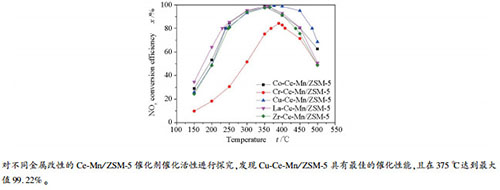
| [1] |
李言顺, 郑逸璇, 刘梦瑶, 郑博, 王婷, 同丹, 粟京平, 王普才, 林金泰, 张强.卫星遥感反演京津冀地区2011-2017年氮氧化物污染变化[J].环境科学学报, 2018, 38(10): 3797-3806. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201810002LI Yan-shun, ZHENG Yi-xuan, LIU Meng-yao, ZHENG Bo, WANG Ting, TONG Dan, LI Jing-ping, WANG Pu-cai, LIN Jin-tai, ZHANG Qiang. Satellite-based observations of changes in nitrogen oxides over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2011 to 2017[J]. J Environ Sci-China, 2018, 38(10): 3797-3806. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201810002
|
| [2] |
COGHLAN A.The curious case of NOx pollution[J].New Sci, 2015, 227(3041): 10-11. doi: 10.1016/S0262-4079(15)31295-1
|
| [3] |
KNIBBS L D, CORTES DE WATERMAN A M, TOELLE B G, GUO Y, DENISON L, JALALUDIN B, MARKS G B, WILLIAMS G M. The Australian Child Health and Air Pollution Study (ACHAPS): A national population-based cross-sectional study of long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution, asthma, and lung function[J]. Environ Int, 2018, 120: 394-403. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.08.025
|
| [4] |
王爱娟, 孙丽丽, 张璟尧.《锅炉大气污染物排放标准》(GB13271-2014)浅析[J].环境研究与监测, 2017, 30(3): 76-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017110100000190WANG Ai-juan, SUN Li-li, ZHANG Jing-yao. Analysis on "Standard for Pollutant Emission from Boilers"(GB13271-2014)[J]. Environ Res Monitor, 2017, 30(3): 76-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017110100000190
|
| [5] |
杨延龙.火电厂氮氧化物减排及SCR烟气脱硝技术浅析[J].能源环境保护, 2017, 31(2): 31-35, 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2017.02.010YANG Yan-long. Emissions reduction of NOx in coal-fired power plant and simple analysis of SCR flue gas denitration technology[J]. Energy Environ Prot, 2017, 31(2): 31-35, 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2017.02.010
|
| [6] |
CHEN C, CAO Y, LIU S, CHEN J M, JIA W B. Review on the latest developments in modified vanadium-titanium-based SCR catalysts[J]. Chin J Catal, 2018, 39 (8): 1347-1365. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(18)63090-6
|
| [7] |
JIANG L J, LIU Q C, RAN G J, KONG G J, REN M, YANG S, LI J, JIANG L. V2O5-modified Mn-Ce/AC catalyst with high SO2 tolerance for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO[J]. Chem Eng J, 2019, 370: 810-821. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.225
|
| [8] |
WEI Y, FAN H, WANG R. Transition metals (Co, Zr, Ti) modified iron-samarium oxide as efficient catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx at low-temperature[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 459: 63-73. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.07.151
|
| [9] |
李晓东, 吕刚, 宋崇林, 宋金瓯, 宾峰, 吴少华.金属改性分子筛型催化剂低温SCR反应机理[J].燃烧科学与技术, 2014, 20(4): 341-347. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rskxyjs201404011LI Xiao-dong, LYU Gang, SONG Chong-lin, SONG Jin-ou, BIN Feng, WU Shao-hua. Mechanism of the Low-Temperature SCR reaction on metal modified ZSM-5 catalysts[J]. J Combust Sci Technol, 2014, 20(4): 341-347. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rskxyjs201404011
|
| [10] |
CARJA G, KAMESHIMA Y, OKADA K, MADHUSOODANA C D. Mn-Ce/ZSM5 as a new superior catalyst for NO reduction with NH3[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ, 2007, 73(1): 60-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=713d6e33dae8be959b7f25976b62a459
|
| [11] |
WANG T, LIU H, ZHANG X, LIU J, ZHANG Y, GUO Y, SUN B. Catalytic conversion of NO assisted by plasma over Mn-Ce/ZSM5-multi-walled carbon nanotubes composites: Investigation of acidity, activity and stability of catalyst in the synergic system[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 457: 187-199. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.216
|
| [12] |
ZHOU G, ZHONG B, WANG W, GUAN X, HUANG B, YE D, WU H. In situ DRIFTS study of NO reduction by NH3 over Fe-Ce-Mn/ZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Catal Today, 2011, 175(1): 157-163. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.06.004
|
| [13] |
PENG C, LIU Z, YONEZAWA Y, YANABA Y, KATADA N, MURAYAMA I, SEGOSHI S, OKUBO T, WAKIHARA T. Ultrafast post-synthesis treatment to prepare ZSM-5@Silicalite-1 as a core-shell structured zeolite catalyst[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2019, 277: 197-202. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.10.036
|
| [14] |
RUI J, LYU J, HU H, ZHANG Q, WANG Q, LI X. Synthesized high-silica hierarchical porous ZSM-5 and optimization of its reaction conditions in benzene alkylation with methanol[J]. Chin Chem Lett, 2019, 30(3): 757-761. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2018.09.016
|
| [15] |
ZHU L, ZHANG L, QU H, ZHONG Q. A study on chemisorbed oxygen and reaction process of Fe-CuOx/ZSM-5 via ultrasonic impregnation method for low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. J Mol Catal A: Chem, 2015, 409: 207-215. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.08.029
|
| [16] |
AND T G D, KANNAN M P. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) studies on the chemical states of some metal species in cellulosic chars and the ellingham diagrams[J]. Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(2): 596-601. doi: 10.1021/ef060395t
|
| [17] |
PANG L, FAN C, SHAO L, SONG K, YI J, CAI X, WANG J, KANG M, LI T. The Ce doping Cu/ZSM-5 as a new superior catalyst to remove NO from diesel engine exhaust[J]. Chem Eng J, 2014, 253: 394-401. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.090
|
| [18] |
LIU X, WU X, WENG D, SHI L. Modification of Cu/ZSM-5 catalyst with CeO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia[J]. J Rare Earths, 2016, 34(10): 1004-1009. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(16)60127-8
|
| [19] |
XU W, ZHANG G, CHEN H, ZHANG G, HAN Y, CHANG Y, GONG P. Mn/beta and Mn/ZSM-5 for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia: Effect of manganese precursors[J]. Chin J Catal, 2018, 39(1): 118-127. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(17)62983-8
|
| [20] |
NANBA T, MASUKAWA S, OGATA A, UCHISAWA J, OBUCHI A. Active sites of Cu-ZSM-5 for the decomposition of acrylonitrile[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ, 2005, 61(3): 288-296. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5a3c36cac218abe507041bd4377fe34d
|
| [21] |
SOWADE T, LIESE T, SCHMIDT C, SCHVTZE F W, YU X, BERNDT H, GRVNERT W. Relations between structure and catalytic activity of Ce-In-ZSM-5 catalysts for the selective reduction of NO by methane: Ⅱ. Interplay between the CeO2 promoter and different indium sites[J]. J Catal, 2004, 225(1): 105-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2004.03.026
|





 下载:
下载: