CuO/ZrO2 catalysts for the production of H2 through the water-gas shift reaction: Effect of calcination temperature of ZrO2
-
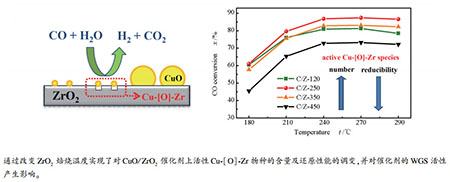
摘要: 以经不同温度(120、250、350、450 ℃)焙烧处理的ZrO2为载体,采用沉积-沉淀法制备了系列CuO/ZrO2催化剂;考察了富氢气氛下催化剂的水煤气变换反应(WGS)催化性能。结果表明,CuO/ZrO2催化剂的催化活性随ZrO2载体焙烧温度的升高呈现先升高后降低的"火山型"变化趋势,在焙烧温度为250 ℃时取得最高值。采用X射线粉末衍射、N2物理吸附-脱附、N2O滴定、H2程序升温还原和CO程序升温还原及质谱跟踪等技术研究了系列ZrO2载体及CuO/ZrO2催化剂的结构和还原性能。结果表明,随着ZrO2焙烧温度的升高,一方面,CuO/ZrO2催化剂的Cu分散度逐渐降低,与ZrO2具有强相互作用的高分散活性Cu-[O]-Zr物种("[]"表示ZrO2表面氧空位)逐渐减少;另一方面,Cu-[O]-Zr物种的还原能力逐渐增强,并诱导催化剂活性表面羟基的还原能力也相应增强(CO为还原剂),即降低了催化剂对WGS反应的起活温度。两方面的综合作用使得ZrO2载体焙烧温度为250 ℃(中等温度)时,CuO/ZrO2催化剂的WGS催化活性最高。
-
关键词:
- CuO/ZrO2催化剂 /
- 水煤气变换反应 /
- ZrO2焙烧温度 /
- CO程序升温还原 /
- 表面羟基
Abstract: A series of CuO/ZrO2 catalysts were prepared by a deposition-precipitation method using ZrO2 calcined at various temperatures (120, 250, 350 and 450℃) as supports. The water-gas shift (WGS) reaction was carried out on these catalysts using H2 rich reactant gas (15% CO, 55% H2, 23% N2, 7% CO2). It was shown that the catalytic activity of the catalysts increased at first and then decreased with increasing calcination temperature of ZrO2. The catalyst supported on ZrO2 calcined at 250℃ showed the highest catalytic activity. The structure and reducibility of CuO/ZrO2 catalysts were studied by various techniques, such as XRD, N2-physisorption, N2O titration, H2-TPR and CO-TPR-MS. The results show that the Cu dispersion and the proportion of catalytically active Cu-[O]-Zr species ("[]" represents an oxygen vacancy on ZrO2 support) decrease with the increase of ZrO2 calcination temperature. The calcination of ZrO2 at higher temperature leads to an improvement of the reducibility of Cu-[O]-Zr species and hydroxyl groups on the CuO/ZrO2 catalysts, resulting in an easier onset of the surface WGS reaction between surface hydroxyl groups and CO reductant. The two factors reach a balance for the catalyst supported on ZrO2 calcined at 250℃ (moderate temperature), as is thought to be responsible for the highest WGS activity of this catalyst. -
表 1 经不同温度焙烧的ZrO2载体及相应CuO/ZrO2催化剂的结构性质
Table 1 Structural properties of the ZrO2 support calcined at different temperatures and corresponding CuO/ZrO2 catalysts
Sample Cu contenta
w/%dCub/% ACuc/% DZrO2d/nm ABET
/(m2·g-1)Pore volume
v/(cm3·g-1)Z-120 - - - 5.2 120 0.261 Z-250 - - - 5.7 124 0.282 Z-350 - - - 6.4 111 0.186 Z-450 - - - 9.2 59 0.147 C/Z-120 8.2 60.6 41.3 4.8 70 0.264 C/Z-250 8.2 57.8 39.4 5.6 80 0.270 C/Z-350 8.4 52.9 37.3 6.8 81 0.297 C/Z-450 8.3 30.2 20.8 9.7 53 0.254 a: measured by ICP-OES; b: Cu dispersion calculated from N2O titration results; c: Cu metal area calculated from N2O titration results; d: crystallite size of m-ZrO2 calculated by the Scherrer equation using the diffraction at 2θ=32.8° 表 2 不同温度焙烧的ZrO2为载体的CuO/ZrO2催化剂的还原性能
Table 2 Reducibility of the CuO/ZrO2 catalysts prepared withthe ZrO2 supports calcined at different temperatures
Sample H2-TPR peak temperature(℃) and
H2 consumption(μmol·g-1)aCO-TPR-MS peak
temperature t/℃Relative concentration
of active OHbpeak α peak β peak γ peak β peak δ C/Z-120 153(366) 170(595) 187(73) 208 287 0.84 C/Z-250 151(382) 164(479) 188(148) 163 254 1.00 C/Z-350 143(278) 153(290) 189(455) 159 233 0.96 C/Z-450 136(115) 144(146) 195(741) 157 230 0.58 a: values in parentheses are the H2 consumption calculated by fitting results; b: calculated from the H2 signal peak (m/z = 2) area in CO-TPR-MS profiles by assuming the relative concentration of active OH in C/Z-250 is 1.00 -
[1] LEVALLEY T L, RICHARD A R, FAN M. The progress in water gas shift and steam reforming hydrogen production technologies-A review[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(30):16983-17000. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.08.041 [2] YAO S, ZHANG X, ZHOU W, GAO R, XU W, YE Y, LIN L, WEN X, LIU P, CHEN B, CRUMLIN E, GUO J, ZUO Z, LI W, XIE J, LU L, KIELY C J, GU L, SHI C, RODRIGUEZ J A, MA D. Atomic-layered Au clusters on α-MoC as catalysts for the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6349):389-393. doi: 10.1126/science.aah4321 [3] STERE C E, ANDERSON J A, CHANSAI S, DELGADO J J, GOGUET A, GRAHAM W G, HARDACRE C, TAYLOR S F R, TU X, WANG Z Y, YANG H. Non-thermal plasma activation of gold-based catalysts for low-temperature water-gas shift catalysis[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2017, 56(20):5579-5583. doi: 10.1002/anie.201612370 [4] PAL D B, CHAND R, UPADHYAY S N, MISHRA P K. Performance of water gas shift reaction catalysts:A review[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev, 2018, 93:549-565. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.05.003 [5] ABDEL-MAGEED A M, KUCEROVA G, BANSMANN J, BEHM R J. Active Au species during the low-temperature water gas shift reaction on Au/CeO2:A time-resolved operando XAS and DRIFTS study[J]. ACS Catal, 2017, 7(10):6471-6484. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01563 [6] PALMA V, PISANO D, MARTINO M. Structured noble metal-based catalysts for the WGS process intensification[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(26):11745-11754. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.01.085 [7] AMMAL S C, HEYDEN A. Water-gas shift activity of atomically dispersed cationic platinum versus metallic platinum clusters on titania supports[J]. ACS Catal, 2017, 7(1):301-309. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b02764 [8] GUAN H L, LIN J, QIAO B T, MIAO S, WANG A Q, WANG X D, ZHANG T. Enhanced performance of Rh1/TiO2 catalyst without methanation in water-gas shift reaction[J]. AIChE J, 2017, 63(6):2081-2088. doi: 10.1002/aic.v63.6 [9] MA Y J, LIU B, JING M M, ZHANG R Y, CHEN J Y, ZHANG Y H, LI J L. Promoted potassium salts based Ru/AC catalysts for water gas shift reaction[J]. Chem Eng J, 2016, 287:155-161. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.119 [10] LIN J, WANG A Q, QIAO B T, LIU X Y, YANG X F, WANG X D, LIANG J X, LI J X, LIU J Y, ZHANG T. Remarkable performance of Ir1/FeOx single-atom catalyst in water gas shift reaction[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135(41):15314-15317. doi: 10.1021/ja408574m [11] XU M, YAO S, RAO D, NIU Y, LIU N, PENG M, ZHAI P, MAN Y, ZHENG L, WANG B, ZHANG B, MA D, WEI M. Insights into interfacial synergistic catalysis over Ni@TiO2-x catalyst toward water-gas shift reaction[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140(36):11241-11251. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b03117 [12] ZHANG Z, WANG S S, SONG R, CAO T, LUO L, CHEN X, GAO Y, LU J, LI W X, HUANG W. The most active Cu facet for low-temperature water gas shift reaction[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8:488. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00620-6 [13] YAN H, QIN X T, YIN Y, TENG Y F, JIN Z, JIA C J. Promoted Cu-Fe3O4 catalysts for low-temperature water gas shift reaction:Optimization of Cu content[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2018, 226:182-193. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.12.050 [14] CHEN C, ZHAN Y, LI D, ZHANG Y, LIN X, JIANG L, ZHENG Q. Preparation of CuO/CeO2 catalyst with enhanced catalytic performance for water-gas shift reaction in hydrogen production[J]. Energy Technol, 2018, 6(6):1096-1103. doi: 10.1002/ente.201700750 [15] CHEN C, ZHAN Y, ZHOU J, LI D, ZHANG Y, LIN X, JIANG L, ZHENG Q. Cu/CeO2 catalyst for water-gas shift reaction:Effect of CeO2 pretreatment[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2018, 19(12):1448-1455. doi: 10.1002/cphc.v19.12 [16] MA Y J, LIU B, OUYANG B, LI J L. Production of hydrogen from water-gas shift reaction over Ru-[BMIM]BF4/ZnO catalyst[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(7):4146-4154. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.10.111 [17] LI J, TA N, SONG W, ZHAN E, SHEN W. Au/ZrO2 catalysts for low-temperature water gas shift reaction:Influence of particle sizes[J]. Gold Bull, 2009, 42(1):48-60. doi: 10.1007/BF03214905 [18] CERÍN M L, HERRERA B, ARAYA P, GRACIA F, TORO-LABBÉ A. Influence of the monoclinic and tetragonal zirconia phases on the water gas shift reaction. A theoretical study[J]. J Mol Model, 2013, 19(7):2885-2891. doi: 10.1007/s00894-012-1706-7 [19] KOUVA S, HONKALA K, LEFFERTS L, KANERVO J. Review:Monoclinic zirconia, its surface sites and their interaction with carbon monoxide[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2015, 5:3473-3490. doi: 10.1039/C5CY00330J [20] KAUPPIK E I, HONKALA K, KRAUSE A O I, KANERVO J M, LEFFERTS L. ZrO2 acting as a redox catalyst[J]. Top Catal, 2016, 59(8/9):823-832. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0fe5103b646f97db090f7759469cbe80 [21] DOW W P, HUANG T J. Effects of oxygen vacancy of yttria-stabilized zirconia support on carbon monoxide oxidation over copper catalyst[J]. J Catal, 1994, 147(1):322-332. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1994.1143 [22] KO J B, BAE C M, JUNG Y S, KIM D H. Cu-ZrO2 catalysts for water-gas-shift reaction at low temperatures[J]. Catal Lett, 2005, 105(3/4):157-161. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fe19c33dbc1930256b29d99efdb62526 [23] CHEN C, RUAN C, ZHAN Y, LIN X, ZHENG Q, WEI K. The significant role of oxygen vacancy in Cu/ZrO2 catalyst for enhancing water-gas-shift performance[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(1):317-324. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.10.074 [24] AGUILA G, VALENZUELA A, GUERRERO S, ARAY P. WGS activity of a novel Cu-ZrO2 catalyst prepared by a reflux method. Comparison with a conventional impregnation method[J]. Catal Commun, 2013, 39:82-85. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.05.007 [25] TANG Q L, LIU Z P. Identification of the active Cu phase in the water-gas shift reaction over Cu/ZrO2 from first principles[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2010, 114(18):8423-8430. doi: 10.1021/jp100864j [26] 张燕杰, 陈崇启, 詹瑛瑛, 林棋, 娄本勇, 郑国才, 郑起. Y修饰CuO/ZrO2催化剂高效催化水煤气变换反应制氢[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(9):1137-1145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.09.015ZHANG Yan-jie, CHEN Chong-qi, ZHAN Ying-ying, LIN Qi, LOU Ben-yong, ZHENG Guo-cai, ZHENG Qi. Highly active Y-promoted CuO/ZrO2 catalysts for the production of hydrogen through water-gas shift reaction[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(9):1137-1145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.09.015 [27] SONG L, CAO X B, LI L. Engineering stable surface oxygen vacancies on ZrO2 by hydrogen-etching technology:An efficient support of gold catalysts for water-gas shift reaction[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10(37):31249-31259. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b07007 [28] ZHANG Y, ZHAN Y, CHEN C, CAO Y, LIN X, ZHENG Q. Highly efficient Au/ZrO2 catalysts for low-temperature water-gas shift reaction:Effect of pre-calcination temperature of ZrO2[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(17):12292-12300. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.06.025 [29] ZHANG Y, CHEN C, LIN X, LI D, CHEN X, ZHAN Y, ZHENG Q. CuO/ZrO2 catalysts for water-gas shift reaction:Nature of catalytically active copper species[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(8):3746-3754. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.12.161 [30] ZOU Z Q, MENG M, GUO L H, ZHA Y Q. Synthesis and characterization of CuO/Ce1-xTixO2 catalysts used for low-temperature CO oxidation[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2009, 163(2/3):835-842. [31] JACKSON S D, HARGREAVES J S J. Metal oxide catalysis (Vol.2)[M]. Weinheim:Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2009. [32] KWAK J H, HU J, MEI D, YI C, KIM D H, PEDEN C H F, ALLARD L F, SZANYI J. Coordinatively unsaturated Al3+ centers as binding sites for active catalyst phases of platinum on gamma-Al2O3[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5948):1670-1673. doi: 10.1126/science.1176745 [33] SING K S W, EVERETT D H, HAUL R A W, MOSCOU L, PIEROTTI R A, ROUQUÉROL J, SIEMIENIEWSKA T. Reporting physisorption date for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity[J]. Pure Appl Chem, 1985, 57(4):603-619. doi: 10.1351/pac198557040603 [34] WITOON T, CHALORNGTHAM J, DUMRONGBUNDITKUL P, CHAREONPANICH M, LIMTRAKUL J. CO2 hydrogenation to methanol over Cu/ZrO2 catalysts:Effects of zirconia phases[J]. Chem Eng J, 2016, 293:327-336. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.069 [35] HEEMEIER M, FRANK M, LIBUDA J, WOLTER K, KUHLENBECK H, BAUMER M, FREUND H J. The influence of OH groups on the growth of rhodium on alumina:A model study[J]. Catal Lett, 2000, 68(1/2):19-24. doi: 10.1023/A:1019058714724 [36] ZHANG X, SHI H, XU B. Vital roles of hydroxyl groups and gold oxidation states in Au/ZrO2 catalysts for 1, 3-butadiene hydrogenation[J]. J Catal, 2011, 279(1):75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2011.01.002 [37] ZHAI Y, PIERRE D, SI R, DENG W, FERRIN P, NILEKAR A U, PENG G, HERRON J A, BELL D C, SALTSBURG H, FLYTZANI-STEPHANOPOULOS M. Alkali-stabilized Pt-OHx species catalyze low-temperature water-gas shift reactions[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5999):1633-1636. doi: 10.1126/science.1192449 [38] SI R, RAITANO J, YI N, ZHANG L, CHAN S, FLYTZANI-STEPHANOPOULOS M. Structure sensitivity of the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction on Cu-CeO2 catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 2012, 180(1):68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.09.008 -





 下载:
下载: