In-situ study on gasification reaction characteristics of Ningdong coal chars with CO2
-
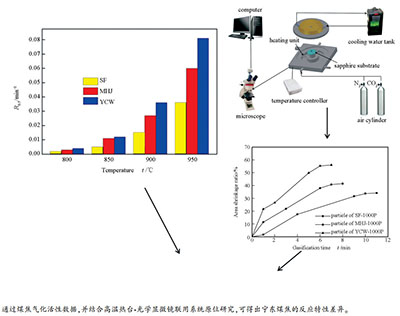
摘要: 以典型宁东煤-梅花井烟煤和羊场湾烟煤焦为气化样品,并与典型气化用煤-神府烟煤焦对比,采用热重分析仪及高温热台-光学显微镜联用系统原位研究煤焦气化反应活性,并结合焦样理化结构特性的系统表征对其进行关联解释。结果表明,在相同气化温度下,三种煤焦的气化反应活性大小顺序为:羊场湾烟煤焦>梅花井烟煤焦>神府烟煤焦。由高温热台实验原位研究可知,随着煤焦-CO2反应的进行,大部分煤焦颗粒反应形式以颗粒收缩进行,到达反应中后期,反应由颗粒收缩转变为缩芯形式,并通过投射面积收缩率可发现,相同反应时间下,羊场湾烟煤焦的投射面积收缩率最大,其后依次为梅花井烟煤焦和神府烟煤焦。气化反应活性的差异主要归因于不同煤焦理化性质间的差异:羊场湾烟煤焦的比表面积、炭结构无序化程度和K、Na、Ca总含量最大,其后依次为梅花井烟煤焦和神府烟煤焦。
-
关键词:
- 宁东煤 /
- 高温热台-光学显微镜联用系统 /
- 气化反应活性 /
- 理化性质
Abstract: Meihuajing coal and Yangchangwan coal from Ningdong, China are chosen as raw materials to study char gasification reactivity using thermogravimetric analyzer and in-situ heating stage microscope, and typical gasification coal-Shenfu bituminous coal char is used as reference char sample. The char physicochemical properties are systematically characterized. The results show that the order for gasification reactivity of 3 chars at the same gasification temperature is Yangchangwan char > Meihuajing char > Shenfu char. In-situ study of heating stage microscope shows that with the progress of char-CO2 gasification, most of char particles react with CO2 as shrinking particle mode, and the particle reaction form changes from shrinking particle mode to shrinking core mode at high carbon conversion level. Additionally, it can be found from the results of shrinkage ratio variation of the particle projected area during gasification that Yangchangwan char shows the largest shrinkage area when undergoes the same reaction time, followed by Meihuajing char and Shenfu char. The difference in gasification reactivity is mainly attributed to the difference of physicochemical properties of chars. i.e., Yangchangwan char shows the largest specific surface area and the total contents of K, Na and Ca and the lowest order degree of carbon structure, followed by Meihuajing char and Shenfu char.1) 本文的英文电子版由Elsevier出版社在ScienceDirect上出版(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/18725813). -
图 4 基于原位高温热台显微镜的SF-1000P CO2气化反应过程固体结构演变
Figure 4 Solid structure evolution during SF-1000P CO2 gasification recorded by the in-situ heating stage microscope
(note: SF-950 ℃-N2 represents heating to 950 ℃ under N2 atmosphere; SF-950 ℃-CO2-1 min represents 1 min of isothermal gasification under CO2 atmosphere and 950 ℃, and so on; the values of length, width and area are the average of 3 particles)
表 1 实验样品的基础分析数据
Table 1 Basic properties of samples
Sample Proximate analysis wd/% Ultimate analysis wd/% Ash fusion temperature t/℃ V FC A C H N S O* DT ST HT FT MHJ 27.87 50.48 21.65 54.71 3.14 0.64 1.32 18.54 1167 1201 1209 1230 YCW 26.64 56.81 16.55 64.42 3.63 0.67 1.14 13.59 1183 1201 1207 1213 SF 29.51 61.92 8.57 73.01 4.18 0.85 0.53 12.86 1161 1175 1187 1198 note: V: volatile matter; FC: fixed carbon; d: dry basis; *: calculated by difference; DT: deformation temperature;
ST: softening temperature; HT: hemispherical temperature; FT: flow temperature表 2 实验样品的灰化学组成
Table 2 Ash chemical compositions of samples
Sample Composition w/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO Na2O K2O MgO MHJ 51.34 22.53 8.01 5.18 1.20 1.97 4.11 YCW 41.59 18.28 9.27 12.25 2.19 1.51 4.77 SF 45.06 19.19 9.06 13.87 2.09 0.90 0.96 表 3 焦样孔结构参数
Table 3 Pore structure parameters of char samples
Sample ABET/(m2·g-1) SF-1000P 3.16 MHJ-1000P 4.53 YCW-1000P 6.15 表 4 焦样拉曼光谱峰面积比
Table 4 Raman band area ratio of char samples
Sample ID1/IG IG/IAll ID3/IG+D2+D3 SF-1000P 4.903 0.120 0.470 MHJ-1000P 5.735 0.109 0.489 YCW-1000P 6.479 0.095 0.512 表 5 焦样的元素组成
Table 5 Element composition of char samples
Sample Content w/% K Na Ca SF-1000P 0.16 0.17 1.50 MHJ-1000P 0.58 0.19 1.55 YCW-1000P 0.40 0.30 1.90 表 6 焦样气化反应活性指数
Table 6 Gasification reactivity index of char samples
Sample R0.5/min-1 800 ℃ 850 ℃ 900 ℃ 950 ℃ SF-1000P 0.002 0.005 0.015 0.036 MHJ-1000P 0.003 0.011 0.027 0.060 YCW-1000P 0.004 0.012 0.036 0.081 -
[1] KIM Y T, SEO D K, HWANG J. Study of the effect of coal type and particle size on char -CO2 gasification via gas analysis[J]. Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(11):5044-5054. doi: 10.1021/ef200745x [2] DUMAN G, UDDIN M A, YANIK J. The effect of char properties on gasification reactivity[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2014, 118(2):75-81. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=dad603cfc3f7e08da3748d5ce8b7e8a6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] MANI T, MAHINPEY N, MURUGAN P. Reaction kinetics and mass transfer studies of biomass char gasification with CO2[J]. Chem Eng Sci, 2011, 66(1):36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2010.09.033 [4] TREMEL A, SPLIETHOFF H. Gasification kinetics during entrained flow gasification -part Ⅱ:Intrinsic char reaction rate and surface area development[J]. Fuel, 2013, 107(9):653-661. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0229718456/ [5] 陈彦, 张济宇. Na2CO3催化剂对福建高变质无烟煤比表面及气化反应特性的影响[J].化工学报, 2011, 62(10):2768-2775. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2011.10.014CHEN Yan, ZHANG Ji-yu. Effect of biomass ash addition on gasification characteristics of anthracite coal char[J]. CIESC J, 2011, 62(10):2768-2775. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2011.10.014 [6] 许修强, 王永刚, 陈国鹏, 陈宗定, 秦中宇, 戴谨泽, 张书, 许德平.水蒸气对褐煤原位气化半焦反应性能及微观结构的影响[J].燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(5):546-553. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.05.005XU Xiu-qiang, WANG Yong-gang, CHEN Guo-peng, CHEN Zong-ding, QIN Zhong-yu, DAI Jin-ze, ZHANG Shu, XU De-ping. Evolution behavior of reactivity and microstructure of lignite char during in-situ gasification with steam[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2015, 43(5):546-553. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2015.05.005 [7] LIU X, XIONG B, HUANG X, DING H, ZHENG Y, LIU Z, ZHENG C. Effect of catalysts on char structural evolution during hydrogasification under high pressure[J]. Fuel, 2017, 188:474-482. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.053 [8] CETIN E, MOGHTADERI B, GUPTA R, WALL T F. Influence of pyrolysis conditions on the structure and gasification reactivity of biomass chars[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83:2139-2150. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2004.05.008 [9] 李昌伦, 王永刚, 林雄超, 田震, 武欣, 杨远平, 张海永, 许德平.内在矿物对高灰褐煤CO2气化的影响研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(7):780-788. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.07.002LI Chang-lun, WANG Yong-gang, LIN Xiong-chao, TIAN Zhen, WU Xin, YANG YUAN-ping, ZHANG Hai-yong, XU De-ping. Influence of inherent minerals on CO2 gasification of a lignite with high ash content[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(7):780-788. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.07.002 [10] 何清, 卫俊涛, 龚岩, 丁路, 于广锁.神府烟煤焦与城市固体废弃物水热炭焦共气化反应特性的实验研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(10):1191-1199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.10.006HE Qing, WEI Jun-tao, GONG Yan, DING Lu, YU Guang-suo. Experimental study on co-gasification reactivity of Shenfu bituminous coal char and MSW-based hydrochar[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(10):1191-1199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.10.006 [11] TAKAYUKI T, TAMAI Y, TOMITA A. Reactivities of 34 coals under steam gasification[J]. Fuel, 1985, 64(10):1438-1442. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(85)90347-3 [12] 竹怀礼.煤的催化气化及基于原位拉曼光谱的煤焦结构演变研究[D].上海: 华东理工大学, 2017.ZHU Huai-li. Research on characteristics of catalytic gasification and the evolution of coal char structure based on in-situ Raman spectroscopy[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science & Technology, 2017. [13] ZHANG Y, ASHIZAWA M, KAJITANI S, MIURA K. Proposal of a semi-empirical kinetic model to reconcile with gasification reactivity profiles of biomass chars[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(4/5):475-481. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f8e50bea9f8a4c777ba51385e77950ff [14] YIP K, TIAN F, HAYASHI J, WU H. Effect of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species on biochar reactivity and syngas compositions during steam gasification[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009, 24(1):173-181. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=96a83d1b65479c6bed00389b11c61748&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [15] 丁路.煤的热解特性及基于可视化技术的气化反应机理研究[D].上海: 华东理工大学, 2016.DING Lu. Research on pyrolysis characteristics and gasification mechanism of coal based on visual technology[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science & Technology, 2016. [16] LIU L, CAO Y, LIU Q. Kinetics studies and structure characteristics of coal char under pressurized CO2 gasification conditions[J]. Fuel, 2015, 146:103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.01.002 [17] FENG B, BHATIA S K. Variation of the pore structure of coal chars during gasification[J]. Carbon, 2003, 41:507-523. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00357-3 [18] ASADULLAH M, ZHANG S, MIN Z, YIMSIRI P, LI C. Effects of biomass char structure on its gasification reactivity[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2010, 101(20):7935-7943. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.048 [19] JEONG H J, PARK S S, HWANG J. Co-gasification of coal-biomass blended char with CO2 at temperatures of 900-1100℃[J]. Fuel, 2014, 116:465-470. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.015 -





 下载:
下载: