Effects of adding CaO on the release and transformation of arsenic and sulfur during coal pyrolysis
-
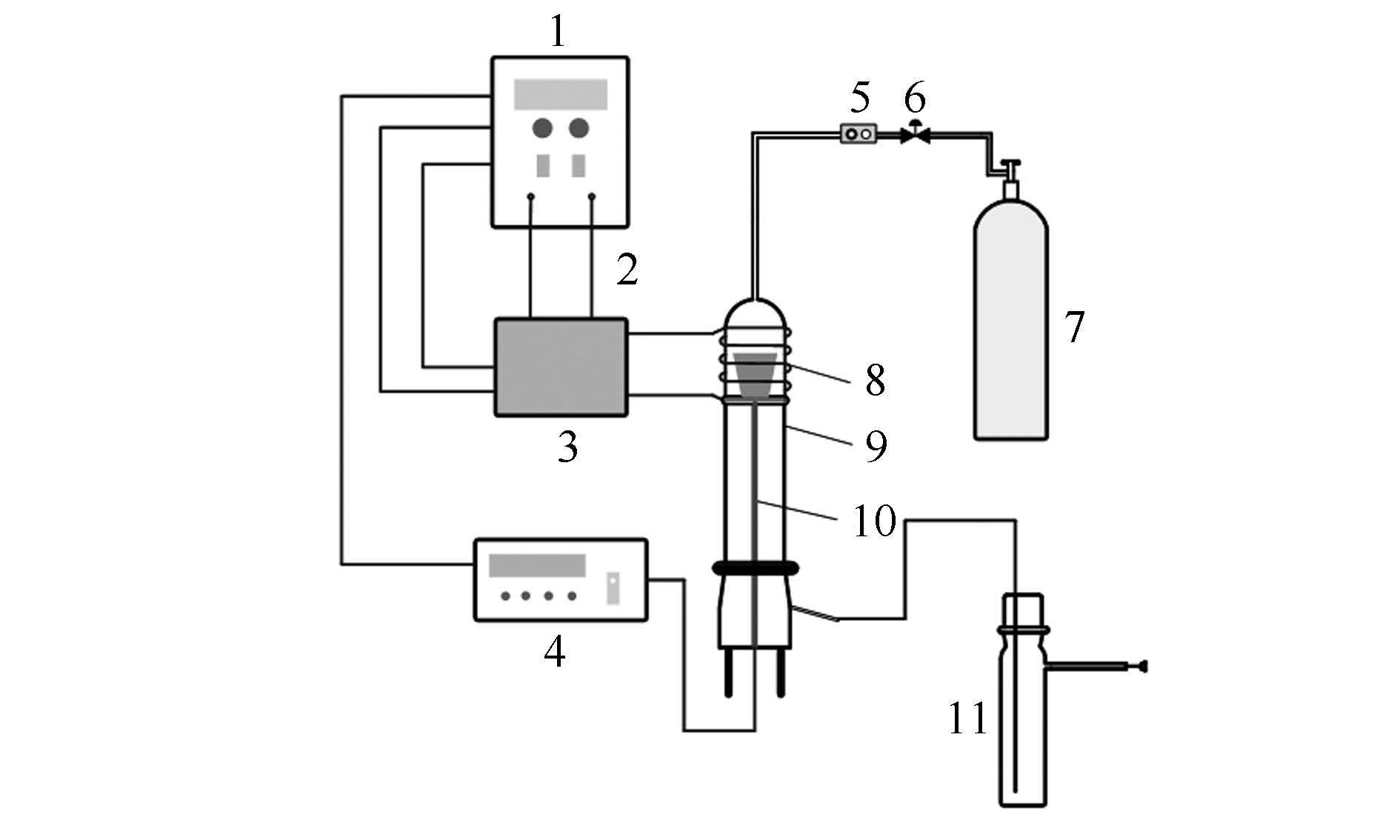
摘要: 利用高频炉反应器在800-1 200℃对添加质量分数10% CaO的云南镇雄煤(YNZX)进行了快速热解实验,采用连续化学提取、X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜-能谱(SEM-EDX)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等分析手段,考察了CaO添加对煤快速热解过程中砷和硫迁移转化的影响。结果表明,CaO能显著抑制砷与硫的释放。CaO对砷释放的抑制率在800℃时最高达41.19%,对硫释放的抑制率在1 000℃时最高,为39.89%;两者的抑制率呈负相关。As-Ca复合物和CaS的形成是砷与硫释放率降低的主要原因;添加CaO后,As-Ca复合物的生成使残渣态砷含量增加,CaS的形成使硫化物结合态砷含量减少。热解后硫元素在CaO表面富集,占据更多的吸附活性位,对砷的固定产生抑制作用;添加CaO后焦中硫仍主要以硫化物的形式存在,亚硫酸盐的含量有所增加。Abstract: The pyrolysis experiments of YNZX coal with 10% CaO at 800-1 200℃ were conducted in a high frequency furnace.The effects of adding CaO on the release and transformation of arsenic and sulfur during pyrolysis have been investigated with the aid of sequential chemical extraction, XRD, SEM-EDX, and XPS.The results show that CaO can inhibit the release of arsenic and sulfur significantly.The retention rate to arsenic amounts to 41.19% at 800℃, and that to sulfur reaches 39.89% at 1 000℃, there is a negative correlation between the two retention rates.The formation of As-Ca compounds and CaS accounts for the decrease of release rates of arsenic and sulfur.The sulfur is enriched on the surface of CaO, which occupies more active adsorption sites after pyrolysis and inhibits the retention of arsenic, most sulfur is presented as sulfides in char and the amount of sulfites increases after adding CaO.
-
Key words:
- pyrolysis /
- arsenic /
- sulfur /
- CaO /
- release and transformation
-
图 7 原料及热解焦的矿物组成
Figure 7 Mineral composition of raw materials and chars
(a): raw coal and chars at 800-1 200 ℃; (b): coal with 10% CaO and chars at 800-1 200 ℃Q-quartz(SiO2); M-mullite(xAl2O3·ySiO2); T-troilite(FeS); O-oldhamite(CaS); L-lime(CaO); K-kaolinite(Al2(Si2O5)(OH)4); P-pyrite(FeS2); C-calcite(CaCO3)
表 1 煤样的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis of coal sample
Sample Proximate analysis wd/% Ultimate analysis w/% A V FC Cd Hd Oa Nd Sd YNZX 25.07 9.39 65.54 60.88 2.18 8.35 0.86 2.66 a: oxygen is calcuated by difference 表 2 煤样的无机矿物组成
Table 2 Ash composition of coal sample
Ash sample Ash chemical composition w/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO SO3 TiO2 MgO Na2O K2O P2O5 others YNZX 49.48 26.74 12.03 4.38 3.09 1.80 0.92 0.64 0.62 0.11 0.19 表 3 原煤中不同赋存形态砷的含量
Table 3 Content of different occurrence forms of As in raw coal
Sample Exchangeable /% As-sulfide /% As-organic /% Residual /% As /(μg·g-1) YNZX 0.05 43.40 2.06 54.48 11.49 表 4 不同热解温度下CaO对砷与硫的抑制率
Table 4 Retention rates of As and S by CaO at different pyrolysis temperatures
Element X2/% 800 ℃ 900 ℃ 1 000 ℃ 1 100 ℃ 1 200 ℃ As 41.19 30.11 25.99 30.19 33.29 S 28.86 35.71 39.89 34.40 35.24 表 5 热解后CaO表面元素分布
Table 5 Element distribution on the surface of CaO after pyrolysis
Element Atomic /% a area 1 b area 1 c area 1 d area 1 d area 2 d spot 1 O 35.30 37.80 47.82 52.70 42.20 69.09 Ca 64.20 44.00 36.16 28.62 41.98 17.73 S 0.50 18.20 16.02 18.68 15.82 13.18 表 6 硫的赋存形态及摩尔含量
Table 6 Chemical forms and mol content of S
Valence state Binding energy E/eV Compound a/% b/% c/% -2 163.8 ± 0.2 sulfide,pyrite 24 74 77 +4 168.0 ± 0.5 sulfoxide,sulfite 48 11 20 +6 170.4 ± 0.3 sulphone,sulfate 28 15 3 -
[1] LOPEZ-ANTON M A, DIAZ-SOMOANO M, FIERRO J L G, MARTINEZ-TARAZONA M R. Retention of arsenic and selenium compounds present in coal combustion and gasification flue gases using activated carbons[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2007, 88(8):799-805. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.03.005 [2] JIA J, WU Y, LE Y, WU P, LI X, SUN X. Human health risk assessment of harmful trace elements in coal gasification residues[J]. J Residuals Sci Technol, 2015, 12:97-104. [3] DUAN L, SUN H, JIANG Y, ANTHONY E J, ZHAO C. Partitioning of trace elements, As, Ba, Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn and Pb, in a 2.5 MW th pilot-scale circulating fluidised bed combustor burning an anthracite and a bituminous coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2016, 146:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.02.003 [4] DEONARINE A, KOLKER A, FOSTER A L, DOUGHTEN M W, HOLLAND J T, BAILOO J D. Arsenic speciation in bituminous coal fly ash and transformations in response to redox conditions[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2016, 50:6099-6106. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b00957 [5] 王辅臣, 于广锁, 龚欣, 刘海峰, 王亦飞, 梁钦峰. 大型煤气化技术的研究与发展[J]. 化工进展, 2009, 28(2):173-180. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJZ200902002.htmWANG Fu-chen, YU Guang-suo, GONG Xin, LIU Hai-feng, WANG Yi-fei, LIANG Qin-feng. Research and development of large-scale coal gasification technology[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2009, 28(2):173-180. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJZ200902002.htm [6] 李伟锋, 于广锁, 龚欣, 王辅臣, 刘海峰, 王亦飞, 周志杰, 代正华, 陈雪莉, 梁钦锋, 郭晓镭, 王兴军, 许建良, 于遵宏. 多喷嘴对置式煤气化技术[J]. 氮肥技术, 2008, 29(6):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDFS200806003.htmLI Wei-feng, YU Guang-suo, GONG Xin, WANG Fu-chen, LIU Hai-feng, WANG Yi-fei, ZHOU Zhi-jie, DAI Zheng-hua, CHEN Xue-li, LIANG Qin-feng, GUO Xiao-lei, WANG Xing-jun, XU Jian-liang, YU Zun-hong. Coal gasification with opposed multi-burners[J]. Nitrogen Fertilizer Technol, 2008, 29(6):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDFS200806003.htm [7] GRYGLEWICZ G. Effectiveness of high temperature pyrolysis in sulfur removal from coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 1996, 46(3):217-226. doi: 10.1016/0378-3820(95)00061-5 [8] NERIN C, DOMENO C, MOLINER R, LAZARO M J, SUELVES I, VALDERRAMA J. Behaviour of different industrial waste oils in a pyrolysis process:Metals distribution and valuable products[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2000, 55(2):171-183. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2370(99)00097-2 [9] LOPEZ-ANTON M A, DIAZ-SOMOANO M, SPEARS D A, MARTINEZ-TARAZONA M R. Arsenic and selenium capture by fly ashes at low temperature[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2006, 40(12):3947-3951. doi: 10.1021/es0522027 [10] LI Y, TONG H, ZHUO Y, LI Y, XU X. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and trace As2O3 from flue gas:Mechanism, kinetics study, and effect of main gases on arsenic capture[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2007, 41(8):2894-2900. doi: 10.1021/es0618494 [11] STERLING R O, HELBLE J J. Reaction of arsenic vapor species with fly ash compounds:Kinetics and speciation of the reaction with calcium silicates[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 51(10):1111-1119. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00722-1 [12] 白进, 孔令学, 李怀柱, 郭振兴, 白宗庆, 尉迟唯, 李文. 山西典型无烟煤灰流动性的调控[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(7):805-813. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18214.shtmlBAI Jin, KONG Ling-xue, LI Huai-zhu, GUO Zhen-xing, BAI Zong-qing, YU CHI-Wei, LI Wen. Adjustment in high temperature flow property of ash from Shanxi typical anthracite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2013, 41(7):805-813. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18214.shtml [13] 白进, 李文, 孔令学, 颜婷圭, 李怀柱, 郭振兴, 白宗庆. 气化过程的灰化学及其应用[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2015, 2:10-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJG201502006.htmBAI Jin, LI Wen, KONG Ling-xue, YAN Ting-gui, LI Huai-zhu, GUO Zhen-xing, BAI Zong-qing. Chemistry of ash from coal gasification and its applications[J]. Coal Process Compr Util, 2015, 2:10-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJG201502006.htm [14] 袁海平, 梁钦锋, 刘海峰, 龚欣. CaCO3对煤灰熔融特性和黏温特性影响的研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(20):49-55.YUAN Hai-ping, LIANG Qin-feng, LIU Hai-feng, GONG Xin. Effects of CaCO3 on the fusion characteristic and viscosity-temperature behaviour of coal ashes[J]. Proc CSEE, 2012, 32(20):49-55. [15] 李平, 梁钦锋, 刘霞, 龚欣. 助熔剂对高灰熔点煤灰流动温度的影响[J]. 华东理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 36(4):475-481. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLDX201004004.htmLI Ping, LIANG Qin-feng, LIU Xia, GONG Xin. Effects of flux on flow temperature of coal ashes[J]. J East China Univ Sci Technol:Nat Sci Ed, 2010, 36(4):475-481. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLDX201004004.htm [16] JADHAV R A, FAN L S. Capture of gas-phase arsenic oxide by lime:Kinetic and mechanistic studies[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2001, 35(4):794-799. doi: 10.1021/es001405m [17] MAHULI S, AGNIHOTRI R, CHAUK S, GHOSH-DASTIDAR A, FAN L S. Mechanism of arsenic sorption by hydrated lime[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1997, 31(11):3226-3231. doi: 10.1021/es9702125 [18] 张军营, 任德贻, 钟秦, 徐复铭, 张衍国. CaO 对煤中砷挥发性的抑制作用[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2000, 28(3):198-200.ZHANG Jun-ying, REN De-yi, ZHONG Qin, XU Fu-ming, ZHANG Yan-guo. Restraining of arsenic volatility using lime in coal combustion[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2000, 28(3):198-200. [19] SEAMES W S, WENDT J O L. Regimes of association of arsenic and selenium during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2007, 31(2):2839-2846. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2006.08.066 [20] CHEN D, HU H, XU Z, LIU H, CAO J, SHEN J, YAO H. Findings of proper temperatures for arsenic capture by CaO in the simulated flue gas with and without SO2[J]. Chem Eng J, 2015, 267:201-206. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.035 [21] 袁帅, 李军, 周志杰, 王辅臣. 吡啶型氮快速热解中HCN和NH3生成机理研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2011, 39(6):413-418. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17751.shtmlYUAN Shuai, LI Jun, ZHOU Zhi-jie, WANG Fu-chen. Mechanisms of HCN and NH3 formation during rapid pyrolysis of pyridinic nitrogen containing substances[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2011, 39(6):413-418. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17751.shtml [22] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Anal Chem, 1979, 51(7):844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [23] QUEROL X, JUAN R, LOPEZ-SOLER A, FERNANDEZ-TURIEL J, RUIZ C R. Mobility of trace elements from coal and combustion wastes[J]. Fuel, 1996, 75(7):821-838. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(96)00027-0 [24] 郭欣. 煤燃烧过程中汞, 砷, 硒的排放与控制研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学, 2005.GUO Xin. Experimental and mechanism study on the mercury, arsenic and selenium transformation and emission control during coal combustion[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2005. [25] 左志军. X光电子能谱及其应用[M]. 北京:中国石化出版社, 2013:117-122.ZUO Zhi-jun. The X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Its Applications[M]. Beijing:China Petrochemical Press, 2013:117-122. [26] 马玲玲, 秦志宏, 张露, 刘旭, 陈航. 煤有机硫分析中XPS分峰拟合方法及参数设置[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(3):277-283. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18367.shtmlMA Ling-ling, QIN Zhi-hong, ZHANG Lu, LIU Xu, CHEN Hang. Peak fitting methods and parameter settings in XPS analysis for organic sulfur in coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(3):277-283. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18367.shtml [27] 杨荣生, 陈衍景, 谢景林. 甘肃阳山金矿床含砷黄铁矿及毒砂的XPS研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11):2791-2800. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911011.htmYANG Rong-sheng, CHEN Yan-jing, XIE Jing-lin. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study on arsenian pyrite and arsenopyrite from the Yangshan gold deposit[J]. Acta Petrol Sin, 2009, 25(11):2791-2800. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911011.htm [28] 李梅, 杨俊和, 张启锋, 夏红波, 常海洲, 孙慧. 高硫煤镜质组热解过程中结构变化及有机硫形态变迁规律研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2014, 42(2):138-145. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18346.shtmlLI Mei, YANG Jun-he, ZHANG Qi-feng, XIA Hong-bo, CHANG Hai-zhou, SUN Hui. Structure change and organic forms transformation during pyrolysis of high sulfur vitrinite[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2014, 42(2):138-145. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18346.shtml [29] LU H, CHEN H, LI W, LI B. Transformation of arsenic in Yima coal during fluidized-bed pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(6):645-650. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.08.020 [30] DIAZ-SOMOANO M, MARTINEZ-TARAZONA M R. Trace element evaporation during coal gasification based on a thermodynamic equilibrium calculation approach[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(2):137-145. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00251-X [31] FRANDSEN F, DAM-JOHANSEN K, RASMUSSEN P. Trace elements from combustion and gasification of coal-an equilibrium approach[J]. Prog Energy Combust Sci, 1994, 20(2):115-138. doi: 10.1016/0360-1285(94)90007-8 [32] 孟韵, 张军营, 钟秦. 煤燃烧过程中有害痕量元素形态分布的化学热力学平衡分析[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2005, 33(1):28-32. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16509.shtmlMENG Yun, ZHANG Jun-ying, ZHONG Qin. Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis of traces elements mobilization during combustion of coal[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2005, 33(1):28-32. http://rlhxxb.sxicc.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16509.shtml [33] SCHULMAN J H, SCHUMB W C. The polymorphism of arsenious oxide1[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1943, 65(5):878-883. doi: 10.1021/ja01245a031 [34] ZHANG L, SATO A, NINOMIYA Y, SASAOKA E. Partitioning of sulfur and calcium during pyrolysis and combustion of high sulfur coals impregnated with calcium acetate as the desulfurization sorbent[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(7):1039-1053. [35] GUAN R, LI W, LI B. Effects of Ca-based additives on desulfurization during coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(15):1961-1966. [36] JADHAV R A, FAN L S. Capture of gas-phase arsenic oxide by lime:Kinetic and mechanistic studies[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2001, 35(4):794-799. doi: 10.1021/es001405m [37] SHIGEMATSU K. Vapor pressure measurements of arsenic compounds[J]. Metall Rev MMIJ, 1986, 3(2):29-48. [38] JIA X, WANG Q, CEN K, CHENG L. Sulfur transformation during the pyrolysis of coal mixed with coal ash in a fixed bed reactor[J]. Fuel, 2016, 177:260-267. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.03.013 [39] ZHANG Y, WANG C, LI W, LIU H, ZHANG Y, HACK P, PAN W. Removal of gas-phase As2O3 by metal oxide adsorbents:Effects of experimental conditions and evaluation of adsorption mechanism[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(10):6578-6585. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00948 [40] MIURA K, MAE K, SHIMADA M, MINAMI H. Analysis of formation rates of sulfur-containing gases during the pyrolysis of various coals[J]. Energy Fuels, 2001, 15(3):629-636. doi: 10.1021/ef000185v [41] ALONSO M, CORDERO J M, ARIAS B, ABANADES J C. Sulfation rates of particles in calcium looping reactors[J]. Chem Eng Technol, 2014, 37(1):15-19. doi: 10.1002/ceat.v37.1 [42] WANG M, HU Y, WANG J, CHANG L, WANG H. Transformation of sulfur during pyrolysis of inertinite-rich coals and correlation with their characteristics[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2013, 104:585-592. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.05.010 -





 下载:
下载: