Effect of calcite on desulfurization and denitration performance of activated coke and its mechanism
-
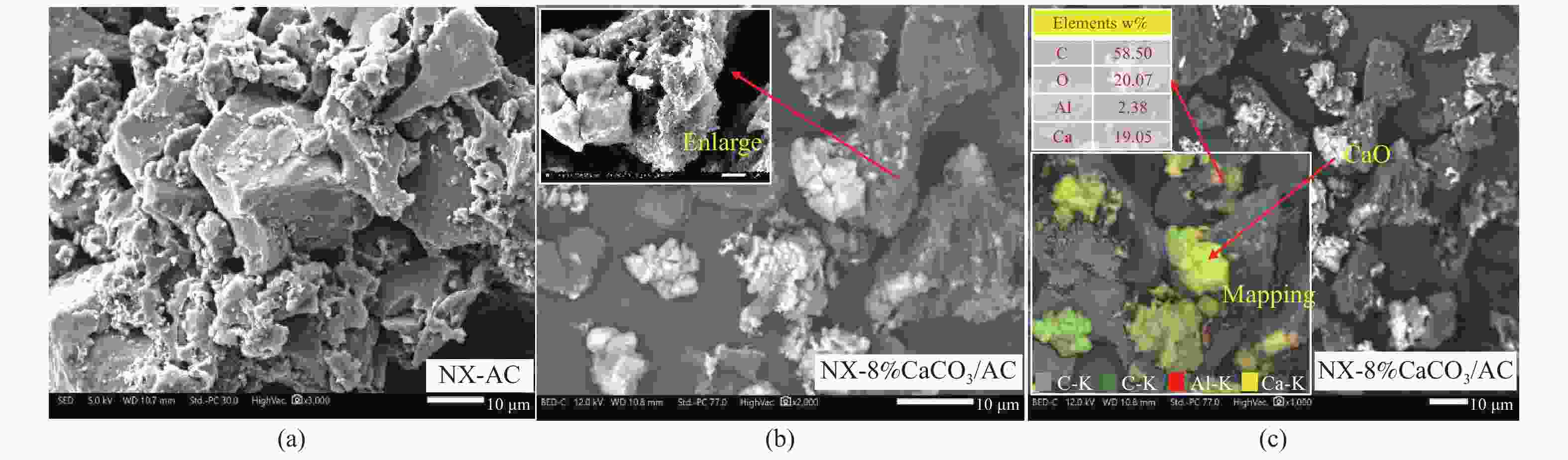
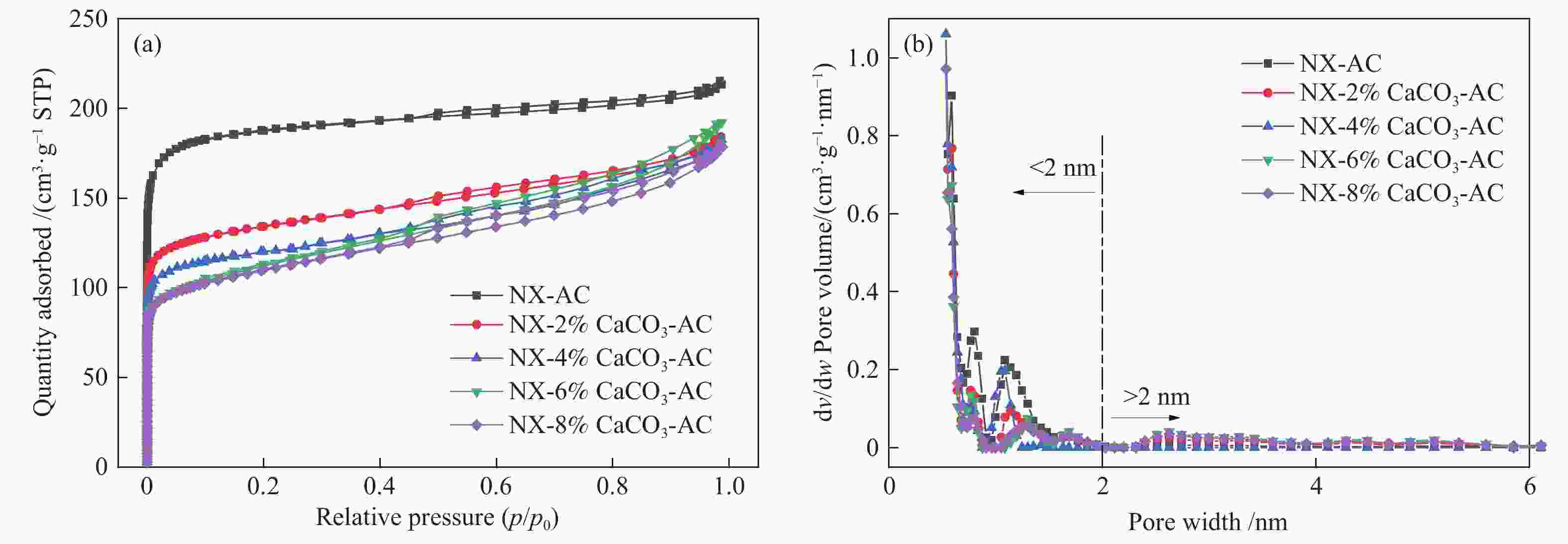
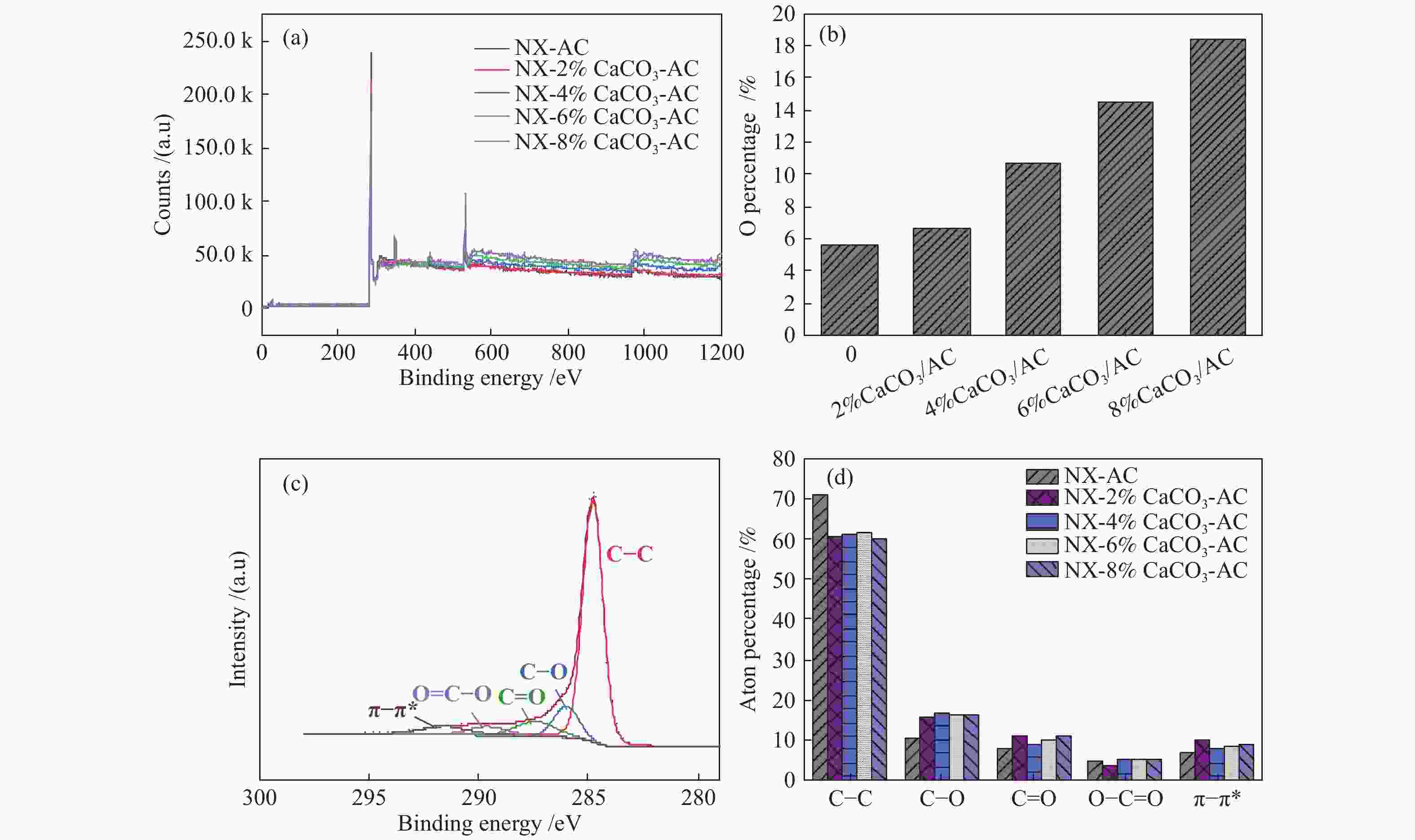
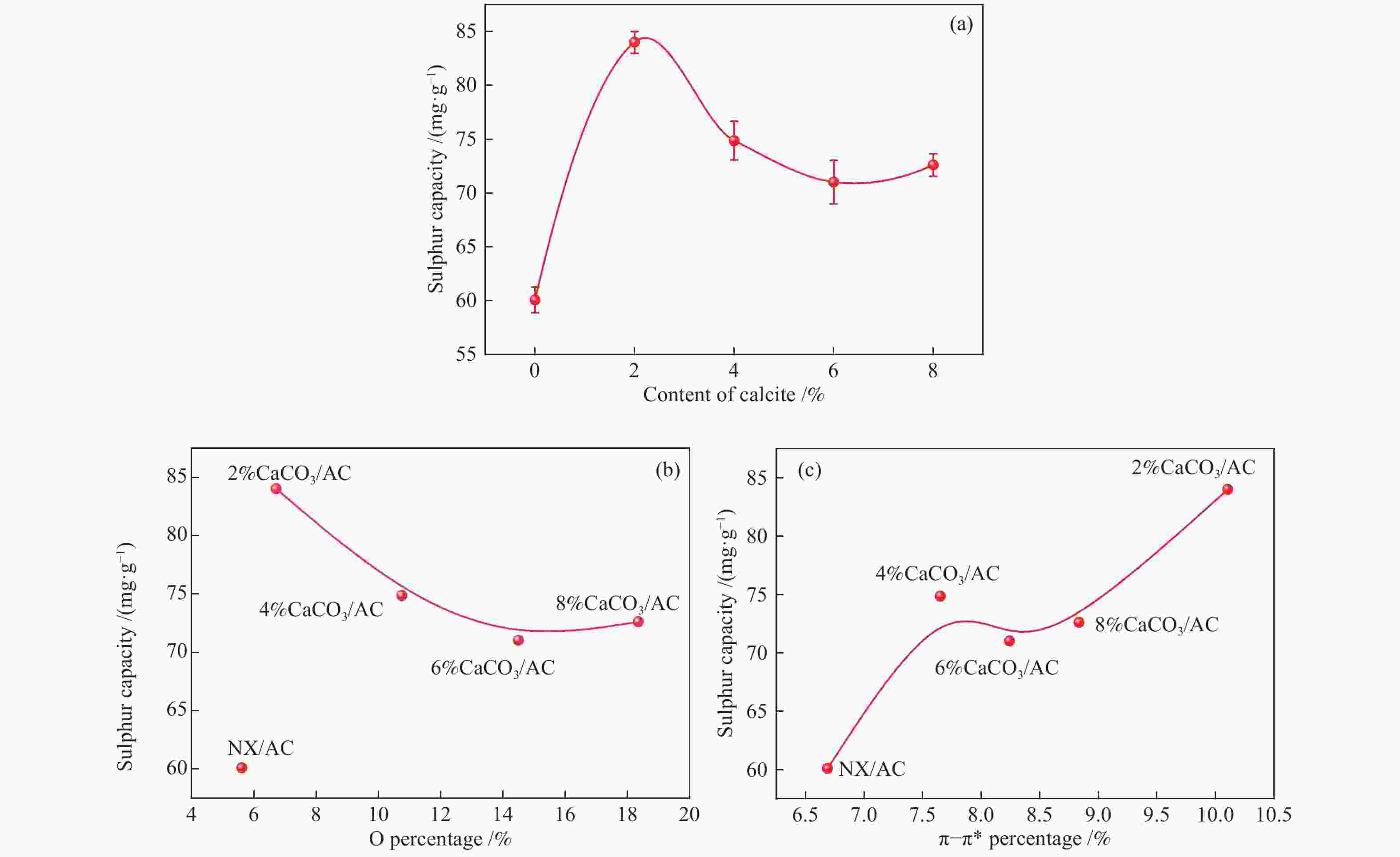
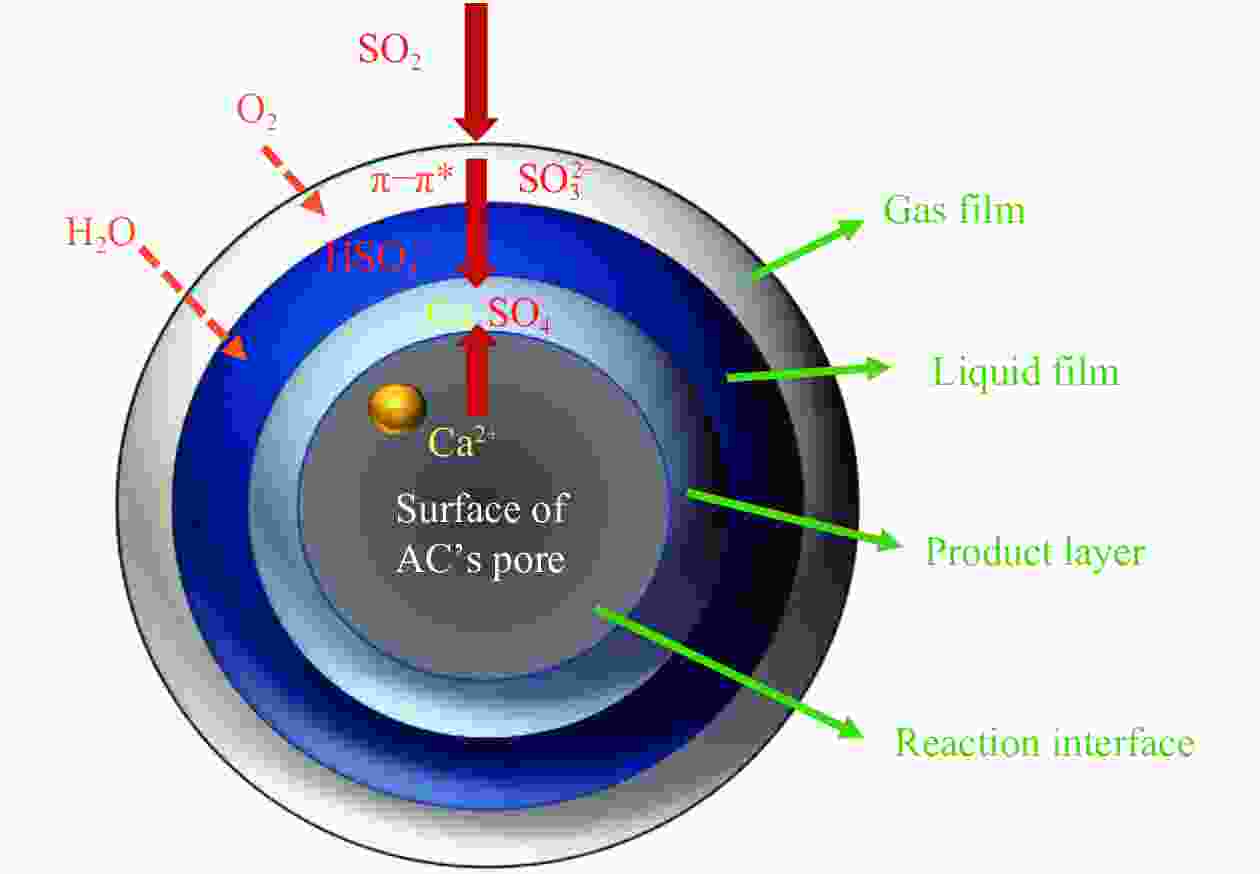
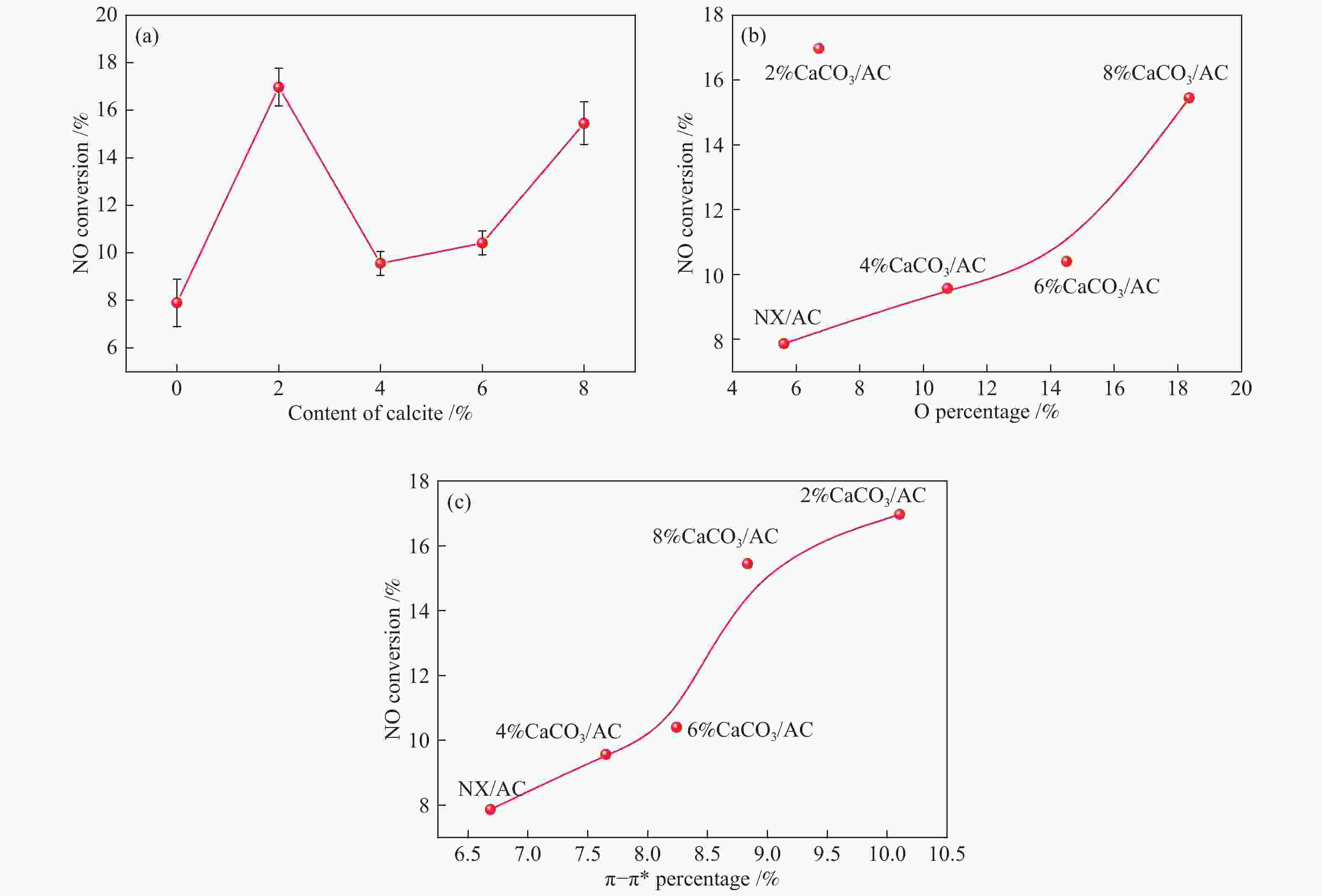
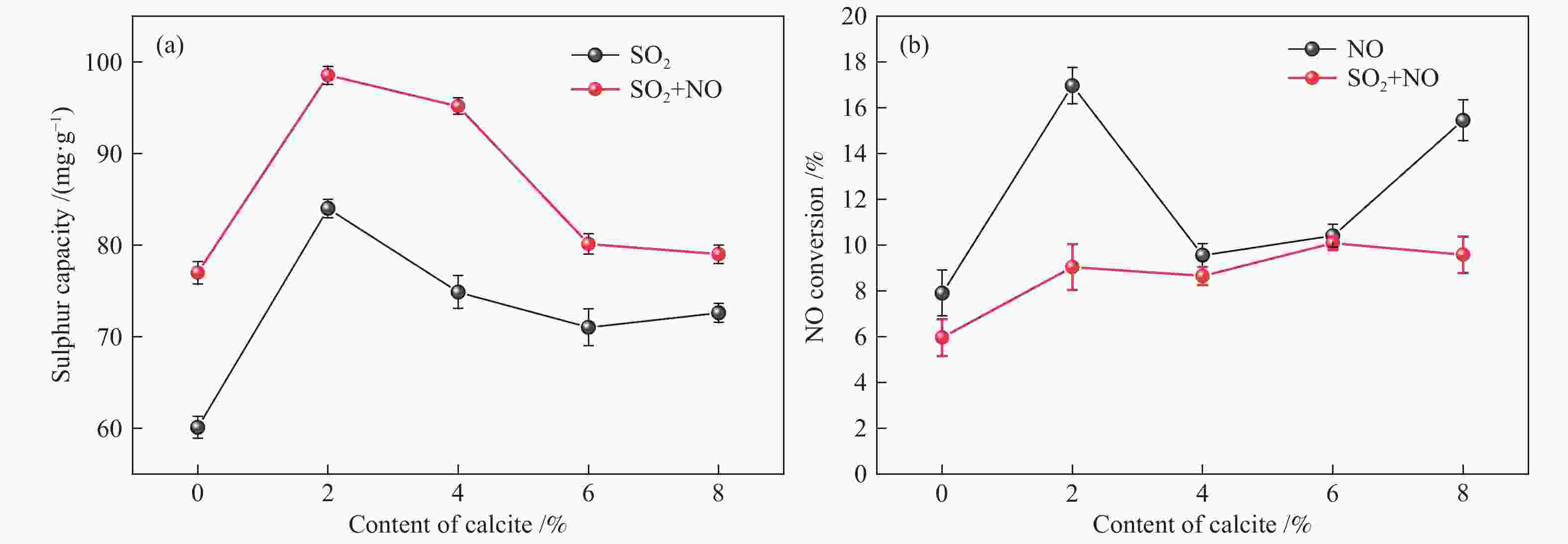
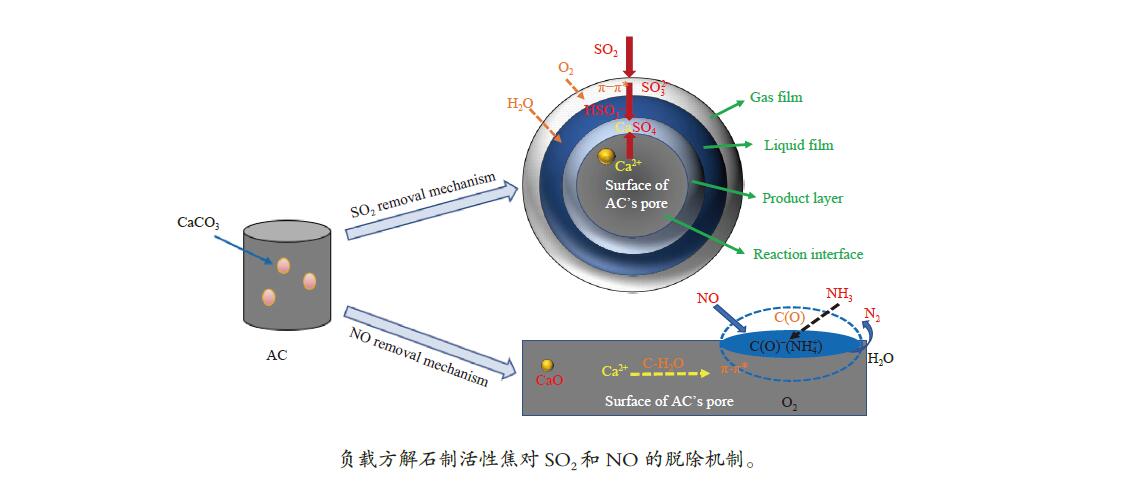
摘要: 方解石是煤中主要含钙矿物质,通过物理混合在脱灰宁夏无烟煤上负载不同含量的方解石制备活性焦,并分析其对制备及脱硫脱硝的影响。结果表明,方解石对活性焦的孔结构和表面化学性质起调控作用。在脱硫过程中,随着方解石含量的增加,活性焦的硫容呈先升高后下降趋势,NX-2%CaCO3-AC表现出最佳的脱硫能力(84.0 mg/g),方解石的加入增加了π−π*含量,促进了SO2氧化过程;在脱硝过程中,CaCO3的添加促进了脱硝,添加2%CaCO3的脱硝率(16.9%)比未添加的活性焦的脱硝率(7.9%)提升了1.14倍,主要是由于碱性基团数量的提高;同时脱硫脱硝过程中,活性焦CaO的存在对脱硫脱硝具有不同程度的促进作用。与单独脱硫/脱硝相比,硫容升高,脱硝效率降低,主要是由于竞争性吸附及铵盐的生成。Abstract: Different contents of calcite (CaCO3) were loaded on a deminerized Ningxia anthracite during the activated coke (AC) preparation, the influence of which on the preparation, desulfurization and/or denitrification of AC was investigated. The results show that calcite can regulate the pore structure and surface chemistry of AC. The total specific surface area and the micropore specific surface area decrease from 746 m2/g and 645 m2/g to 408 m2/g and 244 m2/g, respectively, when the calcite addition is up to 8%. The total volume and the micropore volume also decrease with the increase in the content of calcite, while the volume of mesopores and macropores increases. As the calcite addition rises, the oxygen-containing functional group and π−π* are increased linearly, and the sulfur capacity of AC first increases and then decreases during single desulfurization, the NX-2%CaCO3-AC having the best desulfurization capacity (84.0 mg/g). The increase in the content of π−π* by the addition of calcite promotes the SO2 oxidation process, and also promotes the denitrification process, the NO conversion (16.9%) with the addition of 2%CaCO3 is 1.14 times higher than that of AC (7.9%), mainly owing to the increase in the number of basic groups. However, during simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification, the presence of CaO in the AC promotes the sulfur capacity but decreases the NO removal efficiency due to the competitive adsorption and ammonium salt generation.
-
Key words:
- calcite /
- activated carbon /
- surface chemistry /
- sulfur capacity /
- NO conversion
-
表 1 原煤的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of raw coal
Proximate analysis wad/% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% M V A FC C H St N Oa 0.67 11.22 6.12 81.99 91.33 2.82 0.27 1.27 4.14 M: moisture; A: ash; V: volatile matter; a: by difference 表 2 原煤的灰成分分析
Table 2 Ash component analysis of raw coal
Component w/% SiO2 Al2O3 CaO SO3 Fe2O3 TiO2 MgO Na2O K2O 39 28.3 11.3 7.92 10.4 0.97 3.08 3.17 0.7 表 3 方解石添加含量对活性焦制备过程中的参数变化和孔结构的参数变化
Table 3 Parameters of ACs with different contents of calcite during AC preparation
Sample Weight loss/% Burn-off/% Yield/% Pore structure analysis by BET SBET/
(m2·g−1)Smic/
(m2·g−1)Smic/
SBET/%vmic
(cm3·g−1)vmec+mac
(cm3·g−1)vtotal
(cm3·g−1)dave/nm NX-AC 20.02 40.10 47.91 746 645 86 0.25 0.07 0.32 1.72 NX-2%CaCO3-AC 20.46 54.30 36.35 516 385 75 0.15 0.12 0.27 2.10 NX-4%CaCO3-AC 20.40 64.00 28.66 460 400 87 0.15 0.10 0.16 1.41 NX-6%CaCO3-AC 20.26 65.50 27.51 413 232 56 0.09 0.19 0.28 2.71 NX-8%CaCO3-AC 19.30 66.00 27.44 408 244 60 0.10 0.16 0.26 2.55 -
[1] 林国鑫, 于馨凝, 刘少俊. 煤质成分对煤基活性炭活化成孔的影响机制[J]. 燃烧科学与技术,2020,26(1):81−86.LIN Guo-xin, YU Xin-ning, LIU Shao-jun. Influence mechanism of coal composition on activation pore formation of coal- based activated carbon[J]. J Combust Sci Technol,2020,26(1):81−86. [2] 解炜. 我国煤基活性炭的应用现状及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(10):16−23. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2017.10.003XIE Wei. Application status and development trend of coal-based activated carbon in China.[J]. Coal Sci Technol,2017,45(10):16−23. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2017.10.003 [3] 邱敬贤, 刘君, 彭芬. 煤基活性炭在环保领域的应用发展综述[J]. 中国环保产业,2019,11:23−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5377.2019.09.008QIU Jin-xian, LIU Jun, PENG Fen. Summarization on application development of coal-based activated carbon in environmental protection field[J]. China Environ Protect Ind,2019,11:23−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5377.2019.09.008 [4] 王忠乐. 煤中矿物质的特性及其对焦炭结构和性质的影响研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽工业大学, 2014.WANG Zhong-le. A study on the characteristics of the minerals in coal and their effects on structures and properties of the coke[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Technology, 2014. [5] CLEMENS A H, DAMIANO L F, MATHESON T W. The effect of calcium on the rate and products of steam gasification of char from low rank coal[J]. Fuel,1998,77(9):1017−1020. [6] 熊杰, 周志杰, 许慎启. 碱金属对煤热解和气化反应速率的影响[J]. 化工学报,2011,62(1):192−198.XIONG Jie, ZHOU Zhi-jie J, XU Shen-qi. Effect of alkali metal on rate of coal pyrolysis and gasification[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2011,62(1):192−198. [7] 刘慧君, 周锦文, 王杰. 钙基添加剂对煤慢速和快速热解行为的影响[J]. 现代化工,2011,31(3):70−72.LIU Hui-jun, ZHOU Jin-wen, WANG Jie. Effects of Ca-based additives on behaviors of slow and fast coal pyrolysis[J]. Mod Chem Ind,2011,31(3):70−72. [8] 何旭. 矿物质对煤基活性炭成孔过程影响及催化甲烷裂解行为研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018.HE Xu. Effect of mineral matters on the coal-based activated carbons and catalytic methane decomposition to hydrogen[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. [9] 黄碧珠. 基于造纸白泥制备富钙成型活性炭的工艺优化及其应用[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2015.HUANG Bi-zhu. Optimization on the preparation of calcium-rich shaped activated carbon based on lime mud of paper mill and its application[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2015. [10] HUANG Z, LIU Z, ZHANG X. Inhibition effect of H2O on V2O5/AC catalyst for catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature[J]. Appl Cataly B: Environ,2006,63(3):260−265. [11] ZHANG H, NIU J, YIN X. Role of inherent pyrite in coal on physicochemical structure of activated carbon and adsorption capacity[J]. Fuel,2020,262:116527. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116527 [12] ZHANG K, HE Y, WANG Z. Multi-stage semi-coke activation for the removal of SO2 and NO[J]. Fuel,2017,210:738−747. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.08.107 [13] 许慎启, 周志杰, 代正华. 碱金属及灰分对煤焦碳微晶结构及气化反应特性的影响[J]. 高校化学工程学报,2010,24(1):64−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2010.01.012XU Shen-qi, ZHOU Zhi-jie, DAI Zheng-hua. Effects of alkalimetal and ash on crystallite structure of coal char during pyrolysis and on gasification reactivity[J]. J Chem Eng Chin Univ,2010,24(1):64−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2010.01.012 [14] 熊园斌, 王勤辉, 杨玉坤. 碳酸钙对煤热解特性影响的实验研究[J]. 热力发电,2016,45(1):14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2016.01.014XIONG Yuan-bing, WANG Qin-hui, YANG Yu-kun. Experimentals study on influence of calcium carbonate on coal pyrolysis behaviors[J]. Ther Power Gen,2016,45(1):14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2016.01.014 [15] 刘冬冬, 高继慧, 吴少华. FeCl3和空气预氧化对煤焦结构及活化过程中孔隙生成的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(4):1034−1042.LIU Dong-dong, GAO Ji-hui, WU Shao-hua. The effects of FeCl3 and air pre-oxidation on char structure and pore development during activation[J]. J China Coal Soc,2017,42(4):1034−1042. [16] PANDE A R. Catalytic gasification of active charcoal by carbon dioxide: influence of type of catalyst and carbon particle size[J]. Fuel,1992,71(11):1299−1302. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(92)90057-U [17] CHEN X, GUO Y, CUI J. Activated carbon preparation with the addition of coke-making by-product—coke powder: Texture evolution and mechanism[J]. J Cleaner Prod,2019,237:117812. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117812 [18] ZHANG M-H, FAN J, CHI K. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic performance of NiMo catalysts supported on different crystal alumina materials in the hydrodesulfurization of diesel[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2017,156:446−453. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.10.007 [19] 安东海, 韩晓林, 程星星. 不同烟气组分对粉状活性焦吸附汞的影响机理[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(4):1575−1582.AN Dong-hai, HAN Xiao-lin, CHENG Xing-xing. Effect mechanisms of different flue gas on adsorption of mercury by powder activated coke[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2019,70(4):1575−1582. [20] WANG L, SUN F, GAO J. Adjusting the porosity of coal-based activated carbons based on a catalytic physical activation process for gas and liquid adsorption[J]. Energy Fuels,2018,32(2):1255−1264. [21] SCHÖNHERR J, BUCHHEIM J, SCHOLZ P, ADELHELM P. Boehm Tltration Revisited(Part II): A comparison of Boehm titration with other analytical techniques on the quantification of oxygen-containing surface groups for a variety of carbon materials[J]. C- J Carbon Res, 2018, 4(2): 22. [22] YANG L, JIANG X, JIANG W. Cyclic regeneration of pyrolusite-modified activated coke by blending method for flue gas deslfurization[J]. Energy Fuels,2017,31(4):4556−64. [23] 李阳, 朱玉雯, 高继慧. 活性焦孔结构演变规律及对脱硫性能的影响[J]. 化工学报,2015,66(3):1126−1132.LI Yang, ZHU Yu-weng, GAO Ji-hui. Activated coke pore structure evolution and its influence on desulfuration[J]. J Chem Ind Eng,2015,66(3):1126−1132. [24] GUO F, HECKER W C. Effects of CaO and burnout on the kinetics of NO reduction by beulah zap char.[J] Symp (Int) on Combus, 1996, 26 (2): 2251–2257. [25] ÁLVAREZ P, MODESTO P. Vanadium supported on carbon coated honeycomb monoliths for the selective catalytic reduction of NO at low temperatures: Influence of the oxidation pre-treatment[J]. Carbon,2006,44(3):407−417. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.09.011 [26] BOVANO A, HERRERA C, LARRUBIA M A. Vanadium loaded carbon-based monoliths for the on-board no reduction: Influence of temperature and period of the oxidation treatment[J]. Chem Eng J,2010,160(2):623−633. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.03.086 [27] XIE W, LIANG D, LI L. Surface chemical properties and pore structure of the activated coke and their effects on the denitrification activity of selective catalytic reduction[J]. Int J Coal Sci Technol,2019,6(4):595−602. [28] XIE W, SUN Z, XIONG Y. Effects of surface chemical properties of activated coke on selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over commercial coal-based activated coke[J]. Int J Min Sci Technol,2014,24(4):471−475. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.05.009 [29] YUWEN Z, HAOYU L I, DONGDONG L. Development mechanism of pore structures based on burn-off properties of carbon structures during activation process[J]. J China Coal Soc,2017,42(12):3292−3299. [30] 李兰廷. 活性焦干法联合脱硫脱硝的正交实验[J]. 煤炭学报,2009,34(10):1400−1404. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.10.020LI Lan-ting. Orthogonal test on combined desulphurization and denitration by activated char[J]. J China Coal Soc,2009,34(10):1400−1404. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.10.020 -




 下载:
下载: