Theoretical study on the pyrolysis mechanism of the lignin dimer model compound catalyzed by alkaline earth metal ions Ca2+ and Mg2+
-
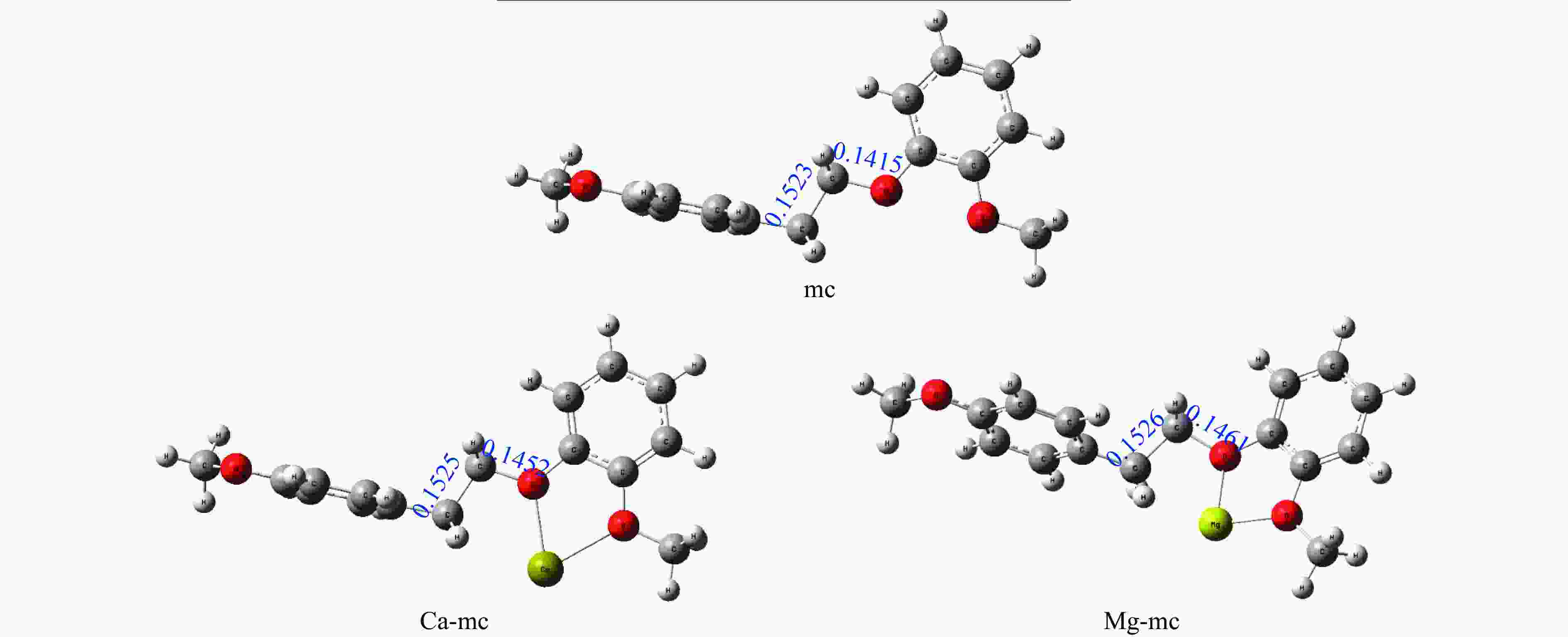
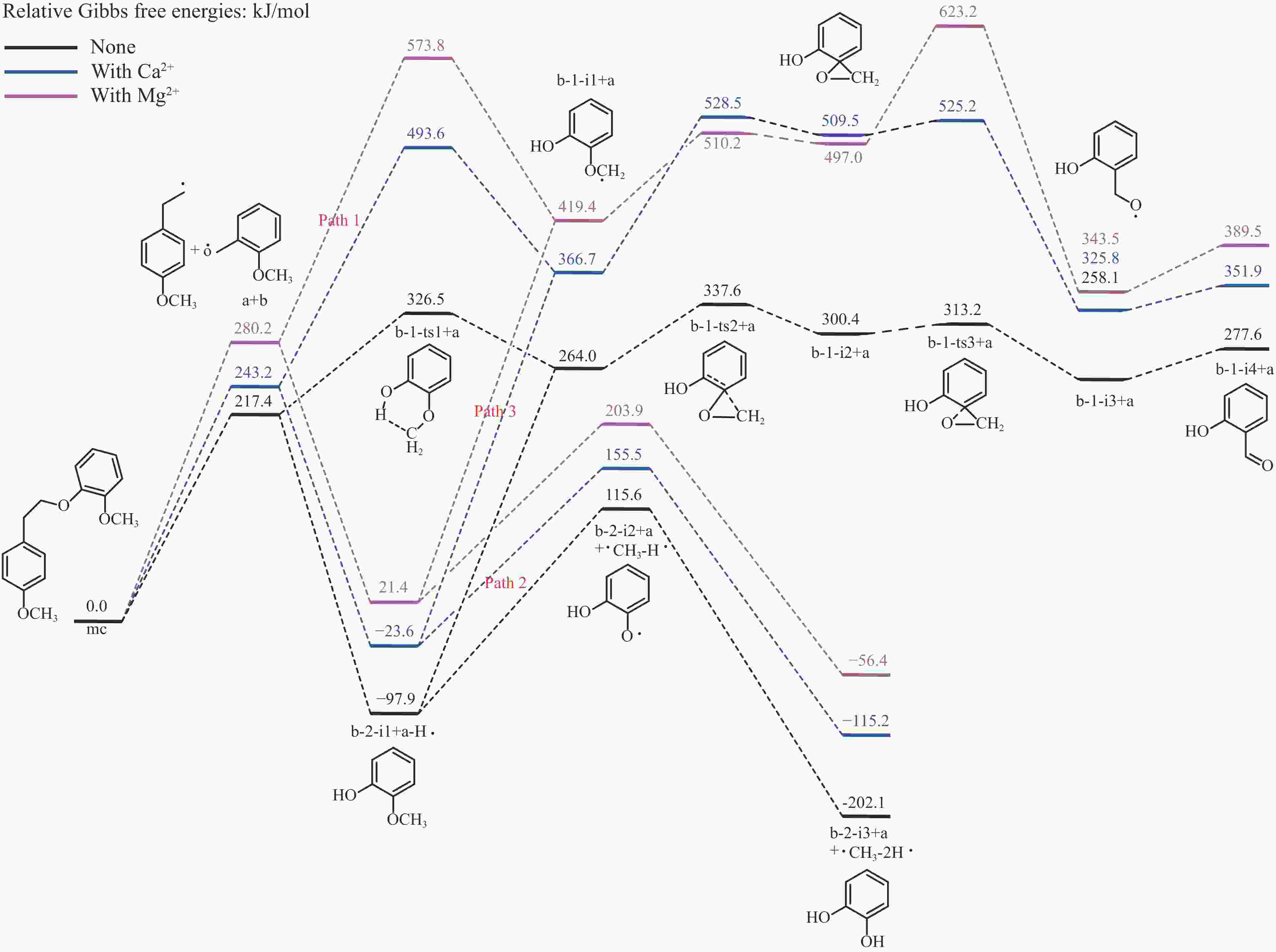
摘要: 本研究采用密度泛函理论方法,对碱土金属离子(Ca2+、Mg2+)作用下的β-O-4型木质素二聚体模型化合物(2-[2-(4-甲氧基苯基)乙氧基]-苯甲醚,mc)的热解反应路径进行了理论计算。计算结果表明,Ca2+和Mg2+会与木质素二聚体模型化合物mc的Cβ位氧原子及甲氧基上的氧原子结合形成稳定的复合物,从而影响Cα−Cβ和Cβ−O的键长和热解反应能垒。在热解过程中,Ca2+和Mg2+会促进协同断裂反应的发生,从而促进产物1-甲氧基-4-乙烯基苯、2-甲氧基苯酚和邻苯二酚的生成;抑制Cα−Cβ键和Cβ−O键的均裂反应,从而抑制产物1-乙基-4-甲氧基苯、2-羟基苯甲醛的生成。Abstract: It is essential to investigate the influence of alkaline earth metals on the pyrolysis mechanism and resulting products of lignin to enhance the efficient thermochemical conversion and utilization of lignin or biomass. In this study, the Density functional theory method was used to simulate the pyrolytic reaction pathways of a β-O-4 type lignin dimer model compound (1-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenethoxy)benzene, mc) affected by alkaline earth metal ions Ca2+ and Mg2+. The computational findings suggest that Ca2+ and Mg2+ tend to combine with the oxygen atom at the Cβ position and the oxygen atom on the methoxy group of the lignin dimer model compound, forming stable complexes that modify the bond lengths of the Cα–Cβ and Cβ–O bonds and affect their pyrolysis energy barriers. During the catalytic pyrolysis process, the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+ can promote the concerted decomposition reaction, leading to increased production of products like 1-methoxy-4-vinylbenzene, 2-methoxyphenol and catechol. Meanwhile, they can suppress homolytic cleavage reactions of the Cβ–O and Cα–Cβ bonds, thereby hindering the formation of other products such as 1-ethyl-4-methoxybenzene and 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
-
Table 1 Reaction energy barriers for the initial pyrolysis mechanisms of the lignin dimer model compound
Preliminary pyrolysis mechanism Alkaline earth metal ion Reaction energy barrier/(kJ·mol−1) Cα–Cβ homolysis none 266.8 Ca2+ 346.6 Mg2+ 387.1 Cβ–O homolysis none 217.4 Ca2+ 243.2 Mg2+ 280.2 Concerted decomposition none 247.0 Ca2+ 167.4 Mg2+ 169.8 -
[1] MA L L, TANG Z H, WANG C W, et al. Research status and future development strategy of biomass energy[J]. Bull Chin Acad Sci,2019,34(4):434−442. [2] COLLARD F X, BLIN J. A review on pyrolysis of biomass constituents: Mechanisms and composition of the products obtained from the conversion of cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2014,38:594−608. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.06.013 [3] YOON J S, LEE Y, RYU J, et al. Production of high carbon number hydrocarbon fuels from a lignin-derived α-O-4 phenolic dimer, benzyl phenyl ether, via isomerization of ether to alcohols on high-surface-area silica-alumina aerogel catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2013,142:668−676. [4] GUO Y L, YIN L, LENG E W, et al. Study on the characteristic of β-O-4 lignin polymer model compound fast pyrolysis catalyzed by K+, Ca2+, Fe2+[J]. J Eng Thermophys,2021,42(12):3073−3082. [5] WANG B. Study on the influence of alkali/alkaline earth metals on the pyrolysis of hemicellulose and lignin[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2021. [6] DING Z X , CAI B, CEN K H, et al. The effect of alkali and alkaline earth metals in biomass ash on the bio-oil components derived from biomass fast pyrolysis[J/OL]. J Fuel Chem Technol, doi: 10.19906/j.cnki.JFCT.2023076. [7] ZAKZESKI J, BRUIJNINCX P C A, JONGERIUS A L, et al. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals[J]. Chem Rev,2010,110(6):3552−3599. doi: 10.1021/cr900354u [8] ELDER T, BESTE A. Density functional theory study of the concerted pyrolysis mechanism for lignin models[J]. Energy Fuels,2014,28(8):5229−5235. doi: 10.1021/ef5013648 [9] JIANG X Y, LU Q, HU B, et al. Intermolecular interaction mechanism of lignin pyrolysis: A joint theoretical and experimental study[J]. Fuel,2018,215:386−394. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.11.084 [10] JIANG X Y, WANG W L, HU B. Formation mechanism of methane during lignin pyrolysis: A theoretical study[J]. J Energy Inst,2022,100:237−244. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2021.11.010 [11] HU B, XIE W L, LI Y, et al. Hydroxyl-assisted hydrogen transfer interaction in lignin pyrolysis: An extended concerted interaction mechanism[J]. Energy Fuels,2021,35(16):13170−13180. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c01606 [12] HU B, ZHANG B, XIE W L, et al. Recent progress in quantum chemistry modeling on the pyrolysis mechanisms of lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Energy Fuels,2020,34(9):10384−10440. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c01948 [13] WANG R, GAO M Y, CAO J P. Effects of alkali/alkaline earth metals on fast pyrolysis of pine sawdust[J]. Chin J Appl Chem,2022,39(2):289−297. [14] JEONG K, JEONG H J, LEE G, et al. Catalytic effect of alkali and alkaline earth metals in the lignin pyrolysis: A density functional theory study[J]. Energy Fuels,2020,34(8):9734−9740. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c01897 [15] JIANG X Y, LU Q, HU B, et al. Effects of alkali metals on pyrolysis mechanism of lignin dimer[J]. J Eng Thermophys,2017,38(5):1117−1121. [16] ZHANG J J, JIANG X Y, YE X N, et al. Pyrolysis mechanism of a β-O-4 type lignin dimer model compound[J]. J Therm Anal Calorim,2016,123(1):501−510. doi: 10.1007/s10973-015-4944-y [17] FRISCH M J, TRUCKS G W, SCHLEGEL H B, et al. Gaussian 09[CP]. Revision D. 01, Gaussian, Inc. , Wallingford CT, 2013. [18] JIANG X Y, WANG W L, BIAN W B, et al. Formation mechanism of methane and its effect on the lignin pyrolysis process[J]. J. Mol. Sci.,2023,39(2):111−117. [19] KIM K H, JEONG K, KIM S S, et al. Kinetic understanding of the effect of Na and Mg on pyrolytic behavior of lignin using a distributed activation energy model and density functional theory modeling[J]. Green Chem.,2019,21(S):1099−1107. [20] TRAN Q K, LY H V, HWANG H T, et al. Study on pyrolysis of organosolv lignin impregnated with alkali and alkaline earth metals: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and product characterization[J]. Fuel,2022,329:1−14. [21] JIANG X Y, LU Q, HU B, et al. A comprehensive study on pyrolysis mechanism of substituted β-O-4 type lignin dimers[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2017,18(11):2364−2377. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112364 -





 下载:
下载: