-
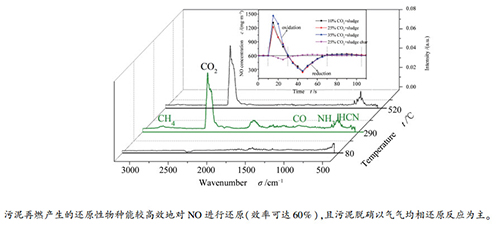
摘要: 在模拟水泥分解炉的实验台架上研究CO2浓度(体积分数0-35%)对污泥再燃还原性气体析出特性及其对污泥与污泥焦还原NO反应的动态变化规律的影响。结果表明,污泥再燃产生的还原性气体主要为HCN、NH3、CH4及CO;当CO2浓度从0增加到25%时,由于CO2与污泥焦气化作用增强,导致HCN、NH3及CH4的析出量缓慢下降,而CO析出量显著增加,最终促进NO还原率从51%增加至61%;继续增加CO2浓度至35%,由于CO2的辐射吸收导致局部热不稳定性增强,气化作用的减弱导致CO析出量下降,且HCN析出量有较大幅度下降,NH3析出量变化不大,CH4析出量有一定幅度上升,综合影响使得NO的还原率逐渐下降至55%。研究表明,实验室条件下污泥再燃能较高效地对烟气中NO进行还原;机理研究表明,污泥再燃过程中同时存在对NO的气气均相还原反应和气固异相还原反应,实验确定污泥焦对NO的气固异相还原率仅为18%,因此,污泥脱硝以气气均相还原反应为主。Abstract: The effect of CO2 content(volume fraction 0-35%) on the reducing gas release characteristics from sewage sludge re-burning and the dynamic properties of NO reduction by sewage sludge and char were investigated in a simulated experimental platform of cement pre-calciner. The experimental results show that the reducing gas release from sewage sludge combustion are mainly HCN, NH3, CH4 and CO. With the increase of CO2 content from 0 to 25%, the release of HCN, NH3 and CH4 slowly decreased due to the enhancing effect of sludge gasification by CO2, while the release of CO increased significantly, eventually promoting the NO reduction rate from 51% to 61%. As continually increasing CO2 content to 35%, the local thermal instability was enhanced due to the radiation absorption of CO2, and the weakening of gasification resulted in the decrease of CO release. Moreover, HCN release decreased significantly, while NH3 release did not change much, CH4 release increased to a certain extent, and the combined effect makes the NO reduction rate gradually decreased to 55%. The results show that sludge re-burning can efficiently reduce NO in flue gas. It is also found that the homogeneous and heterogeneous reduction of NO are concurrence during sludge re-burning, while the experimental studies revealed that the NO reduction rate over the sludge char was only 18%, it implied that sludge denitration is dominated by gas-gas homogeneous reduction.
-
Key words:
- CO2 /
- reducing gas /
- sewage sludge /
- char /
- NO reduction
-
图 1 高温气固悬浮实验系统示意图
Figure 1 Schematic view of bench scale precalciner
1:quartz tube reactor; 2:electric furnace; 3:thermocouple; 4:electric furnace controller; 5:feeding hopper; 6:holder; 7:flue gas analyzer; 8:computer; 9, 10, 11:cylinder; 12, 13, 14:mass flow controller; 15:mixed gas cylinder; 16:filter
表 1 污泥及污泥焦的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of sewage sludge and char
Sample Proximate analysis w/% Ultimate analysis w/% Mad Vad Aad FCad C H N S Sewage sludge 6.83 30.56 58.49 4.12 27.06 3.2 3.78 0.83 Char 1.12 1.93 91.16 5.79 4.02 0.34 0.54 0.15 表 2 污泥中C、N的存在形态的含量
Table 2 Existing form and content of C and N in sewage sludge
Atomic surface composition /% C N COOH C=O C-O C-C/C-H A-N Pr-N N-5 In-N 11.4 9.1 19.8 59.7 33.65 53.73 1.08 11.54 -
[1] 牛欣, 肖军.污泥化学链燃烧过程中氮迁移转化特性研究[J].燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(4):505-512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.04.016NIU Xin, XIAO Jun. Nitrogen transformation in chemical looping combustion of sewage sludge[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2017, 45(4):505-512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.04.016 [2] ABUSOGLU A, OZAHI E, KUTLAR A I, AL-JAF H. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of digested sewage sludge incineration for heat and power production[J].J Clean Prod, 2017, 142(4):1684-1692. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652616319734 [3] JIN R, ZHAN J Y, LIU G R, ZHAO Y Y, ZHENG M H, YANG L L, WANG M. Profiles of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in cement kilns co-processing solid waste[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 174:165-172. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.115 [4] 邓飞飞, 毛志伟, 程群, 廖晓樱, 廖玉云, 王梦瑜.水泥窑协同处置污泥降低NOx排放工程实例分析[J].中国水泥, 2016, (7):80-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8321.2016.07.015DENG Fei-fei, MAO Zhi-wei, CHENG Qun, LIAO Xiao-yin, LIAO Yu-yun, WANG Meng-yu. The analysis of NOx emission reduction in practical engineering through the co-combustion of sludge in cement kiln[J]. China Cement, 2016, (7):80-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8321.2016.07.015 [5] LV D, ZHU T L, LIU R W, LV Q Z, SUN Y, WANG H M, LIU Y, ZHANG F. Effects of co-processing sewage sludge in cement kiln on NOx, NH3 and PAHs emissions[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 159:595-601. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.06.062 [6] FANG P, TANG Z J, HUANG J H, CEN C P, TANG Z X, CHEN X B. Using sewage sludge as a denitration agent and secondary fuel in a cement plant:A case study[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2015, 137:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.03.014 [7] 廖艳芬, 马晓茜.城市污水污泥燃烧特性和动力学特性分析[J].燃料化学学报, 2009, 37(3):296-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.03.008LIAO Yan-fen, MA Xiao-qian. Combustion behavier and kinetic characteristic of a city sewage sludge[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2009, 37(3):296-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2009.03.008 [8] CHEN J B, MU L, JIANG B, YIN H C, SONG X G, LI A M. TG/DSC-FTIR and Py-GC investigation on pyrolysis characteristics of petrochemical wastewater sludge[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2015, 192:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.05.031 [9] 胡益, 李培生, 余亮英.污泥与煤混烧中含碳官能团的演化过程[J].武汉大学学报, 2013, 46(5):649-653. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD201305020.htmHU Yi, LI Pei-sheng, YU Liang-ying. Evolution of carbon functionalities in sewage sludge and coal during their co-combustion[J]. Eng J Wuhan Univ, 2013, 46(5):649-653. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD201305020.htm [10] LIU H, ZHANG Q, HU H Y, LIU P, HU X W, LI A J, YAO H. Catalytic role of conditioner CaO in nitrogen transformation during sewage sludge pyrolysis[J]. Proc Combust Inst, 2015, 35(3):2759-2766. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.06.034 [11] 段春雷.低中变质程度煤的结构特征及热解过程中甲烧、氨气的生成机理[D].太原: 太原理工大学, 2007.DUAN Chun-lei. Structural characteristics of low and medium grade coal and formation mechanism of methane and ammonia during pyrolysis[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2007. [12] LI X P, ZHANG S H, YANG W, LIU Y, YANG H P, CHEN H P. Evolution of NOx precursors during rapid pyrolysis of coals in cO2 atmospheres[J]. Energy Fuels, 2015, 29(11):7474-7482. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b01509 [13] TIAN Y, ZHANG J, ZUO W, CHEN L, CUI Y N, TAN T. Nitrogen conversion in relation to NH3 and HCN during microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2013, 47(7):3498-3505. doi: 10.1021/es304248j [14] TIAN F J, LI B Q, CHEN Y, LI C Z. Formation of NOx precursors during the pyrolysis of coal and biomass. Part V. Pyrolysis of a sewage sludge[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(17):2203-2208. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00139-4 [15] LIU F S, GUO H S, SMALLWOOD G J. The chemical effect of CO2 replacement of N2 in air on the burning velocity of CH4 and H2 premixed flames[J]. Combust Flame, 2003, 133(4):495-497. doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(03)00019-1 [16] 孟德润, 周俊虎, 赵翔, 赵晓辉, 刘彦, 杨卫娟, 岑可法. O2/CO2气氛下氮反应机理的研究[J].环境科学学报, 2005, 25(8):1011-1014. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2005.08.003MENG De-run, ZHOU Jun-hu, ZHAO Xiang, ZHAO Xiao-hui, LIU Yan, YANG Wei-juan, CEN Ke-fa. Research on reaction mechanism of nitrogen in O2/CO2[J]. Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2005, 25(8):1011-1014. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2005.08.003 [17] HU Y, NAITO S, KOBAYASHI N, HASATANI M. CO2, NOx and SO2 emissions from the combustion of coal with high oxygen concentration gases[J]. Fuel, 2000, 79(15):1925-1932. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(00)00047-8 [18] 白宗庆, 陈皓侃, 李文, 李保庆.热重-质谱联用研究焦炭在甲烷气氛下的热行为[J].燃料化学学报, 2005, 33(4):426-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2005.04.009BAI Zong-qing, CHEN Hao-kai, LI Wen, LI Bao-qing.Study on the thermal performance of metallurgical coke under methane ba TG-MS[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol, 2005, 33(4):426-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2005.04.009 [19] LI C Z, TAN L L. Formation of NOx and SOx precursors during the pyrolysis of coal and biomass. Part Ⅲ. Further discussion on the formation of HCN and NH3 during pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2000, 79(15):1899-1906. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(00)00008-9 [20] HIDEO H, TOSHIMASA H. NOx and N2O Emission in bubbling fluidized-bed coal combustion with oxygen and recycled flue gas:Macroscopic characteristics of their formation and reduction[J]. Energy Fuels, 1998, 12(1):102-108. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/30011137631 -





 下载:
下载: