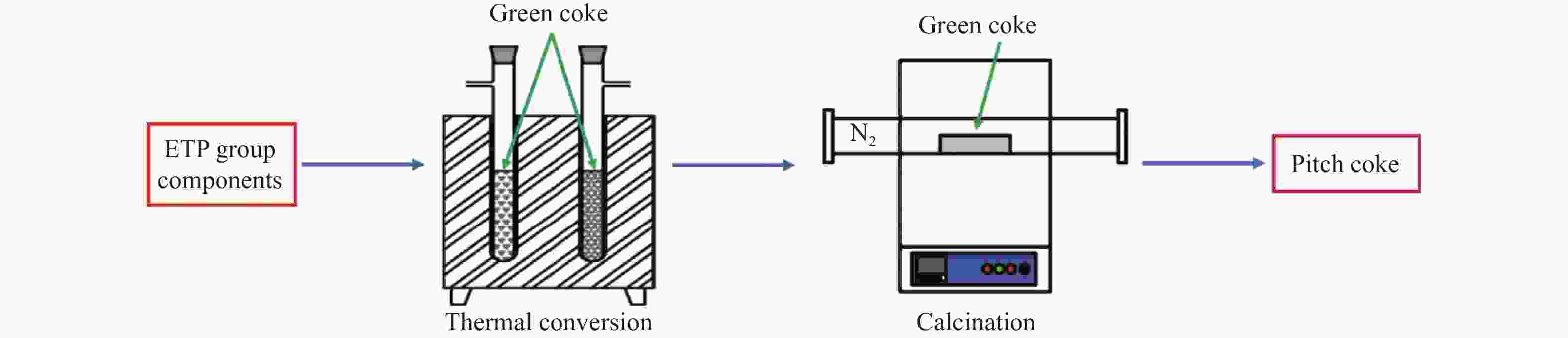
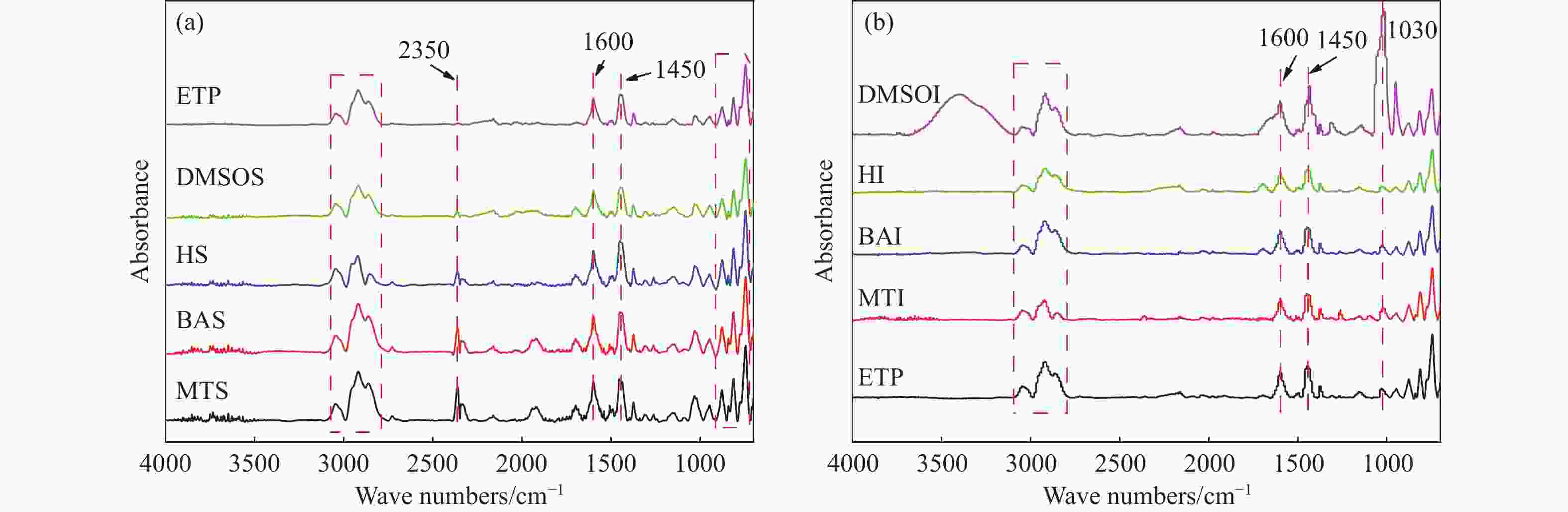
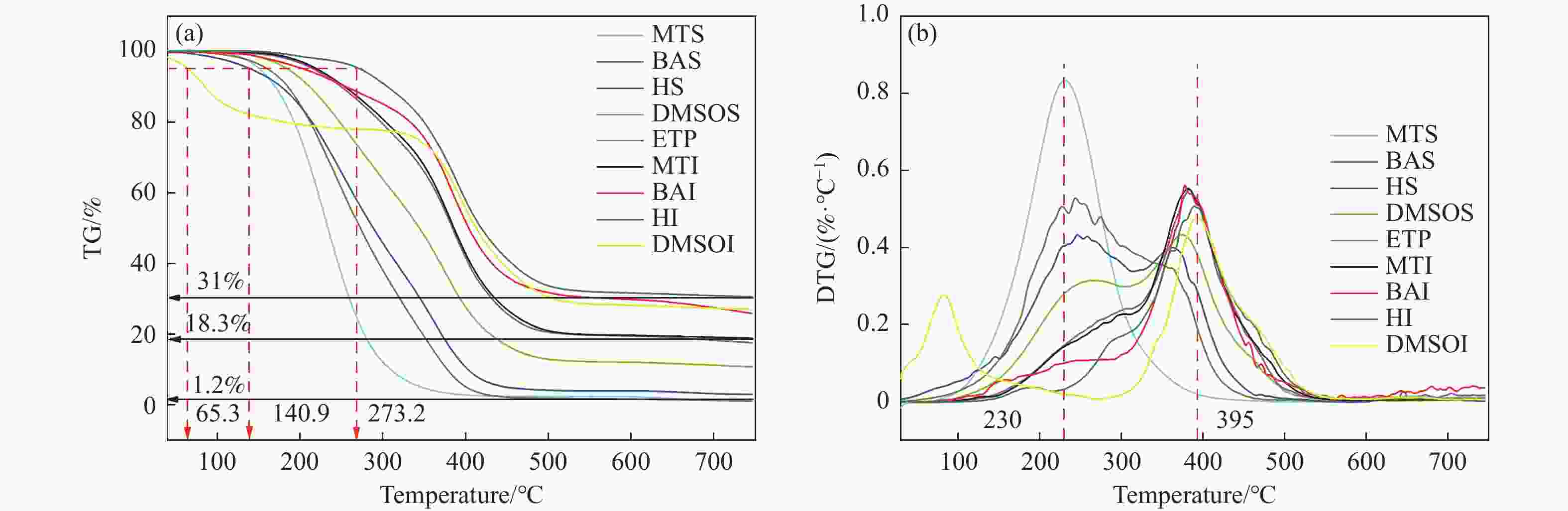
Research on coking performance of ethylene residue pitch components
-
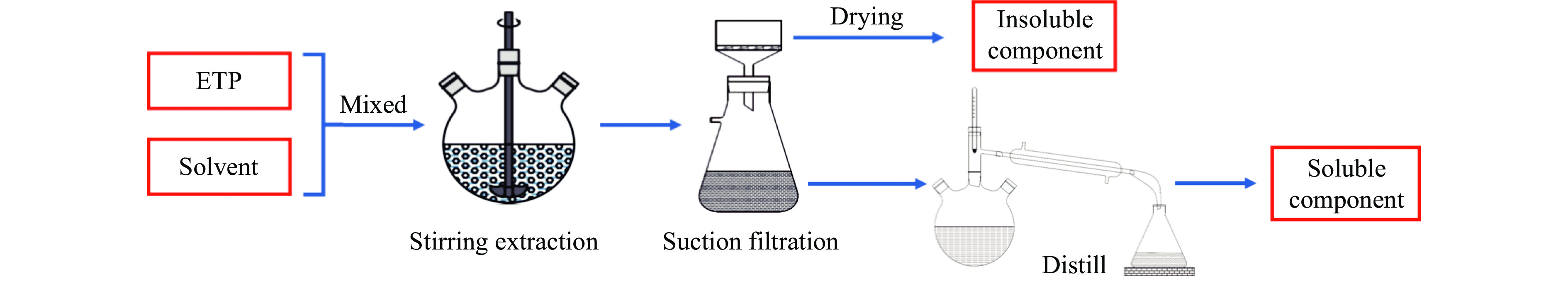
摘要: 乙烯渣油沥青作为乙烯渣油中的重质组分具有含碳量高、芳香度较高及杂原子(S、N)含量低的特点,被广泛用作制备石油基人造炭材料的优选原料。为充分研究乙烯渣油沥青的成焦性,本研究选取四种溶剂(甲醇、正丁醇、正庚烷、二甲基亚砜)对乙烯渣油沥青进行萃取分离,获得八种乙烯渣油沥青组分(四种可溶组分和四种不溶组分),并对获得的乙烯渣油沥青组分进行热转化和炭化处理(热转化温度和炭化温度分别为500和1400 ℃)获得系列乙烯渣油沥青焦。采用红外光谱、热重分析仪、1H-NMR对乙烯渣油沥青组分的基础物性进行研究;利用偏光显微镜、X射线单晶衍射仪、拉曼光谱仪、扫描电子显微镜等对系列石油系沥青焦结构进行研究。结果表明,乙烯渣油沥青不溶组分芳香性略高于可溶组分,且不溶组分支链略少于可溶组分;不溶组分热转化和炭化后得到的乙烯渣油沥青焦显微强度高于可溶组分获得的乙烯渣油沥青焦,且乙烯渣油沥青沥青焦HS-C的真密度高达2.0554 g/cm3。Abstract: Ethylene residue pitch (the heavy component in ethylene residue tar) was widely used as the preferred raw material for preparing petroleum based artificial carbon materials with the characteristics of high carbon content, high aromaticity, and low heteroatom (S, N) content. In order to a detailed study on the coking properties of ethylene residue pitch, 8 components of ethylene residue pitch (four soluble and four insoluble components) were obtained by extraction and separation method. Factually, methanol, n-butanol, n-hexane, and dimethyl sulfoxide were selected as the solvents to extract and separate the ethylene residue pitch. A series of petroleum based pitch coke were gained by the thermal conversion and carbonization treatment (thermal conversion temperature and carbonization temperature were 500 and 1400 ℃, respectively) of each pitch components. The basic physical properties of ethylene residue pitch components were studied using infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and 1H-NMR. The micro-structure of a series of petroleum based pitch coke was studied by polarizing microscopy, X-ray single crystal diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy. The results shown that: The aromaticity of insoluble components in ethylene residue pitch is slightly higher than that of soluble components, and the branching chains of insoluble components are slightly less than those of soluble components. The microstrength of ethylene residue pitch coke obtained by thermal conversion and carbonization of insoluble components is higher than that of ethylene residue pitch coke obtained by soluble components, and the true density of ethylene residue pitch coke HS-C is as high as 2.0554 g/cm3.
-
Key words:
- ethylene residue pitch /
- components /
- coking performance /
- pitch coke
-
表 1 ETP的工业分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis of ETP
Sample Content w/% SP/℃ QI TI CV V ETP 0.41 0.59 32.64 76.93 126 表 2 沥青组分的工业分析
Table 2 Proximate analysis of pitch components
Sample Yield/% Content w/% SP/℃ QI TI CV V ETP 100 0.41 0.59 32.64 76.93 126 MTI 96.68 0.01 0.05 37.13 77.30 168 BAI 73.46 0.10 0.15 37.51 70.86 178 HI 68.31 1.03 9.93 43.76 66.59 178 DMSOI 34.57 0.37 0.60 37.41 75.13 124 MTS 3.32 − − 4.97 97.57 − BAS 26.54 − − 11.88 94.46 − HS 31.69 − − 12.93 93.20 − DMSOS 65.43 − − 28.46 83.24 51 表 3 沥青组分的元素分析
Table 3 Ultimate analysis of pitch components
Sample Content w/% C/H C H N S O ETP 91.00 6.42 0.06 0.00 2.52 1.18 MTI 93.37 6.59 0.04 0.00 0.00 1.18 BAI 93.52 6.43 0.05 0.00 0.00 1.21 HI 89.21 6.07 0.06 0.00 4.66 1.22 DMSOI 90.30 6.28 0.06 1.33 2.03 1.20 DMSOS 91.19 6.35 0.08 0.16 2.23 1.20 HS 92.77 7.15 0.08 0.00 0.00 1.08 BAS 91.67 6.82 0.10 0.00 1.42 1.12 MTS 89.33 6.26 0.36 0.00 4.04 1.19 表 4 偏光显微镜下各光学组织的测定标准
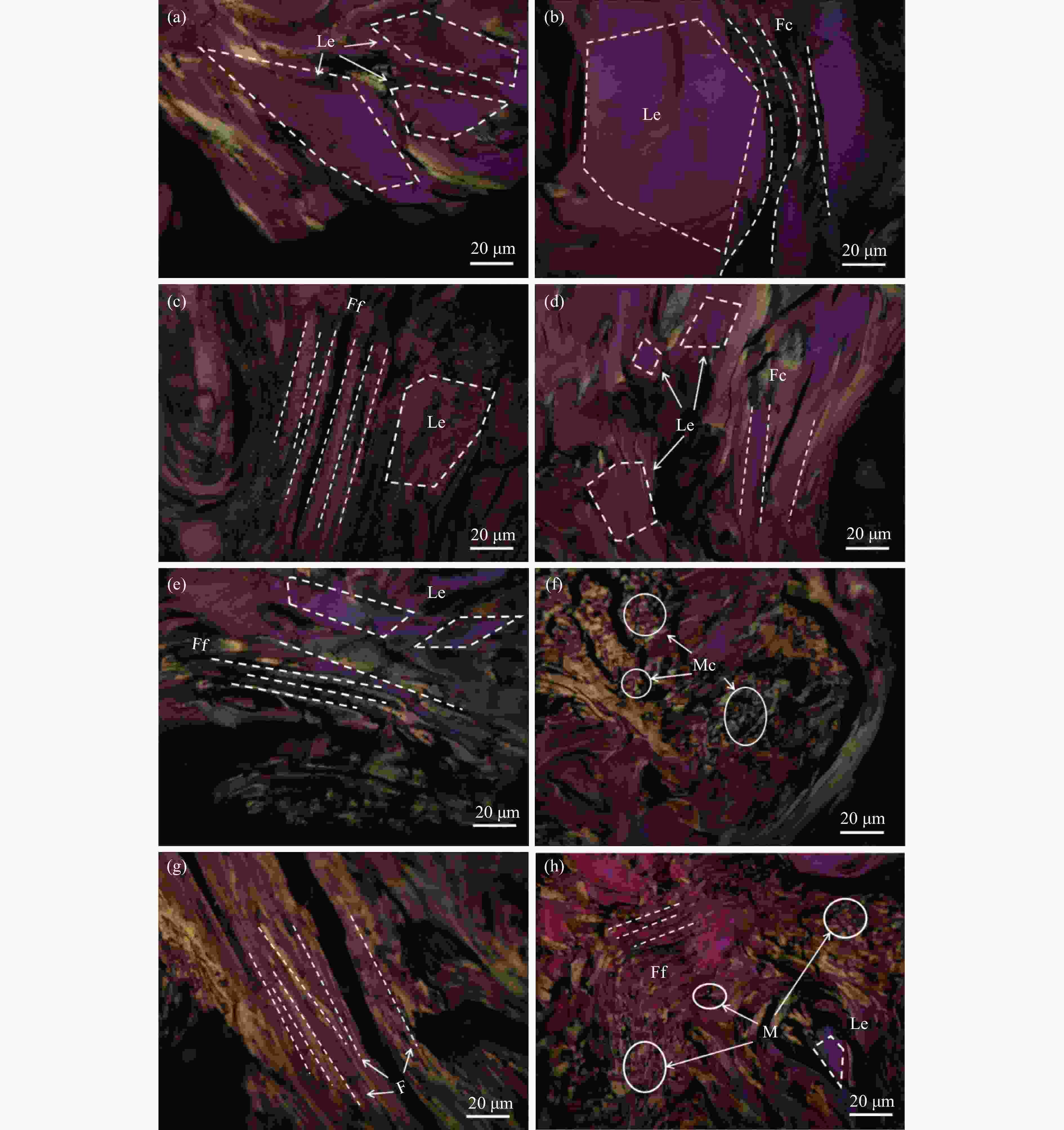
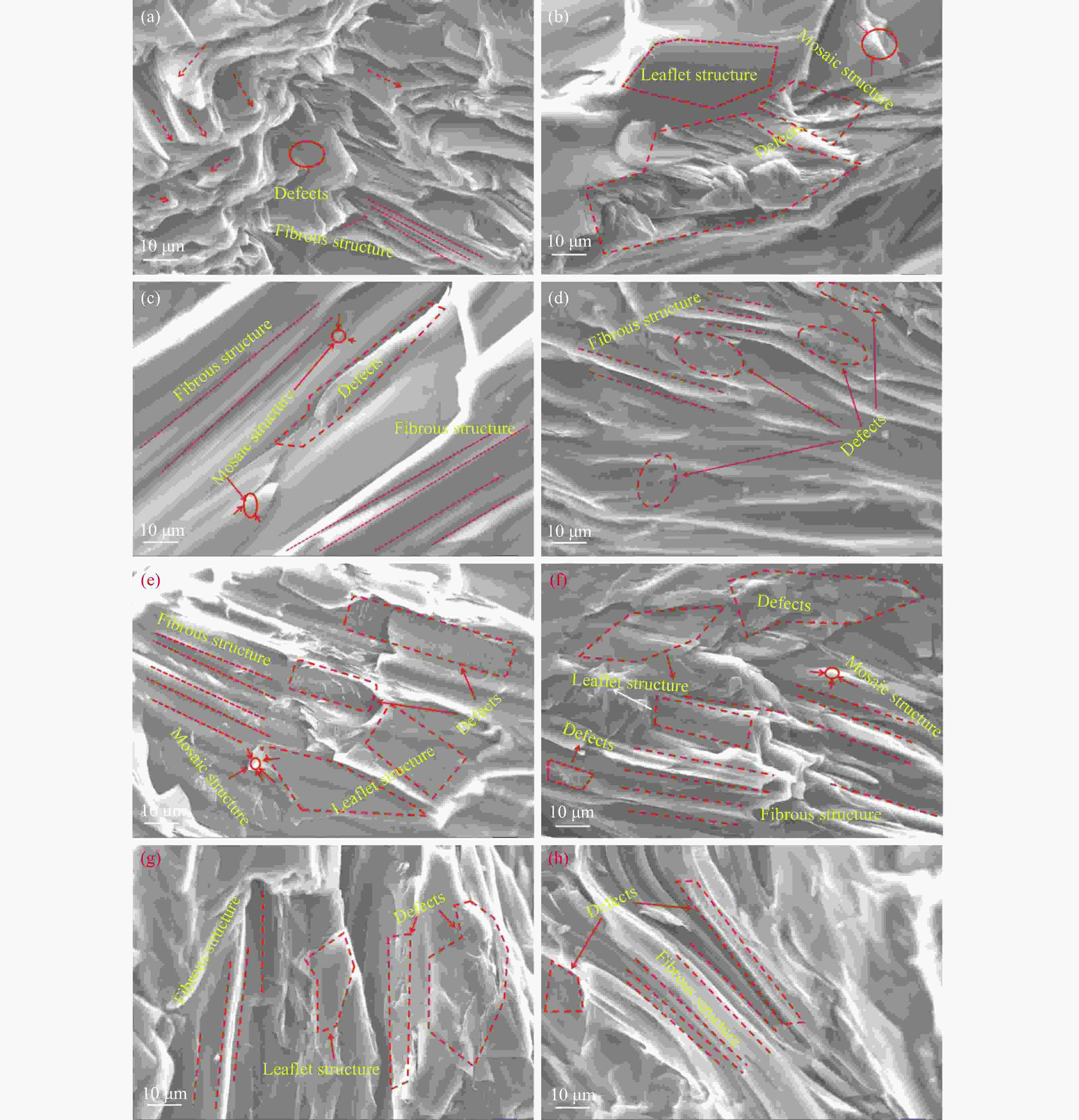
Table 4 Standard for the determination of various optical structures under polarizing microscope
Optical organization Size/μm Length Width Mf ≤1 <1 Mm 1−5 1−5 Mc 5−10 5−10 Ff >30 <10 Fc >30 >10 Le ≥10 ≥10 表 5 组分的氢原子分布
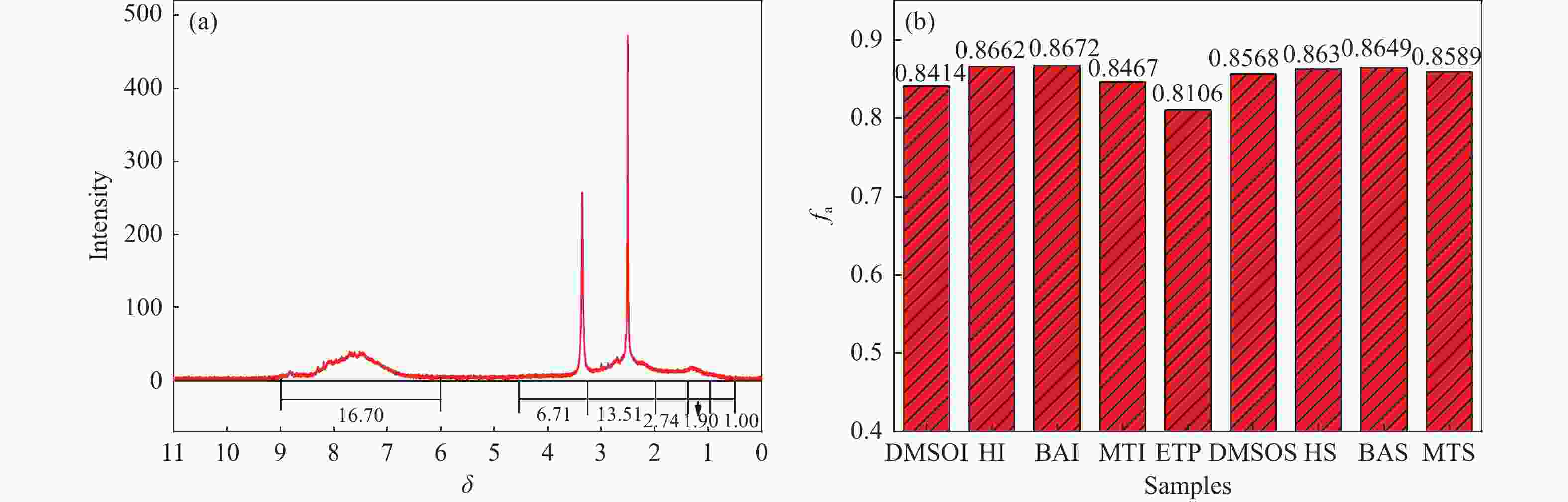
Table 5 Distribution of hydrogen atoms in components
Sample hydrogen ratio Har HF Hα HN Hβ Hγ DMSOI 0.283 0.200 0.319 0.060 0.098 0.039 HI 0.257 0.296 0.248 0.055 0.087 0.057 BAI 0.392 0.158 0.317 0.064 0.045 0.023 MTI 0.274 0.231 0.284 0.061 0.091 0.059 ETP 0.158 0.263 0.481 0.043 0.029 0.026 DMSOS 0.237 0.286 0.272 0.064 0.076 0.064 HS 0.338 0.261 0.301 0.045 0.041 0.013 BAS 0.353 0.215 0.280 0.068 0.062 0.021 MTS 0.336 0.200 0.330 0.061 0.043 0.030 表 6 系列生焦收率
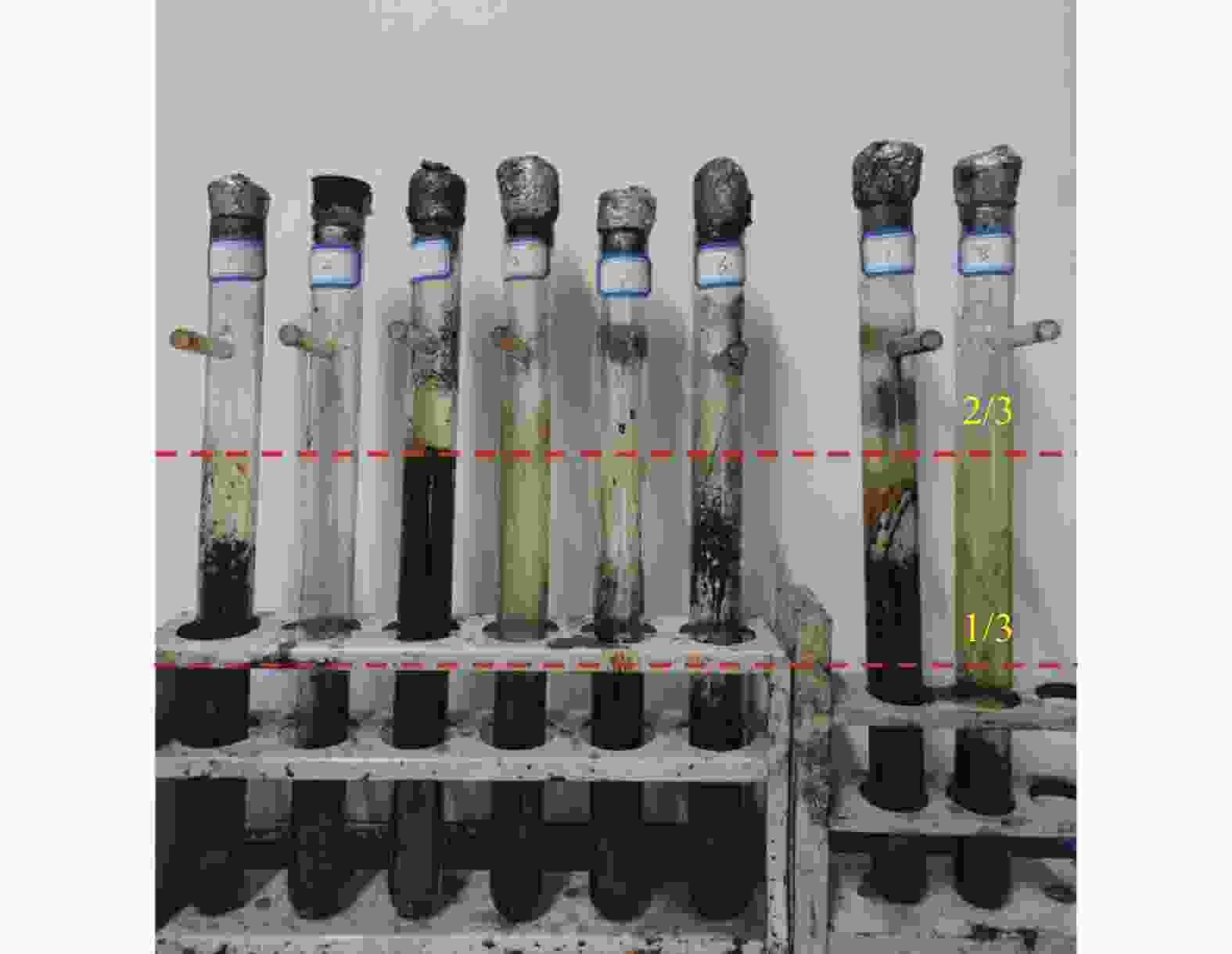
Table 6 Yield of green cokes
Sample Yield/% ETP-G 52.75 DMSOS-G 43.66 BAS-G 33.45 HS-G 34.16 DMSOI-G 53.17 MTI-G 53.50 BAI-G 52.88 HI-G 54.18 表 7 各组分沥青焦偏光
Table 7 Polarizing results of each pitch cokes
Sample Mf/% Mm/% Mc/% Ff/% Fc/% Le/% F+L/% ETP-C 2.00 7.86 5.34 7.81 13.39 63.60 84.80 MTI-C 0.45 11.86 7.21 7.56 13.96 58.95 80.47 BAI-C 0.96 9.52 5.96 0.98 1.46 81.12 83.56 HI-C 2.00 15.50 8.00 4.50 10.00 60.00 74.50 DMSOI-C 0.65 7.35 2.00 2.00 13.00 75.00 90.00 DMSOS-C 0.56 6.81 1.13 11.50 4.50 75.50 91.50 HS-C 1.62 4.86 2.83 10.93 13.36 66.40 90.69 BAS-C 1.50 7.49 4.56 6.25 10.70 69.50 86.45 表 8 焦炭002峰拟合数据及计算
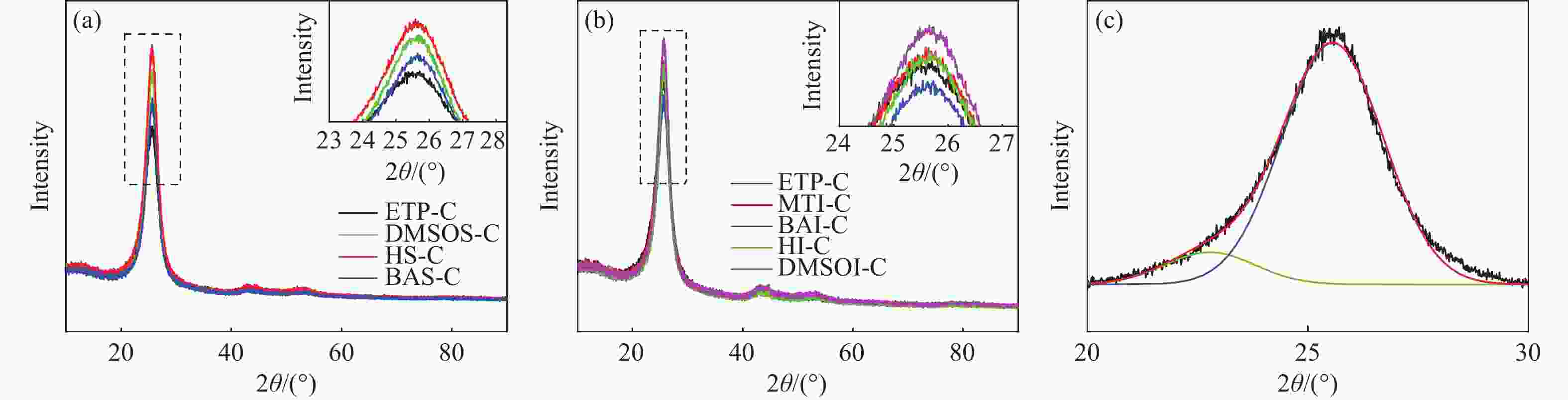
Table 8 Cokes 002 peak fitting data and calculation results
Sample 2θc/° βc d002/nm Lc/nm N n ETP-C 25.563 0.047 0.348 2.972 10 29 DMSOS-C 25.581 0.041 0.348 3.389 11 37 HS-C 25.662 0.041 0.348 3.199 10 33 BAS-C 25.630 0.044 0.347 3.411 11 37 MTI-C 25.609 0.044 0.348 3.167 10 33 BAI-C 25.607 0.044 0.347 3.218 10 34 HI-C 25.656 0.044 0.347 3.200 10 33 DMSOI-C 25.638 0.041 0.347 3.399 11 37 表 9 系列沥青焦的拉曼特征参数
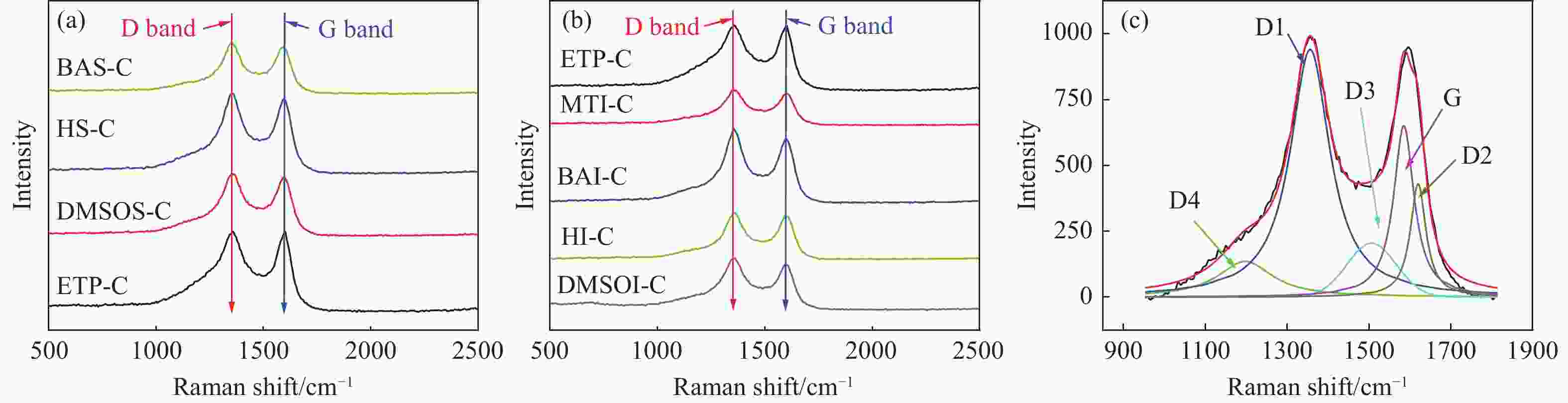
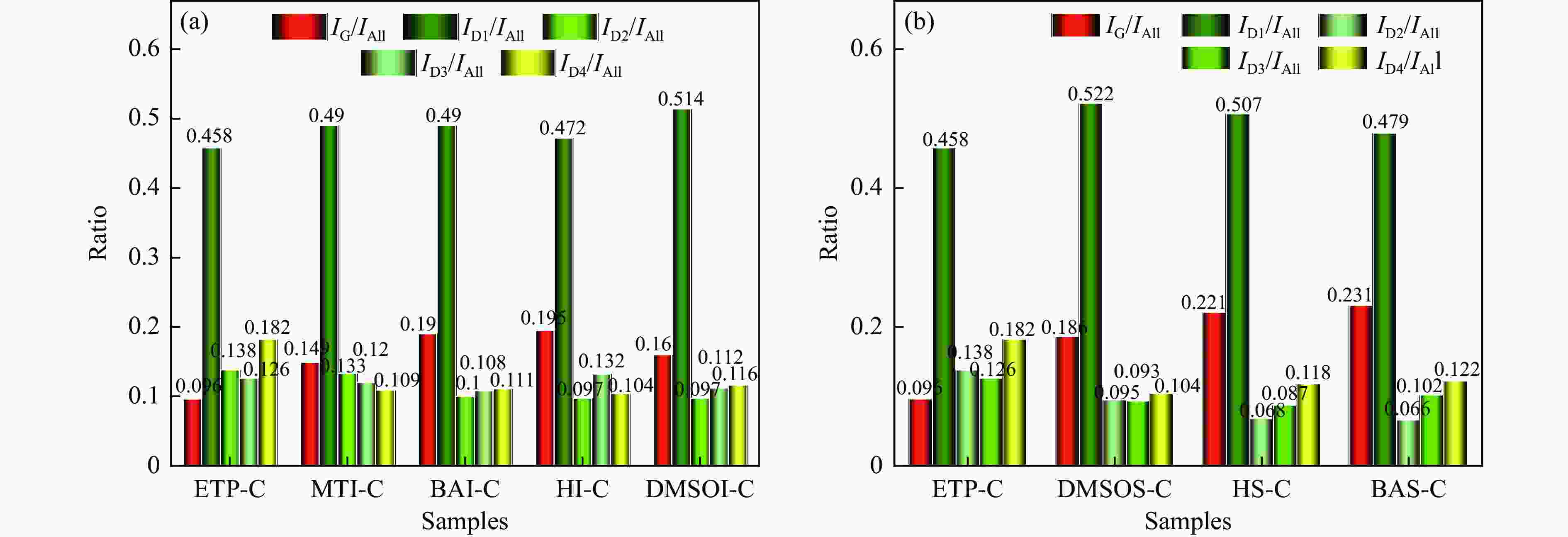
Table 9 Characteristic Raman index of series pitch coke
Sample Area/105 ID1 ID2 ID3 ID4 IG 1.937 0.583 0.533 0.770 0.407 MTI-C 1.017 0.275 0.248 0.226 0.308 BAI-C 2.011 0.411 0.445 0.456 0.782 HI-C 1.274 0.263 0.358 0.280 0.527 DMSOI-C 1.661 0.313 0.363 0.375 0.517 DMSOS-C 1.739 0.315 0.309 0.347 0.620 HS-C 2.101 0.282 0.359 0.488 0.918 BAS-C 1.201 0.166 0.256 0.306 0.578 表 10 系列沥青焦炭宏观性能指标
Table 10 Index of macroscopic properties of series pitch coke
Sample TD/(g·cm−3) PR/(mΩ·mm) MS/% ETP-C 2.0145 484 66.0 DMSOS-C 1.8393 440 59.5 HS-C 2.0554 449 68.5 BAS-C 1.9744 467 71.5 MTI-C 2.0434 455 67.5 BAI-C 2.0100 475 75.0 HI-C 1.8402 450 70.5 DMSOI-C 2.0172 434 78.0 -
[1] HU H, WU M B. Heavy oil-derived carbon for energy storage applications[J]. J Mater Chem A,2020,8(15):7066−7082. doi: 10.1039/D0TA00095G [2] KONG D Q, CAI T H, FAN H D, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as a new class of promising cathode materials for aluminum-ion batteries[J]. Angew Chem Int Edit,2022,61:e202114681. doi: 10.1002/anie.202114681 [3] LIU Y H, LIU X P, MA Z K, et al. A new preparation method of graphite cones from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons/polyimide composite carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2022,196:128−135. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.04.069 [4] JIANG B, QI C L, YANG H, et al. Recent advances of carbon-based electromagnetic wave absorption materials facing the actual situations[J]. Carbon,2023,208:390−409. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.04.002 [5] WU C H, XU Q, NING H, et al. Petroleum pitch derived carbon as both cathode and anode materials for advanced potassium-ion hybrid capacitors[J]. Carbon,2022,196:727−735. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.05.021 [6] YANG W, WANG C N, JIANG B, et al. Lightweight 3D interconnected porous carbon with robust cavity skeleton derived from petroleum pitch for effective multi-band electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2022,200:390−400. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.08.069 [7] YANG W, ZHANG C X, LI Y F. Crumpled nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets derived from petroleum pitch for high-performance and flexible electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2022,61:2799−2808. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.1c04481 [8] WU W, ZHANG X X, YANG J X, et al. Facile preparation of oxygen-rich activated carbon from petroleum coke for enhancing methylene blue adsorption[J]. Carbon Lett,2020(30):627−636. [9] CHAI L N, LOU B, LI J, et al. Insight into the reactivity of aromatic-rich fractions co-carbonized with polyethylene glycol for preparation of isotropic pitch with superior spinnability[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2022,237:107433. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107433 [10] YANG J X, SHI K, LI X K, et al. Preparation of isotropic spinnable pitch and carbon fiber from biomass tar through the co-carbonization with ethylene bottom oil[J]. Carbon Lett,2018,25:89−94. [11] SHI K, YANG J X, LI J, et al. Effect of oxygen-introduced pitch precursor on the properties and structure evolution of isotropic pitch-based fibers during carbonization and graphitization[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2020,199:106291. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106291 [12] GONG X, GUO S H, DING Y Y, et al. Preparation of mesocarbon microbeads as anode material for lithium-ion battery by co-carbonization of FCC decant oil and conductive carbon black[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2022,227:107110. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.107110 [13] GONG X, LOU B, YU R, et al. Carbonization of mesocarbon microbeads prepared from mesophase pitch with different anisotropic contents and their application in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2021,217:106832. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.106832 [14] WANG F, JIAO S H, LIU W C, et al. Preparation of mesophase carbon microbeads from fluidized catalytic cracking residue oil: The effect of active structures on their coalescence[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrol,2021,156:105166. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105166 [15] LOU B, LIU D, QIU Y, et al. Modified effect on properties of mesophase pitch prepared from various two-stage thermotreatments of FCC decant oil[J]. Fuel,2021,284:119034. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119034 [16] LI J, LOU B, CHAI L N, FU Y, et al. Influence of boron trifluoride complex addition on structure and composition of mesophase pitch from FCC decant oil via two-stage thermotreatment[J]. Fuel,2022,325:124801. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124801 [17] LIAO G, SHI K, YE C, et al. Influence of resin on the formation and development of mesophase in fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) slurry oil[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrol,2023,172:105997. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2023.105997 [18] GUO J G, LU S H, XIE J R, et al. Preparation of mesophase pitch with domain textures by molecular regulation of ethylene tar pitch for boosting the performance of its carbon materials[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrol,2023,170:105932 doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2023.105932 [19] JIAO S H, GUO A J, WANG F, et al. Sequential pretreatments of an FCC slurry oil sample for preparation of feedstocks for high-value solid carbon materials[J]. Fuel,2021,285:119169. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119169 [20] ZHANG Z C, HUANG X Q, ZHANG L J, et al. Study on the evolution of oxygenated structures in low-temperature coal tar during the preparation of needle coke by co-carbonization[J]. Fuel,2022,307:121811. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121811 [21] ZHANG Z C, YU E Q, LIU Y J, et al. The effect of composition change and allocation in raw material on the carbonaceous structural evolution during calcination process[J]. Fuel,2022,309:122173. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122173 [22] ZHANG Z C, CHEN K, LIU D, et al. Comparative study of the carbonization process and structural evolution during needle coke preparation from petroleum and coal feedstock[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrol,2021,156:105097. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105097 [23] ZHU Y M, ZHAO C L, XU Y L, et al. Preparation and characterization of coal pitch-based needle coke (part Ⅰ): the effects of aromatic index (fa) in refined coal pitch[J]. Energy Fuels,2019,33(4):3456−3464. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b00160 [24] 李磊, 林雄超, 刘哲, 等. 煤系针状焦偏光显微结构的识别及定量分析[J]. 燃料化学学报,2021,49(3):265−273.LI Lei, LIN Xiongchao, LIU Zhe, et al. Identification and quantitative analysis of polarized light microstructure of coal-derived needle coke[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2021,49(3):265−273. [25] 张春阳, 朱亚明, 徐允良, 等. 镶嵌结构沥青焦的制备与表征: 重相沥青中QI含量的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2021,49(10):1412−1420.ZHANG Chunyang, ZHU Yaming, XU Yunliang, et al. Preparation and characterization of pitch-based mosaic coke from heavy-phase coal pitch: Effects of quinoline insoluble[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2021,49(10):1412−1420. [26] 高丽娟, 赵雪飞, 赖仕全, 等. 煤焦油精制软沥青组成及结构的表征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2009,29(8):2152−2156 doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)08-2152-05GAO Lijuan, ZHAO Xuefei, LAI Shiquan, et al. Characterization of composition and structure of refined soft pitch from coal tar[J]. Spectrosc Spect Anal,2009,29(8):2152−2156 doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)08-2152-05 -





 下载:
下载: