Effect of co-pyrolysis of different plastics with sewage sludge on heavy metals in the biochar
-
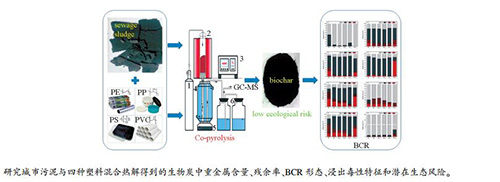
摘要: 利用高温管式炉开展城市污泥(SS)与四种塑料(PE、PP、PS和PVC)混合热解实验,分别得到四种生物炭(SSCPE、SSCPP、SSCPS和SSCPVC),研究了生物炭中重金属(Cr、Mn、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd和Pb)含量、残余率、BCR形态和TCLP浸出毒性特征,并开展潜在生态风险评估。结果表明,添加不同塑料与污泥混合热解能够降低除Cd以外重金属的残余率。与污泥单独热解所得生物炭(SSC)相比,添加PE、PP和PS能够促进生物炭中的重金属向相对稳定态(F3+F4)转化,实现固化稳定;添加PVC仅对生物炭中Cr和As有固化稳定作用,对其他重金属有明显活化作用。四种生物炭中的重金属浸出量低于GB5085.3-2007浸出毒性鉴别标准规定的限值,生态风险均明显地降低至轻微风险水平,表明添加PE、PP、PS和PVC与污泥混合热解所得生物炭的应用不会带来新的环境风险,这为污泥与废塑料协同处置工艺提供了良好的理论支撑。Abstract: The experiments of sewage sludge (SS) co-pyrolysis with four kinds of plastics (PE, PP, PS and PVC) were carried out in a high temperature tubular furnace to obtain four kinds of biochar (SSCPE, SSCPP, SSCPS and SSCPVC), respectively. The contents, residual rates, BCR speciation, leaching toxicity and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals (Cr, Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd and Pb) in biochar were studied. The results show that the residues of heavy metals except Cd are reduced by adding different kinds of plastics during SS pyrolysis. Compared with the biochar (SSC) obtained by SS pyrolysis, the addition of PE, PP and PS can promote the transformation of heavy metals speciation in biochar to more stable fractions (F3+F4) and achieve the immobilization of heavy metals. The addition of PVC only promotes the immobilization of Cr and As in biochar, while exhibiting an obvious activation effect on other heavy metals. The concentrations of leaching heavy metals in four kinds of biochar are lower than the limit value of the identification standard for extraction (GB5085.3-2007), and the potential ecological risks of the four kinds of biochar are all in a slight level. This work provides a good theoretical support for the process of the cooperative disposal of SS and waste plastics.
-
Key words:
- sewage sludge /
- plastics /
- co-pyrolysis /
- heavy metals /
- speciation analysis /
- leaching toxicity /
- risk assessment
-
表 1 实验材料的基本性质
Table 1 Basic properties of experimental materials
Sample Proximate analysisa wa/% Ultimate analysis wa/% Qb, a/(kJ·g-1) V A FC C H N S Ob SS 29.97 68.29 1.74 15.79 3.13 1.81 0.72 10.26 11.50 PE 99.72 0.23 0.05 83.99 13.89 0.03 1.30 0.56 45.90 PP 98.19 0.82 0.99 83.91 13.55 0.56 0.92 0.24 44.00 PS 99.15 0.77 0.08 91.05 7.12 0.02 0.85 0.19 45.90 PVC 98.15 1.31 0.54 38.90 5.67 0.01 0.78 53.33 18.80 a: dry basis; b: by difference Fraction Extraction steps F1 exchangeable fraction 0.5 g of dry sample is mixed with 20 mL of 0.11 mol/L acetic acid by shaking for 16 h (25 ℃) F2 reducible fraction the dry residue of F1 is mixed with 20 mL of 0.5 mol/L hydroxylamine hydrochloride by shaking for 16 h (25 ℃) F3 oxidizable fraction the dry residue of F2 is mixed 5 mL 30% hydrogen peroxide for 1 h at room temperature and then another 5 mL of hydrogen peroxide is added after digestion for 1 h at 85 ℃; when the solution is evaporated to be near dried the residue is mixed with 25 mL of 1 mol/L ammonium acetate by shaking for 16 h (25 ℃) F4 residual fraction 0.1g dry residue of F3 is digested in an acid mixture (HNO3-HClO4-HF/HNO3-H2O2) by graphite digester Er IR Potential ecological risk Er≤40 IR≤150 low 40<Er≤80 150<IR≤300 moderate 80<Er≤160 300<IR≤600 considerate 160<Er≤320 IR>600 high Er>320 very high 表 4 污泥及生物炭中重金属的浸出量
Table 4 Leaching concentrations of heavy metals in sludge and biochars
Sample Concentration c/(mg·L-1) Cr Mn Ni Cu Zn As Cd Pb SS 0.57±0.01 5.08±1.03 39.50±5.00 4.15±0.01 44.76±8.82 0.07±0.01 0.16±0.01 0.01±0.00 SSC 0.04±0.00 2.80±0.86 0.62±0.01 6.43±0.09 16.88±3.22 0.05±0.00 0.01±0.00 0.01±0.00 SSCPE 0.13±0.00 3.60±0.55 1.30±0.00 34.73±9.09 86.48±9.38 0.03±0.00 0.05±0.01 0.00±0.00 SSCPP 0.05±0.00 3.45±0.25 1.40±0.05 35.79±1.34 91.79±7.09 0.02±0.00 0.06±0.02 0.00±0.00 SSCPS 0.03±0.00 4.95±0.28 0.75±0.09 3.54±0.51 19.35±1.29 0.05±0.01 0.01±0.00 0.00±0.00 SSCPVC 0.02±0.00 9.51±1.25 2.40±0.07 98.23±10.12 74.40±5.54 0.01±0.00 0.04±0.01 0.02±0.01 Limits
value[42]*15 - 5 100 100 5 1 5 *: from 《dentification standards for hazardous wastes-Identification for extraction toxicity》(GB5085.3—2007) 表 5 污泥及生物炭中重金属的潜在生态风险系数与指数
Table 5 Potential ecological risk factors and indices of heavy metals in sludge and biochar
Sample Er IR Potential ecological risk Cr Mn Ni Cu Zn As Cd Pb SS 51.88 3.57 67.05 40.00 3.93 4.51 131.82 0.08 302.84 considerate SSC 2.22 3.57 39.40 24.75 6.60 5.53 25.68 0.09 107.86 low SSCPE 1.04 3.52 38.86 17.69 4.72 6.36 8.99 0.09 81.27 low SSCPP 1.37 3.06 43.85 19.19 4.91 4.05 16.18 0.10 92.73 low SSCPS 4.77 3.90 56.34 26.41 5.87 3.27 4.61 0.10 105.27 low SSCPVC 0.00 4.46 24.41 28.81 5.59 2.21 5.61 0.40 71.48 low -
[1] 彭成法, 肖汀璇, 李志建.热解温度对污泥基生物炭结构特性及对重金属吸附性能的影响[J].环境科学研究, 2017, 30(10):1637-1644. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxyj201710018PENG Cheng-fa, XIAO Ting-xuan, LI Zhi-jian. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on structural properties of sludge-based biochar and its adsorption for heavy metals[J]. Res Environ Sci, 2017, 30(10):1637-1644. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxyj201710018 [2] FERNÁNDEZ J M, NIETO M A, LÓPEZDESÁ E G, GASCÓ G, MÓNDEZ A, PLAZA C. Carbon dioxide emissions from semi-arid soils amended with biochar alone or combined with mineral and organic fertilizers[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2014, 482/483(1):1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_f6c3c9569d953bc0681cb00c3e5e4501 [3] RULKENS W. Sewage Sludge as a biomass resource for the production of energy:Overview and assessment of the various options[J]. Energy Fuels, 2008, 22(1):9-15. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f736efc935bc7f81c860925832f3d98c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [4] JIN J W, WANG M Y, CAO Y C, WU S C, LIANG P, LI Y N, ZHANG J Y, WONG M H, SHAN S D, CHRISTIE P. Cumulative effects of bamboo sawdust addition on pyrolysis of sewage sludge:Biochar properties and environmental risk from metals[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2017, 228:218-226. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=09386f378201de7b210beceddb565161&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] KISTLER R C, WIDMER F, BRUNNER P H. Behavior of chromium, nickel, copper, zinc, cadmium, mercury, and lead during the pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1987, 21(7):704-708. doi: 10.1021/es00161a012 [6] DEVI P, SAROHA A K. Risk analysis of pyrolyzed biochar made from paper mill effluent treatment plant sludge for bioavailability and eco-toxicity of heavy metals[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2014, 162(162C):308-315. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c0ec0616961176af1f933755be7bcd39 [7] PINTO F, COSTA P, GULYURTLU I, CABRITA I. Pyrolysis of plastic wastes. 1. Effect of plastic waste composition on product yield[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 1999, 51(1/2):39-55. doi: 10.1016-S0165-2370(99)00007-8/ [8] LETTIERI P, AL-SALEM S M. Thermochemical treatment of plastic solid waste[J]. J Cardiovasc Surg, 2011, 10(4):314-319. [9] WILLIAMS P T, SLANEY E. Analysis of products from the pyrolysis and liquefaction of single plastics and waste plastic mixtures[J]. Resour Conserv Recycl, 2007, 51(4):754-769. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2006.12.002 [10] SARKER M. Converting waste plastic to hydrocarbon fuel materials[J]. Energy Eng, 2011, 108(2):35-43. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e485bb1a0d0c8c41274a28c7fd09e6a2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] UÇAR S, KARAGÖZ S, YANIK J, SAGLAM M, YUKSEL M. Copyrolysis of scrap tires with waste lubricant oil[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2005, 87(1):53-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2005.06.001 [12] THOMPSON R C, SWAN S H, MOORE C J, VOM SAAL F S. Our plastic age[J]. Philos Trans R Soc B, 2009, 364(1526):1973. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0054 [13] YAMAMOTO T, YASUHARA A, SHIRAISHI H, NAKASUGI O. Bisphenol A in hazardous waste landfill leachates[J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 42(4):415-418. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00079-5 [14] LI C X, WANG X D, ZHANG G Y, YU G W, LIN J J, WANG Y. Hydrothermal and alkaline hydrothermal pretreatments plus anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge for dewatering and biogas production:Bench-scale research and pilot-scale verification[J]. Water Res, 2017, 117:49-57. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a699c5e8f29b9291a108e2cffb139907&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [15] WANG X D, LI C X, ZHANG B, LIN J J, CHI Q Q, WANG Y. Migration and risk assessment of heavy metals in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment combined with pyrolysis[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2016, 221:560-567. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.069 [16] LI C X, WANG X D, ZHANG G Y, LI J, LI Z, YU G, WANG Y W. A process combining hydrothermal pretreatment, anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis for sewage sludge dewatering and co-production of biogas and biochar:Pilot-scale verification[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2018, 254:187-193. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b28444a0f2f1fbc786c91871e1dbcd4d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] 谢胜禹, 余广炜, 李杰, 尤甫天, 汪刚, 汪印, 马建立, 商晓甫.污泥水热联合热解处理对固相产物中重金属的影响[J].环境工程学报, 2018, 12(7):2114-2122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201807030XIE Sheng-yu, YU Guang-wei, LI Jie, YOU Fu-tian, WANG Gang, WANG Yin, MA Jian-li, SHANG Xiao-fu. Effects of hydrothermal treatment coupled pyrolysis on heavy metals in solid products from sewage sludge[J]. J Environ Eng, 2018, 12(7):2114-2122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201807030 [18] 李智伟, 王兴栋, 林景江, 陆江银, 赵焕平, 汪印.污泥生物炭制备过程中氮磷钾及重金属的迁移行为[J].环境工程学报, 2016, 10(3):1392-1399. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201603062LI Zhi-wei, WANG Xing-dong, LIN Jing-jiang, LU Jiang-yin, CHAO Huan-ping, WANG Yin. Transformation of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and heavy metals during sewage sludge biochar preparation[J]. J Environ Eng, 2016, 10(3):1392-1399. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201603062 [19] YU G W, WANG Y, ZHANG X, TANG X D, LI J, YU Z, WANG X D, YOU F T. Influence of sludge and sludge biochar on the transfer of available heavy metals in soil[J]. J Mater Cycles Waste, 2016, 42(1):814-823. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0ec6c043952fb5bb68257626f1e7d403&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] LI J, YU G W, XIE S Y, PAN L J, LI C X, YOU F T, WANG Y. Immobilization of heavy metals in ceramsite produced from sewage sludge biochar[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2018, 628/629:131-140. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.036 [21] 余广炜, 廖洪强, 钱凯, 李保庆, 蔡九菊, 李东涛.利用焦化工艺处理废塑料技术研究Ⅰ.热天平与10 g固定床实验[J].燃料化学学报, 2004, 32(1):23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2004.01.005YU Guang-wei, LIAO Hong-qiang, QIAN Kai, LI Bao-qing, CAI Jiu-ju, LI Dong-tao. Disposal of waste plastics by coking processⅠ. Experiments of TG and 10g fixed-bed reactor[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2004, 32(1):23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2004.01.005 [22] 余广炜, 廖洪强, 钱凯, 李东涛, 蔡九菊.利用焦化工艺处理废塑料技术研究Ⅱ. 200kg焦炉中试试验[J].燃料化学学报, 2004, 32(1):27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2004.01.006YU Guang-wei, LIAO Hong-qiang, QIAN Kai, LI Dong-tao, CAI Jiu-ju. Disposal of waste plastics by coking processⅡ. 200kg coking-oven Experiment[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2004, 32(1):27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2004.01.006 [23] 余广炜, 汪印, 王兴栋, 邢贞娇, 李智伟, 李蒙.一种废塑料与污泥混合制备炭吸附材料的方法及系统: 中国, 103951153A[P]. 2014-07-30.YU Guang-wei, WANG Yin, WANG Xing-dong, XING Zhen-jiao, LI Zhi-wei, LI Meng. Method and system for preparing carbon adsorbent material by mixing waste plastics with sludge: CN, 103951153A[P]. 2014-07-30. [24] SCOTT D S, CZERNIK S R, PISKORZ J, RADLEIN D S A G. Fast pyrolysis of plastic wastes[J]. Energy Fuels, 1990, 4(4):407-411. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e06f0604a47897a5e2afd99e73c3d241&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [25] SUNGUR A, SOYLAK M, OZCAN H. Investigation of heavy metal mobility and availability by the BCR sequential extraction procedure:Relationship between soil properties and heavy metals availability[J]. Chem Spec Bioavailability, 2014, 26(4):219-230. doi: 10.3184/095422914X14147781158674 [26] 李杰, 潘兰佳, 余广炜, 汪印, 尤甫天, 谢胜禹.污泥生物炭制备吸附陶粒[J].环境科学, 2017, 38(9):3970-3978. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201709051LI Jie, PAN Lan-jia, YU Guang-wei, WANG Yin, YOU Fu-tian, XIE Sheng-yu. Preparation of adsorption ceramsite derived from sludge biochar[J]. Environ Sci, 2017, 38(9):3970-3978. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201709051 [27] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:A sediment ecological approach[J]. Water Res, 1980, 14(8):975-1001. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=914b2e137e72e20dd44b58b5b2a946f1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [28] 刘敬勇, 孙水裕, 陈涛.固体添加剂对污泥焚烧过程中重金属迁移行为的影响[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(3):1166-1173. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201303049LIU Jing-yong, SUN Shui-yu, CHEN Tao. Effects of adsorbents on partitioning and fixation of heavy metals in the incineration process of sewage sludge[J]. Environ Sci, 2013, 34(3):1166-1173. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201303049 [29] 于洁.城市生活垃圾(MSW)热处理过程中重金属的迁移与分布[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2013.YU Jie. The behavior and partitioning of heavy metals during thermal treatment of municipal solid waste[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2013. [30] 钱亚平.煤和生物质共气化过程中铬、汞和铅的迁移[D].上海: 华东理工大学, 2013.QIAN Ya-ping. Migration of Cr, Hg and Pb in Coal and Biomass Co-gasification[D]. Shanghai: East China University Of Science And Technology, 2013. [31] CHIANG K Y, WANG K S, LIN F L, CHU W T. Chloride effects on the speciation and partitioning of heavy metal during the municipal solid waste incineration process[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2010, 203(2):129-140. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=76c0618d8fea8f01b0bbf87834bf51f0 [32] SAQIB N, BÄCKSTRÖM M. Trace element partitioning in ashes from boilers firing pure wood or mixtures of solid waste with respect to fuel composition, chlorine content and temperature[J]. Waste Manage, 2014, 34(12):2505-2519. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.08.025 [33] 赵晶晶, 周少奇, 陈安安, 林奕明.城市污泥与花生壳制活性炭的重金属形态分析及生态风险评价[J].农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(11):2284-2289.ZHAO Jing-jing, ZHOU Shao-qi, CHEN An-an, LIN Yi-ming. Morphological analysis and ecological risk assessment on heavy metals in the activated carbon prepared from sewage sludge and peanut hull[J]. J Agro Environ Sci, 2012, 31(11):2284-2289. [34] 刘亚纳, 郭旭明, 周鸣, 朱书法, 苗娟, 赫文莉.洛阳城市污水处理厂污泥中重金属形态及潜在生态风险评价[J].环境工程学报, 2017, 11(2):1217-1222. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201702087LIU Ya-na, GUO Xu-ming, ZHOU Ming, ZHU Shu-fa, MIAO Juan, HE Wen-li. Heavy metal speciation and its potential ecological risk assessment in sewage sludge of Luoyang[J]. J Environ Eng, 2017, 11(2):1217-1222. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201702087 [35] HUANG H J, YUAN X Z. The migration and transformation behaviors of heavy metals during the hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2016, 200:991-998. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f916fb7d8c52b3b583c3a018c59a66e1 [36] 郭波, 许思思, 李评, 徐自壹.废塑料的处理与利用技术研究[J].中国人口·资源与环境, 2013, 23(S2):408-411. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200401005GUO Bo, XU Si-si, LI Ping, XU Zi-yi. Study on processing and application technologies of waste plastics[J]. China Popul Resour Environ, 2013, 23(S2):408-411. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rlhxxb200401005 [37] FUENTES A, LLORÉNS M, SÁEZ J, AGUILAR M A I, ORTUÑO J F, MESEGUER V F. Comparative study of six different sludges by sequential speciation of heavy metals[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2008, 99(3):517-525. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.025 [38] SHI W S, LIU C G, SHU Y J, FENG C P, LEI Z F, ZHANG Z Y. Synergistic effect of rice husk addition on hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge:Fate and environmental risk of heavy metals[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2013, 149(12):496-502. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d2ddcf32ab7803261c043bc944a38ef3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [39] 张大磊, 李公伟, 李卫华, 孔海南, 孙英杰.聚乙烯塑料/铬渣共热解还原Cr(Ⅵ)的实验研究[J].中国环境科学, 2017, 37(5):1852-1857. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.031ZHANG Da-lei, LI Gong-wei, LI Wei-hua, KONG Hai-nan, SUN Ying-jie. Experimental study on reduction of Cr(VI) by co-pyrolysis of polyethylene/chromite ore processing residue[J]. China Environ Sci, 2017, 37(5):1852-1857. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.031 [40] TANG P, ZHOU Y C, MIAO Z. Immobilization of heavy metals in sludge using phosphoric acid and monobasic calcium phosphate[J]. J Zhenjiang Univ-Sci A(Appl Phys Eng), 2013, 14(3):177-186. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjdxxb-e201303002 [41] POOLE D, ARGENT B B, SHARIFI V N, SWITHENBANK J. Prediction of the distribution of alkali and trace elements between the condensed and gaseous phases in a municipal solid waste incinerator[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(7):1318-1333. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ebc1fd2a1b6d23fb208d1a6227e7b6c2 [42] GB5085.3-2007, 危险废物鉴别标准浸出毒性鉴别[S].GB5085.3-2007, Identification standards for hazardous wastes-Identification for extraction toxicity[S]. -





 下载:
下载: