-
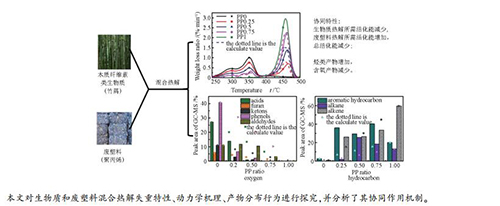
摘要: 选取聚丙烯(PP)和竹屑作为废塑料与生物质的典型代表,在热重分析仪和固定床台架上研究了塑料掺混比例对混合热解失重特性、动力学机理、产物分布行为等特性的影响,并分析了混合热解时生物质和废塑料间的协同作用机制。结果表明,随着塑料掺混比例的增加,混合热解终止温度由501℃降低至471℃,主要热解温度区间缩短;混合热解所需活化能呈现先减小后增大的趋势,在塑料掺混比例为0.25时取得最小值。通过对比实验数据和理论数据发现,生物质与废塑料混合热解具有很强的协同作用:该协同作用降低了生物质反应所需能量,增加了废塑料反应所需能量,降低了混合热解过程的总活化能;此外,协同作用促进大分子挥发分转化为小分子气体,促进芳烃、烷烃等烃类生成,抑制CO2、苯酚、羧酸、呋喃和酮类等含氧物质生成。Abstract: Polypropylene (PP) and bamboo were selected as typical representatives of waste plastics and biomass. And the biomass and plastic co-pyrolysis weight loss, kinetic mechanism and product distribution were studied by thermogravimetric analyzer and fixed-bed reactor. The synergistic mechanism between biomass and plastic during co-pyrolysis was discussed. As the ratio of plastic increases, the ending temperature of co-pyrolysis decreases from 501 to 471℃, while the main temperature range for co-pyrolysis is shortened. What's more, the total activation energy required for the co-pyrolysis decreases when the plastic ratio is below 0.25 and then increases. Comparing the experimental with theoretical data, it is found that the synergistic effect during biomass and waste plastics co-pyrolysis is obvious. Due to the synergistic effect, the total activation energy for co-pyrolysis is much lower than calculated value. In addition, the synergistic effect can promote the conversion of macromolecular volatiles into small-molecule gas, accelerate the generation of hydrocarbons like aromatics and alkanes, and inhibit the formation of oxygen-containing substances like CO2, phenol, carboxylic acids, furans and ketones.
-
Key words:
- waste solids /
- co-pyrolysis /
- kinetic analysis /
- products component /
- synergistic effect
-
表 1 样品的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis of samples
Sample Proximate analysis wd/% Ultimate analysis wd/% V A FC C H Oa N S Bamboo 81.44 0.73 17.83 47.28 6.04 46.39 0.17 0.12 PP 99.88 0.07 0.05 85.18 13.74 0.91 0.00 0.17 a: by difference 表 2 生物质灰成分分析
Table 2 Inorganic composition analysis of biomass
Sample Mass fraction wad/% Mg Al Si P S K Ca Ti Mn Fe Zn Bamboo 10.60 1.85 5.91 7.29 9.16 50.12 9.65 0.17 3.97 0.81 0.47 表 3 生物质、废塑料热解/混合热解特性参数表
Table 3 Pyrolysis characteristic parameters of individual samples and biomass/waste plastic blend
Sample tb/℃ tm /℃ tf/℃ Dm /(%·min-1) P1 P2 P3 P1 P2 P3 PP0 265 299 353 - 501 0.47 1.05 - PP0.25 268 298 352 468 482 0.36 0.83 0.71 PP0.5 266 298 353 463 477 0.24 0.55 1.44 PP0.75 274 300 350 462 475 0.13 0.36 2.33 PP1 417 - - 455 471 - - 3.06 a:tb: the start temperature, while the conversion ratio is 5×(1-x)%; Pn: n weight loss range; tm: the temperature while the weight loss ratio is the largest; tf: the ending temperature, while the conversion ratio is 95%; Dm: the largest weight loss ratio 表 4 生物质与废塑料混合热解反应动力参数
Table 4 Pyrolysis kinetic parameters of individual samples and biomass/waste plastics blend
Sample Temperature
t/℃Weight loss w/% n E/
(kJ·mol-1)A/
min-1R2 E-ave/
(kJ·mol-1)E-cal/
(kJ·mol-1)PP0 265-304 21.58 1 101.88 1.86×108 0.9948 70.84 304-391 68.72 1 70.52 1.68×105 0.9784 391-501 9.70 1 4.050 4.62×10-2 0.9597 PP0.25 268-309 16.19 1 97.86 4.72×107 0.9916 57.79 126.07 309-390 45.19 1 55.60 4.11×103 0.9617 390-482 38.62 0.5 43.55 3.97×1013 0.9183 PP0.25-cal 266-304 14.55 1 98.83 6.34×107 0.9938 58.64 304-391 47.45 1 54.97 3.63×103 0.9668 391-474 37.99 0.5 47.84 9.40×1013 0.9120 PP0.5 266-310 10.70 1 96.72 2.17×107 0.9866 62.13 181.31 310-379 27.07 1 53.73 1.52×103 0.9864 379-477 62.23 0.5 59.84 5.92×1014 0.8797 PP0.5-cal 268-311 10.54 1 89.38 4.50×106 0.9877 69.59 311-391 27.70 1 47.19 3.83×102 0.9499 391-472 61.76 0.5 76.26 1.31×1016 0.8893 PP0.75 274-311 4.64 1 101.85 2.96×107 0.9869 91.31 236.54 311-377 12.61 1 56.44 1.18×103 0.9847 377-475 82.75 0.5 96.03 3.00×1017 0.8741 PP0.75-cal 269-311 4.82 1 87.14 1.25×106 0.9866 100.05 311-384 13.03 1 47.57 1.84×102 0.9718 384-471 82.14 0.5 109.15 3.31×1018 0.8890 PP1 417-471 100.00 1 291.77 9.97×1031 0.9987 291.77 PP0.25-cal: the theoretical value when the plastic ratio is 25%; E-ave: the average total activation energy; E-cal: the linear total activation energy -
[1] ISAHAK W N R W, HISHAM M W M, YARMO M A, HIN T Y. A review on bio-oil production from biomass by using pyrolysis method[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev, 2012, 16(8):5910-5923. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2012.05.039 [2] AL-SALEM S M, ANTELAVA A, CONSTANTINOU A, MANOS G, DUTTA A. A review on thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of plastic solid waste (PSW)[J]. J Environ Manage, 2017, 197:177-198. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.084 [3] 周利民, 王一平, 黄群武, 蔡俊青.生物质/塑料共热解热重分析及动力学研究[J].太阳能学报, 2007, 28(9):979-983. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-0096.2007.09.008ZHOU Li-min, WANG Yi-ping, HUANG Qun-wu, CAI Jun-qing. TG analysis and kinetics of biomass/plastic co-pyrolysis[J]. Acta Energ Sol Sin, 2007, 28(9):979-983. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-0096.2007.09.008 [4] BU Q, CHEN K, XIE W, LIU Y Y, GAO M J, KONG X H, CHU Q L, MAO H P. Hydrocarbon rich bio-oil production, thermal behavior analysis and kinetic study of microwave-assisted co-pyrolysis of microwave-torrefied lignin with low density polyethylene[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2019, 291:121860. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121860 [5] HASSAN H, LIM J K, HAMEED B H. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of sugarcane bagasse and waste high-density polyethylene over faujasite-type zeolite[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2019, 284:406-414. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.137 [6] HASSAN H, HAMEED B H, LIM J K. Co-pyrolysis of sugarcane bagasse and waste high-density polyethylene:Synergistic effect and product distributions[J]. Energy, 2020, 191:116545. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.116545 [7] OZSIN G, PUTUN A E. Insights into pyrolysis and co-pyrolysis of biomass and polystyrene:Thermochemical behaviors, kinetics and evolved gas analysis[J]. Energy Convers Manage, 2017, 149:675-685. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.07.059 [8] CHEN W, LI K X, XIA M W, YANG H P, CHEN Y Q, CHEN X, CHE Q F, CHEN H P. Catalytic deoxygenation co-pyrolysis of bamboo wastes and microalgae with biochar catalyst[J]. Energy, 2018, 157:472-482. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.05.149 [9] 武宏香, 李海滨, 赵增立.煤与生物质热重分析及动力学研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2009, 37(5):538-545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.05.005WU Hong-xiang, LI Hai-bin, ZHAO Zeng-li. Thermogravimetric analysis and pyrolytic kinetic study on coal/biomas s blends[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2009, 37(5):538-545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.05.005 [10] LI X Y, LI J, ZHOU G Q, FENG Y, WANG Y J, YU G, DENG S B, HUANG J, WANG B. Enhancing the production of renewable petrochemicals by co-feeding of biomass with plastics in catalytic fast pyrolysis with ZSM-5 zeolites[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2014, 481:173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.05.015 [11] JAKAB E, VARHEGYI G, FAIX O. Thermal decomposition of polypropylene in the presence of wood-derived materials[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2000, 56(2):273-285. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2370(00)00101-7 [12] 彭锦星, 邵千钧, 陈丰农, 陈奋学, 袁伯增.基于超临界乙醇的竹子与聚乙烯共液化研究[J].太阳能学报, 2009, 30(8):1139-1144. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-0096.2009.08.027PENG Jin-xing, SHAO Qian-jun, CHEN Feng-nong, CHEN Fen-xue, YUAN Bo-zeng. Experimental study on co-liquefaction of bamboo and PE in supercritical ethanol[J]. Acta Energ Sol Sin, 2009, 30(8):1139-1144. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-0096.2009.08.027 [13] BLOCK C, EPHRAIM A, HORTALA W E, MINH D P, VANDECASTEELE C A N. Co-pyrogasification of plastics and biomass, a review[J]. Waste Biomass Valorization, 2019, 10(3):483-509. doi: 10.1007/s12649-018-0219-8 [14] BURRA K G, GUPTA A K. Kinetics of synergistic effects in co-pyrolysis of biomass with plastic wastes[J]. Appl Energy, 2018, 220:408-418. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.03.117 [15] XIANG Z P, LIANG J H, HERVAN Z, LIU Y Y, MAO H P, BU Q. Thermal behavior and kinetic study for co-pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass with polyethylene over cobalt modified ZSM-5 catalyst by thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2018, 247:804-811. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.178 [16] BURRA K G, GUPTA A K. Synergistic effects in steam gasification of combined biomass and plastic waste mixtures[J]. Appl Energy, 2018, 211:230-236. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.130 -





 下载:
下载: