Study on the transformation characteristics of microstructure in Shengli lignite during low-temperature oxidation
-
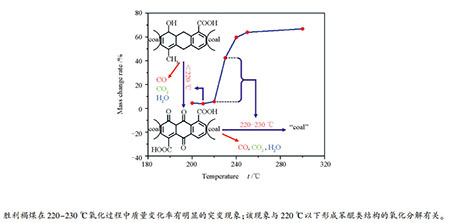
摘要: 选用内蒙古的胜利褐煤作为研究对象,通过固定床反应装置对褐煤进行不同温度(200-300 ℃)下的低温氧化,利用FT-IR、Raman和XPS等方法对氧化处理后煤样的结构进行了表征,考察了不同温度下低温氧化对褐煤微结构和质量变化的影响,并利用热重分析仪研究了氧化后煤样的燃烧反应性能。结果表明,温度对低温氧化过程中胜利褐煤的质量变化率影响较大,低于220 ℃时,褐煤的质量变化率很小,高于220 ℃时,质量变化率有明显的改变。特别在220-230 ℃,煤样的质量变化率由5.80%(220 ℃)突变为42.55%(230 ℃)。FT-IR/Raman/XPS表征结果显示,220 ℃氧化后的煤样中有明显的苯醌类结构形成,此结构的形成使苯环骨架C=C的伸缩振动吸收峰发生红移,且Raman谱图中D峰位置偏移,D峰和G峰两峰间距增大。氧化温度低于220 ℃的煤样表面C-O-和C=O的含量均增加,推测煤样在220-230 ℃质量变化率的突变主要与苯醌类结构的氧化分解有关。Abstract: A Shengli lignite from Inner Mongolia was selected as the research object, with which the low-temperature oxidation experiments were carried out at different temperatures (200-300℃) in a fixed bed reactor. The structure of coal samples after oxidation treatment was characterized by FT-IR, Raman and XPS. The effects of low-temperature oxidation at different temperatures on the microstructure and mass change of lignite were investigated and the combustion performance was determined by TGA. The results show that the temperature has a significant influence on mass change rate of Shengli lignite during low-temperature oxidation. The mass change rate of lignite is very limited when temperature is below 220℃ and it changes obviously when the temperature is higher than 220℃. Especially at 220-230℃, the mass change rate of coal samples is changed from 5.80% (220℃) to 42.55% (230℃). The FT-IR/Raman/XPS characterization results show that the analogous benzoquinone structure forms after oxidized at 220℃, and these lead to the stretching vibration absorption peak of the aromatic C=C shift to lower wavenumber. In Raman spectra, the position of the D peak shifts, and the distance between the peaks of D and G increases. The content of C-O-and C=O on the surface of coal samples increases at oxidation temperature lower than 220℃. It is speculated that the jump of mass change rate of coal samples at 220-230℃ is mainly related to the oxidative decomposition of analogous benzoquinone structure.
-
图 1 实验装置示意图
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the experimental installation
1: reaction carried gas; 2: gas chromatography; 3: mass flowmeter; 4: temperature thermocouple; 5: thermo detector; 6: temperature controlled thermocouple; 7: temperature control meter; 8: reactor; 9: ice-bath; 10: cold hydrazine; 11: treater; 12: back pressure meter; 13: six-way valve; 14: gas chromatography
表 1 SL的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of SL
Sample Proximate analysis wad/% Ultimate analysis w/% M A V FC C H S N & O SL 3.21 12.43 37.90 46.46 57.60 3.53 1.51 24.93 note: ad: air dried; M: moisture; A: ash content; V: volatile; FC: fixed carbon 表 2 SL及不同温度低温氧化煤样Raman光谱图中峰位置和峰间距
Table 2 Peak locations and spacing distances in the Raman spectra of SL and coal samples after low-temperature oxidation at different temperatures
Sample F(D) /cm-1 F(G) /cm-1 d(G-D)/cm-1 SL 1371 1594 223 SL-T (200, 210) 1371 1588 217 SL-220 1358 1588 230 SL-T (230, 240, 250, 300) 1371 1585 214 表 3 煤样中碳元素键合比例的分析
Table 3 Analysis for the content of carbon bonding forms in coal samples
Sample Carbon form (content w/%) C-C/C-H C*-C* C-O- C=O COO- SL 76.06 6.82 8.02 4.67 4.43 SL-200 76.28 6.14 8.36 4.72 4.50 SL-210 76.12 5.95 8.30 5.11 4.52 SL-220 76.34 5.13 8.46 5.40 4.67 SL-230 77.89 3.88 8.31 5.35 4.57 SL-240 78.68 3.74 7.73 5.32 4.53 SL-250 79.27 3.59 7.43 5.20 4.51 SL-300 78.51 3.58 7.97 5.31 4.63 -
[1] 宋洪柱.中国煤炭资源分布特征与勘查开发前景研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2013.SONG Hong-zhu. Study on the distribution characteristics and the exploration and development prospect of coal resource of China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2013. [2] 王美君, 付春慧, 常丽萍, 谢克昌.逐级酸处理对锡盟褐煤的结构及热解特性的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(8):906-911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.08.002WANG Mei-jun, FU Chun-hui, CHANG Li-ping, XIE Ke-chang. Effect of fractional step acid treatment process on the structure and pyrolysis characteristics of Ximeng brown coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(8):906-911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.08.002 [3] BARIS K, KIZGUT S, DIDARI V. Low-temperature oxidation of some Turkish coals[J]. Fuel, 2012, 93(1):423-432. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=831bc32a28cb96681ea1032249e29606 [4] KUCUK A, KADIOGLU Y, GULABOGLU M S. A study of spontaneous combustion characteristics of a Turkish lignite:Particle size, moisture of coal, humidity of air[J]. Combust Flame, 2003, 133(3):255-261. doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(02)00553-9 [5] SU H T, ZHOU F B, LI J S, QI H N. Effects of oxygen supply on low-temperature oxidation of coal:A case study of Jurassic coal in Yima, China[J]. Fuel, 2017, 202, 446-454. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.055 [6] 周沛然.煤低温氧化结构变化的红外光谱研究[J].煤炭转化, 2014, 37(1):15-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2014.01.004ZHOU Pei-ran. Infrared spectroscopy study on the change of low temperature oxidation structure of coal[J]. Coal Convers, 2014, 37(1):15-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2014.01.004 [7] LI B, CHEN G, ZHANG H, SHENG G D. Development of non-isothermal TGA-DSC for kinetics analysis of low temperature coal oxidation prior to ignition[J]. Fuel, 2014, 118(8):385-391. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=aae26c0de8ceac91d43860c3c6a9f5a1 [8] ZHOU C H, ZHANG Y L, WANG J F, XUE S, WU J M, CHANG L P. Study on the relationship between microscopic functional group and coal mass changes during low-temperature oxidation of coal[J]. Int J Coal Geol, 2017, 171:212-222. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2017.01.013 [9] QI X Y, CHEN L Z, ZHANG L B, BAI C W, XIN H H, RAO Z. In situ FT-IR study on real-time changes of active groups during lignite reaction under low oxygen concentration conditions[J]. J Energy Inst, 2018, 1-10. [10] WANG H, DLUGOGORSKI B Z, KENNEDY E M. Thermal decomposition of solid oxygenated complexes formed by coal oxidation at low temperatures[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(15):1913-1923. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00122-9 [11] 薛冰, 李再峰, 陈兴权, 李永昕, AGARWAL P K.低阶煤在干燥氧气下低温氧化过程的机理研究[J].煤炭转化, 2006, 29(2):12-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2006.02.004XUE Bing, LI Zai-feng, CHEN Xing-quan, LI Yong-xin, AGARWAL P K. Mechanism study on low temperature oxidation process of low rank coal under dry oxygen[J]. Coal Convers, 2006, 29(2):12-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2006.02.004 [12] 葛岭梅, 薛韩玲, 徐精彩, 邓军, 张辛亥.对煤分子中活性基团氧化机理的分析[J].煤炭转化, 2001, 24(3):23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2001.03.006GE Ling-mei, XUE Han-ling, XU Jing-cai, DENG Jun, ZHANG Xin-hai. Analysis of the oxidation mechanism of reactive groups in coal molecules[J]. Coal Convers, 2001, 24(3):23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2001.03.006 [13] 王彩萍, 邓军, 王伟峰.煤低温氧化过程中活性基团的FT-IR实验研究[J].电子世界, 2012, (18):74-75.WANG Cai-ping, DENG Jun, WANG Wei-feng. FT-IR experimental study of active groups in low temperature oxidation of coal[J]. Electron World, 2012, (18):74-75. [14] 李涛, 张辛亥, 吴康华, 王楠.煤低温氧化的红外光谱研究[J].价值工程, 2011, 30(21):32-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2011.21.022LI Tao, ZHANG Xin-hai, WU Kang-hua, WANG Nan. Research on coal low temperature oxidation with FTIR[J]. Value Eng, 2011, 30(21):32-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2011.21.022 [15] 褚廷湘, 杨胜强, 孙燕, 孙京凯, 刘增平.煤的低温氧化实验研究及红外光谱分析[J].中国安全科学学报, 2008, 18(1):171-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2008.01.030CHU Ting-xiang, YANG Sheng-qiang, SUN Yan, SUN Jing-kai, LIU Zeng-ping. Experimental study on low temperature oxidization of coal and its infrared spectrum analysis[J]. CSSJ, 2008, 18(1):171-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2008.01.030 [16] WANG G H, ZHOU A N. Time evolution of coal structure during low temperature air oxidation[J]. Int J Min Sci Technol, 2012, 22(4):517-521. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2012.01.013 [17] QI X Y, WANG D M, XIN H H, QI G S. An in situ testing method for analyzing the changes of active groups in coal oxidation at low temperatures[J]. Spectr Lett, 2014, 47(7):495-503. doi: 10.1080/00387010.2013.817433 [18] FUJITSUKA H, ASHIDA R, KAWASE M, MIURA K. Examination of low-temperature oxidation of low-rank coals, aiming at understanding their self-ignition tendency[J]. Energy Fuels, 2014, 28(4):2402-2407. doi: 10.1021/ef402484u [19] 董庆年, 陈学艺, 靳国强, 顾永达.红外发射光谱法原位研究褐煤的低温氧化过程[J].燃料化学学报, 1997, 25(4):333-338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RLHX704.009.htmDONG Qing-nian, CHEN Xue-yi, JIN Guo-qiang, GU Yong-da. In-situ study of low temperature oxidation of lignite by infrared emission spectroscopy[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 1997, 25(4):333-338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RLHX704.009.htm [20] 宋银敏, 李娜, 班延鹏, 滕英跃, 智科端, 何润霞, 周华从, 刘全生.燃烧反应过程中胜利脱灰褐煤微结构演变特性研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(12):1417-1423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.12.002SONG Yin-min, LI Na, BAN Yan-peng, TENG Ying-yue, ZHI Ke-duan, HE Run-xia, ZHOU Hua-cong, LIU Quan-sheng. Microstructure evolution characteristics of Shengli lignite during combustion process[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(12):1417-1423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.12.002 [21] LI Y, WANG Z H, HUANG Z Y, LIU J Z, ZHOU J H, CEN K F. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on lignite char properties and slurrying ability[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 134:52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.01.007 [22] 石金明, 向军, 胡松, 孙路石, 苏胜, 徐朝芬, 许凯.洗煤过程中煤结构的变化[J].化工学报, 2010, 61:3220-3227. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201012028SHI Jin-ming, XIANG Jun, HU Song, SUN Lu-shi, SU Sheng, XU Chao-fen, XU Kai. Change of coal structure during washing process[J]. CIESC J, 2010, 61:3220-3227. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201012028 [23] YURUM Y, ALTUNTAS N. Air oxidation of Beypazari lignite at 50℃, 100℃ and 150℃[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(15):1809-1814. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00067-2 [24] WU Q S, LI S P. Effect of surfactant/silica and hydrothermal time on the specific surface area of mesoporous materials from coal-measure kaolin[J]. J Wuhan Univ Technol, 2011, 26(3):514-518. doi: 10.1007/s11595-011-0259-4 [25] FERRARI A C, ROBERTSON J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon[J]. Phys Rev B, 2000, 61(20):14095-14107. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.61.14095 [26] FERREIRA E H M, MOUTINHO M V O, STAVALE F, LUCCHESE M M. CAPAZ R B, ACHETE C A, JORIO A. Evolution of the Raman spectra from single-, few-, and many-layer graphene with increasing disorder[J]. Phys Rev B, 2010, 82(12):4079-4085. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3220e92375a7840adf6c13947e830952 [27] 陈旺, 焦娜, 徐樑华, 曹维宇.碳纤维在石墨化处理过程中的sp2结构转变[J].宇航材料工艺, 2013, 43(5):46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2013.05.010CHEN Wang, JIAO Na, XU Liang-hua, CAO Wei-yu. Transition of sp2 hybridization structure during graphitization of carbon fiber[J]. Aerosp Mater Technol, 2013, 43(5):46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2013.05.010 [28] LI X J, HAYASHI J, LI C Z. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part Ⅷ. Catalysis and changes in char structure during gasification in steam[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(10):1518-1525. [29] DATSYUK V, GUERRET-PIECOURT C, DAGREOU S, BILLON L, DUPIN J C, FLAHAUT E, PEIGNEY A, LAURENT C. Double walled carbon nanotube/polymer composites via in situ nitroxide mediated polymerisation of amphiphilic block copolymers[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(4):873-876. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.10.052 [30] ZHANG N, XIE J, VARADAN V. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes by potassium permanganate assisted with phase transfer catalyst[J]. Smart Mater Struct, 2002, 11(6):962-965. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/11/6/318 [31] AGO H, KUGLER T, CACIALLI F, SALANECK W R, SHAFFER M S P, WINDLE A H, FRIEND R H. Work functions and surface functional groups of multiwall carbon nanotubes[J]. J Phys Chem B, 1999, 103(38):8116-8121. doi: 10.1021/jp991659y [32] 常海洲, 王传格, 曾凡桂, 李军, 李文英, 谢克昌.不同还原程度煤显微组分组表面结构XPS对比分析[J].燃料化学学报, 2006, 34(4):389-394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2006.04.002CHANG Hai-zhou, WANG Chuan-ge, ZENG Fan-gui, LI Jun, LI Wen-ying, XIE Ke-chang. XPS comparative analysis of coal macerals with different reducibility[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2006, 34(4):389-394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2006.04.002 -





 下载:
下载: