-
摘要: 分别采用共沉淀法和水热法制备了ZnCrOx复合金属氧化物和HZSM-5沸石,通过物理混合得到双功能催化剂,实现了合成气一步高选择性制备异构烷烃。采用XRD、TEM、氮吸附和NH3-TPD等技术对催化剂进行了表征,考察了双功能催化剂中HZSM-5沸石组分硅铝比以及ZnCrOx/HZSM-5质量比(OX/ZEO mass ratio)对合成气催化转化反应性能的影响。结果表明,随着HZSM-5硅铝比的增加,催化剂酸密度下降,CO转化率略有下降,产物中C5+选择性显著提高,异构烷烃比例不断增加。此外,在保证CO转化率的前提下提高双功能催化剂中ZnCrOx组分的比例,产物中C5+的选择性也显著上升。在400 ℃、2.0 MPa、进料空速(GHSV)为3600 mL/(h·gcat)的条件下,合成气(H2/CO(volume ratio)=2)转化率达到35%,C5+选择性超过44%,且C5+中异戊烷比例高达65%。Abstract: ZnCrOx composite oxide and HZSM-5 zeolite were prepared by using the coprecipitation and hydrothermal methods, respectively; after that, a bi-functional ZnCrOx/HZSM-5 catalyst was obtained through physical mixing of ZnCrOx with HZSM-5 and used in the direct synthesis of isoalkanes from syngas. The ZnCrOx/HZSM-5 catalyst was characterized by XRD, TEM, N2 sorption, and NH3-TPD and the effects of Si/Al ratio in HZSM-5 and the mass ratio of ZnCrOx to HZSM-5 (OX/ZEO mass ratio) on the catalytic performance of ZnCrOx/HZSM-5 in syngas conversion were investigated. The results indicated that with the increase of Si/Al ratio in HZSM-5, the catalyst acid density is decreased, resulting in a lower CO conversion but higher selectivity to C5+ products and higher isoparaffin fraction. Moreover, the selectivity to C5+ products is significantly increased by increasing the proportion of ZnCrOx components in the bifunctional catalyst without losing CO conversion. For the syngas conversion over ZnCrOx/HZSM-5 catalyst under the conditions of 400 ℃, 2.0 MPa, gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 3600 mL/(h·gcat), the conversion of syngas reaches 35%, with a selectivity of 44% to C5+ products and an isopentane fraction up to 65% in the C5+ products.
-
Key words:
- bifunctional catalyst /
- syngas /
- acid-catalyzed /
- isopentane
-
图 4 不同温度下ZnCrOx/ HZSM-5(160)的催化反应性能
Figure 4 Catalytic performance of ZnCrOx/ HZSM-5(160) in syngas conversion at different temperatures reaction conditions: 0.5 g ZnCrOx/HZSM-5
(mass ratio = 1:1), H2/CO(volume ratio)=2, p=2.0 MPa, GHSV=3600 mL/(h·gcat), TOS= 4 h, C2-4=: C2-4 olefins, C2-4o: C2-4 alkanes, C5+: hydrocarbons with more than 5 carbons except aromatics, Ar: aromatics
表 1 ZnCrOx和HZSM-5样品的物理化学性质
Table 1 Textural properties of the ZnCrOx and HZSM-5 samplesa
Sample ABET/(m2·g-1) Amicro/(m2·g-1) Ameso/(m2·g-1) vpore/(mL·g-1) vmicro/(mL·g-1) ZnCrOx 88 0 88 0.407 0 HZSM-5(20) 342 289 53 0.223 0.135 HZSM-5(40) 356 303 53 0.312 0.135 HZSM-5(80) 375 296 79 0.233 0.126 HZSM-5(160) 363 283 80 0.226 0.121 a: obtained by N2 physisorption 表 2 HZSM-5样品的表面酸性质
Table 2 Surface acidity of H-ZSM-5 samplesa
Sample t1/℃ Weak acidity/ (mmol·g-1) Weak acidity density /(μmol·m-2) t2 /℃ Strong acidity/ (mmol·g-1) Strong acidity density/ (μmol·m-2) HZSM-5(20) 172 0.41 1.19 267 0.24 0.70 HZSM-5(40) 169 0.28 0.77 346 0.24 0.67 HZSM-5(80) 158 0.13 0.34 333 0.13 0.33 HZSM-5(160) 152 0.07 0.20 326 0.09 0.25 a: obtained by NH3-TPD 表 3 不同硅铝比ZnCrOx/HZSM-5的催化反应性能
Table 3 Catalytic performance of ZnCrOx/ HZSM-5 with different Si/Al ratios
Catalyst CO
conversion x/%CO2
selectivity s/%ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(20) 39.9 42.0 ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(40) 38.8 41.8 ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(80) 37.3 40.6 ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(160) 36.9 42.6 ZnCrOx 5.6 42.9 reaction conditions: 0.5 g ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(mass ratio=1:1), H2/CO(volume ratio)=2, 400 ℃, 2.0 MPa, GHSV=3600 mL/(h·gcat), TOS= 8 h 表 4 不同硅铝比ZnCrOx/HZSM-5催化反应产物中的C5+分布
Table 4 C5+ distribution of hybrid ZnCrOx/HZSM-5 with different Si/Al ratios
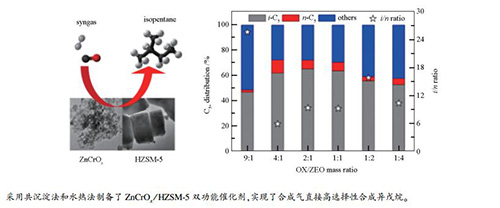
Catalyst C5+ distribution/% i/n ratio i-C5 n-C5 others ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(20) 48.7 13.9 37.4 3.5 ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(40) 50.2 10.1 39.7 5.0 ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(80) 56.6 9.7 33.7 5.8 ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(160) 63.8 6.8 29.4 9.3 reaction conditions: 0.5 g ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(mass ratio=1:1), H2/CO(volume ratio)=2, t=400 ℃, p=2.0 MPa, GHSV=3600 mL/(h·gcat), TOS=8 h 表 5 不同OX/ZEO质量比ZnCrOx/HZSM-5的催化反应性能
Table 5 Catalytic performance of ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(160) with different OX/ZEO mass ratios
OX/ZEO (mass ratio) CO conversion x/% CO2 selectivity s/% 9:1 24.8 37.8 4:1 27.4 37.7 2:1 35.5 41.0 1:1 36.9 42.6 1:2 37.1 43.3 1:4 36.5 45.3 reaction conditions: 0.5 g ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(160), H2/CO(volume ratio)= 2, 400 ℃, 2.0 MPa, GHSV=3600 mL/(h·gcat), TOS=8 h 表 6 不同质量比ZnCrOx/HZSM-5催化反应产物中的C5+分布
Table 6 C5+ distribution for syngas conversion over hybrid ZnCrOx/HZSM-5 with different OX/ZEO mass ratios
OX/ZEO (mass ratio) C5+ distribution/% i/n ratio i-C5 n-C5 others 9:1 47.1 1.8 51.1 25.8 4:1 62.0 10.4 27.6 6.0 2:1 65.4 6.9 27.7 9.4 1:1 63.8 6.8 29.4 9.3 1:2 55.9 3.5 40.6 15.9 1:4 52.9 5.1 42.1 10.5 reaction conditions: 0.5 g ZnCrOx/HZSM-5(160), H2/CO(volume ratio)=2, t=400 ℃, p=2.0 MPa, GHSV=3600 mL/(h·gcat), TOS=8 h -
[1] TORRES GALVIS H M, BITTER J H, KHARE C B, RUITENBEEK M, DUGULAN A I, DE JONG K P. Supported iron nanoparticles as catalysts for sustainable production of lower olefins[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6070):835-838. doi: 10.1126/science.1215614 [2] FU X-P, SHEN Q-K, SHI D, WU K, JIN Z, WANG X, SI R, SONG Q-S, JIA C-J, YAN C-H. Co3O4-Al2O3 mesoporous hollow spheres as efficient catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2017, 211:176-187. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.036 [3] ZHONG L, YU F, AN Y, ZHAO Y, SUN Y, LI Z, LIN T, LIN Y, QI X, DAI Y, GU L, HU J, JIN S, SHEN Q, WANG H. Cobalt carbide nanoprisms for direct production of lower olefins from syngas[J]. Nature, 2016, 538:84-87. doi: 10.1038/nature19786 [4] LI X, FENG X, GE Q, FUJIMOTO K. Direct synthesis of iso-paraffins from syngas with slurry phase reaction[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(4):534-538. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cf4a6ebb11489c6626ff7010bfbcc244&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] ZHAO B, ZHAI P, WANG P F, LI J Q, LI T, PENG M, ZHAO M, HU G, YANG Y, LI Y W, ZHANG Q, FAN W, MA D. Direct transformation of syngas to aromatics over Na-Zn-Fe5C2 and hierarchical HZSM-5 tandem catalysts[J]. Chem, 2017, 3(2):323-333. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2017.06.017 [6] JIAO F, LI J, PAN X, XIAO J, LI H, MA H, WEI M, PAN Y, ZHOU Z, LI M, MIAO S, LI J, ZHU Y F, XIAO D, HE T, YANG J H, QI F, FU Q, BAO X H. Selective conversion of syngas to light olefins[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6277):1065-1068. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1835 [7] CHENG K, GU B, LIU X, KANG J, ZHANG Q, WANG Y. Direct and highly selective conversion of synthesis gas into lower olefins:design of a bifunctional catalyst combining methanol synthesis and carbon-carbon coupling[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55(15):4725-4728. doi: 10.1002/anie.201601208 [8] CHENG K, ZHOU W, KANG J, HE S, SHI S, ZHANG Q, PAN Y, WEN W, WANG Y. Bifunctional catalysts for one-step conversion of syngas into aromatics with excellent selectivity and stability[J]. Chem, 2017, 3(2):334-347. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2017.05.007 [9] YANG J, PAN X, JIAO F, LI J, BAO X. Direct conversion of syngas to aromatics[J]. Chem Commun, 2017, 53(81):11146-11149. doi: 10.1039/C7CC04768A [10] ZHANG P, TAN L, YANG G, TSUBAKI N. One-pass selective conversion of syngas to paraxylene[J]. Chem Sci, 2017, 8(12):7941-7946. doi: 10.1039/C7SC03427J [11] HOFF T C, THILAKARATNE R, GARDNER D W, BROWN R C, TESSONNIER J-P. Thermal stability of aluminum-rich ZSM-5 zeolites and consequences on aromatization reactions[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2016, 120(36):20103-20113. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b04671 [12] PÉREZ-URIARTE P, GAMERO M, ATEKA A, DÍAZ M, AGUAYO A T, BILBAO J. Effect of the acidity of HZSM-5 zeolite and the binder in the DME transformation to olefins[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2016, 55(6):1513-1521. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b04477 [13] BORTNOVSKY O, SAZAMA P, WICHTERLOVA B. Cracking of pentenes to C2-4 light olefins over zeolites and zeotypes role of topology and acid site strength and concentration[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen, 2005, 287(2):203-213. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2005.03.037 -





 下载:
下载: