Refined Ni, Co-Induced Synthesis of NiCoP Nanoparticles Uniformly Embedded in NCNTs: A Robust Dual-Functional Electrocatalyst for Water Splitting
-
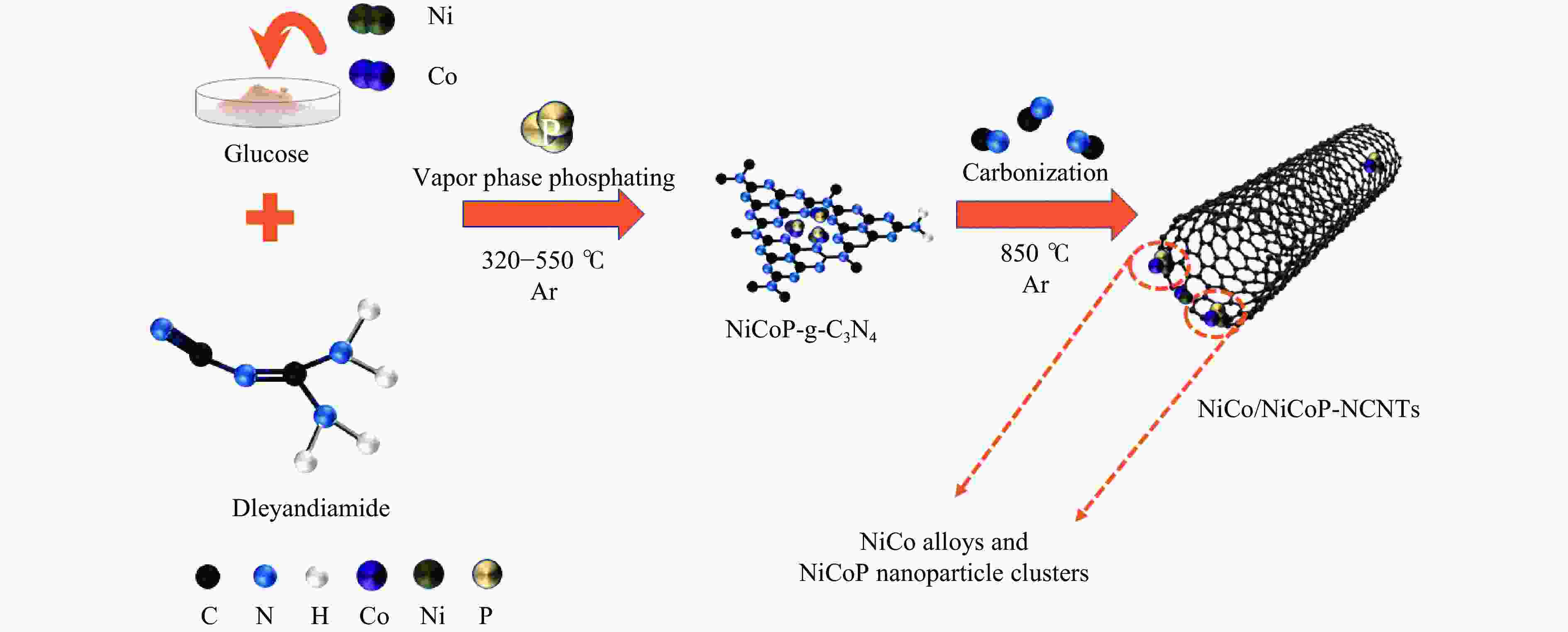
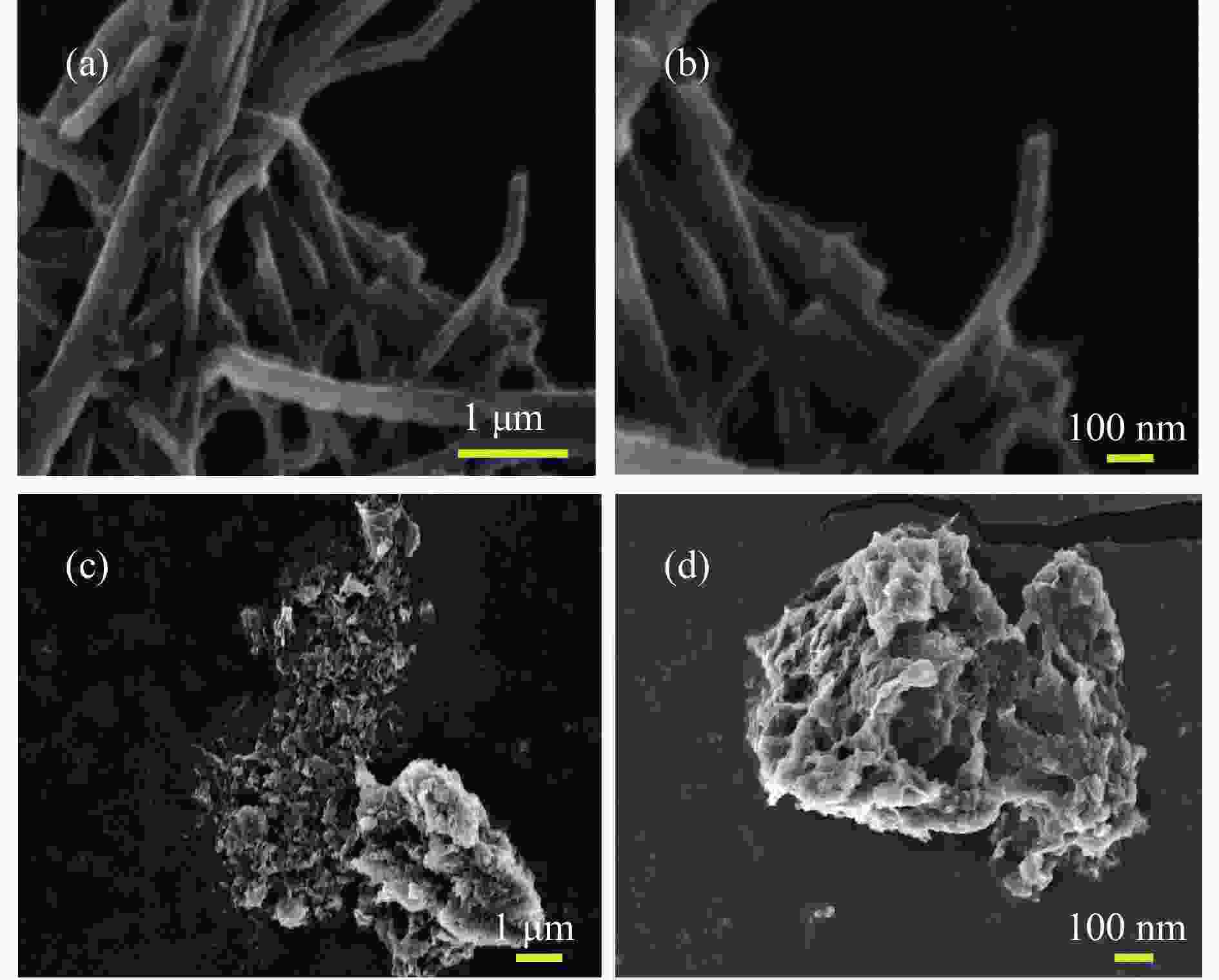
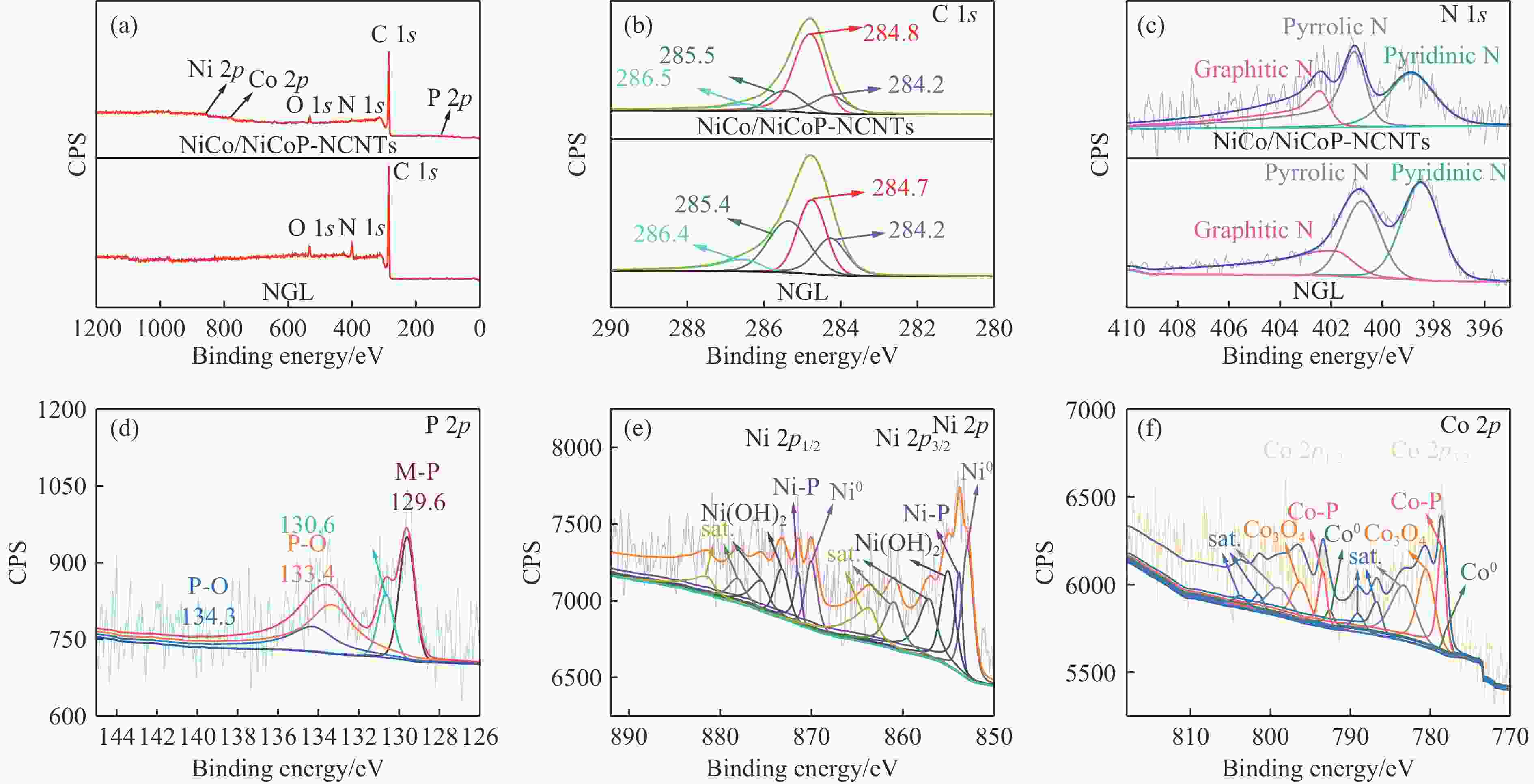
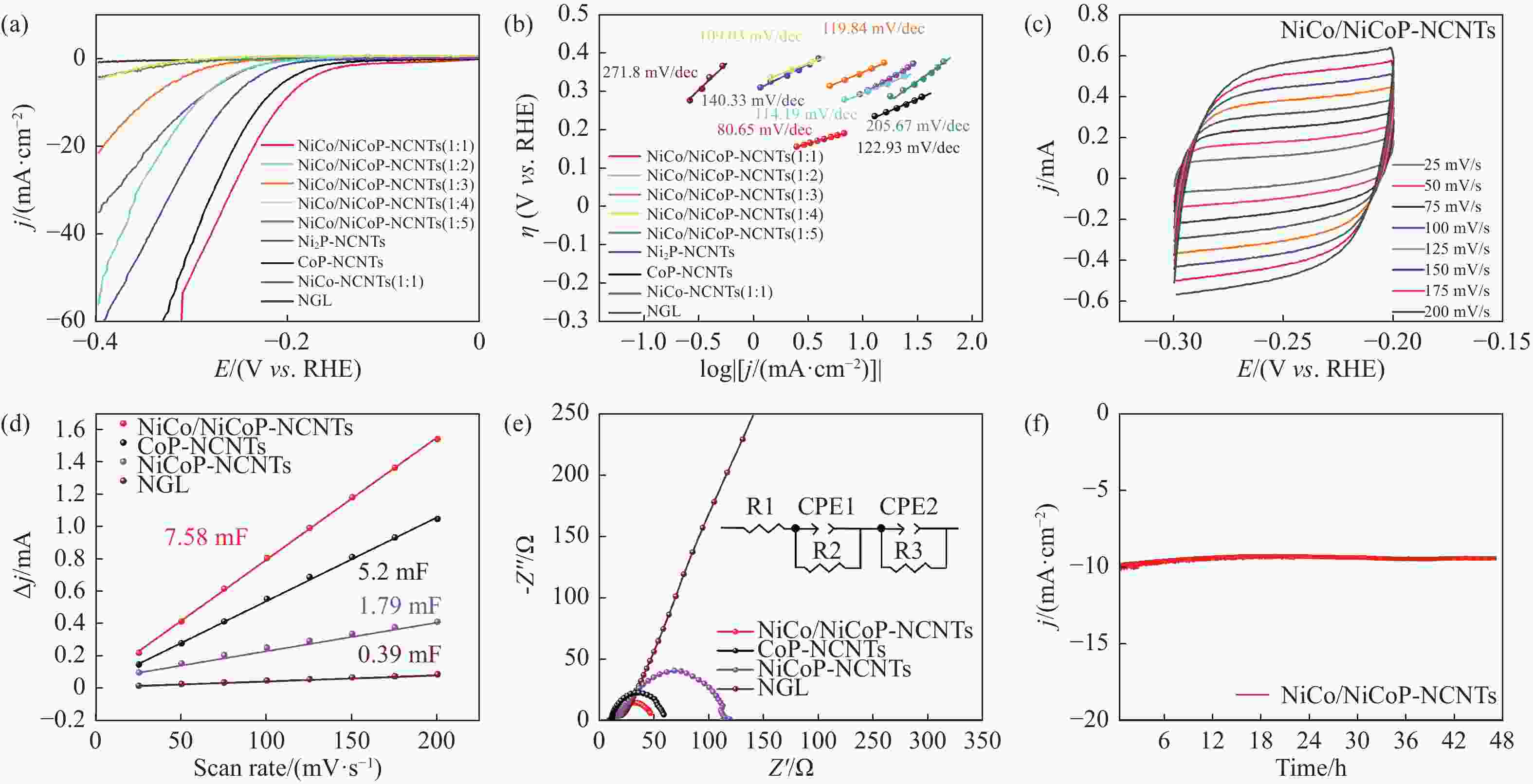
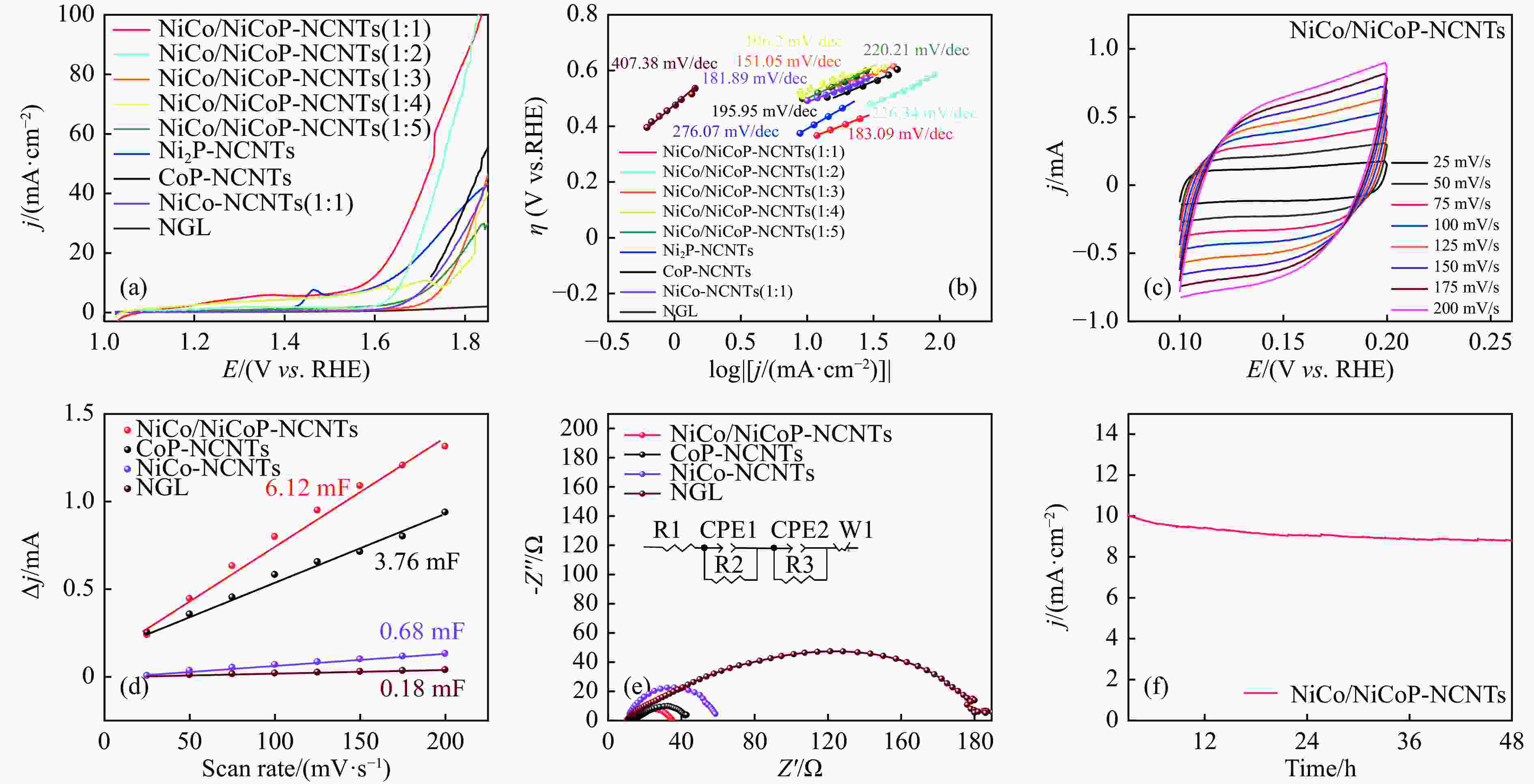
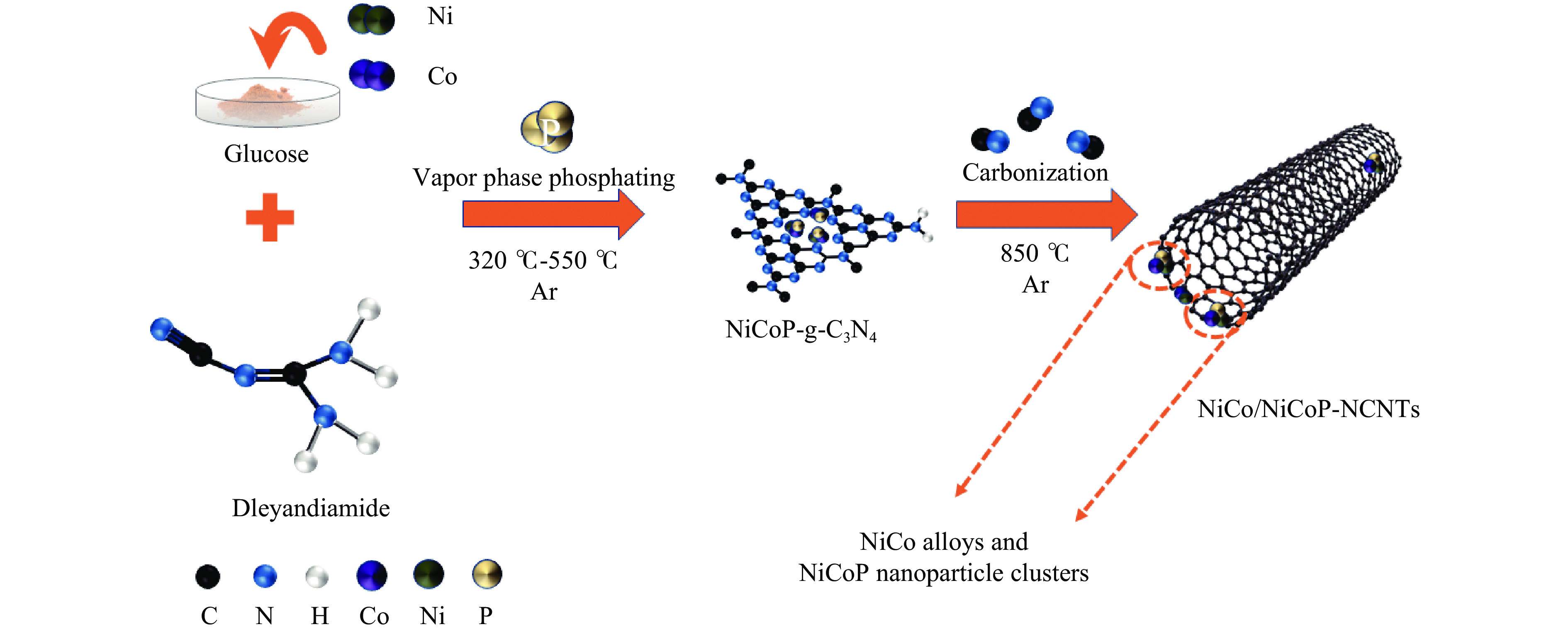
摘要: 通过一步磷化碳化直接合成了Ni、Co诱导的高度分散的NiCoP纳米颗粒嵌入氮掺杂碳纳米管(NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs)。NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs作为水分解的双功能电催化剂,在0.5 M H2SO4和1 M KOH溶液中分别仅需206 mV的HER过电位和360 mV的OER过电位。NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs在10 mA·cm−2的电流密度下表现出稳定的1.68 V电池电压,在48小时仅有10%的电流密度下降,表现出卓越的稳定性。催化活性的增强归因于NiCoP纳米颗粒的整合以及NCNTs和NiCo合金之间的协同作用。此外,改善的电催化活性与增加的电化学活性表面积和降低的电子传递电阻有关。总体而言,NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs在高效水电解应用中展现出显著的性能。Abstract: Ni, Co-induced highly distributed NiCoP nanoparticles embedded nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes (NCNTs) (NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs) were directly synthesized by a one-step phosphorization and carbonization process. As a bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting, NiCo/NiCoP NCNTs show impressive catalytic performance with an overpotential of only 206 mV for the hydrogen evolution reaction and 360 mV for the oxygen evolution reaction in 0.5 M H2SO4 and 1 M KOH solutions, respectively. In addition, NiCo/NiCoP NCNTs maintain a stable cell voltage of 1.68 V at 10 mA cm-2 with only a 10% decrease in current density over 48 hours, showing remarkable stability. The improved catalytic activity can be attributed to the integration of NiCoP nanoparticles and the synergies between NCNTs and NiCo alloy. Additionally, the improved electrocatalytic performance can be attributed to the increased electrochemically active surface area and the reduced electron transfer resistance of the NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs. Overall, the NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs demonstrated significant performance for advanced water electrolysis applications.
-
Table 1 Electrochemical performance of bifunctional catalysts HER and OER
Catalysts ηHER/V ηOER/V Ecell/V Reference NiCo/NiCoP-NCNTs 206 360 1.68 This work Ni2P-NCNTs 260 410 1.94 This work CoP-NCNTs 225 490 1.89 This work NiCoP NWAs/NF 197 370 1.64@20 [31] NiCo2N/NF 180 290 1.70 [32] Ni@NC-800 205 280 1.60 [33] Ni-Fe-P-350 182 271 1.68 [34] NiFe-NC 197 271 1.67 [35] Co/PNC 298 370 1.64 [36] -
[1] GAO J X, TIAN W J, ZHANG H Y. Progress of Nb-containing catalysts for carbon dioxide reduction: a minireview[J]. Tungsten,2022,4(4):284−295. [2] JIAO Y, ZHENG Y, JARONIEC M, et al. Design of electrocatalysts for oxygen-and hydrogen-involving energy conversion reactions[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2015,44(8):2060−2086. [3] HUO W Y, WANG S Q, ZHU W H, et al. Recent progress on high-entropy materials for electrocatalytic water splitting applications[J]. Tungsten,2021,3(2):161−180. [4] WANG J, ZHANG J, ZHANG P, et al. Uniformly dispersed NiO/FeNi3 alloy nanoparticles embedded in N-doped porous carbon as electrocatalysts for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction[J]. J Alloys Compd, 2023, 968. [5] ZHANG T, DU J, XI P, et al. Hybrids of Cobalt/Iron Phosphides Derived from Bimetal-Organic Frameworks as Highly Efficient Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,9(1):362−370. [6] LIU Y, WANG B, SRINIVAS K, et al. CNT-interconnected iron-doped NiP2/Ni2P heterostructural nanoflowers as high-efficiency electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2022,47(26):12903−12913. [7] WANG J, FU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Designing N-doped graphene-like supported highly dispersed bimetallic NiCoP NPs as an efficient electrocatalyst for water oxidation[J]. Dalton Transactions,2023,52(37):13079−13088. [8] TANG T, WANG Z, GUAN J. A review of defect engineering in two-dimensional materials for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2022,43(3):636−678. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63945-1 [9] LIU J, NING G, SHI K, et al. N-doped hollow porous carbon spheres@Co Cu Fe alloy nanospheres as novel non-precious metal electrocatalysts for HER and OER[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2022,47(9):5947−5960. [10] WANG Z, WEI C, ZHU X, et al. A hierarchical carbon nanotube forest supported metal phosphide electrode for efficient overall water splitting[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2021,9(2):1150−1158. [11] JANG D, LEE S, KWON N. H, et al. Preparation of carbon nitride nanotubes with P-doping and their photocatalytic properties for hydrogen evolution[J]. Carbon,2023,208:290−302. [12] CHEN L, LIU Z, GUO Z, et al. Regulation of intrinsic physicochemical properties of metal oxide nanomaterials for energy conversion and environmental detection applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2020,8(34):17326−17359. [13] YU H, LI J, GAO G, et al. Metal-organic frameworks derived carbon-incorporated cobalt/dicobalt phosphide microspheres as Mott–Schottky electrocatalyst for efficient and stable hydrogen evolution reaction in wide-pH environment[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci,2020,565:513−522. [14] MONDAL S, DUTTA S, MAL S, et al. Lattice mismatch guided nickel-indium heterogeneous alloy electrocatalysts for promoting the alkaline hydrogen evolution[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2023, 10.1002/anie. 202301269: e202301269. [15] WANG Z, ZHANG S, LV X, et al. Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution on iron-cobalt nanoparticles encapsulated in nitrogenated carbon nanotube[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2019,44(31):16478−16486. [16] TESSONNIER J P, SU D S. Recent progress on the growth mechanism of carbon nanotubes: A review[J]. ChemSusChem,2011,4(7):824−847. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201100175 [17] WANG J, CHEN W, WANG T, et al. A strategy for highly dispersed Mo2C/MoN hybrid nitrogen-doped graphene via ion-exchange resin synthesis for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen reduction[J]. Nano Research,2018,11(9):4535−4548. [18] LOUCHEV O. A, SATO Y. and KANDA H. Growth mechanism of carbon nanotube forests by chemical vapor deposition[J]. Appl Phys Lett,2002,80(15):2752−2754. [19] WANG J, ZHANG J, LIU Z, et al. Convenient synthesis of nico alloy nanoparticles encapsulated by N-Doped porous carbon for the oxygen evolution reaction[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials,2023,6(21):19858−19866. [20] PAN Y, CHEN Y, LIN Y, et al. Cobalt nickel phosphide nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes as advanced hybrid catalysts for hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4(38):14675−14686. [21] MATSOSO B. J, RANGANATHAN K, MUTUMA B. K, et al. Time-dependent evolution of the nitrogen configurations in N-doped graphene films[J]. RSC Advances,2016,6(108):106914−106920. [22] ZHOU Y, XU X, SHAN B, et al. Tuning and understanding the supercapacitance of heteroatom-doped graphene[J]. Energy Storage Materials,2015,1:103−111. [23] GAYATHRI S, ARUNKUMAR P. and HAN J. H. Scanty graphene-driven phase control and heteroatom functionalization of ZIF-67-derived CoP-draped N-doped carbon/graphene as a hybrid electrode for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2021, 582(Pt B): 1136-1148. [24] GAYATHRI S, ARUNKUMAR P, SAHA D, et al. Composition engineering of ZIF-derived cobalt phosphide/cobalt monoxide heterostructures for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci,2021,588:557−570. [25] YAN G, TAN H, WANG Y, et al. Amorphous quaternary alloy phosphide hierarchical nanoarrays with pagoda-like structure grown on Ni foam as pH-universal electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2019,489:519−527. [26] FAN H, YU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Fe-Doped Ni3C nanodots in N-Doped carbon nanosheets for efficient hydrogen-evolution and oxygen-evolution electrocatalysis[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2017,56(41):12566−12570. [27] SUGITA Y. , MIYAKE T. and MOTOME Y. Electronic band structure of 4d and 5d transition metal trichalcogenides[J]. Physica B:Condensed Matter,2018,536:48−50. [28] ZHANG R, WANG X, YU S, et al. Ternary NiCo(2) P(x) Nanowires as ph-universal electrocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Adv Mater, 2017, 29 (9): [29] SINGH S. K, KUMAR D, DHAVALE V. M, et al. strategic preparation of efficient and durable nico alloy supported N-Doped porous graphene as an oxygen evolution electrocatalyst: A theoretical and experimental investigation[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2016, 3 (20): [30] DU C, YANG L, YANG F, et al. Nest-like nicop for highly efficient overall water splitting[J]. ACS Catalysis,2017,7(6):4131−4137. [31] LI J, WEI G, ZHU Y, et al. Hierarchical NiCoP nanocone arrays supported on Ni foam as an efficient and stable bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(28):14828−14837. [32] WANG Y, ZHANG B, PAN W, et al. 3 D porous nickel-cobalt nitrides supported on nickel foam as efficient electrocatalysts for overall water splitting[J]. ChemSusChem,2017,10(21):4170−4177. [33] XU Y, TU W, ZHANG B, et al. Nickel nanoparticles encapsulated in few-layer nitrogen-doped graphene derived from metal-organic frameworks as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting[J]. Adv Mater, 2017, 29 (11): [34] XUAN C, WANG J, XIA W, et al. Porous structured Ni-Fe-P nanocubes derived from a prussian blue analogue as an electrocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces,2017,9(31):26134−26142. [35] JAYARAMULU K, MASA J, TOMANEC O, et al. Nanoporous nitrogen-doped graphene oxide/nickel sulfide composite sheets derived from a metal-organic framework as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27 (33): [36] LI X, NIU Z, JIANG J, et al. Cobalt nanoparticles embedded in porous N-rich carbon as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4(9):3204−3209. -





 下载:
下载: