Catalytic performance of CuCoCe supported on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas
-
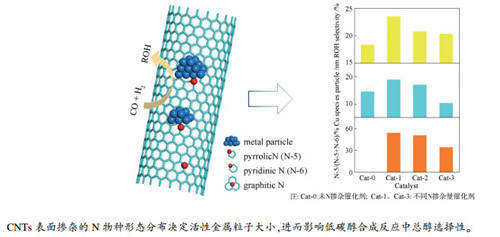
摘要: 以三聚氰胺为氮源,控制其与碳纳米管混合比例,经过高温焙烧得到不同氮含量的氮掺杂碳纳米管(xN-CNTs)载体;通过浸渍法制备xN-CNTs担载的CuCoCe催化剂,研究了氮掺杂对其催化合成气制低碳醇性能的影响。采用X射线衍射(XRD)、N2吸附-脱附、H2程序升温还原(H2-TPR)、NH3程序升温脱附(NH3-TPD)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等表征手段,分析催化剂结构特性,关联了构效关系。结果表明,氮的掺杂量会影响催化剂活性组分Cu的存在状态及分散情况,减少可还原Co物种的数量,降低催化剂表面酸强度及酸量,使得长链烃类的生成受到抑制,总醇选择性明显提高。分析认为,掺杂在碳管上N的形态分布及掺杂量是影响上述因素的关键。Abstract: A series of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes (xN-CNTs) were obtained by treating the mixture of melamine and carbon nanotubes at high temperature; the CuCoCe catalysts supported on xN-CNTs were then prepared by impregnation method and used in the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas. The CuCoCe/xN-CNTs catalysts were characterized by XRD, N2 sorption, H2-TPR, NH3-TPD and XPS and the effect of nitrogen content in xN-CNTs on the catalytic performance of CuCoCe/xN-CNTs in the higher alcohols synthesis was investigated. The results show that the content of nitrogen in xN-CNTs has a significant influence on the existence and dispersion of Cu on the CuCoCe/xN-CNTs catalysts; the presence of nitrogen can reduce the number of reducible Co species and lower the acid strength and amount on the catalyst surface, which helps to suppress the long-chain hydrocarbons formation and improve total alcohol selectivity. It is proposed that the morphological distribution and doping amount of nitrogen on the carbon tubes may play a crucial role in enhancing the catalytic performance of CuCoCe/xN-CNTs in the higher alcohols synthesis.
-
Key words:
- nitrogen doping /
- carbon nanotubes /
- syngas /
- higher alcohols /
- CuCoCe
-
表 1 不同氮含量载体的元素分析
Table 1 Elemental analysis results of the xN-CNTs supports with different nitrogen contents
Support Melamine/CNTs
ratio by weightw/% N C H O CNTs 0/3 0.09 95.19 0.69 4.03 0.1N-CNTs 0.1/3 1.31 96.39 0.71 1.59 0.3N-CNTs 0.3/3 2.28 95.35 0.58 1.79 0.6N-CNTs 0.6/3 3.08 94.61 0.60 1.71 表 2 载体及对应催化剂的织构性质
Table 2 Textural properties of the xN-CNTs supports and corresponding CuCoCe/xN-CNTs catalysts
Support A/(m2·g-1) d /nm vp/(cm3·g-1) Catalyst A/(m2·g-1) d /nm vp/(cm3·g-1) CNTs 199.3 20.3 0.84 Cat-0 153.6 13.2 0.46 0.1N-CNTs 195.6 15.4 0.61 Cat-1 160.4 10.5 0.35 0.3N-CNTs 186.5 14.5 0.53 Cat-2 164.7 10.6 0.35 0.6N-CNTs 177.0 16.8 0.51 Cat-3 160.5 10.3 0.36 notes: A: specific surface area; d: average pore diameter; vp: pore volume 表 3 不同催化剂反应前后Cu物种平均晶粒粒径
Table 3 Average crystallite size of Cu species in different catalysts before and after reaction
Catalyst Before reaction After reaction Cu2O crystal size d/nm Cu0 crystal size d/nm Cat-0 14.4 22.9 Cat-1 18.8 32.3 Cat-2 17.0 30.1 Cat-3 10.3 (CuO) 31.8 表 4 H2-TPR耗氢量
Table 4 Hydrogen consumption of various CuCoCe/xN-CNTs catalysts determined from H2-TPR
Catalyst Reduction peak
t/℃H2 consumption
/(mmol·gcat-1)Cu2+/Cu+
(mol ratio)Cat-0 181 229 472 2.12 0.96 1.05 1.10 Cat-1 175 252 481 1.71 1.42 0.55 0.60 Cat-2 191 256 503 1.99 1.06 0.49 0.94 Cat-3 195 260 504 2.59 0.84 0.50 1.54 表 5 催化剂的酸中心分布
Table 5 Distribution of acid sites on the catalysts
Catalyst Desorption peak t/℃ Peak area weak acid middle acid strong acid weak acid middle acid strong acid Cat-0 150 217/283 394 140 86 31 Cat-1 135 195/280 381 88 104.6 16 Cat-2 133 192/258 384 68 89 12 Cat-3 130 188/256 381 67 74 7 表 6 XPS分析中各物种的结合能
Table 6 Binding energy data of different Cu and Co species on CuCoCe/xN-CNTs from XPS analysis
Catalyst Binding energy E/eV pyridinic N pyrrolic N graphitic N Cu 2p3/2 (Cu+) Cu 2p3/2(Cu2+) Co 2p3/2(Co2+) Cat-0 - - - 932.4 934.3 779.8 Cat-1 398.2 400.2 403.4 932.6 934.5 780.4 Cat-2 398.5 400.4 403.3 932.6 934.5 780.2 Cat-3 398.7 400.8 403.7 932.5 934.6 780.1 表 7 不同催化剂的催化性能
Table 7 Performance of various CuCoCe/xN-CNTs catalysts in the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas
Catalyst CO conversion
x/%Selectivity s/C-mol% C2+OH/ROH
/C-mol%STYROH
/(mg·g-1·h-1)CH4 C2-5 ROH CO2 Cat-0 17.9 23.2 46.9 18.3 11.6 81.3 102.0 Cat-1 12.5 30.7 33.5 23.5 12.3 70.4 96.9 Cat-2 10.7 32.1 36.1 20.7 11.1 68.4 73.5 Cat-3 12.0 29.9 38.3 20.3 11.5 72.2 79.3 notes: CH4 and C2-5, hydrocarbons; ROH, total alcohols; reaction conditions: 300℃, 3.0MPa, V(H2)/V(CO) = 2, feed flow rate of 150mL/min; the data reported are the average data in the 48h reaction process -
[1] GUPTA M, SMITH M, SPIVEY J. Heterogeneous catalytic conversion of dry syngas to ethanol and higher alcohols on Cu-based catalysts[J]. ACS Catal, 2011, 1(6):641-656. doi: 10.1021/cs2001048 [2] SUBRAMANI V, GANGWAL S K. A review of recent literature to search for an efficient catalytic process for the conversion of syngas to ethanol[J]. Energy Fuels, 2008, 22(2):117-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8b83abd191f56aabbe5297a61fd1b46a [3] LUK H T, MONDELLI C, FERRÉ D C, STEWART J A, PÉREZ-RAMÍREZ J. Status and prospects in higher alcohols synthesis from syngas[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2017, 46(5):1358-1426. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00324A [4] AO M, PHAM G H, SUNARSO J, TADE M, LIU S. Active centers of catalysts for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas:A review[J]. ACS Catal, 2018, 8(8):7025-7050. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b01391 [5] XIAO K, BAO Z H, QI X Z, WANG X X. Advances in bifunctional catalysis for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas[J]. Chin J Catal, 2013, 34(1):116-129. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cuihuaxb201301010 [6] XU X D, E-B-M-DOESBURG. Synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas-recently patented catalysts and tentative ideas on the mechanism[J]. Catal Today, 1987, 2(1):125-170. doi: 10.1016/0920-5861(87)80002-0 [7] SHI L, WEI C, DENG S. Catalytic properties of Cu-Co catalysts supported on HNO3-pretreated CNTs for higher-alcohol synthesis[J]. J Nat Gas Chem, 2011, 1:53-57. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqhxzz-e201101007 [8] FANG Y, LIU Y, DENG W. Cu-Co bi-metal catalyst prepared by perovskite CuO/LaCoO3 used for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas[J]. J Energy Chem, 2014, 4:527-534. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqhxzz-e201404017 [9] ANTON J, NEBEL J, GÖBEL C, GABRYSCH J, SONG H, FROESE C, RULAND H, MUHLER M, KALVZA S. CO hydrogenation to higher alcohols over Cu-Co-based catalysts derived from hydrotalcite-type precursors[J]. Top Catal, 2016, 59(15/16):1361-1370. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5550c60c0c5a05287c80e21a1dad2457 [10] HUANG C, ZHANG M, ZHU C. Fabrication of highly stable SiO2 encapsulated multiple CuFe nanoparticles for higher alcohols synthesis via CO hydrogenation[J]. Catal Lett, 2018, 148(4):1080-1092. doi: 10.1007/s10562-018-2329-0 [11] LIN M, FANG K, LI D. CO hydrogenation to mixed alcohols over co-precipitated Cu-Fe catalysts[J]. Catal Commun, 2008, 9(9):1869-1873. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2008.03.004 [12] BAO Z, XIAO K, QI X. Higher alcohol synthesis over Cu-Fe composite oxides with high selectivity to C2+OH[J]. J Energy Chem, 2013, 22(1):107-113. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/84213X/201301/44987872.html [13] CHEN T, SU J, ZHANG Z. Structure evolution of Co-CoOx interface for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas over Co/CeO2 catalysts[J]. ACS Catal, 2018, 8(9):8606-8617. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b00453 [14] PEI Y, DING Y, ZHU H. Study on the effect of alkali promoters on the formation of cobalt carbide (Co2C) and on the performance of Co2C via CO hydrogenation reaction[J]. React Kinet Mech Catal, 2014, 111(2):505-520. doi: 10.1007/s11144-013-0663-1 [15] ZHAO Z, LU W, YANG R. Insight into the formation of Co@Co2C catalysts for direct synthesis of higher alcohols and olefins from syngas[J]. ACS Catal, 2017, 8(1):228-241. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=eabc1698d4d16a5dc0e669c3e43fa2e4 [16] PAN X L, BAO X H. The effects of confinement inside carbon nanotubes on catalysis[J]. Accounts Chem Res, 2011, 44(8):553-562. doi: 10.1021/ar100160t [17] PAN X L, BAO X H. Reactions over catalysts confined in carbon nanotubes[J]. Chem Commun, 2008, 47:6271-6281. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19048128 [18] LEE W J, MAITI U N, LEE J M, LIM J, HAN T H, KIM S O. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes and graphene composite structures for energy and catalytic applications[J]. Chem Commun, 2014, 5(52):6683-6818. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e8b6f296a040181b8004bbd1d2b14af9 [19] SOARES OS G P, ROCHA R P, GONÇALVES A G, FIGUEIREDO J L. Easy method to prepare N-doped carbon nanotubes by ball milling[J]. Carbon, 2015, 91:114-121. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.04.050 [20] CHEN S, QI P, CHEN J. Platinum nanoparticles supported on N-doped carbon nanotubes for the selective oxidation of glycerol to glyceric acid in a base-free aqueous solution[J]. Rsc Adv, 2015, 5:31566-31574. doi: 10.1039/C5RA02112J [21] HE L, WENIGER F, NEUMANN H. Synthesis, characterization, and application of metal nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped carbon:Catalysis beyond elec[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55:12582-12594. doi: 10.1002/anie.201603198 [22] LU J Z, YANG L J, XU B L, W Q, ZHANG D, YUAN S J, ZHAI Y, WANG X Z, FAN Y N, HU Z. Promotion effects of nitrogen doping into carbon nanotubes on supported iron Fischer-Tropsch catalysts for lower olefins[J]. ACS Catal, 2013, 4(2):613-621. doi: 10.1021/cs400931z [23] FU T J, LI Z H. Highly dispersed cobalt on N-doped carbon nanotubes with improved Fischer-Tropsch synthesis activity[J]. Catal Commun, 2014, 47:54-57. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2014.01.008 [24] SHI X P, YU H B, GAO S, LI X Y, FANG H H, LI R J, LI Y Y. Synergistic effect of nitrogen-doped carbon-nanotube-supported Cu-Fe catalyst for the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas[J]. Fuel, 2017, 210:241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.08.064 [25] 李志文, 陈从标, 王俊刚, 林明桂, 侯博, 贾丽涛, 李德宝.氮掺杂介孔炭负载FeCu双金属催化剂及其CO加氢性能研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(6):709-717. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.06.008LI Zhi-wen, CHEN Cong-biao, WANG Jun-gang, LIN Ming-gui, HOU Bo, JIA Li-tao, LI De-bao. Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon supported FeCu bimetallic catalyst and its CO hydrogenation performance[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2019, 47(6):709-717. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.06.008 [26] XIAO K, QI X Z, BAO Z H, WANG X X, ZHONG L S, FANG K G, LIN M G, SUN Y H. CuFe, CuCo and CuNi nanoparticles as catalysts for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas:A comparative study[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2013, 3(6):1162-1591. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2013/cy/c3cy00063j [27] 韩涛, 黄伟, 王晓东, 唐钰, 刘双强, 游向轩. Ce-Cu-Co/CNTs催化剂催化合成气制低碳醇及乙醇的研究[J].物理化学学报, 2014, 30(11):2127-2133. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201409121HAN Tao, HUANG Wei, WANG Xiao-dong, TANG Yu, LIU Shuang-qiang, YOU Xiang-xuan. Study of Ce-Cu-Co/CNTs Catalysts for the synthesis of higher alcohols and ethanol from syngas[J]. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2014, 30(11):2127-2133. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201409121 [28] 杭祖圣, 谈玲华, 居法银, 周斌, 应三九.非等温热重分析三聚氰胺热分解动力学[J].分析科学学报, 2011, 27(3):279-283. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxkxxb201103002HANG Zu-sheng, TAN Ling-hua, JU Fa-yin, ZHOU Bin, YING San-jiu. Non-isothermal kinetic studies on the thermal decomposition of melamine by thermogravimetric analysis[J]. J Analyt Sci, 2011, 27(3):279-283. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxkxxb201103002 [29] KUNDU S, WANG Y, XIA W. Thermal stability and reducibility of oxygen-containing functional groups on multiwalled carbon nanotube surfaces:A quantitative high-resolution XPS and TPD/TPR study[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112(43):16869-16878. doi: 10.1021/jp804413a [30] TARAWNEH K M, AI-AQTASH N. Boron-and nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes with surface defects:An Ab initio study(Article)[J]. J Comput Theor Nanos, 2013, 6:1446-1452. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013JCTN...10.1446A [31] AI P P, TAN M H, YAMANE N, LIU G G, FAN R G, YANG G H, YONEYAMA Y. Synergistic effect of boron-doped carbon nanotubes supported Cu catalyst for selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethanol[J]. Chem-Eur J, 2017, 23(34):8252-8261. doi: 10.1002/chem.201700821 [32] POLSTER C S, NAIR H, BAERTSCH C D. Study of active sites and mechanism responsible for highly selective CO oxidation in H2, rich atmospheres on a mixed Cu and Ce oxide catalyst[J]. J Catal, 2009, 266(2):308-319. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a3585d993986cd42302d94e057d0ef30 [33] KIM J Y, RODRIGUEZ J A, HANSON J C, FRENKEL A I, LEE P L. Reduction of CuO and Cu2O with H2:H Embedding and kinetic effects in the formation of suboxides[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125(35):10684-10692. doi: 10.1021/ja0301673 [34] WANG P, ZHANG J F, BAI Y X, XIAO H, TIAN S P, XIE H J, YANG G H, TSUBAKI N, HAN Y Z, TAN Y S. Ternary copper-cobalt-cerium catalyst for the production of ethanol and higher alcohols through CO hydrogenation[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2016, 514:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2016.01.007 [35] 张宇, 王康军, 张雅静, 杜杰, 李德豹, 任宝锦, 吴静. CO2加氢制二甲醚La1-yZryCu0.7Zn0.3Ox/HZSM-5催化剂的性能研究[J].分子催化, 2015, 6:525-533. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzch201506003ZHANG Yu, WANG Kang-jun, ZHANG Ya-jing, DU Jie, LI De-bao, REN Bao-jin, WU Jing. Synthesis of dimethyl ether from CO2 hydrogenation over La1-yZryCu0.7Zn0.3Ox/HZSM-5 catalysts[J]. J Mol Catal, 2015, 6:525-533. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzch201506003 [36] LI B, SUN X, SU D. Calibration of the basic strength of the nitrogen groups on the nanostructured carbon materials[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2015, 17(10):6691-6694. doi: 10.1039/C4CP05765A [37] FENG W, WANG Q W, JIANG B, JI P J. Carbon nanotubes coated on silica gels as a support of Cu-Co catalyst for the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2011, 50(19):11067-11072. doi: 10.1021/ie2014907 [38] FIERRO G, JACONO M L, INVERSI M, DRAGONE R, PORTA P. TPR and XPS study of cobalt-copper mixed oxide catalysts:Evidence of a strong Co-Cu interaction[J]. Top Catal, 2000, 10(1):39-48. doi: 10.1023%2FA%3A1019151731177 [39] LU R L, MAO D S, YU J. Enhanced activity of Cu-Fe/SiO2 catalyst for CO hydrogenation to higher alcohols by pretreating the support with ammonia[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2015, 25:338-343. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2014.11.013 [40] 郭强胜, 毛东森, 俞俊, 韩璐蓬.不同载体对负载型Cu-Fe催化剂CO加氢反应性能的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(9):1103-1109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.013GUO Qiang-sheng, MAO Dong-sen, YU Jun, HAN Lu-peng. Effects of different supports on the catalytic performance of supported Cu-Fe catalyst for CO hydrogenation[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(9):1103-1109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.013 [41] LI X L, ZHANG J F, ZHANG M, ZHANG W, ZHANG M. The support effects on the direct conversion of syngas to higher alcohol synthesis over copper-based catalysts[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(2):199. doi: 10.3390/catal9020199 [42] HERACLEOUS E, LIAKAKOU E T, LAPPAS A A, LEMONIDOU A A. Investigation of K-promoted Cu-Zn-Al, Cu-X-Al and Cu-Zn-X (X=Cr, Mn) catalysts for carbon monoxide hydrogenation to higher alcohols[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2013, 455:145-154. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.02.001 [43] 孙予罕, 陈建刚, 王俊刚, 贾丽涛, 侯博, 李德宝, 张娟.费托合成钴基催化剂的研究进展[J].催化学报, 2010, 31(8):919-927. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cuihuaxb201008007SUN Yu-han, CHEN Jian-gang, WANG Jun-gang, JIA Li-tao, HOU Bo, LI De-bao, ZHANG Juan. The development of cobalt-based catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Chin J Catal, 2010, 31(8):919-927. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cuihuaxb201008007 -





 下载:
下载: