Effect of framework structure of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 zeolites on their catalytic performance in the conversion of methanol to olefins
-
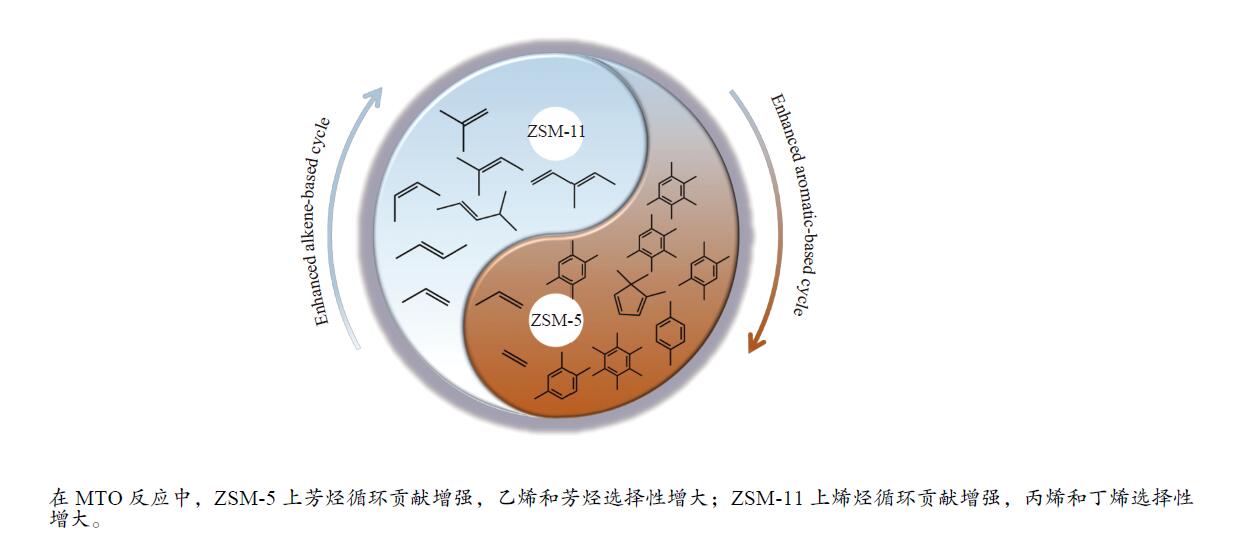
摘要: 本工作采用水热合成法制备了具有相似形貌、粒径、织构性质和酸性的ZSM-11和ZSM-5分子筛,借助多种表征技术研究了这两类分子筛的十元环孔道结构差异对其甲醇转化制烯烃(MTO)催化性能的影响。结果表明,由于ZSM-5的正弦孔道比ZSM-11的直孔道的扩散阻力大,反应中间体和产物分子在ZSM-5分子筛上的停留时间较长,强化了长链烯烃氢转移反应,导致生成更多的甲基苯物种,从而增强了芳烃循环的贡献;相比之下,ZSM-11分子筛的直孔道限制了长链烯烃的氢转移反应,减少了多甲基苯物种的产生,有利于提高烯烃循环的贡献。因此,与具有相似形貌、粒径、织构性质和酸性的ZSM-5-60分子筛相比,ZSM-11-60分子筛对MTO反应具有更长的催化寿命(98.3 h对比65.4 h)和更高的丙烯选择性(34.6%对比27.4%)。这些结果深化了对分子筛MTO催化性能与其孔道结构关系的认识,有助于新型高效的甲醇转化分子筛催化剂的开发和反应过程的探索。Abstract: The catalytic performance of zeolites is closely related to their framework structure and a clear understanding of such a structure-performance relationship is of great significance in revealing catalytic reaction mechanism as well as in developing efficient zeolite catalysts. Herein, ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 zeolites with similar morphology, crystal size, textural properties and acidity were hydrothermally synthesized; the effects of their differences in the 10-ring channels on the catalytic performance in the conversion of methanol to olefins (MTO) were investigated by using various characterization techniques. The results indicate that in comparison with the straight channel of ZSM-11, the sinusoidal channel of ZSM-5 has stronger diffusion resistance, which promotes the hydrogen-transfer in higher olefins, leads to forming more polymethylbenzene species and then raises the contribution of aromatic-based cycle. In contrast, ZSM-11 with straight channel can reduce the formation of polymethylbenzene species and enhance the alkene-based cycle. As a result, compared with ZSM-5-60 with similar morphology and acidity, ZSM-11-60 as a catalyst in MTO exhibits longer lifetime (98.3 h vs. 65.4 h) and higher selectivity to propene (34.6% vs. 27.4%). The insight shown in this work helps to have a better understanding of the relation between zeolite structure and catalytic performance in MTO and is then beneficial to the development of better catalysts and processes for MTO.
-
Key words:
- ZSM-11 /
- ZSM-5 /
- straight channel /
- sinusoidal channel /
- methanol to olefins
-
图 4 ZSM-11和ZSM-5分子筛的(a)NH3-TPD,(b)Py-IR,(c)dTBPy-IR和(d)分峰拟合后的硅核磁谱图
Figure 4 (a) NH3-TPD profiles, (b) Py-IR spectra, (c) dTBPy-IR spectra and (d) deconvoluted 29Si MAS NMR spectra of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 zeolites
In the deconvoluted 29Si MAS NMR spectra, the weak peak at −106 is attributed to the Q3 (Si(OAl)1(OSi)3), whereas four peaks around −110.4, −112.3, −113.7 and −115.7, and at −110, −112.5, −115 and −117.5 are assigned to Q4 (Si(0Al)) of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5, respectively
图 8 ZSM-11和ZSM-5分子筛催化MTO反应时的C4-HTI (a)、C5-HTI (b)、(P−E)/E (c)随反应时间的变化以及失活后的ZSM-11和ZSM-5分子筛的热重曲线 (d)
Figure 8 A comparison of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 as the catalyst for MTO in the C4 hydride transfer index (C4-HTI) (a), the C5 hydride transfer index (C5-HTI) (b), (P−E)/E ratio (c), and TGA curves (d) of spent catalysts. C4/5-HTI is denoted as the ratio of (C4/5 0 )/( C4/5 0 + C4/5 = )
表 1 ZSM-11和ZSM-5分子筛的织构性质
Table 1 Textural properties of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 zeolites
Zeolite Crystal size /
μmSurface area /
(m2·g−1)Pore volume /
(cm3·g−1)total micro ext total micro meso ZSM-11-60 0.62 336 242 94 0.25 0.12 0.13 ZSM-5-60 0.63 337 249 88 0.23 0.11 0.12 表 2 ZSM-11和ZSM-5分子筛的元素组成和酸性性质
Table 2 Elemental composition and acidic properties of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 zeolites
Zeolite Si/Al by ICP Si/AlF Acidity by NH3-TPD /(μmol·g−1) Acidity by Py-IR or dTBPy-IR /(μmol·g−1) strong weak total Brønsted Lewis total dTBPy-Brønsted ZSM-11-60 51 54 228 116 344 175 43 218 19 ZSM-5-60 48 52 217 158 375 175 55 230 20 Note: framework Si/AlF ratio is derived from the 29Si MAS NMR spectra [19] 表 3 ZSM-11和ZSM-5分子筛 27Al MAS NMR分峰拟合信号峰面积占总峰面积比例
Table 3 Proportion of integrated peaks obtained by deconvolution of the 27Al MAS NMR spectra of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 zeolites
Zeolite AlF /% AlEF /% Aluminum distribution /% 48.5–49.0 53.0–53.2 55.6–56.0 58.0–58.1 ZSM-11-60 99.5 0.5 6.4 38.1 45.1 10.4 ZSM-5-60 99.2 0.8 6.4 42.9 39.6 11.1 表 4 Co-ZSM-11和Co-ZSM-5分子筛中不同类型铝物种的分布比
Table 4 Distribution of different types of Al species in Co-ZSM-11 and Co-ZSM-5 zeolites
Zeolite Alpairs /% Alsingle /% Aluminum distribution /% α β γ ZSM-11-60 64 36 15.6 63.6 20.8 ZSM-5-60 58 42 12.4 63.5 24.1 Note: contents of Alpairs and Alsingle were calculated as [Alpairs]= 2 × [Co] and [Alsingle] = [Altotal] – [Alpairs], where [Altotal] and [Co] are the contents of Al and Co in the Co-ZSM-11/Co-ZSM-5 samples, respectively, measured by ICP-OES 表 5 ZSM-11和ZSM-5的 MTO催化反应
Table 5 Catalytic results of ZSM-11 and ZSM-5 zeolites in MTO
Zeolite xM /% Product distribution /% (P−E)/E TON
× 104Life time /h C1 0 C2–5 0 C2 = C3 = C4 = C5 = C6 + arom. ZSM-11-60 99.9 2.1 9.3 8.3 34.6 24.4 9.0 2.9 9.4 3.2 8.1 98.3 ZSM-5-60 99.9 2.6 17.6 9.7 27.4 17.1 6.1 3.8 15.7 1.8 5.3 65.4 ZSM-11-30 99.9 4.5 19.1 8.9 24.6 15.3 4.7 3.6 19.3 1.8 2.3 48.7 ZSM-5-30 99.9 4.3 24.0 11.0 20.4 12.0 3.6 3.9 20.8 0.9 1.5 41.2 Note: methanol conversion and product distribution reported were acquired at half life time of each zeolite catalyst -
[1] CHANG C D, SILVESTRI A J. The conversion of methanol and other O-compounds to hydrocarbons over zeolite catalysts[J]. J Catal,1977,47(2):249−259. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(77)90172-5 [2] OLSBYE U, SVELLE S, BJORGEN M, BEATO P, JANSSENS T V W, JOENSEN F, BORDIGA S, LILLERUD K P. Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons: how zeolite cavity and pore size controls product selectivity[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2012,51(24):5810−5831. doi: 10.1002/anie.201103657 [3] TIAN P, WEI Y X, YE M, LIU Z M. Methanol to olefins (MTO): from fundamentals to commercialization[J]. ACS Catal,2015,5(3):1922−1938. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00007 [4] SHI J, WANG Y D, YANG W M, TANG Y, XIE Z K. Recent advances of pore system construction in zeolite-catalyzed chemical industry processes[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2015,44(24):8877−8903. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00626K [5] YARULINA I, CHOWDHURY A D, MEIRER F, WECKHUYSEN B M, GASCON J. Recent trends and fundamental insights in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons process[J]. Nat Catal,2018,1(6):398−411. doi: 10.1038/s41929-018-0078-5 [6] BJØRGEN M, SVELLE S, JOENSEN F, NERLOV J, KOLBOE S, BONINO F, PALUMBO L, BORDIGA S, OLSBYE U. Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons over zeolite H-ZSM-5: on the origin of the olefinic species[J]. J Catal,2007,249(2):195−207. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.04.006 [7] SVELLE S, JOENSEN F, NERLOV J, OLSBYE U, LILLERUD K P, KOLBOE S, BJØRGEN M. Conversion of methanol into hydrocarbons over zeolite H-ZSM-5: Ethene formation is mechanistically separated from the formation of higher alkenes[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2006,128(46):14770−14771. doi: 10.1021/ja065810a [8] WANG Q, CUI Z M, CAO C Y, SONG W G. 0.3 Å makes the difference: Dramatic changes in methanol-to-olefin activities between H-ZSM-12 and H-ZSM-22 zeolites[J]. J Phys Chem C,2011,115(50):24987−24992. doi: 10.1021/jp209182u [9] CHU Y Y, SUN X Y, YI X F, DING L H, ZHENG A M, DENG F. Diffusion dependence of the dual-cycle mechanism for MTO reaction inside ZSM-12 and ZSM-22 zeolites[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2015,5(7):3507−3517. doi: 10.1039/C5CY00312A [10] LIU Z Q, CHU Y Y, TANG X M, HUANG L, LI G C, YI X F, ZHENG A M. Diffusion dependence of the dual-cycle mechanism for MTO reaction inside ZSM-12 and ZSM-22 zeolites[J]. J Phys Chem C,2017,121(41):22872−22882. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07374 [11] SHEN Y F, LE T T, FU D L, SCHMIDT J E, FILEZ M, WECKHUYSEN B M, RIMER J D. Deconvoluting the competing effects of zeolite framework topology and diffusion path length on methanol to hydrocarbons reaction[J]. ACS Catal,2018,8(12):11042−11053. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02274 [12] WANG S, WANG P F, QIN Z F, CHEN Y Y, DONG M, LI J F, ZHANG K, LIU P, WANG J G, FAN W B. Relation of catalytic performance to the aluminum siting of acidic zeolites in the conversion of methanol to olefins, viewed via a comparison between ZSM-5 and ZSM-11[J]. ACS Catal,2018,8(12):5485−5505. [13] YUAN K, JIA X Y, WANG S, FAN S, HE S P, WANG P F, QIN Z F, DONG M, FAN W B, WANG J G. Regulating the distribution of acid sites in ZSM-11 zeolite with different halogen anions to enhance its catalytic performance in the conversion of methanol to olefins[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2022,341:112051. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.112051 [14] WANG S, LI Z K, QIN Z F, DONG M, LI J F, FAN W B, WANG J G. Catalytic roles of the acid sites in different pore channels of H-ZSM-5 zeolite for methanol-to-olefins conversion[J]. Chin J Catal,2021,42(7):1126−1136. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63732-9 [15] NIU X J, GAO J, MIAO Q, DONG M, WANG G F, FAN W B, QIN Z F, WANG J G. Influence of preparation method on the performance of Zn-containing HZSM-5 catalysts in methanol-to-aromatics[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2014,197:252−261. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.06.027 [16] CORMA A, FORNES V, FORNI L, MARQUEZ F, MARTINEZ-TRIGUERO J, MOSCOTTI D. 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-pyridine as a probe molecule to measure external acidity of zeolites[J]. J Catal,1998,179(2):451−458. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1998.2233 [17] GORA-MAREK K, TARACH K, CHOI M. 2, 6-Di-tert-butylpyridine sorption approach to quantify the external acidity in hierarchical zeolites[J]. J Phys Chem C,2014,118(23):12266−12274. doi: 10.1021/jp501928k [18] DEDECEK J, SOBALIK Z, WICHTERLOVA B. Siting and distribution of framework aluminium atoms in silicon-rich zeolites and impact on catalysis[J]. Cat Rev-Sci Eng,2012,54(2):135−223. doi: 10.1080/01614940.2012.632662 [19] LIANG T Y, CHEN J L, QIN Z F, LI J F, WANG P F, WANG S, WANG G F, DONG M, FAN W B, WANG J G. Conversion of methanol to olefins over H-ZSM-5 zeolite: Reaction pathway is related to the framework aluminum siting[J]. ACS Catal,2016,6(11):7311−7325. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01771 [20] ZENG S, XU S T, GAO S S, GAO M B, ZHANG W N, WEI Y X, LIU Z M. Differentiating diffusivity in different channels of ZSM-5 zeolite by Pulsed Field Gradient (PFG) NMR[J]. ChemCatChem,2020,12(2):463−468. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201901689 [21] MADEIRA F F, TAYEB K B, PINARD L, VEZIN H, MAURY S, CADRAN N. Ethanol transformation into hydrocarbons on ZSM-5 zeolites: Influence of Si/Al ratio on catalytic performances and deactivation rate. Study of the radical species role[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2014,443-444:171−180. [22] WANG S, ZHANG L, LI S Y, QIN Z F, SHI D Z, HE S P, YUAN K, WANG P F, ZHAO T S, FAN S B, DONG M, LI J F, FAN W B, WANG J G. Tuning the siting of aluminum in ZSM-11 zeolite and regulating its catalytic performance in the conversion of methanol to olefins[J]. J Catal,2019,377:81−97. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2019.07.028 [23] XUE Y F, LI J F, WANG P F, CUI X J, ZHENG H Y, NIU Y L, DONG M, QIN Z F, WANG J G, FAN W B. Regulating Al distribution of ZSM-5 by Sn incorporation for improving catalytic properties in methanol to olefins[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2021,280:119391. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119391 [24] WANG C, WANG Q, XU J, QI G D, GAO P, WANG W Y, ZOU Y Y, FENG N D, LIU X L, DENG F. Direct detection of supramolecular reaction centers in the methanol-to-olefins conversion over zeolite H-ZSM-5 by 13C–27Al solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2016,55(7):2507−5511. doi: 10.1002/anie.201510920 [25] PARK J W, KIM S J, SEO M, KIM S Y, SUGI Y, SEO G. Product selectivity and catalytic deactivation of MOR zeolites with different acid site densities in methanol-to-olefin (MTO) reactions[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2008,349:76−85. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2008.07.006 [26] WANG J B, WEI Y X, LI J Z, XU S T, ZHANG W N, HE Y L, CHEN J R, ZHANG M Z, ZHENG A M, DENG F, GUO X W, LIU Z M. Direct observation of methylcyclopentenyl cations (MCP + ) and olefin generation in methanol conversion over TON zeolite[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2016,6(1):89−97. doi: 10.1039/C5CY01420D -





 下载:
下载: