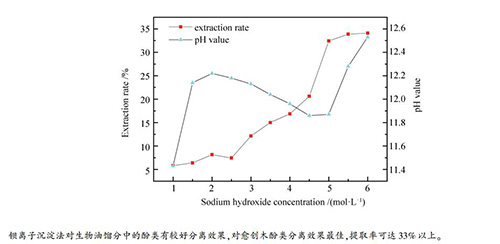
-
摘要: 从NaOH试剂浓度、反应温度与反应时间三个方面,对钡离子沉淀法提取不同温度段收集的生物油馏分中的酚类物质进行了实验研究,并利用气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-MS)对提取效果进行了分析。实验结果表明,钡离子沉淀法对愈创木酚类物质的提取效果较为突出,且NaOH浓度(1.0-6.0mol/L)、反应温度(30-50℃)与反应时间(10-40min)对愈创木酚的提取率影响较大。在NaOH浓度为5.5mol/L、反应温度为35℃、反应时间为20min时,提取率达到最大,其中,三个温度段收集的生物油即低温水相馏分、低温油相馏分与高温馏分中的愈创木酚提取率分别为34.1%、33.8%和33.5%。Abstract: The phenolic substances in the bio-oil fractions collected at different temperature intervals were extracted by barium ion precipitation method at different concentrations of NaOH reagent, reaction temperatures and reaction times, and the extraction effect was analyzed by GC-MS. The results show that the effect of barium ion precipitation on guaiacols separation is more outstanding. The temperature (30-50℃), concentration of NaOH (1.0-6.0 mol/L) and reaction time (10-40 min) have great influence on the extraction rate of guaiacols. The optimum reaction parameters include the NaOH solution of 5.5 mol/L, the temperature of 35℃ and the reaction time of 20 min. Under the optimum condition, the extraction rate of guaiacols in the three fractions of low temperature water, low temperature oil and high temperature are 34.1%, 33.8% and 33.5%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- bio-oil /
- bio-oil fraction /
- phenol /
- barium ion precipitation method /
- recycling
-
表 1 各馏分的得率与水分含量
Table 1 Yield and moisture content of each fraction
Name A B C Yield w/% 35.1 4.0 7.6 Moisture content w/% 63.7 5.8 6.7 A: the low-temperature water fraction; B: the low-temperature oil fraction; C: the high-temperature fraction 表 2 各馏分中所含酚类物质
Table 2 Chemical compositions of phenolic compounds from each fractions of bio-oil
Chemical compound Molecular formula Molecular weight/(g·mol-1) Structure Peak area/% A B C Phenol C6H6O 94 
0.81 0.35 o-Cresol C7H8O 108 
1.83 0.44 Guaiacol C7H8O2 124 
9.15 15.18 7.42 3, 4-dimethylphenol C8H10O 122 
0.6 2-methoxy-4-methylphenol C8H10O2 138 
2.79 7.34 1.52 3-methoxy-2-benzenediol C7H8O3 140 
1.27 4-ethyl-2-methoxyphenol C9H12O2 152 
0.55 4.48 9.66 1, 2, 3-benzenetriol, 5-(1, 1-dimethylethyl)- C10H14O3 182 
3.69 2, 6-dimethoxyphenol C8H10O3 154 
5.67 Phenol, 2-methoxy- 4-propyl- C10H14O2 166 
3.26 3-methylpheno C7H8O 108 
0.84 2, 3-dimethylphenol C8H10O 122 
0.8 5-allylguaiacol C10H12O2 164 
1.98 12.05 Phenol, 2-methoxy- 5-methyl-isocreosol(6CI) C8H10O2 138 
0.5 表 3 乙酸乙酯层GC-MS分析
Table 3 Phenolic compounds identified in the ethyl acetate layer by GC-MS
Chemical compound Molecular formula Molecular weight/(g·mol-1) Structure Peak area/% D E F Guaiacol C7H8O2 124 
8.95 10.65 6.49 2-methoxy-4-methylphenol C8H10O2 138 
7.85 14.32 11.24 4-ethyl-2-methoxyphenol C9H12O2 152 
6.33 15.15 11.62 2, 6-dimethoxyphenol C8H10O3 154 
2.75 8.38 5-allylguaiacol C10H12O2 164 
3.67 Phenol, 2-methoxy-4-propyl- C10H14O2 166 
4.9 14.1 14.72 Phenol, 2-methoxy- 4-(1-propen-1-yl)- C10H12O2 164 
1.56 6.51 1, 2, 3-benzenetriol, 5- (1, 1-dimethylethyl)- C10H14O3 182 
2.49 5.55 3-methoxy-2-benzenediol C7H8O3 140 
1.49 Naphthalene C10H8 128 
1.22 Benzenemethanol, 2, 5-dimethoxy- C9H12O3 168 
3.26 8.78 D: ethyl acetate layer obtained from the low-temperature water fraction; E: ethyl acetate layer obtained from the low-temperature oil fraction; F: ethyl acetate layer obtained from the high-temperature fraction -
[1] ŽILNIK L F, JAZBINŠEK A. Recovery of renewable phenolic fraction from pyrolysis oil[J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2012, 86(8):157-170. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4e26ff3fcaa0d1a7b1ad371c2aaca00d [2] QIANG L, LI W Z, ZHU X F. Overview of fuel properties of biomass fast pyrolysis oils[J].Energy Convers Manage, 2009, 50(5):1376-1383. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2009.01.001 [3] XIU S, SHAHBAZI A. Bio-oil production and upgrading research:A review[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev, 2012, 16(7):4406-4414. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2012.04.028 [4] 邹勇, 尉芹, 郑冀鲁, 李宏伟, 马希汉.生物油中酚类物质的富集工艺优化研究[J].西北林学院学报, 2016, 31(1):226-230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2016.01.39ZOU Yong, WEI Qin, ZHENG Ji-lu, LI Hong-wei, MA Xi-han. Optimization of the technology of enriching phenolic components from bio-oil[J]. J NW For Univ, 2016, 31(1):226-230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2016.01.39 [5] 赵欣, 李凯, 李明, 马善为, 朱锡锋.沉淀法回收生物油高温馏分中的酚类物质[J].燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(2):201-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2016.02.010ZHAO Xin, LI Kai, LI Ming, MA Shan-wei, ZHU Xi-feng.Separating phenols from high-temperature fraction of bio-oil by precipitation[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2016, 44(2):201-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2016.02.010 [6] 吕东灿, 刘运权, 王夺, 叶跃元.生物油的分离及其产品应用[J].林产化学与工业, 2013, 33(4):137-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2013.04.026LU Dong-can, LIU Yun-quan, WANG Duo, YE Yue-yuan.Separation of chemicals from bio-oil and their application prospects[J].Chem Ind For Prod, 2013, 33(4):137-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2013.04.026 [7] KANG S, LI X, FAN J. Classified separation of lignin hydrothermal liquefied products[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2011, 50(19):11288-11296. doi: 10.1021/ie2011356 [8] KIM J S. Production, separation and applications of phenolic-rich bio-oil-A review.[J]. Bioresource Technol, 2015, 178:90-98. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.121 [9] REVERCHON E, MARCO I D. Supercritical fluid extraction and fractionation of natural matter[J]. J Supercrit Fluid, 2006, 38(2):146-166. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2006.03.020 [10] AMEN-CHEN C, PAKDEL H, ROY C. Separation of phenols from eucalyptus, wood tar[J]. Biomass Bioenergy, 1997, 13(1):25-37. doi: 10.1016-j.jtcvs.2009.06.017/ [11] LI J H, CHAO W, YANG Z Y. Production and separation of phenols from biomass-derived bio-petroleum.[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2010, 89(2):218-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2010.08.004 [12] WANG D, LI D, LIU Y. Study of a new complex method for extraction of phenolic compounds from bio-oils[J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2014, 134(5):132-138. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fc8188145ffd8c0321547e71414b65ed [13] FU D, FARAG S, CHAOUKI J. Extraction of phenols from lignin microwave-pyrolysis oil using a switchable hydrophilicity solvent[J]. Bioresource Technol, 2014, 154(2):101-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=156bafac8f83eedef5d70d6642384ad2 [14] 葛宜掌, 金红, 李斌. Ba~(2+)离子沉淀法回收酚类化学过程的研究[J].燃料化学学报, 1996, 24(3):266-270. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600430536GE Yi-zhang, JIN Hong, LI Bin. Study on the chemical process of recovering phenols by Ba~(2+) ion precipitation[J].J Fuel Chem Technol, 1996, 24(3):266-270. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600430536 [15] 杨续来, 陆强, 朱锡锋.生物油的蒸馏特性及其应用[C].中国生物质能科学技术论坛, 2007. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=6589754YANG Xu-lai, LU Qiang, ZHU Xi-feng.Distillation characteristics and applications of biological oils[C]. Forum Biomass Energy Science and Technology in China, 2007. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=6589754 [16] GE Y, JIN H. Recovery process for phenolic compounds from coal-derived oils by ions of soluble metal salts[J]. Fuel, 1996, 75(14):1681-1683. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)00276-6 [17] GROENEWOLD G S, JOHNSON K M, FOX S C. Pyrolysis two-dimensional GC-MS of miscanthus biomass:Quantitative measurement using an internal standard method[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(2):1620-1630. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02645 [18] LEE J, CHO S, RODRIGUEZ J P. Determination of fatty acids from perilla cultivars and edible oils by GC-FID[J]. Planta Med, 2016, 81(S 01):S1-S381. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27976251 [19] 明珠, 吴云海, 阿依妮尕尔·艾尔肯.茶汤与金属离子络合反应的研究[J].环境科技, 2015, (4):5-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2015.04.002MING Zhu, WU Yun-hai, ARKEN Ayinigar.Study on complexation reaction of tea infusion with metal ions[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2015, (4):5-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2015.04.002 -





 下载:
下载: