Effect of calcination temperature on the properties of the mixed TiO2-ZrO2 oxides and their performance in the dehydration of octadecanol to octadecene
-
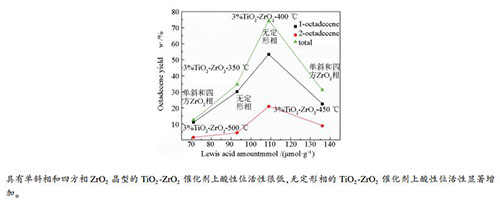
摘要: 通过在ZrO2中掺杂TiO2,并在350-500 ℃下焙烧,制备了系列TiO2-ZrO2复合氧化物催化剂,将其应用于十八醇脱水制十八烯反应。随焙烧温度的升高,催化剂表面的Lewis酸性位量逐渐增加,450 ℃焙烧的催化剂Lewis酸性位量最多,焙烧温度继续升高则Lewis酸性位量降低;催化剂中未发现Brønsted酸性位。焙烧温度≤400 ℃的TiO2-ZrO2复合氧化物形成Ti-O-Zr键,呈无定形态;焙烧温度>400 ℃的TiO2-ZrO2复合氧化物呈单斜相和四方相ZrO2晶型。晶相结构和酸性位量综合影响催化剂的十八醇脱水性能,具有单斜相和四方相ZrO2晶型的催化剂上酸性位活性很低,具有无定形相的催化剂上酸性位活性显著增加,400 ℃焙烧的催化剂1-十八烯收率最高。
-
关键词:
- 脂肪醇脱水 /
- TiO2-ZrO2复合氧化物 /
- α-烯烃 /
- 酸性位
Abstract: A series of mixed TiO2-ZrO2 oxide catalysts used for the dehydration of octadecanol to octadecene were prepared by doping TiO2 in ZrO2 and calcining at 350-500 ℃. With the increase of calcination temperature, the amount of Lewis acid sites on the catalyst surface gradually increases. The amount of Lewis acid sites on the catalyst calcined at 450 ℃ is the most, and when the calcination temperature is over 450 ℃, the amount of Lewis acid sites decreases. No Brønsted acid sites are found on the catalysts. The mixed TiO2-ZrO2 oxides calcined at temperature below 400 ℃ contain Ti-O-Zr bonds and amorphous structure. The mixed TiO2-ZrO2 oxides with calcination temperature above 400 ℃ show monoclinic and tetragonal phases of ZrO2. The crystalline phase of the metal oxides and amount of the acid sites simultaneously affect the performance of the catalysts. The acid sites on the mixed TiO2-ZrO2 oxides with amorphous structure have much higher dehydration activity than those with monoclinic and tetragonal zirconia crystalline phases. The catalyst calcined at 400 ℃ has the highest yield of 1-octadecene.-
Key words:
- fatty alcohol dehydration /
- TiO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides /
- α-olefins /
- acid sites
-
表 1 催化剂的织构性质
Table 1 Textural parameters of the 3%TiO2-ZrO2 composite oxides calcined at different temperatures
Sample ABET / (m2·g-1) Pore volumev/(cm3·g-1) Average pore diameterd/nm 3%TiO2-ZrO2-350℃ 198 0.197 4.21 3%TiO2-ZrO2-400℃ 190 0.149 3.46 3%TiO2-ZrO2-450℃ 128 0.214 6.69 3%TiO2-ZrO2-500℃ 72 0.179 10.1 表 2 催化剂的Lewis酸量和BrØnsted酸量
Table 2 Acid amount of Lewis and BrØnsted acid on the catalysts
Catalyst Acid amount /(μmol·g-1) B L total 3%TiO2-ZrO2-350℃ - 93 93 3%TiO2-ZrO2-400℃ - 109 109 3%TiO2-ZrO2-450℃ - 136 136 3%TiO2-ZrO2-500℃ - 71 71 表 3 催化剂的十八醇转化率及产物选择性
Table 3 Catalytic performance of the catalysts
Catalyst Conversionx/% Selectivitys/% 1-18C= trans-2-18C= cis-2-18C= 18C-O-C18 18HC=O others 3%TiO 2-ZrO 2-350℃ 41.44 72.61 5.43 5.35 5.85 1.46 9.30 3%TiO 2-ZrO 2-400℃ 79.21 67.28 12.84 13.47 0.08 0.28 6.54 3%TiO 2-ZrO 2-450℃ 40.37 55.43 11.31 10.38 6.58 0.37 15.93 3%TiO 2-ZrO 2-500℃ 20.45 53.46 4.09 3.58 22.30 0.71 15.86 reaction conditions:t=300℃, LHSV=0.6h -1, N2 GHSV=400h-1, atmospheric pressure, 1-18C=: linear 1-octadecene, trans-2-18C=: trans-2-octadecene, cis-2-18C=: cis-2-octadecene, 18C-O-C18: dioctadecyl ether, 18HC=O: stearaldehyde, others:by-products -
[1] ECHAROJ S, SANTIKUNAPORN M, CHAVADEJ S. Transformation of bioderived 1-decanol to diesel-like fuel and biobased oil via dehydration and oligomerization reactions[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(9):9465-9476. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b01247 [2] 李影辉, 曾群英, 万书宝, 迟克彬, 杜海. α-烯烃合成工艺及市场[J].精细石油化工进展, 2004, 5(11):12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8348.2004.11.004LI Ying-hui, ZENG Qun-ying, WAN Shu-bao, CHI Ke-bin, DU Hai. Synthesis process and market of α-olefin[J]. Adv Fine Petrochem, 2004, 5(11):12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8348.2004.11.004 [3] 李影辉, 曾群英, 肖海成, 万书宝, 迟克彬. α-烯烃合成工艺技术进展[J].天然气化工, 2005, 30(2):55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9219.2005.02.013LI Ying-hui, ZENG Qun-ying, XIAO Hai-cheng, WAN Shu-bao, CHI Ke-bin. Progress in alpha olefin synhesis processes[J]. Nat Gas Chem Ind, 2005, 30(2):55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9219.2005.02.013 [4] 赵惠萍. 1-辛烯生产工艺[J].石化技术, 2006, (1):59-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2006.01.017ZHAO Hui-ping. Octene-1 manufacturing process[J]. Petrochem Ind Technol, 2006, (1):59-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2006.01.017 [5] 郑来昌, 王如文, 杨小辉, 杨克.植物油生产α-烯烃技术进展[J].润滑油, 2015, 30(4):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3119.2015.04.001ZHENG Lai-chang, WANG Ru-wen, YANG Xiao-hui, YANG Ke. Technical progress of α-olefin production from vegetabe oil[J]. Lubr Oil, 2015, 30(4):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3119.2015.04.001 [6] SONG W, LIU Y, BARATH E, WANG L L, ZHAO C, MEI D, LERCHER J A. Dehydration of 1-octadecanol over H-BEA:A combined experimental and computational study[J]. ACS Catal, 2016, 6(2):878-889. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b01217 [7] CHOKKARAM S, DAVIS B H. Dehydration of 2-octanol over zirconia catalysts:Influence of crystal structure, sulfate addition and pretreatment[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 1997, 118(1):89-99. doi: 10.1016/S1381-1169(96)00380-9 [8] KOSTESTKYY P, YU J, GORTE R J, MPOURMPAKIS G. Structure-activity relationships on metal-oxides:Alcohol dehydration[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2014, 4:3861-3869. doi: 10.1039/C4CY00632A [9] SATO S, TAKAHASHI R, SODESAWA T, YAMAMOTO N. Dehydration of 1, 4-butanediol into 3-buten-1-ol catalyzed by ceria[J]. Catal Commun, 2004, 5(8):397-400. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2004.05.006 [10] CHEN B H, LU J Z, WU L P, CHAO Z S. Dehydration of bio-ethanol to ethylene over iron exchanged HZSM-5[J]. Chin J Catal, 2016, 37(11):1941-1948. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(16)62524-X [11] TAKAHASHI N, SUDA A, HACHISUKA I, SUGIURA M, SOBUKAWA H, SHINJOH H. Sulfur durability of NOx storage and reduction catalyst with supports of TiO2, ZrO2 and ZrO2-TiO2 mixed oxides[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2007, 72(1/2):187-195. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e0779edbd3e7600fc0cd22d942cabf2c [12] MAITY S, RANA M, BEJ S, ANCHEYTA-JUAREZ J, DHAR G M, RAO T P. TiO2-ZrO2 mixed oxide as a support for hydrotreating catalyst[J]. Catal lett, 2001, 72:115-119. doi: 10.1023/A:1009045412926 [13] LI K T, WANG I, WU J C. Surface and catalytic properties of TiO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides[J]. Catal Surv Asia, 2012, 16(4):240-248. doi: 10.1007/s10563-012-9147-y [14] MANRIQUEZ M, LOPEZ T, GOMEZ R, NAVARRETE J. Preparation of TiO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides with controlled acid-basic properties[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2004, 220(2):229-237. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2004.06.003 [15] AN M, LI L, CAO Y, MA F, LIU D, GU F. Coral reef-like Pt/TiO2-ZrO2 porous composites for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production performance[J]. Mol Catal, 2019, 475:110482. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2019.110482 [16] FAN M, SI Z, SUN W, ZHANG P. Sulfonated ZrO2-TiO2 nanorods as efficient solid acid catalysts for heterogeneous esterification of palmitic acid[J]. Fuel, 2019, 252:254-261. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.121 [17] 梁晓峰, 杨世源, 王军霞.醇热合成ZrO2粉末的X射线衍射及拉曼散射特征[J].人工晶体学报, 2008, 37(4):1037-1041. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2008.04.054LIANG Xiao-feng, YANG Shi-yuan, WANG Jun-xia. X-ray and raman studies of ZrO2 particles synthesized by alcohol-thermal method[J]. J Synth Cryst, 2008, 37(4):1037-1041. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2008.04.054 [18] POWERS D, GRAY H B, Characterization of the thermal dehydration of zirconium oxide halide octahydrates[J]. Inorg Chem, 1973, 12(11):2721-2726. doi: 10.1021/ic50129a045 [19] KILO M, SCHILD C, WOKAUN A, BAIKER A. Surface oxidic phases of binary and ternary zirconia-supported metal catalysts investigated by raman spectroscopy[J]. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans, 1992, 88:1453-1457. doi: 10.1039/ft9928801453 [20] MICIUKIEWICZ J, MANG T, KNOZINGER H. Raman spectroscopy characterization of molybdena supported on titania-zirconia mixed oxide[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 1995, 122(2):151-159. doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(94)00236-3 [21] 孙传智. TiO2基催化剂的制备、表征及其在环境催化中应用的基础研究[M].南京:南京大学, 2011.SUN Chuan-zhi. Synthesis and Characterization of Titanium Oxide Based Catalysts and Their Application in the Environmental Catalysis[M]. Nanjing:Nanjing University, 2011. [22] REDDY B M, CHOWDHURY B, SMIRNIOTIS P G. An XPS study of the dispersion of MoO3 on TiO2-ZrO2, TiO2-SiO2, TiO2-Al2O3, SiO2-ZrO2, and SiO2-TiO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2001, 211(1):19-30. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00834-6 [23] MULLINS W, AVERBACH B. Bias-reference X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy of sapphire and yttrium aluminum garnet crystals[J]. Surf Sci, 1988, 206(1/2):29-40. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/003960288890012X [24] STEPHENSON D, BINKOWSKI N. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of silica in theory and experiment[J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 1976, 22(2):399-421. doi: 10.1016/0022-3093(76)90069-7 [25] BARTHOS R, LONYI F, ENGELHARDT J, VALYON J. A study of the acidic and catalytic properties of pure and sulfated zirconia-titania and zirconia-silica mixed oxides[J]. Top Catal, 2000, 10:79-87. doi: 10.1023/A:1019112017065 [26] GOTT T, OYAMA S T. A general method for determining the role of spectroscopically observed species in reaction mechanisms:Analysis of coverage transients(ACT)[J]. J Catal, 2009, 263(2):359-371. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2009.02.028 [27] HONG E, BAEK S W, SHIN M, SUH Y W, SHIN C H. Effect of aging temperature during refluxing on the textural and surface acidic properties of zirconia catalysts[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2017, 54:137-145. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.05.026 [28] EMEIS C. Determination of integrated molar extinction coefficients for infrared absorption bands of pyridine adsorbed on solid acid catalysts[J]. J Catal, 1993, 141:347-354. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1993.1145 [29] TANABE K, SUMIYOSHI T, SHIBATA K, KIYOURA T, KITAGAWA J. A new hypothesis regarding the surface acidity of binary metal oxides[J]. Bull Chem Soc Jpn, 1974, 47:1064-1066. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.47.1064 [30] DAS D, MISHRA H K, PARIDA K M. Preparation, physico-chemical characterization and catalytic activity of sulphated ZrO2-TiO2 mixed oxides[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2002, 189:271-282. doi: 10.1016/S1381-1169(02)00363-1 -





 下载:
下载: