CeOx doping on a TiO2-SiO2 supporter enhances Ag based adsorptive desulfurization for diesel
-
摘要: 以钛酸丁酯的乙醇溶液为钛源, 硝酸铈的水溶液为沉淀剂, 采用共浸渍法制备CeOx/TiO2-SiO2复合氧化物作为Ag基柴油脱硫吸附剂的载体, 探究CeOx掺杂TiO2-SiO2载体对吸附剂结构及脱硫性能的影响.结果表明, 采用共浸渍法制备的CeOx/TiO2-SiO2载体中, Ce物种和Ti物种均处于充分分散的状态, 掺杂CeOx可促进Ag活性物种的分散, 还会促进金属态Ag活性物种的氧化, 形成高度分散的Ag氧化物 (Ag2O2) 活性中心, 从而提高吸附剂的脱硫性能 (22.5%).在静态吸附实验中, Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2对中国国II柴油 (硫含量952.9mg/kg) 的吸附硫容可达5.38mg/g, 在剂油比为1:10时可将中国国IV柴油 (硫含量39.0mg/kg) 中的硫含量降至10mg/kg以下, 达到中国国V柴油的标准.Abstract: In this work, the impact of CeOx doping on a TiO2-SiO2 supporter on the Ag based adsorptive desulfurization for Chinese standard diesel was studied. The dispersion and valence states of Ce, Ti and Ag species were characterized, and the impact of Ce doping was investigated. The results indicated that Ce species and Ti species were dispersed evenly on the surface of SiO2 via a novel co-impregnation method. Following CeOx doping, the Ag species were in the form of oxides (about 5nm) instead of metallic Ag particles (about 35nm), which is due to the large amount of coordinative unsaturated sites provided by the interaction between CeOx and TiO2, as well as the oxidation-reduction property of CeOx. The Ag in the active oxide state (Ag2O2) and dispersed evenly on the supporter could interact with sulfur compounds more favorably, and therefore showed a good performance in the adsorptive desulfurization. In both static batch and dynamic breakthrough desulfurization tests, Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 was proved to be a more efficient adsorbent compared with Ag-TiO2-SiO2. It was found that the desulfurization performance of Ag-TiO2-SiO2 exhibited an excellent improvement (22.5%) after being doped with CeOx. In the static equilibrium tests, the equilibrium sulfur capacity of Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 was up to 5.38mg/g for CN-II diesel (sulfur content 952.9mg/kg) and the sulfur content of the CN-IV diesel (sulfur content 39.0mg/kg) after desulfurization was less than 10mg/kg, which could meet the CN-V standard.
-
Key words:
- commercial diesel /
- adsorptive desulfurization /
- Ag oxides /
- CeOx doping /
- adequate dispersion
-
Figure 8 Breakthrough curves of adsorbents obtained with CN-IV diesel at 298 K, atmospheric pressure and different LHSV
■: Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 LHSV=0.3 h-1;
●: Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 LHSV=0.6 h-1;
▲: Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 LHSV=0.9 h-1;
▼: Ag-TiO2-SiO2 LHSV=0.3 h-1;
◆: Ag-TiO2-SiO2 LHSV=0.6 h-1;
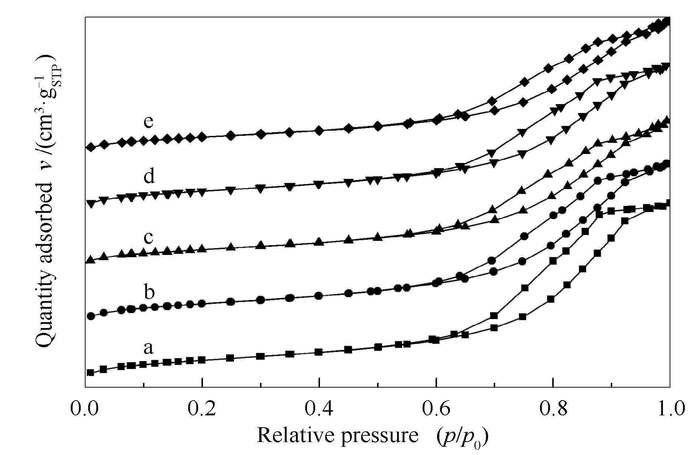
◀: Ag-TiO2-SiO2 LHSV=0.9 h-1Table 1 Porous parameters of different adsorbents and supports
Sample ID Surface area A/(m2·g-1) Pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) Pore diameter d/nm SiO2 341.3 1.00 11.7 TiO2-SiO2 335.9 0.91 10.8 Ag-TiO2-SiO2 297.2 0.83 11.1 CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 318.0 0.82 10.3 Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 278.8 0.76 10.8 Table 3 Static equilibrium test results of different adsorbents and supports
Adsorbent A/Fb /(g·mL-1) Diesel Cea, b /(mg·kg-1) ηa, b /% CSa, b /(mg·g-1) SiO2 1:30 CN-IV 30.6 21.6 0.21 TiO2-SiO2 1:30 CN-IV 26.5 32.0 0.31 CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 1:30 CN-IV 25.6 34.4 0.35 Ag-SiO2 1:30 CN-IV 27.6 29.3 0.29 Ag-TiO2-SiO2 1:30 CN-IV 23.1 40.8 0.40 Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 1:30 CN-IV 19.7 49.5 0.49 Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 1:20 CN-IV 14.8 62.0 0.41 Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 1:10 CN-IV 8.1 79.1 0.26 Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 1:30 CN-III 166.6 43.0 3.16 Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 1:30 CN-II 738.5 22.4 5.38 Ag-TiO2-Al2O3 1:30 CN-IV 29.3 25.0 0.25 a all the desulfurization were processed at 333 K and atmospheric pressure, the adsorbents were mixed with the diesels under mechanical shaking for 48 h, respectively;
b A/F represent adsorbent to diesel fuel ratios; Ce represent the equilibrium concentration; η is the desulphurization efficiencies; CS represent the sulfur adsorption capacityTable 2 XPS binding energy of O 1s, Si 2p and Ce 3d peaks
Levels Peak Binding energy EB/eV reference CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 Ag-CeOx/TiO2-SiO2 Ce 3d5/2a v0 880.6 - - v 882.6 883.6 883.8 v1 885.45 - - v2 888.85 887.2 887.5 v3 898.4 899.9 900.5 Ce 3d3/2a u0 898.9 - - u 901.05 902 902.3 u1 904.05 - - u2 907.45 905.8 906.1 u3 916.7 918.2 918.8 Si 2pb 103.7 102.9 103.0 O 1sb 533.2 532.9 533.1 a: the reference binding energy of the ten Ce 3d peaks were from reference[33];
b: the reference binding energy of O 1s and Si 2p in silica gel were from reference[34] -
[1] WU L, XIAO J, WU Y, XIAN S, MIAO G, WANG H, LI Z. A combined experimental/computational study on the adsorption of organosulfur compounds over metal-organic frameworks from fuels[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(4):1080-1088. doi: 10.1021/la404540j [2] PALOMINO J M, TRAN D T, HAUSER J L, DONG H, OLIVER S R. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for high capacity adsorptive desulfurization[J]. J Mater Chem, 2014, 2(36):14890-14895. doi: 10.1039/C4TA02570A [3] XU X, ZHANG S, LI P, SHEN Y. Adsorptive desulfurization of liquid Jet-A fuel at ambient conditions with an improved adsorbent for on-board fuel treatment for SOFC applications[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 124:140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.03.001 [4] XIAO J, WANG X, CHEN Y, FUJⅡ M, SONG C. Ultra-deep adsorptive desulfurization of light-irradiated diesel fuel over supported TiO2-CeO2 adsorbents[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2013, 52(45):15746-15755. doi: 10.1021/ie402724q [5] HUSSAIN A S, TATARCHUK B J. Adsorptive desulfurization of jet and diesel fuels using Ag/TiOx-Al2O3 and Ag/TiOx-SiO2 adsorbents[J]. Fuel, 2013, 107:465-473. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.11.030 [6] QIN Y, MO Z, YU W, DONG S, DUAN L, GAO X, SONG L. Adsorption behaviors of thiophene, benzene, and cyclohexene on FAU zeolites:Comparison of CeY obtained by liquid-, and solid-state ion exchange[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 292:5-15. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.11.036 [7] KHAN N A, HASAN Z, JHUNG S H. Ionic liquids supported on metal-organic frameworks:Remarkable adsorbents for adsorptive desulfurization[J]. Chem Eur J, 2014, 20(2):376-380. doi: 10.1002/chem.v20.2 [8] HUSSAIN A S, TATARCHUK B J. Mechanism of hydrocarbon fuel desulfurization using Ag/TiO2-Al2O3 adsorbent[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 126:233-242. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.05.006 [9] HUSSAIN A S, MCKEE M L, HEINZEL J M, SUN X, TATARCHUK B J. Density functional theory study of organosulfur selective adsorption on Ag-TiO2 adsorbents[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2014, 118(27):14938-14947. doi: 10.1021/jp503097y [10] LIU B, ZHU Y, LIU S, MAO J. Adsorption equilibrium of thiophenic sulfur compounds on the Cu-BTC metal-organic framework[J]. J Chem Eng Data, 2012, 57(4):1326-1330. doi: 10.1021/je300130s [11] YANG R T, HERNANDEZ-MALDONADO A J, YANG F H. Desulfurization of transportation fuels with zeolites under ambient conditions[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5629):79-81. doi: 10.1126/science.1085088 [12] HE G, SUN L, SONG X, LIU X, YIN Y, WANG Y. Adjusting host properties to promote cuprous chloride dispersion and adsorptive desulfurization sites formation on SBA-15[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(8):3506-3513. doi: 10.1021/ef200723m [13] XU X, ZHANG S, LI P, SHEN Y. Equilibrium and kinetics of Jet-A fuel desulfurization by selective adsorption at room temperatures[J]. Fuel, 2013, 111:172-179. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.04.068 [14] MA X, SPRAGUE M, SONG C. Deep desulfurization of gasoline by selective adsorption over nickel-based adsorbent for fuel cell applications[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2005, 44(15):5768-5775. doi: 10.1021/ie0492810 [15] VELU S, MA X, SONG C, NAMAZIAN M, SETHURAMAN S, VENKATARAMAN G. Desulfurization of JP-8 jet fuel by selective adsorption over a Ni-based adsorbent for micro solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Energy Fuels, 2005, 19(3):1116-1125. doi: 10.1021/ef049800b [16] SHEN Y, XU X, LI P. A novel potential adsorbent for ultra deep desulfurization of jet fuels at room temperature[J]. RSC Adv, 2012, 2(15):6155-6160. doi: 10.1039/c2ra20224g [17] TRIANTAFYLLIDIS K S, DELIYANNI E A. Desulfurization of diesel fuels:Adsorption of 4, 6-DMDBT on different origin and surface chemistry nanoporous activated carbons[J]. Chem Eng J, 2014, 236:406-414. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.099 [18] WANG L, YANG R T, SUN C L. Graphene and other carbon sorbents for selective adsorption of thiophene from liquid fuel[J]. AlChE J, 2013, 59(1):29-32. doi: 10.1002/aic.v59.1 [19] BALTZOPOULOU P, KALLIS K X, KARAGIANNAKIS G, KONSTANDOPOULOS A G. Diesel fuel desulfurization via adsorption with the aid of activated carbon:Laboratory-and pilot-scale studies[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(9):5640-5648. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01133 [20] XU X, ZHANG S, LI P, SHEN Y. Desulfurization of Jet-A fuel in a fixed-bed reactor at room temperature and ambient pressure using a novel selective adsorbent[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117:499-508. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.074 [21] GUO J, JANIK M J, SONG C. Density functional theory study on the role of ceria addition in TixCe1-xO2 adsorbents for thiophene adsorption[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2012, 116(5):3457-3466. doi: 10.1021/jp2063996 [22] TIAN F, SHEN Q, FU Z, WU Y, JIA C. Enhanced adsorption desulfurization performance over hierarchically structured zeolite Y[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 128:176-182. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.07.018 [23] WANG Y, YANG R T, HEINZEL J M. Desulfurization of jet fuel byπ-complexation adsorption with metal halides supported on MCM-41 and SBA-15 mesoporous materials[J]. Chem Eng Sci, 2008, 63(2):356-365. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2007.09.002 [24] HERNANDEZ-MALDONADO A J, YANG R T. Desulfurization of commercial liquid fuels by selective adsorption viaπ-complexation with Cu (I)-Y zeolite[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2003, 42(13):3103-3110. doi: 10.1021/ie0301132 [25] PERALTA D, CHAPLAIS G, SIMON-MASSERON A, BARTHELET K, PIRNGRUBER G D. Metal-organic framework materials for desulfurization by adsorption[J]. Energy Fuels, 2012, 26(8):4953-4960. doi: 10.1021/ef300762z [26] LIU X, WANG J, LI Q, JIANG S, ZHANG T, JI S. Synthesis of rare earth metal-organic frameworks (Ln-MOFs) and their properties of adsorption desulfurization[J]. J Rare Earths, 2014, 32(2):189-194. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60050-8 [27] NAIR S, TATARCHUK B J. Supported silver adsorbents for selective removal of sulfur species from hydrocarbon fuels[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(11):3218-3225. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.05.006 [28] WATANABE S, MA X, SONG C. Characterization of structural and surface properties of nanocrystalline TiO2-CeO2 mixed oxides by XRD, XPS, TPR, and TPD[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2009, 113(32):14249-14257. doi: 10.1021/jp8110309 [29] SCIRE S, MINICO S, CRISAFULLI C, SATRIANO C, PISTONE A. Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds on gold/cerium oxide catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2003, 40(1):43-49. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(02)00127-3 [30] ZHANG Y, ANDERSSON S, MUHAMMED M. Nanophase catalytic oxides:I. Synthesis of doped cerium oxides as oxygen storage promoters[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 1995, 6(4):325-337. doi: 10.1016/0926-3373(95)00041-0 [31] XIAO J, WANG X, FUJⅡ M, YANG Q, SONG C. A novel approach for ultra-deep adsorptive desulfurization of diesel fuel over TiO2-CeO2/MCM-48 under ambient conditions[J]. AlChE J, 2013, 59(5):1441-1445. doi: 10.1002/aic.14085 [32] GONBEAU D, GUIMON C, PFISTER-GUILLOUZO G, LEVASSEUR A, MEUNIER G, DORMOY R. XPS study of thin films of titanium oxysulfides[J]. Surf Sci, 1991, 254(1):81-89. [33] ROMEO M, BAK K, FALLAH J E, NORMAND F L, HILAIRE L. XPS study of the reduction of cerium dioxide[J]. Surf Interface Anal, 1993, 20(6):508-512. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9918 [34] GROSS T, RAMM M, SONNTAG H, UNGER W, WEIJERS H M, ADEM E H. An XPS analysis of different SiO2 modifications employing a C 1s as well as an Au 4f7/2 static charge reference[J]. Surf Interface Anal, 1992, 18(1):59-64. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9918 [35] NAGPURE I, PITALE S S, TSHABALALA K, KUMAR V, NTWAEABORWA O, TERBLANS J, SWART H. Luminescence response and CL degradation of combustion synthesized spherical SiO2:Ce nanophosphor[J]. Mater Res Bull, 2011, 46(12):2359-2366. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.08.051 [36] LARACHI F, PIERRE J, ADNOT A, BERNIS A. Ce 3d XPS study of composite CexMn1-xO2-y wet oxidation catalysts[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2002, 195(1):236-250. [37] SAMOKHVALOV A, NAIR S, DUIN E C, TATARCHUK B J. Surface characterization of Ag/titania adsorbents[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 256(11):3647-3652. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.01.002 -





 下载:
下载: