630.5 1635 Oxide Sb2O3 656 1456* Chloride SbCl3 73.4 223.5 SbCl5 3.5 140 Sulphide Sb2S3 546 1150 *:decompostion 表 3 煤燃烧过程中锑的质量平衡
Table 3 Mass balance of antimony during coal combustion
Unit Fly ash/% Bottom ash/% Flue gas/% Others/% Reference 600 MW 94.31 1.9 3.79 ND Lu et al. 2018[51] 350 MW 98.87 ND ND 1.13 Che et al. 2019[52] 320 MW 99.08 0.79 0.05 0.08 Zhao et al. 2018[53] 320 MW 89.38 2.91 0.04 10.58 Wang et al. 2018[54] - 69.8 14.0 0.06 10.02 Ito et al. 2006[16] 600 MW 95.7 4.3 ND - Nodelman et al. 2000[55] 600 MW 64-68 13-17 3.7-4.0 15 Qi et al. 2016[56] note: all the furnaces in the table are pulverized coal furnaces; -: not provided; others: gypsum, slug, waste water, etc.; ND: not detected 表 4 污染物脱除设备对锑的脱除效果
Table 4 Removal efficiencies of Sb by different APCDs
Control device Removal efficiency of Sb/% Reference ESP 98.9 Meij et al. 2007[68] 69.8 Ito et al. 2006[16] 83.50 Tian et al. 2011[5] 60 Zhao et al. 2016[69] 77-80 Qi et al. 2016[56] 41.79 Wang et al. 2018[54] FF 94.3 Tian et al. 2011[5] >98 Nodelman et al. 2000[55] WFGD 19-21 Qi et al. 2016[56] 72.7 Zhao et al. 2016[69] 82.1 Meij et al. 2007[68] 33.33 Wang et al. 2018[54] WESP 60 Zhao et al. 2016[69] 15 Wang et al. 2018[54] ESP+WFGD 81-84 Qi et al. 2016[56] 99.81 Meij et al. 2007[68] 97.05 Zhu et al. 2016[70] ESP+WFGD+WESP >99.9 Zhao et al. 2016[69] FF+WFGD 98.98 SCR+ESP+ WFGD 98.98 Zhu et al. 2016[70] -
[1] HE M, WANG X, WU F, FU Z. Antimony pollution in China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2012, 421-422: 41-50. [2] LI J, ZHENG B, HE Y, ZHOU Y, CHEN X, RUAN S, YANG Y, DAI C, TANG L. Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: A review[J]. Ecotox Environ Safe, 2018, 156: 125-134. [3] TIAN H, ZHOU J, ZHU C, ZHAO D, GAO J, HAO J, HE M, LIU K, WANG K, HUA S. A comprehensive global inventory of atmospheric antimony emissions from anthropogenic activities, 1995-2010[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2014, 48(17): 10235-10241. [4] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.中华人民共和国2019年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R]. 2019.www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/202002/t20200228_1728913.html (National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Statistical Communique of the People's Republic of China on the 2019[R]. National Economic and Social Development. 2019.www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/202002/t20200228_1728913.html. [5] TIAN H Z, ZHAO D, HE M C, WANG Y, CHENG K. Temporal and spatial distribution of atmospheric antimony emission inventories from coal combustion in China[J]. Environ Pollut, 2011, 159(6): 1613-1619. [6] National emission standards for hazardous air pollutants from coaland oil-fired electric utility steam generating units and standards of performance for fossil-fuel-fired electric utility, industrial-commercial- institutional, and small industrial[S]. Federal Register, 2016. [7] 何孟常, 万红艳.环境中锑的分布、存在形态及毒性和生物有效性[J].化学进展, 2004, 16(1): 131-135.HE Meng-chang, WAN Hong-yan. Distribution, speciation, toxicity and bioavailability of antimony in the environment[J]. Prog Chem, 2004, 16(1): 131-135. [8] SWAINE D J. Trace Elements in Coal[J]. Butterworth, London, 1990. [9] QI C, LIU G, CHOU C, ZHENG L. Environmental geochemistry of antimony in Chinese coals[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2008, 389(2/3): 225-234. [10] REN D, ZHAO F, WANG Y, YANG S. Distributions of minor and trace elements in Chinese coals[J]. Int J Coal Geol 1999, 40(2): 109-118. [11] 赵继尧, 唐修义, 黄文辉.中国煤中微量元素的丰度[J].中国煤田地质, 2002, 14(S1): 6-14.ZHAO Ji-yao, TANG Xiu-yi, HUANG Wen-hui. Abundance of trace elements in coal of China[J]. Coal Geol China, 2002, 14(S1): 6-14. [12] 白向飞, 李文华, 陈亚飞, 姜英.中国煤中微量元素分布基本特征[J].煤质技术, 2007, (1): 1-4.BAI Xiang-fei, LI Wen-hua, CHEN Ya-fei, JIANG ying. The general distributions of trace elements in Chinese coals[J]. Coal Quality Technol, 2007, (1): 1-4. [13] DAI S, ZHOU Y, REN D, WANG X, LI D, ZHAO L. Geochemistry and mineralogy of the Late Permian coals from the Songzo Coalfield, Chongqing, southwestern China[J]. Sci in China Series D: Earth Sci, 2007, 50(5): 678-688. [14] SIA S, ABDULLAH W H. Enrichment of arsenic, lead, and antimony in Balingian coal from Sarawak, Malaysia: Modes of occurrence, origin, and partitioning behaviour during coal combustion[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2012, 101: 1-15. [15] DALE L, LAVRENCIC S. Trace elements in Australian export thermal coals[J]. Aust Coal J, 1993, 39: 17-21. [16] ITO S, YOKOYAMA T, ASAKURA K. Emissions of mercury and other trace elements from coal-fired power plants in Japan[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2006, 368(1): 397-402. [17] FINKELMAN R B. Trace and minor elements in coal[C]. New York: Plenum press, 1993: 593-607. [18] KETRIS M P, YUDOVICH Y E. Estimations of clarkes for carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2009, 78(2): 135-148. [19] SENIOR C L, ZENG T, CHE J, AMES M R, SAROFIM A F, OLMEZ I, HUGGINS F E, SHAH N, HUFFMAN G P, KOLKER A, MROCZKOWSKI S, PALMER C, FINKELMAN R. Distribution of trace elements in selected pulverized coals as a function of particle size and density[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 63(2): 215-241. [20] SIA S, ABDULLAH W H. Concentration and association of minor and trace elements in Mukah coal from Sarawak, Malaysia, with emphasis on the potentially hazardous trace elements[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2011, 88(4): 179-193. [21] 梁虎珍, 曾凡桂, 相建华, 李美芬.伊敏褐煤中微量元素的地球化学特征及其无机-有机亲和性分析[J].燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(10): 1173-1183.LIANG Hu-zhen, ZENG Fan-gui, XIANG Jian-hua, LI Mei-fen. Geochemical characteristics and inorganic organic affinity analysis of trace elements in Yimin lignite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(10): 1173-1183. [22] 吴江平.淮南煤田东部煤中微量元素及其环境意义研究[D].淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2006.WU Jiang-ping. Study on trace elements in coal of Eastern Huainan: coalfield and its environmental significance[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2006.) [23] 齐翠翠, 刘桂建, 匡武.锑在淮南煤中的分布特征与富集成因[J].中国煤炭地质, 2016, 28(12): 9-13.QI Cui-cui, LIU Gui-jian, KUANG Wu. Distribution characteristics and enrichment genesis of antimony in Huainan coal[J]. Coal Geol China, 2016, 28(12): 9-13. [24] 赵峰华, 彭苏萍, 李大华, 唐跃刚, 任德贻, 许德伟.低煤级煤中部分元素有机亲合性的定量研究[J].中国矿业大学学报, 2003, 22(1): 21-25.ZHAO Feng-hua, PENG Su-ping, LI Da-hua, TANG Yue-gang, REN De-yi, XU De-wei. Quantitative study on organic affinity of some elements in low rank coal[J]. J China Univ Min Technol, 2003, 22(1): 21-25. [25] 杨建业.煤中微量元素的酸脱除率与元素周期—以渭北晚古生代5号煤层为例[J].燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(5): 522-527.YANG Jian-ye. Acid removal rate and element periodicity of trace elements in coal—a case study of No.5 coal seam of Late Paleozoic in Weibei area[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2010, 38(5): 522-527. [26] GOODARZI F, SWAINE D J. Chalcophile elements in western Canadian coals[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 1993, 24(1): 281-292. [27] FINKELMAN R B, ARUSCAVAGE P J. Concentration of some platinum-group metals in coal[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 1981, 1(2): 95-99. [28] FINKELMAN R B, PALMER C A, KRASNOW M R, ARUSCAVAGE P J, SELLERS G A, DULONG F T. Combustion and leaching behavior of elements in the Argonne Premium Coal Samples[J]. Energy Fuels, 1990, 4(6): 755-766. [29] DAI S, ZOU J, JIANG Y, WARD C R, WANG X, LI T, XUE W, LIU S, TIAN H, SUN X, ZHOU D. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the Pennsylvanian coal in the Adaohai Mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Modes of occurrence and origin of diaspore, gorceixite, and ammonian illite[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2012, 94: 250-270. [30] DAI S, ZENG R, SUN Y. Enrichment of arsenic, antimony, mercury, and thallium in a Late Permian anthracite from Xingren, Guizhou, Southwest China[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2006, 66(3): 217-226. [31] 冯新斌, 倪建宇, 洪业汤, 朱建明, 周斌.贵州省煤中挥发性和半挥发性微量元素分布规律的初步研究[J].环境化学, 1998, 17(2): 3-5.FENG Xin-bin, NI Jian-yu, HONG Ye-tang, ZHU Jian-ming, ZHOU Bin. Preliminary study on the distribution of volatile and semi volatile trace elements in coal of Guizhou Province[J]. Environ Chem, 1998, 17(2): 3-5. [32] 庄新国, 龚家强, 王占岐, 曾荣树, 徐文东.贵州六枝、水城煤田晚二叠世煤的微量元素特征[J].地质科技情报, 2001, 20(3): 53-58.ZHUANG Xin-guo, GONG Jia-qiang, WANG Zhan-qi, ZENG Rong-shu, XU Wen-dong. Trace element characteristics of Late Permian coal in Liuzhi and Shuicheng coalfields, Guizhou Province[J]. Geol Sci Inform, 2001, 20(3): 53-58. [33] FINKELMAN R B, PALMER C A, WANG P. Quantification of the modes of occurrence of 42 elements in coal[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2018, 185: 138-160. [34] ZHOU C, LIU G, XU Z, SUN H, KWAN SING LAM P. Retention mechanisms of ash compositions on toxic elements (Sb, Se and Pb) during fluidized bed combustion[J]. Fuel, 2018, 213: 98-105. [35] 庄新国, 曾荣树, 徐文东.山西平朔安太堡露天矿9号煤层中的微量元素[J].地球科学, 1998, 23(6): 3-5.ZHUANG Xin-guo, ZENG Rong-shu, XU Wen-dong. Trace elements in No.9 coal seam of Antaibao open pit mine, Pingshuo, Shanxi province[J]. Earth Sci, 1998, 23(6): 3-5. [36] DAI S, REN D, TANG Y, YUE M, HAO L. Concentration and distribution of elements in Late Permian coals from western Guizhou province, China[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2005, 61(1/2): 119-137. [37] 任德贻, 许德伟, 张军营, 赵峰华, 郦桂芝, 谢烈文.沈北煤田煤中伴生元素分布特征[J].中国矿业大学学报, 1999, 28(1): 3-5.REN De-yi, XU De-wei, ZHANG Jun-ying, ZHAO Feng-hua, LI Gui-zhi, XIE Lie-wen. Distribution characteristics of associated elements in coal of Shenbei coalfield[J]. J China Univ Min Technol, 1999, 28(1): 3-5. [38] 胡广青.淮南煤田煤中典型有害元素的环境地球化学及洁净等级评价[D].合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2019.HU Guang-qing. Evaluation of environmental geochemistry and cleanliness grade of typical harmful elements in coal of Huainan coalfield[D]. Hefei: China University of Science and Technology, 2019. [39] CLARKE L B. The fate of trace elements during coal combustion and gasification: An overview[J]. Fuel, 1993, 72(6): 731-736. [40] 孟韵.煤燃烧过程中有害元素和亚微米颗粒物排放与控制的理论与实验研究[D].南京: 南京理工大学, 2004.MENG Yun. Theoretical and experimental study on emission and control of harmful elements and submicron particles during coal combustion[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2004. [41] VASSILEV S V, BRAEKMAN-DANHEUX C, LAURENT P, THIEMANN T, FONTANA A. Behaviour, capture and inertization of some trace elements during combustion of refuse-derived char from municipal solid waste[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(10): 1131-1145. [42] 张军营, 郑楚光, 刘晶, 刘海明.燃煤易挥发微量重金属元素行为的试验研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2003, 24(6): 1043-1046.ZHANG Jun-ying, ZHENG Chu-guang, LIU Jing, LIU Hai-ming. Experimental study on volatility trace heavy metals in coal combustion[J]. J Eng Thermophys-Rus, 2003, 24(6): 1043-1046. [43] 王馨, 姚多喜, 冯启言.褐煤燃烧过程中重金属元素分布特征及其对环境影响评价[J].环境科学学报, 2013, 33(5): 1389-1395.WANG Xin, YAO Duo-xi, FENG Qi-yan. Distribution characteristics and environmental impact of heavy metals during lignite combustion[J]. Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(5): 1389-1395. [44] DÍAZ-SOMOANO M, MARTÍNEZ-TARAZONA M R. Trace element evaporation during coal gasification based on a thermodynamic equilibrium calculation approach[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(2): 137-145. [45] 王泉海, 邱建荣, 温存, 孔凡海, 熊全军, 吴辉, 张小平, 刘豪.氧燃烧方式下痕量元素形态转化的试验和模拟研究[J].工程热物理学报, 2006, 27(S2): 199-202.WANG Quan-hai, QIU Jian-rong, WEN Cun, KONG Fan-hai, XIONG Quan-jun, WU Hui, ZHANG Xiao-ping, LIU Hao. A experimental and simulative study on the morpho-logical transformation of the trace element under oxygen-combustion atmosphere[J]. J Eng Thermophys, 2006, 27(S2): 199-202. [46] FILELLA M, HENNEBERT P, OKKENHAUG G, TURNER A. Occurrence and fate of antimony in plastics[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2020, 390: 121764. [47] FU B, LIU G, MIAN M M, SUN M, WU D. Characteristics and speciation of heavy metals in fly ash and FGD gypsum from Chinese coal-fired power plants[J]. Fuel, 2019, 251: 593-602. [48] ZENG T, SAROFIM A F, SENIOR C L. Vaporization of arsenic, selenium and antimony during coal combustion[J]. Combust Flame, 2001, 126(3): 1714-1724. [49] JAMES D W, KRISHNAMOORTHY G, BENSON S A, SEAMES W S. Modeling trace element partitioning during coal combustion[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 126: 284-297. [50] BARNES D I. Understanding pulverised coal, biomass and waste combustion-A brief overview[J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2015, 74: 89-95. [51] 卢锦程, 段钰锋, 赵士林, 白李一, 陈聪, 李春峰, 陶君. 600MW燃煤电厂痕量元素排放特性实验研究[J].中国环境科学, 2018, 38(12): 4444-4450.LU Jin-cheng, DUAN Yu-feng, ZHAO Shi-lin, BAI Li-yi, CHEN Cong, LI Chun-feng, TAO jun. Experimental study on emission characteristics of trace elements in 600MW coal fired power plant[J]. China Environ Sci, 2018, 38(12): 4444-4450. [52] 车凯, 郑庆宇, 韩忠阁, 陈崇明, 郁金星.燃煤电厂痕量元素协同脱除及排放[J].中国电力, 2019, 52(4): 161-166.CHE Kai, ZHENG Qing-yu, HAN Zhong-ge, CHEN Chong-ming, YU Jin-xing. Research on Co-removal and Emission of Trace Elements in the Coal-Fired Power Plant[J]. Electr Pow, 2019, 52(4): 161-166. [53] 赵士林, 段钰锋, 丁艳军, 谷小兵, 杜明生, 姚婷, 陈聪, 刘猛, 吕剑虹. 320 MW燃煤电厂痕量元素的分布、脱除及排放特性[J].化工学报, 2017, 68(7): 2910-2917.ZHAO Shi-lin, DUAN Yu-feng, DING Yan-jun, GU Xiao-bing, DU Ming-sheng, YAO ting, CHEN Cong, LIU Meng, LU Jian-hong. Distribution, co-removal and emission characteristic of trace elements in 320 MW coal-fired power plant[J]. CIESC J, 2017, 68(7): 2910-2917. [54] WANG J, ZHANG Y, LIU Z, GU Y, NORRIS P, XU H, PAN W. Coeffect of air pollution control devices on trace element emissions in an ultralow emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Energy Fuels, 2018, 33(1): 248-256. [55] NODELMAN I G, PISUPATI S V, MILLER S F, SCARONI A W. Partitioning behavior of trace elements during pilot-scale combustion of pulverized coal and coal-water slurry fuel[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2000, 74(1): 47-59. [56] 齐翠翠, 刘桂建.淮南燃煤电厂锑的分配、富集与释放通量[J].环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(S1): 243-246.QI Cui-cui, LIU Gui-jian, The distribution, enrichment and emissions of antimony in Huainan coal-fired power plant[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2016, 39(S1): 243-246. [57] FU B, LIU G, SUN M, HOWER J C, MIAN M M, WU D, WANG R, HU G. Emission and transformation behavior of minerals and hazardous trace elements (HTEs) during coal combustion in a circulating fluidized bed boiler[J]. Environ Pollut, 2018, 242: 1950-1960. [58] 魏晓飞, 张国平, 李玲, 项萌, 蔡永兵.黔西南煤燃烧产物微量元素分布特征及富集规律研究[J].环境科学, 2012, 33(5): 1457-1462.WEI Xiao-fei, ZHANG Guo-ping, LI Ling, XIANG Meng, CAI Yong-bing. Distribution and enrichment of trace elements in coal combustion products from southwestern guizhou[J]. Environ Sci, 2012, 33(5): 1457-1462.) [59] LUTTRELL G H, KOHMUENCH J N, YOON R. An evaluation of coal preparation technologies for controlling trace element emissions[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2000, 65-66: 407-422. [60] 田贺忠, 赵丹, 何孟常, 王艳, 程轲, 曲益萍. 2005年中国燃煤大气锑排放清单[J].中国环境科学, 2010, 30(11): 1550-1557.TIAN He-zhong, ZHAO Dan, HE Meng-chang, WANG Yan, CHENG Ke, QU Yi-ping. Atmospheric antimony emission inventories from coal combustion in China in 2005[J]. China Environ Sci, 2010, 30(11): 1550-1557. [61] VASSILEV S V, BRAEKMAN-DANHEUX C, LAURENT P, THIEMANN T, FONTANA A. Behaviour, capture and inertization of some trace elements during combustion of refuse-derived char from municipal solid waste[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(10): 1131-1145. [62] 姚多喜, 支霞臣, 王馨, 郑宝山.分级燃烧工况下高岭土对煤中微量元素排放的影响研究[J].环境科学学报, 2004, 24(2): 210-214.YAO Duo-xi, ZHI Xia-chen, WANG Xin, ZHENG Bao-shan. Study on the effect of kaolin on the emission of trace elements during staged combustion of coal[J]. Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2004, 24(2): 210-214. [63] 李小乐, 孙海程, 段伦博, 赵长遂.不同添加剂/吸附剂对循环流化床燃烧痕量元素迁移的影响规律[J].燃烧科学与技术, 2016, 22(1): 45-49.LI Xiao-le, SUN Hai-cheng, DUAN Lun-bo, ZHAO Chang-sui. Influence of different additives/absorbents on migration of trace elements in CFB combustion[J]. J Combust Sci Technol, 2016, 22(1): 45-49. [64] JIAO F, NINOMIYA Y, ZHANG L, YAMADA N, SATO A, DONG Z. Effect of coal blending on the leaching characteristics of arsenic in fly ash from fluidized bed coal combustion[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2013, 106: 769-775. [65] ZHANG S, JIANG X, LIU B, LV G, JIN Y, YAN J. Co-combustion of bituminous coal and pickling sludge in a drop-tube furnace: Thermodynamic study and experimental data on the distribution of Cr, Ni, Mn, As, Cu, Sb, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Sn[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(3): 3019-3028. [66] GOGEBAKAN Z, SELÇUK N. Trace elements partitioning during co-firing biomass with lignite in a pilot-scale fluidized bed combustor[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2009, 162(2/3): 1129-1134. [67] NZIHOU A, STANMORE B R. The formation of aerosols during the co-combustion of coal and biomass[J]. Waste Biomass Valori, 2015, 6(6): 947-957. [68] MEIJ R, TE WINKEL H. The emissions of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from modern coal-fired power stations[J]. Atmos Environ, 2007, 41(40): 9262-9272. [69] ZHAO S, DUAN Y, TAN H, LIU M, WANG X, WU L, WANG C, LV J, YAO T, SHE M, TANG H. Migration and emission characteristics of trace elements in a 660 MW coal-fired power plant of china[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30(7): 5937-5944. [70] ZHU C, TIAN H, CHENG K, LIU K, WANG K, HUA S, GAO J, ZHOU J. Potentials of whole process control of heavy metals emissions from coal-fired power plants in China[J]. J Clean Prod, 2016, 114: 343-351. [71] 卢元明.燃煤电厂湿式电除尘技术研究及应用[D].保定: 华北电力大学, 2015.LU Yuan-ming. Coal fired power plant wet electric dust removal technology research and Application[D]. Baoding: North China Electric Power University, 2015. [72] 阮仁晖, 谭厚章, 段钰锋, 杜勇乐, 刘鹤欣, 萧嘉繁, 杨富鑫, 张朋.超低排放燃煤电厂颗粒物脱除特性[J].环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 126-134.RUAN Ren-hui, TAN Hou-zhang, DUAN Yu-feng, DU Yong-le, LIU He-xin, XIAO Jia-fan, YANG Fu-xin, ZHANG Peng. Particle removal characteristics of an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Environ Sci, 2019, 40(1): 126-134. [73] 王建朋, 段璐, 王乃继, 李杰.燃煤锅炉烟气脱硫技术对颗粒物排放影响研究进展[J].洁净煤技术, 2020, 26(2): 34-42.WANG Jian-peng, DUAN Lu, WANG Nai-ji, LI Jie. Research progress on the effect of flue gas desulfurization technonlogy of coal-fired boiler on particulate matter emission[J]. Clean Coal Technol, 2020, 26(2): 34-42. [74] 阮仁晖, 谭厚章, 段钰锋, 杜勇乐, 刘鹤欣, 萧嘉繁, 杨富鑫, 张朋.超低排放燃煤电厂颗粒物脱除特性[J].环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 126-134.RUAN Ren-hui, TAN Hou-zhang, DUAN Yu-feng, DU Yong-le, LIU He-xin, XIAO Jia-fan, YANG Fu-xin, ZHANG Peng. Particle removal characteristics of an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Environ Sci, 2019, 40(1): 126-134. -





 下载:
下载: