CO hydrogenation to ethanol over copper-nickel bimetallic catalyst prepared by isomorphous substitution method
-
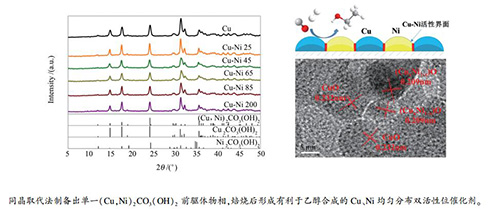
摘要: 采用定向同晶取代法制备了一系列镍孔雀石前驱体的Cu-Ni双金属催化剂。考察了前驱体结构以及催化剂表面组成对催化剂催化性能的影响,并采用浆态床反应器对催化剂的CO加氢制乙醇性能进行评价。实验结果表明,采用定向同晶取代法可以制备出(Cu,Ni)2CO3(OH)2纯物相,取代后的Ni2+主要富集在前驱体(Cu,Ni)2CO3(OH)2表面。焙烧后形成的(Cux,Ni1-x)O固溶体均匀地分散在CuO晶体结构中。还原后的催化剂中Cu、Ni相互均匀分散形成活性界面,促进了低碳醇的合成。其中,不连续分布的Ni活性位点阻止了碳链的进一步增长,从而提高了乙醇选择性。当Ni/Cu原料比为45:100时,(Cux,Ni1-x)O固溶体与CuO之间有较强的相互作用,表现出最好的反应活性和乙醇选择性。Abstract: A series of Cu-Ni bimetallic catalysts derived from nickel-malachite were prepared by an oriented isomorphous substitution method. The effects of the precursor structure and catalysts surface composition on the catalytic performance CO hydrogenation to ethanol were investigated in an agitated slurry autoclave reactor. The studies demonstrated that the pure (Cu, Ni)2CO3(OH)2 phase was obtained by oriented isomorphous substitution method and Ni2+ was rich on the (Cu, Ni)2CO3(OH)2 precursor surface. Uniform distribution of (Cux, Ni1-x)O solid solution were found in CuO crystal lattice. After calcination, the (Cux, Ni1-x)O solid solution dispersed in the crystal structure of CuO uniformly. Cu and Ni dispersed in the catalysts evenly to form an active interface after reduction, which promoted the synthesis of higher alcohols. Discontinuously distributed Ni-active sites prevented the carbon chain from growing further, and enhanced the selectivity of ethanol. The catalyst prepared by the feeding materials with Ni/Cu molar ratio=45:100 was found to exhibit higher activity and ethanol selectivity due to the strong interaction between (Cux, Ni1-x)O solid solution and CuO phase.
-
Key words:
- syngas /
- ethanol /
- oriented isomorphous substitution method /
- malachite structure /
- Cu-Ni catalyst
-
图 5 孔雀石焙烧形成的CuO和Cu-Ni 45催化剂在不同倍数下的TEM照片
Figure 5 TEM images of the CuO catalyst derived from malachite and Cu-Ni 45 catalyst with different magnification times
(a): TEM image of CuO catalyst with 50 nm; (a1): TEM image of CuO catalyst with 5 nm;
(b): TEM image of Cu-Ni 45 catalyst with 50 nm; (b1): TEM image of Cu-Ni 45 catalyst with 5 nm表 1 前驱体(Cu, Ni)2CO3(OH)2的晶胞参数和平均晶粒粒径
Table 1 Lattice parameters and average crystallite size of the (Cu, Ni)2CO3(OH)2 precursors
Catalyst d20-1a d21-1a va/nm3 Db/nm Cu 2.861 2.781 0.3646 28.5 Cu-Ni 25 2.859 2.777 0.3646 24.8 Cu-Ni 45 2.845 2.775 0.3644 15.4 Cu-Ni 65 2.844 2.769 0.3644 18.1 Cu-Ni 85 2.841 2.769 0.3632 18.3 Cu-Ni 200 2.836 2.768 0.3633 19.0 a: the lattice parameters of (Cu, Ni)2CO3(OH)2 were calculated from the XRD patterns;
b:D: crystallite size of the precursors, derived from XRD peak 2θ=31.3°表 2 前驱体(Cu, Ni)2CO3(OH)2的ICP分析
Table 2 ICP determination for the (Cu, Ni)2CO3(OH)2 precursors
Catalyst Feed molar ratio Ni/Cu Ni/Cu
(molar ratio)Ni/(Cu+Ni) by ICP(molar ratio) Ni/(Cu+Ni) by XPS(molar ratio) Cu-Ni 25 25:100 0.22 0.18 0.65 Cu-Ni 45 45:100 0.40 0.28 0.66 Cu-Ni 65 65:100 0.47 0.32 0.73 Cu-Ni 85 85:100 0.49 0.33 0.79 Cu-Ni 200 200:100 0.51 0.34 0.86 表 3 Cu-Ni催化剂的织构性质
Table 3 Textural properties of the Cu-Ni catalysts
Catalyst ABET/(m2·g-1) D/nm CuO (Cux, Ni1-x)O Cu 14.7 24.7 - Cu-Ni 25 28.3 15.8 18.5 Cu-Ni 45 41.3 13.5 9.3 Cu-Ni 65 34.7 14.2 11.7 Cu-Ni 85 33.1 13.8 11.1 Cu-Ni 200 19.8 17.9 16.0 ABET: specific surface area of the Cu-Ni catalysts;
D: crystallite size of CuO, derived from XRD peak 2θ=38.7°表 4 Cu-Ni催化剂催化CO加氢合成醇性能
Table 4 Catalytic performance of the copper-nickel bimetallic catalysts for CO hydrogenation to ethanol
Catalyst xCO /% ectivity s/% CH4 CH3OH C2H5OH C3H7OH C4H9OH CxOH Cu-Ni 25 28.6 35.2 19.4 15.8 6.8 3.3 45.3 Cu-Ni 45 35.3 38.5 21.8 19.1 5.3 2.9 49.1 Cu-Ni 65 28.7 49.3 24.4 13.2 4.0 1.6 43.2 Cu-Ni 85 25.8 50.4 31.0 11.7 2.2 0.9 45.8 Cu-Ni 200 22.8 51.4 17.8 9.6 1.7 0.5 29.6 reaction conditions: 270 ℃, 5.0 MPa, CO:H2(volume ratio)=1:2, 3000 L/(kg·h) -
[1] AO M, PHAM G H, SUNARSO J, TADE M O, LIU S. Active centers of catalysts for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas:A review[J]. ACS Catal, 2018, 8(8):7025-7050. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b01391 [2] LUK H T, MONDELLI C, FERRE D C, STEWART J A, PEREZ-RAMIREZ J. Status and prospects in higher alcohols synthesis from syngas[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2017, 46(5):1358-1426. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00324A [3] WANG L F, CAO A, LIU G L, ZHANG L H, LIU Y. Bimetallic CuCo nanoparticles derived from hydrotalcite supported on carbon fibers for higher alcohols synthesis from syngas[J]. Appl Sur Sci, 2016, 360:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.234 [4] XU X D, DOESBURG E B M, SCHOLTEN J J F. Synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas-recently patented catalysts and tentative ideas on the mechanism[J]. Catal Today, 1987, 2(1):125-170. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=92e8d545efc1881626c51133df0a3949&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] SU J J, MAO W, XU X C, YANG Z, LI H L, XU J, HAN Y F. Kinetic study of higher alcohol synthesis directly from syngas over CoCu/SiO2 catalysts[J]. AIChE J, 2014, 60(5):1797-1809. doi: 10.1002/aic.v60.5 [6] WANG P, CHEN S Y, BAI Y X, GAO X F, LI X L, SUN K, XIE H J, YANG G H, HAN Y Z, TAN Y S. Effect of the promoter and support on cobalt-based catalysts for higher alcohols synthesis through CO hydrogenation[J]. Fuel, 2017, 195:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.01.050 [7] XU R, YANG C, WEI W, LI W H, SUN Y H, HU T D. Fe-modified CuMnZrO2 catalysts for higher alcohols synthesis from syngas[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem, 2004, 221:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2004.07.003 [8] ZHAO N, XU R, WEI W, SUN Y H. CuMnZrO2 catalyst for alcohol synthesis by fischertropsch modified element[J]. React Kinet Catal Lett, 2002, 75(2):297-304. doi: 10.1023/A:1015203113811 [9] XIAO K, QI X Z, BAO Z H, WANG X X, ZHONG L S, FANG K G, LIN M G, SUN Y H. CuFe, CuCo and CuNi nanoparticles as catalysts for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas:A comparative study[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2013, 3(6):1591-1602. doi: 10.1039/c3cy00063j [10] NAGHASH A R, ETSELL T H, XU S. XRD and XPS study of Cu-Ni interactions on reduced copper-nickel-aluminum oxide solid solution catalysts[J]. Chem Mater, 2006, 18:2480-2488. doi: 10.1021/cm051910o [11] ZANDER S, E L KUNKES E L, SCHUSTER M E, SCHUMANN J, WEINBERG G, TESCHNER D, JACOBSEN N, SCHLOGL R, BEHRENS M. The role of the oxide component in the development of copper composite catalysts for methanol synthesis[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng, 2013, 52(25):6536-6540. doi: 10.1002/anie.201301419 [12] 李忠, 张小兵, 郭启海, 刘岩, 郑华艳.沉淀及老化温度对浆态床合成甲醇CuO/ZnO/Al2O3催化剂活性及稳定性的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(5):569-575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.05.010LI Zhong, ZHANG Xiao-bing, GUO Qi-hai, LIU Yan, ZHENG Hua-yan. Influence of precipitation and aging temperature on the performance of CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for methanol synthesis in slurry reactor[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(5):569-575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.05.010 [13] BEHRENS M, GIRGSDIES F. Structural effects of Cu/Zn substitution in the malachite-rosasite system[J]. Z Anorg Allg Chem, 2010, 636(6):919-927. doi: 10.1002/zaac.201000028 [14] BEHRENS M. Coprecipitation:An excellent tool for the synthesis of supported metal catalysts-from the understanding of the well known recipes to new materials[J]. Catal Today, 2015, 246:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.07.050 [15] BEHRENS M. Meso-and nano-structuring of industrial Cu/ZnO/(Al2O3) catalysts[J]. J Catal, 2009, 267(1):24-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=913a94f28cfbe76c4f82140052fd3cb9 [16] LI J, ZHENG H Y, ZHANG X C, LI Z. First-principles investigation on Cu/ZnO catalyst precursor:Energetic, structural and electronic properties of Zn-doped Cu2(OH)2CO3[J]. Comp Mater Sci, 2015, 96:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2014.08.038 [17] 房德仁, 刘中民, 徐秀峰, 张慧敏.老化时间对Cu/ZnO/Al2O3合成甲醇催化剂性能的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2006, 34(1):96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2006.01.020FANG De-ren, LIU Zhong-ming, XU Xiu-feng, ZHANG Hui-min. Influence of aging time on the properties of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for methanol synthesis[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2006, 34(1):96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2006.01.020 [18] TARASOV A, SCHUMANN J, GIRGSDIES F, THOMAS N, BEHRENS M. Thermokinetic investigation of binary Cu/Zn hydroxycarbonates as precursors for Cu/ZnO catalysts[J]. Thermochim Acta, 2014, 591(0):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a3b6b7af127f47c47db90613f54cac6c [19] GAO Y, MENG F H, JI K M, SONG Y, LI Z. Slurry phase methanation of carbon monoxide over nanosized Ni-Al2O3 catalysts prepared by microwave-assisted solution combustion[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2016, 510:74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.11.006 [20] 荆洁颖, 张子毅, 王世东, 李文英.焙烧温度对Ni/CaO-Al2O3结构及其催化重整性能的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2018, 46(6):673-679. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.06.005JING Jie-ying, ZHANG Zi-yi, WANG Shi-dong, LI Wen-ying. Influence of calcination temperature on the structure and catalytic reforming performance of Ni/CaO-Al2O3 catalyst[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2018, 46(6):673-679. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.06.005 [21] BEHRENS M, STUDT F, KASATKIN I, KUHL S, HAVECKER M, ABILD-PEDERSEN F, ZANDER S, GIRGSDIES F, KURR P, KNIEP B L, TOVAR M, FISCHER R W, NORSKOV J K, SCHLOGL R. The active site of methanol synthesis over Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 industrial catalysts[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6083):893-897. doi: 10.1126/science.1219831 [22] WU Q X, DUCHSTEIN L D L, CHIARELLO G L, CHRISTENSEN J M, DAMSGAARD C D, ELKJAR C F, WAGNER J B, TEMEL B, GRUNWALDT J D, JENSEN A D. In situ observation of Cu-Ni alloy nanoparticle formation by X-Ray diffraction, X-Ray absorption spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy:Influence of Cu/Ni ratio[J]. ChemCatChem, 2014, 6(1):301-310. doi: 10.1002/cctc.v6.1 [23] CAO A, LIU G L, YUE Y Z, ZHANG L H, LIU Y. Nanoparticles of Cu-Co alloy derived from layered double hydroxides and their catalytic performance for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas[J]. RSC Adv, 2015, 5(72):58804-58812. doi: 10.1039/C5RA05190H [24] 郭强胜, 毛东森, 俞俊, 韩璐蓬.不同载体对负载型Cu-Fe催化剂CO加氢反应性能的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(9):1103-1109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.013GUO Qiang-sheng, MAO Dong-sen, YU Jun, HAN Lu-peng. Effects of different supports on the catalytic performance of supported Cu-Fe catalyst for CO hydrogenation[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(9):1103-1109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.013 -





 下载:
下载: