Study on the influence of raw material composition on the structure of needle coke
-
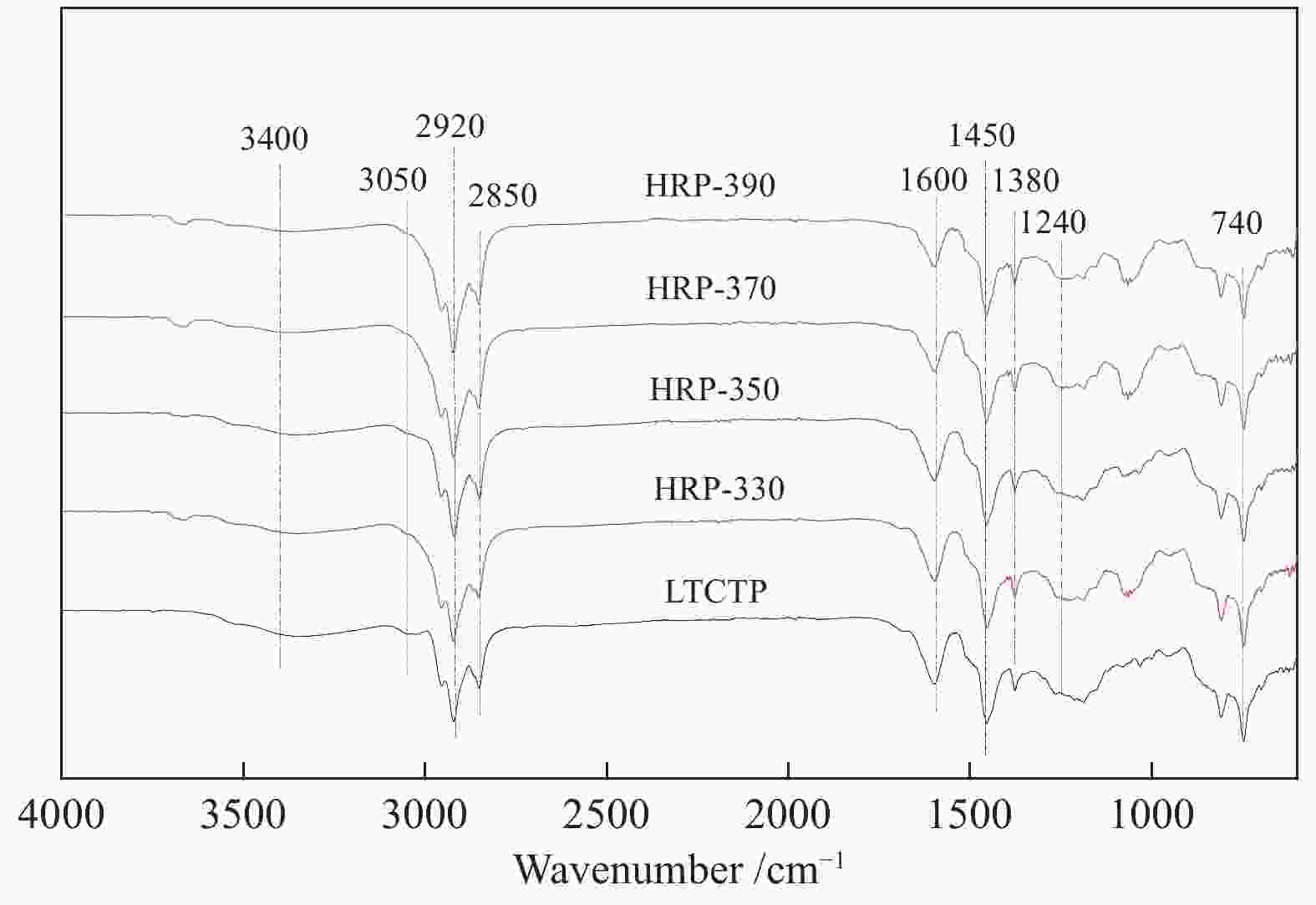
摘要: 在330–390 °C、8 MPa、加氢时间为1.5 h和剂油比为1∶40的条件下对中低温煤焦油原料进行加氢处理,得到精制原料后再通过热聚合煅烧等过程制得针状焦。通过元素分析、红外光谱(FT-IR)、气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-MS)等检测方法分析了精制原料组成,并采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)和偏光显微镜等方法测试了不同原料所制备出的针状焦结构,研究了加氢温度和精制原料组成对针状焦结构的影响。结果表明,提高缓和加氢精制温度有利于脱除杂原子(尤其是S),但当加氢温度为390 °C时,原料中的芳烃会因为裂解和缩聚而发生两极分化。此外,精制原料中3环和4环芳烃的含量越高,所制备出针状焦石墨化程度越高。Abstract: The refined raw material was first prepared from the low-medium temperature coal tar through hydrogenation for 1.5 h under 330–390 °C and 8 MPa, with a catalyst/oil mass ratio of 1∶40, which was then used to produce needle coke through thermal polymerization and calcination. The composition of refined raw materials was analyzed by elemental analysis, Fourier-transform IR spectroscopy (FT-IR) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and the structure of needle coke was characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and polarizing microscope; the effect of raw material composition (related to the hydrogenation temperature) on the structure of needle coke was then investigated. The results indicate that a proper increase in the hydrofining temperature is beneficial to the removal of heteroatoms (especially sulfur). By hydrogenation at 390 °C, the aromatics in the feedstock are polarized due to the cracking and polycondensation. In addition, a higher content of tricyclic and tetracyclic aromatics in the refined raw materials may also lead to a higher graphitization degree for the needle coke product.
-
Key words:
- coal tar hydrogenation /
- refined raw materials /
- needle coke /
- optical structure
-
表 1 原料的元素分析
Table 1 Elemental composition of the raw low-medium temperature coal tar (LTCT)
Material Mass composition/% H/C
atomic ratioQuinoline
insoluble/%C H O N S LTCT 82.48 8.53 7.57 1.08 0.34 1.241 1.04 note: low-medium temperature coal tar is referred to as LTCT 表 2 不同加氢温度下所得到的精制原料的元素分析
Table 2 Elemental analysis results of refined raw materials at different hydrogenation temperatures
Sample Mass composition/% H/C
atomic ratioQI/% C H O N S LTCTP 84.50 7.89 6.40 0.98 0.23 1.120 0.66 HRP-330 84.68 7.97 6.25 0.91 0.19 1.129 0.51 HRP-350 84.94 8.12 5.97 0.83 0.14 1.147 0.46 HRP-370 84.95 8.33 5.85 0.76 0.11 1.177 0.40 HRP-390 85.10 8.37 5.74 0.72 0.07 1.180 0.31 note: HRP-330, HRP-350, HRP-370 and HRP-390 refer to the refined raw asphalt samples obtained by hydrogenation at 330, 350, 370 and 390 °C, respectively 表 3 不同精制原料的分子类型
Table 3 Molecular types and their contents in the refined raw materials obtained by hydrogenation at different temperatures
Sample Content w/% alkanes alkene aromatic hydrocarbon oxygenated compounds nitrogenous compounds sulfur compounds LTCTP 39.92 1.09 42.37 13.83 2.17 0.62 HRP-330 41.02 0.54 44.73 11.27 1.93 0.51 HRP-350 42.97 0.41 45.49 9.33 1.38 0.42 HRP-370 44.16 0.17 45.78 8.26 1.32 0.31 HRP-390 43.45 0 47.42 7.83 1.04 0.26 表 4 不同精制原料的芳烃类型
Table 4 Types of aromatics and their contents in the refined raw materials obtained by hydrogenation at different temperatures
Sample Content w/% 1-ring 2-ring 3-ring 4-ring 5-ring 1+1S 2+1S 3+1S 4+1S LTCTP 0.14 8.45 22.47 5.38 0.68 0.03 2.05 3.17 0 HRP-330 0.07 9.12 23.71 6.26 0.49 0.09 1.65 3.34 0 HRP-350 0.34 7.57 24.79 7.36 0.93 0.27 1.68 2.36 0.19 HRP-370 0.67 8.39 23.84 7.42 0.87 0.43 1.72 2.21 0.23 HRP-390 0.61 10.81 22.67 7.53 1.06 0.83 1.67 2.13 0.11 note: “ n-ring” refers to the molecules containing n aromatic rings; “ n + 1S” refers to the molecule containing n aromatic rings combined with one saturated ring 表 5 不同精制原料所制备的针状焦微晶结构参数
Table 5 Crystal structure parameters of the needle coke products prepared from different refined raw materials
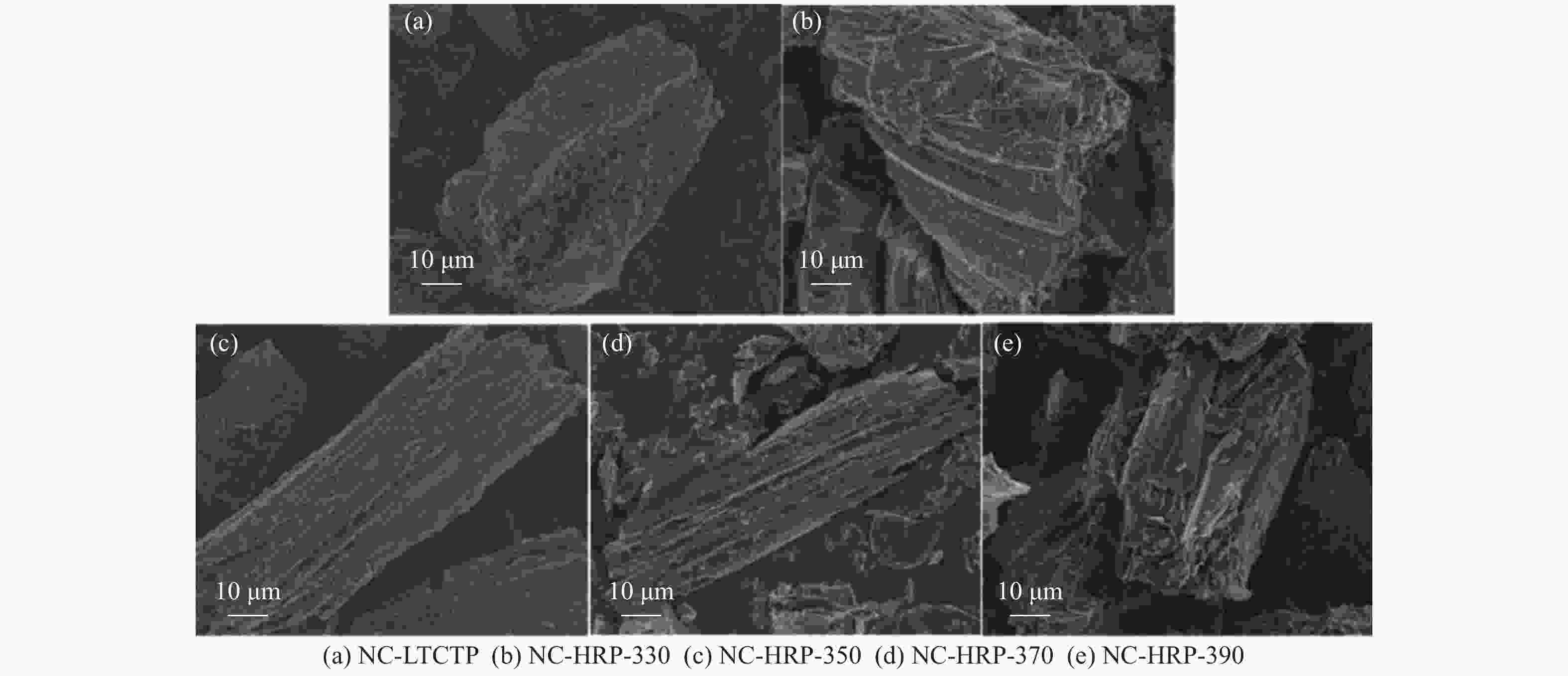
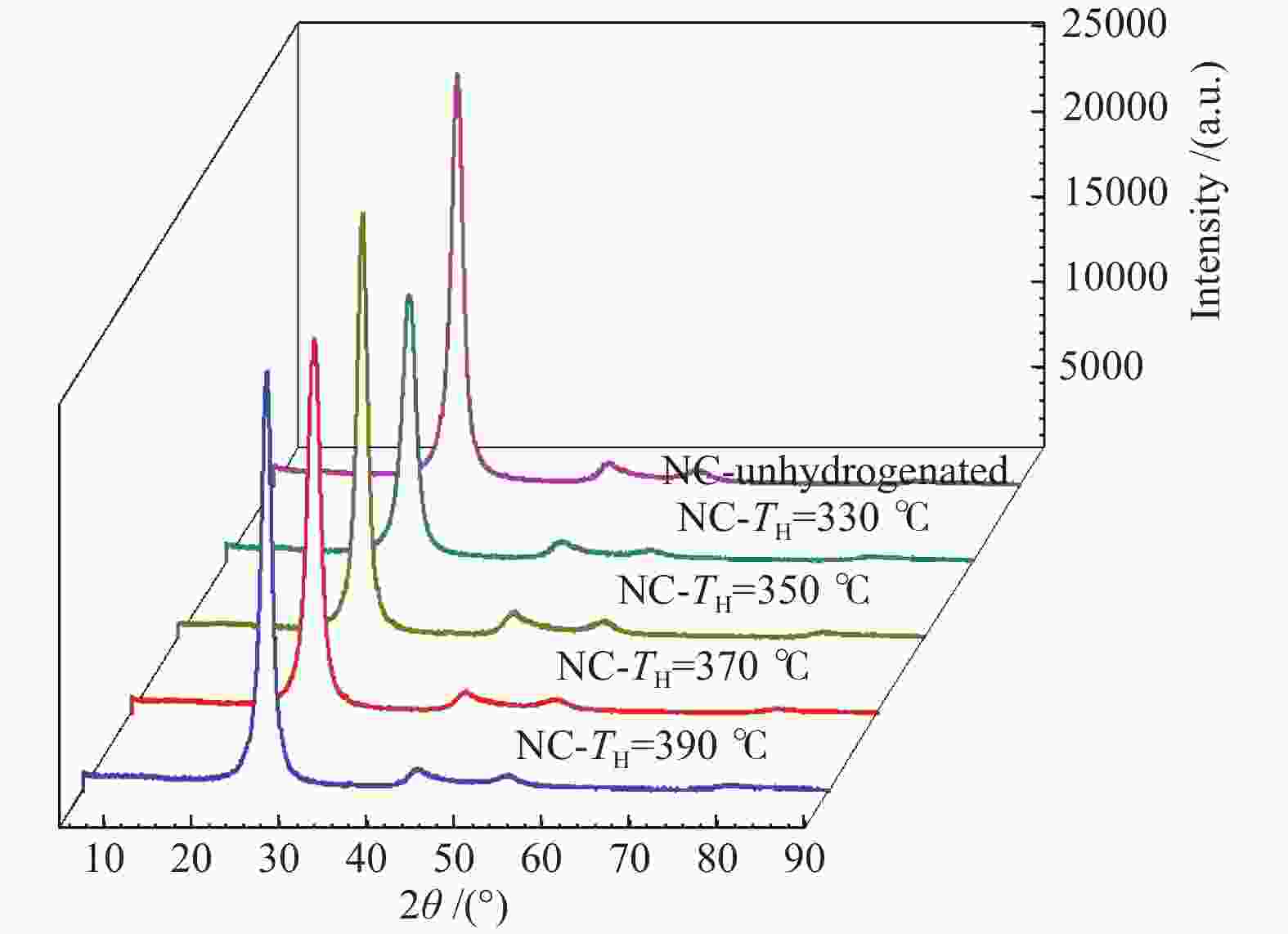
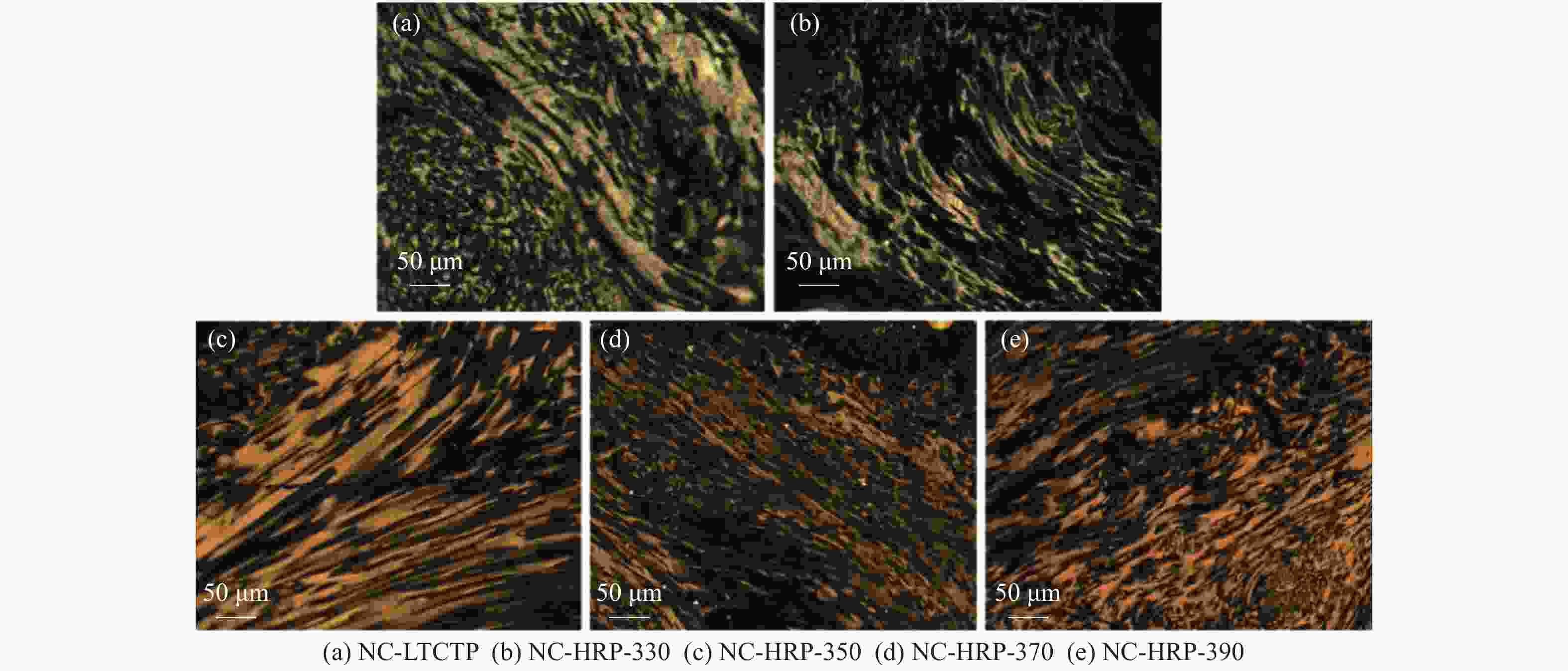
Sample 2θ002/(°) d002/nm B002/(°) 2θ100/(°) B100/(°) La/nm Lc/nm G/% NC-LTCTP 25.82 0.3449 0.953 43.010 0.900 19.402 8.459 −10.47 NC-HRP-330 25.90 0.3438 0.977 43.320 0.919 19.021 8.253 2.33 NC-HRP-350 25.96 0.3430 0.907 42.861 0.860 20.294 8.891 11.63 NC-HRP-370 25.94 0.3433 0.918 42.291 0.935 18.670 8.784 8.14 NC-HRP-390 25.84 0.3446 0.961 43.122 0.895 19.518 8.389 −6.98 -
[1] 张怀平, 吕春祥, 李开喜, 刘春林, 凌立成. 针状焦的结构和原料[J]. 煤炭转化,2001,24(1):22−26.ZHANG Huai-ping, LV Chun-xiang, LI Kai-xi, LIU Chun-lin, LING Li-cheng. The structure and raw materials of needle coke[J]. Coal Convers,2001,24(1):22−26. [2] MOCHIDA I, QING F, Y, KORAI Y, FUJIMOTO K, YAMASHITA R. Carbonization in the tube bomb leading to needle coke: III. Carbonization properties of several coal-tar pitches[J]. Carbon,1989,27:375−380. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(89)90069-9 [3] MONDAL S, YADAV A, KUMAR R, BANSAL V, DAS S K, CHRISTOPHER J, KAPUR G S. Molecular-level structural insight into clarified oil by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: Estimation of hydrocarbon types and average structural parameters[J]. Energy Fuels,2017,31:7682−7692. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00994 [4] CAO Q. GUO L C, Dong Y W, XIE X L, JIN L E. Autocatalytic modification of coal tar pitch using benzoyl chloride and its effect on the structure of char[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2015,129:61−66. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.08.017 [5] CAO Q, XIE X L, LI J, DONG J P, JIN L E. A novel method for removing quinoline insolubles and ash in coal tar pitch using electrostatic fields[J]. Fuel,2012,96:314−318. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.12.061 [6] CRADDOCK J D, RANTELL T D, HOWER J C, WHITOW D T, WISEMAN J, WEISENERGER M C. Anode coke from coal - A low cost approach[J]. Fuel,2017,187:229−241. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.09.045 [7] FAN C L, CHEN H. Preparation, structure, and electrochemical performance of anodes from artificial graphite scrap for lithium ionbatteries[J]. J Mater Sci,2011,46:2140−2147. doi: 10.1007/s10853-010-5050-y [8] CAI Y, FAN C L. Influences of conductive additives on eletrochemical performances of artficial graphite anode with different shapes for lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochim Acta,2011,58:481−487. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2011.09.080 [9] 余文凤, 周霞萍, 徐东升, 尹思聪, 张丕祥. 针状焦用煤沥青的调制研究[J]. 洁净煤技术,2011,17(5):77−81.YU Wen-feng, ZHOU Xia-ping, XU Dong-sheng, YIN Si-cong, ZHANG Pi-xiang. Study on the preparation of coal pitch for needle coke[J]. Clean Coal Technol,2011,17(5):77−81. [10] FENNADEZ A L, GRANDA M, BERNMEJO J, MENENDEZ R, BERNAD P. Carbon precursors from anthracene oil. Insight into the reactins of anthracene oil with sulfur[J]. Energy Fuels,1998,12(5):949−957. doi: 10.1021/ef9800258 [11] MOCHIDA I, ANDO T, MAEDA K, FUJITSU H, TAKESHITA K. Catalytic carbonization of aromatic hydrocarbons-IX: Carbonization mechanism of heterocyclic sulfur compounds leading to the anisotropic coke[J]. Carbon,1980,18(2):131−136. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(80)90021-4 [12] MOCHIDA I, ANDO T, MAEDA K, FUJITSU H, TAKESHITA K. Catalytic carbonization of aromatic hydrocarbons-VII: Carbonization mechanism of heterocyclic nitrogen compounds catalyzed by aluminum chloride[J]. Carbon,1978,16(6):453−458. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(78)90092-1 [13] ZHU Y M, ZHAO C L, XU Y L, HU C S, ZHAO X F. Preparation and characterization of coal pitch-based needle coke (PartⅠ): The effects of aromatic index (fa) in refined coal pitch[J]. Energy Fuels,2019,33:3456−3464. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b00160 [14] XING G Z, WANG F M, ZHANG X H, JIN L E, XIE X L, CAO Q. Effect of petroleum pitch on the structure and electrical properties of coal tar pitch coke[J]. Mater Sci Technol,2017,25:44−49. [15] KERSHAW J R, SMART P J. Extraction of coal-tar pitch and the effect on carbonization[J]. Carbon,1994,32(1):85−92. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(94)90012-4 [16] FAN X, FEI Y Q, CHEN L, LI W. Distribution and structural analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons abundant in coal tar pitch[J]. Energy Fuels,2017,31(5):4694−4704. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03113 [17] LI X, LI Q. Rheological properties and carbonization of coal-tar pitch[J]. Fuel,1996,75(1):3−7. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)00190-5 [18] XUE Y B, GE Z F, LI F C, SU S, LI B Z. Modified asphalt properties by blending petroleum asphalt and coal tar pitch[J]. Fuel,2017,207:64−70. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.06.064 [19] MIYAKE M, IDA T, YOSHIDA H, WAKISAKA S, NOMURA M, HAMAGUCHI M, NISHIZAWA T. Effects of reductively introduced alkyl groups and hydrogen to mesophase pitch on carbonization properties[J]. Carbon,1993,31(5):705−714. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(93)90007-W [20] KORAI Y, MOCHIDA I. Preparation and properties of carbonaceous mesophase-i soluble mesophase produced from A240 and coal tar pitch[J]. Carbon,1985,23(1):97−103. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(85)90203-9 [21] 赵雪飞, 高丽娟, 赖仕全, 张雅茹. 我国煤系针状焦的研究及生产状况[J]. 燃料与化工,2010,41(4):1−4+7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2010.04.001ZHAO Xue-fei, GAO Li-juan, LAI Shi-quan, ZHANG Ya-ru. Research and production status of needle coke from coal measures in my country[J]. Fuel Chem Ind,2010,41(4):1−4+7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2010.04.001 [22] 孙艳锐, 熊杰明, 易玉峰, 孙国娟. 混合溶剂法脱除煤沥青的喹啉不溶物[J]. 炭素技术,2010,29(3):11−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3741.2010.03.003SUN Yan-rui, XIONG Jie-ming, YI Yu-feng, SUN Guo-juan. Removal of quinoline insolubles from coal pitch by mixed solvent method[J]. Carbon Technol,2010,29(3):11−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3741.2010.03.003 [23] 解小玲. 对煤基沥青中间相形成因素及针状焦结构影响的研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2014.XIE Xiao-ling. Research on the influence of coal-based pitch mesophase formation factors and needle coke structure[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2014. [24] ZHU Y M, ZHAO X F, GAO L J, LI J, CHENG J X, LI L, SHI Q. Quantitative study of the microcrystal structure on coal based on needle coke with curve-fitted of XRD and Raman spectrum[J]. Spectrosc Spectral Anal,2017,37:1919−1924. [25] ZHU Y M, ZHAO X F, GAO L J, LI J, CHENG J X, LI L, SHI Q. Study on the pyrolysis characteristic and the microstructure of the pyrolysis products of β resins from different coal tar pitch[J]. J Chem Soc Pak,2018,40:343−353. [26] WANG W Y, Yang Y Q, LUO H A, LIU W Y. Effect of additive (Co, La) for Ni-Mo-B amorphous catalyst and its hydrodeoxygenation properties[J]. Catal Commun,2010,11(9):803−807. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2010.02.019 [27] ZHU Y M, ZHAO X F, CHENG J X, LIU W, LV J, WANG Y. Pyrolysis characteristics and properties of thermal conversion products on toluene soluble component from medium pitch[J]. Mater Rev,2017,31:109−114. [28] PETROVA B, TSYNTSARSKIi B, BUDINOVA T, PETER N, ANIA C O, PARRA J B, MLADENOV M, TZVETKOV P. Synthesis of nanoporous carbons from mixtures of coal tar pitch and furfural and their application as electrode materials[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2010,91(11):1710−1716. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.07.008 [29] WANG G, ESER S. Molecular composition of the high-boiling components of needle coke feedstocks and mesophase development[J]. Energy Fuels,2007,21(6):3563−3572. [30] 张龙力, 王春岚, 赵元生, 杨国华, 杨朝合. 塔河常压渣油沥青质含硫官能团形态与其性质的关系研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2012,40(9):1081−1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.009ZHANG Long-li, WANG Chun-lan, ZHAO Yuan-sheng, YANG Guo-hua, YANG Chao-he. Study on the relationship between the morphology of sulfur-containing functional groups and their properties in Tahe atmospheric residue asphaltenes[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2012,40(9):1081−1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2012.09.009 [31] RANAN M S, VICENTE S, ANCHEYTA J, DIAZ J A I. A review of recent advances on process technologies for upgrading of Heavy oils and residua[J]. Fuel,2007,86(9):1216−1231. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.08.004 [32] ZHU Y, HUANG J, DAN Y, WANG, L, LI, D. Analysis and characterization of medium/low temperature coal tar asphaltene[J]. Acta Pet Sin,2016,32(2):334−342. [33] ECHEANDIA S, ARIAS P L, BARRRIO V L, PAWELEC B, FIERRO J L G. Synergy effect in the hdo of phenol over Ni-W catalysts supported on active carbon: Effect of tungsten precursors[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2010,101(1/2):1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.08.018 [34] LAINE R M. Comments on the mechanisms of heterogeneous cataysis of the hydrodenitrogenation reaction[J]. Catal Rev Sci Eng,1983,25(3):459−474. doi: 10.1080/01614948308078053 [35] NELSON N, LEVY, R B. The organic chemistry of hydrodenitrogenation[J]. J Catal,1979,58(3):485−488. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(79)90286-0 [36] ŞENOL O I, RYYMIN E M, VILJAVA T R, KRAUSE A O I. Effect of hydrogen sulphide on the hydrodeoxygenation of aromatic and aliphatic oxygenates on sulphided catalysts[J]. J Mol Catal A: Chem,2007,277(1):107−112. [37] SHI Q, PAN N, LONG H, CUI D H, GUO X F, LONG Y H, CHUNG K H, ZHAO S Q, XU C M, HSU C S. Characterization of middle-temperature gasification coal tar. Part 3: Molecular composition of acidic compounds[J]. Energy Fuels,2013,27:108−117. doi: 10.1021/ef301431y [38] JONES D G, ROTTENDORF H, WILSON M A, COLLION P J. Hydrogenation of liddell coal. yields and mean chemical structures of the products[J]. Fuel,1980,59(1):19−26. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(80)90005-8 [39] 任志惠. 焦化重蜡油热处理制备针状焦[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2007.REN Zhi-hui. Heat treatment of coking heavy wax oil to prepare needle coke[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2007. [40] 王亮. 原料组成对针状焦形成的影响[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2009.WANG Liang. The effect of raw material composition on the formation of needle coke[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2009. [41] QIAN S A. On the nature of the molecular structure of the soluble intermediate phase and its formation[J]. New Res Carbon Mater,1994,(2):1−3. [42] QIAN, S A. Basic principles of needle coke morphology and structure process[J]. China Pet Process Petrochem Technol,1998,(1):14−25. -





 下载:
下载: