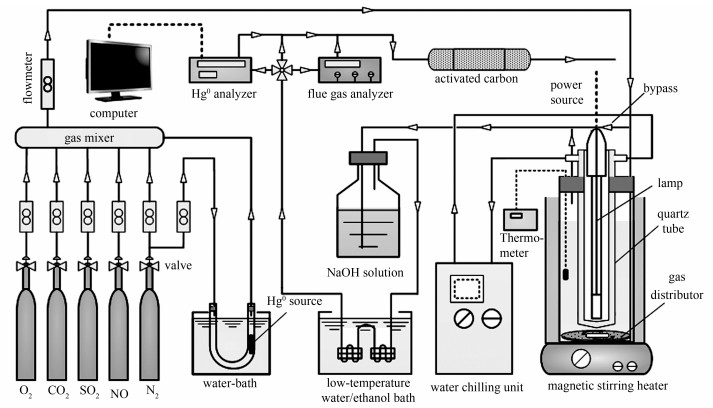
Effects of experimental parameters on Hg0 removal over magnetic AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 photocatalysts using wet process
-
摘要: 采用水热-共沉淀法制备了一种新型的磁性AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4复合材料光催化剂,考察了荧光灯辐照下光催化剂脱除模拟烟气中单质汞(Hg0)的性能,研究了实验参数对脱汞性能的影响及反应产物。结果表明,AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4光催化剂的热稳定性较差,当煅烧温度超过400 ℃时该光催化剂的化学成分会发生变化;随着催化剂用量、反应溶液pH值、反应溶液温度和烟气中O2浓度的增加,脱汞效率先增加后不变或下降;反应溶液中存在的CO32-和SO42-对脱汞效率有一定的抑制作用;当通入SO2时,脱汞效率急剧下降;而NO对脱汞效率的抑制作用相对较小。反应产物分析表明,SO2、NO和Hg0的最终氧化产物分别是SO42-、NO3-和Hg2+。
-
关键词:
- 磁分离 /
- AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 /
- 脱汞 /
- 荧光灯照射 /
- 实验参数
Abstract: A novel magnetic AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 hybrid composites were prepared via a solvothermal and subsequent coprecipitation method, and utilized to remove Hg0 from coal-fired flue gas under fluorescent light irradiation. The experimental parameters and main products presented in solution after reaction were investigated in detail. The experimental results showed that the AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 composites showing a poor thermal stability would transform into other compounds when the calcinated temperature was above 400℃. With the increases of photocatalyst dosage, reaction solution pH, temperature of reaction solution in reactor and O2 concentration, the Hg0 removal efficiencies were first increased and then unchanged or decreased. The presences of inorganic anions such as CO32- and SO42- in solution exhibited some inhibitory effects on Hg0 removal. Furthermore, the presence of SO2 had a dramatic inhibition on Hg0 removal, while the inhibitory effect of NO on Hg0 removal was relatively small. SO42-, NO3- and Hg2+ species were the final oxidation products of SO2, NO and Hg0 by reactive species. -
Figure 10 (a) Cycling runs for photocatalytic oxidation of Hg0 over AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 and (b) magnetic hysteresis loops for AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 after four consecutive runs
error bars represent standard deviation of means (n=3) conditions: Hg0=55.0 μ g/m3, t=35 ℃, initial pH=7, solution volume=1 L, FSL radiation intensity=11 W/L, catalyst dosage=200 mg/L
Table 1 Physical features of AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 hybrids calcinated at different temperatures
Sample BET surface area A/(m2·g-1) Total pore volume v/(cm3·g-1) Without calcination 20.7 0.066 200 ℃ calcination 33.9 0.114 400 ℃ calcination 15.1 0.056 600 ℃ calcination 1.5 0.002 Table 2 Reaction products of SO2 and NO by AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4
Ion category SO32- SO42- NO2- NO3- Measured concentration 0 40.32 mg/L 0 15.50 mg/L -
[1] YANG S J, GUO Y F, YAN N Q, WU D Q, HE H P, XIE J K, QU Z, JIA J P. Remarkable effect of the incorporation of titanium on the catalytic activity and SO2 poisoning resistance of magnetic Mn-Fe spinel for elemental mercury capture[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2011, 10(3/4):698-708. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/460393 [2] ZHOU Q, DUAN Y F, HONG Y G, ZHU C, SHE M, ZHANG J, WEI H Q. Experimental and kinetic studies of gas-phase mercury adsorption by raw and bromine modified activated carbon[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 134:325-332. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.12.052 [3] YOU C F, XU X C. Coal combustion and its pollution control in China[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(11):4467-4472. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2009.04.019 [4] WU J, LI C E, ZHAO X Y, WU Q, QI X M, CHEN X T, HU T, CAO Y. Photocatalytic oxidation of gas-phase Hg0 by CuO/TiO2[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2015, 176/177:559-569. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.044 [5] 张华伟, 陈江艳, 赵可, 牛庆欣, 王力. Mn/Ce掺杂改性半焦对模拟煤气中单质汞的脱除性能研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(4):394-400. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18805.shtmlZHANG Hua-wei, CHEN Jiang-yan, ZHAO Ke, NIU Qing-xin, WANG Li. Removal of vapor-phase elemental mercury from simulated syngas using semi-coke modified by Mn/Ce doping[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2016, 44(4):394-400. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract18805.shtml [6] HAN L N, HE X X, YUE C X, HU Y F, LI L N, CHANG L P, WANG H, WANG J C. Fe doping Pd/AC sorbent efficiently improving the Hg0 removal from the coal-derived fuel gas[J]. Fuel, 2016, 182:64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.05.046 [7] WANG F M, LI G L, SHEN B X, WANG Y Y, HE C. Mercury removal over the vanadia-titania catalyst in CO2-enriched conditions[J]. Chem Eng J, 2015, 263:356-363. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.091 [8] JEON S H, EOM Y J, LEE T G. Photocatalytic oxidation of gas-phase elemental mercury by nanotitanosilicate fibers[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 71(5):969-974. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.050 [9] WU J, LI X, REN J X, QI X M, HE P, NI B, ZHANG C, HU C Z, ZHOU J. Experimental study of TiO2 hollow microspheres removal on elemental mercury in simulated flue gas[J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2015, 32:49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2015.07.019 [10] SNIDER G, ARIYA P. Photo-catalytic oxidation reaction of gaseous mercury over titanium dioxide nanoparticle surfaces[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2010, 491(1/3):23-28. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009261410004604 [11] SHEN H Z, IE I R, YUAN C S, HUNG C H, CHEN W H, LUO J J, JEN Y H. Enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous elemental mercury by TiO2 in a high temperature environment[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2015, 289:235-243. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.033 [12] 袁媛, 张军营, 赵永椿, 王宇翔, 郑楚光. SO2和NO浓度对TiO2-硅酸铝纤维脱除元素汞的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2012, 40(5):630-635. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract17955.shtmlYUAN Yuan, ZHANG Jun-ying, ZHAO Yong-chun, WANG Yu-xiang, ZHENG Chu-guang. Effects of SO2 and NO on removal of elemental mercury using a TiO2-aluminum silicate fiber[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2012, 40(5):630-635. http://manu60.magtech.com.cn/rlhxxb/CN/abstract/abstract17955.shtml [13] LI Y, WU C Y. Kinetic study for photocatalytic oxidation of elemental mercury on a SiO2-TiO2 nanocomposite[J]. Environ Eng Sci, 2007, 24(1):3-12. doi: 10.1089/ees.2007.24.3 [14] YUAN Y, ZHANG J Y, LI H L, LI Y, ZHAO Y C, ZHENG C G. Simultaneous removal of SO2, NO and mercury using TiO2-aluminum silicate fiber by photocatalysis[J]. Chem Eng J, 2012, 192(2):21-28. http://www.doc88.com/p-9843440989534.html [15] QI X M, GU M L, ZHU X Y, WU J, LONG H M, HE K, WU Q. Fabrication of BiOIO3 nanosheets with remarkable photocatalytic oxidation removal for gaseous elemental mercury[J]. Chem Eng J, 2016, 285:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.055 [16] DONG G H, HO W K, ZHANG L Z. Photocatalytic NO removal on BiOI surface:The change from nonselective oxidation to selective oxidation[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2015, 168/169:490-496. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337315000193 [17] OU M, ZHONG Q, ZHANG S L, NIE H Y, LV Z J, CAI W. Graphene-decorated 3D BiVO4 superstructure:Highly reactive (040) facets formation and enhanced visible-light-induced photocatalytic oxidation of NO in gas phase[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2016, 193:160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.029 [18] ZHANG A C, XING W B, ZHANG D, WANG H, CHEN G Y, XIANG J. A novel low-cost method for Hg0removal from flue gas by visible-light-driven BiOX (X=Cl, Br, I) photocatalysts[J]. Catal Commun, 2016, 87:57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.09.003 [19] ZHANG A C, ZHANG L X, CHEN X Z, ZHU Q F, LIU Z C, XIANG J. Photocatalytic oxidation removal of Hg0 using ternary Ag/AgI-Ag2CO3 hybrids in wet scrubbing process under fluorescent light[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 392:1107-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.116 [20] ZHANG L X, ZHANG A C, LU H, SUN Z J, SHENG W, SUN L S, XIANG J. Magnetically separable AgI-BiOI/CoFe2O4 hybrid composites for Hg0 removal:Characterization, activity and mechanism[J]. RSC Adv, 2017, 7(50):31448-31456. doi: 10.1039/C7RA04175F [21] CHENG H F, HUANG B B, DAI Y, QIN X Y, ZHANG X Y. One-Step synthesis of the nanostructured AgI/BiOI composites with highly enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performances[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(9):6618-6624. doi: 10.1021/la903943s [22] YU C L, FAN C F, YU J C, ZHOU W Q, YANG K. Preparation of bismuth oxyiodides and oxides and their photooxidation characteristic under visible/UV light irradiation[J]. Mater Res Bull, 2011, 46(1):140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.08.013 [23] CAO J, LI X, LIN H L, XU B Y, LUO B D, CHEN S F. Low temperature synthesis of novel rodlike Bi5O7I with visible light photocatalytic performance[J]. Mater Lett, 2012, 76(6):181-183. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925838817304371 [24] RAUF M A, MARZOUKI N, KORBAHTI B K. Photolytic decolorization of Rose Bengal by UV/H2O2 and data optimization using response surface method[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2008, 159(2/3):602-609. doi: 10.1021/jp909855p [25] SANTIAGO D E, ARANA J, GONZÁLEZ-D O, ALEMÁN-D M E, ACOSTA-D A C, FERNANDEZ-R C, PÉREZ-P J, DONA-R J M. Effect of inorganic ions on the photocatalytic treatment of agro-industrial wastewaters containing imazalil[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ, 2014, 156/157(3):284-292. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337314001775 [26] CHEN J, HU Z, WANG D, GAO C, JI R. Photocatalytic mineralization of dimethoate in aqueous solutions using TiO2:Parameters and by-products analysis[J]. Desalination, 2010, 258(1):28-33. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0011916410002092 [27] ZHAO Y, HAO R L. Macrokinetics of Hg0 removal by a vaporized multicomponent oxidant[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2014, 53(27):10899-10905. doi: 10.1021/ie5009376 [28] XIA D H, HU L L, HE C, PAN W Q, YANG T S, YANG Y C, SHU D. Simultaneous photocatalytic elimination of gaseous NO and SO2 in a BiOI/Al2O3-padded trickling scrubber under visible light[J]. Chem Eng J, 2015, 279:929-938. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.097 [29] KIM J, LEE C W, CHOI W. Platinized WO3 as an environmental photocatalyst that generates OH radicals under visible light[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2010, 44(17):6849-6854. doi: 10.1021/es101981r [30] LIU Y X, ZHANG J, SHENG C D, ZHANG Y C, ZHAO L. Simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 from coal-fired flue gas by UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process[J]. Chem Eng J, 2010, 162(3):1006-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.07.009 [31] LASEK J, YU Y H, WU J C S. Removal of NOx by photocatalytic processes[J]. J Photochem Photobiol C, 2013, 14(1):29-52. doi: 10.1021/jp912201h?src=recsys [32] MCLARNON C R, GRANITE E J, PENNLINE H W. The PCO Process for photochemical removal of mercury from flue gas[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2005, 87(1):85-89. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2005.07.001 [33] LIU Y X, ZHANG J, SHENG C D, ZHANG Y C, ZHAO L. Preliminary study on a new technique for wet removal of nitric oxide from simulated flue gas with an ultraviolet (UV)/H2O2 process[J]. Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(9):4925-4930. doi: 10.1021/ef1006325 -





 下载:
下载: