Identification and quantitative analysis of polarized light microstructure of coal-derived needle coke
-
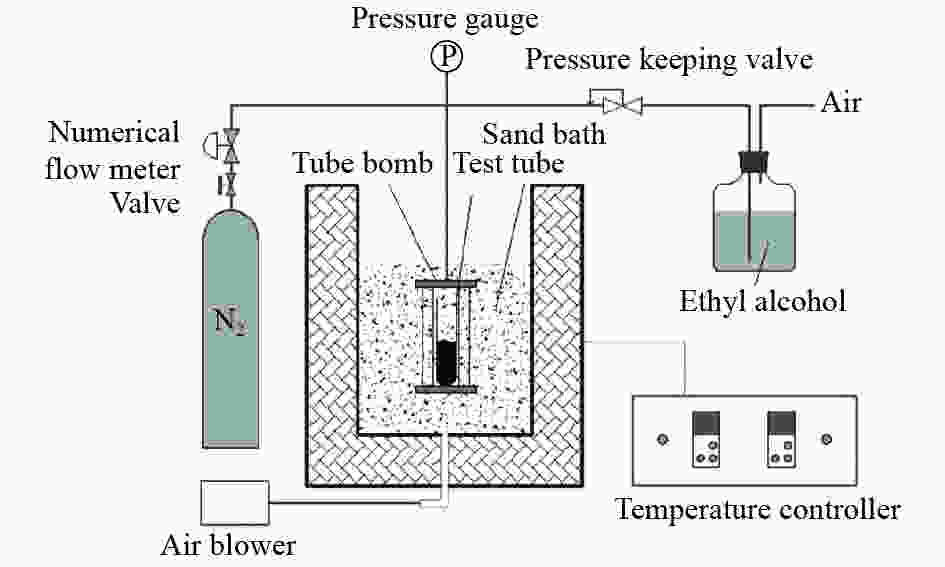
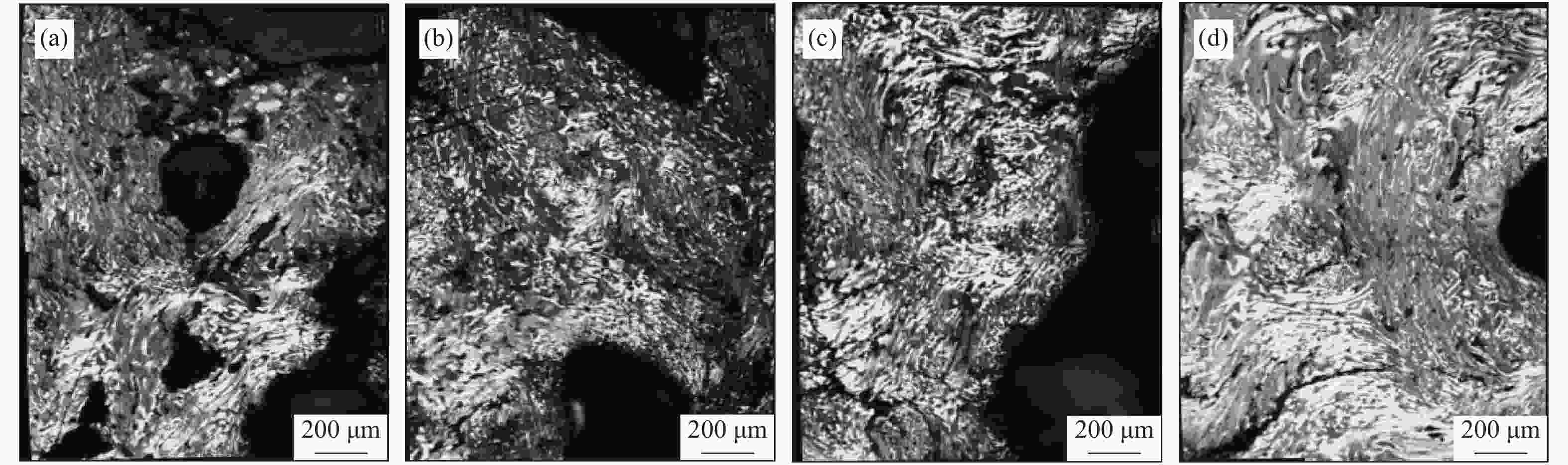
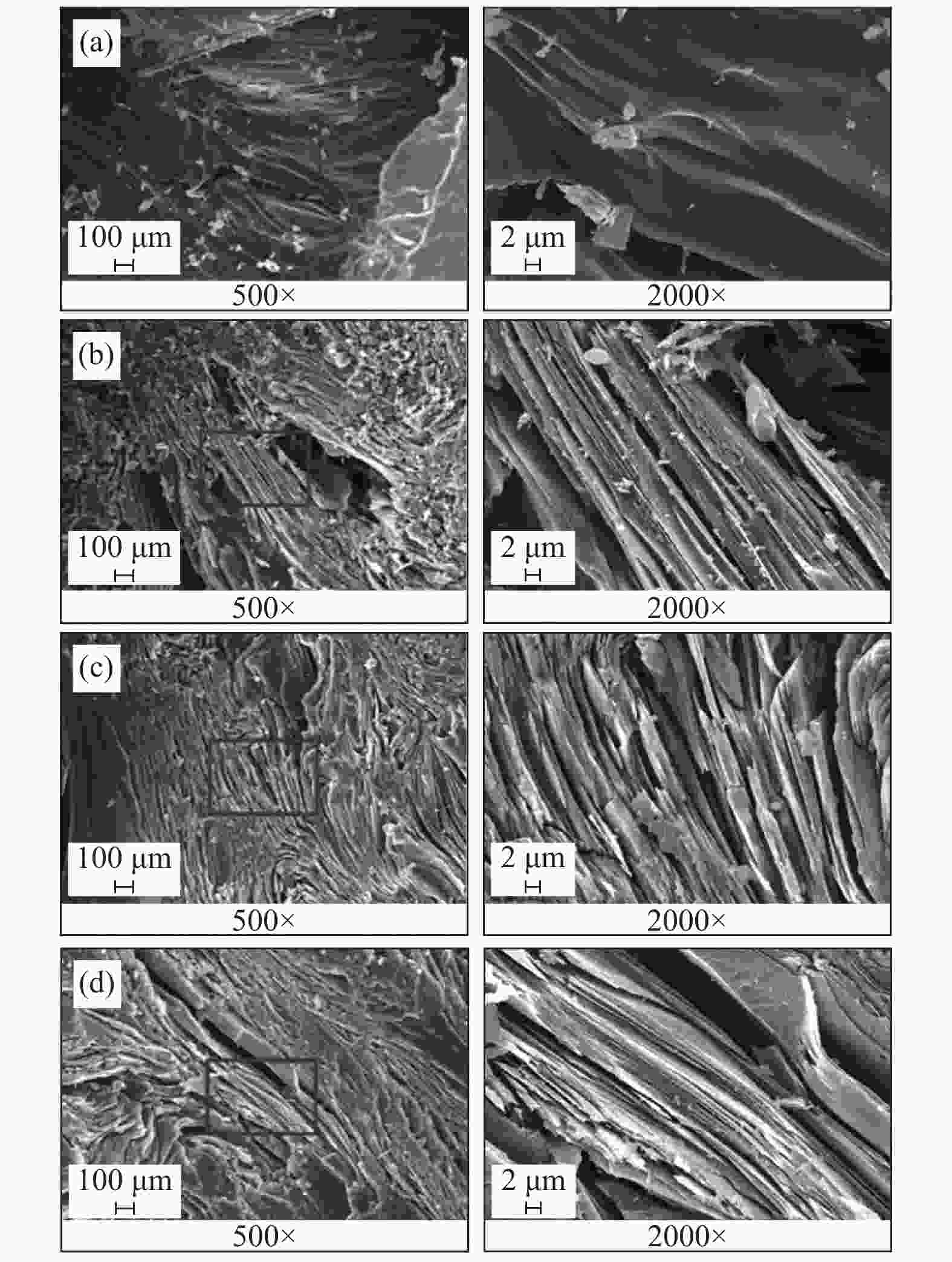
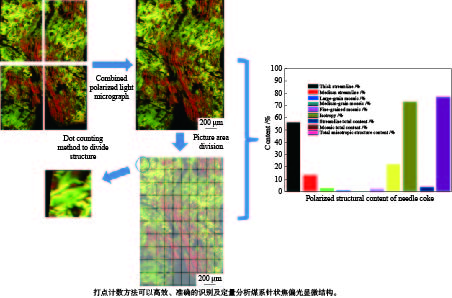
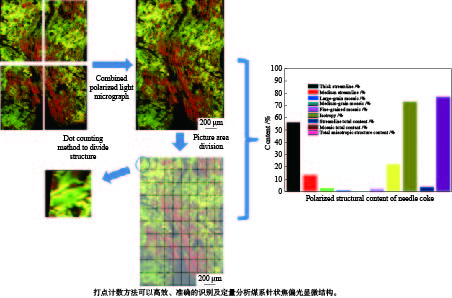
摘要: 以精制煤焦油沥青为原料制备针状焦。利用bricc-m煤岩自动测试系统和RICC-Imager图像分析软件,使用打点计数方法,对煤系针状焦偏光显微结构进行定量分析。进一步利用扫描电子显微镜进行针状焦微观结构解析。结果表明,在炭化温度为490 ℃、炭化压力为0.2 MPa、反应时间为6 h条件下制备的生焦,定量分析其广域流线型结构含量为87.8%,显示出较好的光学显微结构。对比传统人工定量分析方法,使用计算机打点计数方法进行定量分析,提高了测试结果的准确性,更加高效,是针状焦显微结构识别和定量分析的有效手段。Abstract: Coal-derived needle coke was prepared using refined coal tar pitch as feedstock. Its polarized light microstructure was quantitatively analyzed by bricc-m coal macerals automatic testing system with RICC-Imager analysis software and the dot counting method. Microstructure of needle coke was characterized using scanning electron microscope. The results indicate that the large domain streamline structure content of the prepared green coke is 87.8% under carbonization conditions of 490 ℃, 0.2 MPa and 6 h, which shows good optical microstructure. Compared with the traditional quantitative analysis method, the quantitative analysis using dot counting method is more accurate and efficient. It can be used as an effective means for quantitative analysis of needle coke microstructure.
-
Key words:
- pyrolysis /
- coking /
- microstructure /
- numerical analysis /
- quantitative analysis
-
表 1 煤焦油沥青性质
Table 1 Properties of coal tar pitch and components
Sample Element composition w/% C/H (atomic ratio) Fraction distribution②w/% Ash w/% C H N S O① QI HS HI-TS TI-QS CTP 92.32 4.42 1.28 0.51 1.47 1.74 5.78 26.73 49.09 18.40 0.115 Refined CTP 92.25 4.40 1.20 1.58 0.57 1.75 0.08 13.50 47.49 43.21 0.085 notes:①: by difference; ②: HS: hexane soluble; HI-TS: hexane insoluble but toluene soluble; TI-QS: toluene insoluble but quinoline soluble; QI: quinoline insoluble 表 2 各向异性组分划分标准
Table 2 Textures standard for dividing anisotropic components
Texture category Optical properties Wide domain streamline length > 60 μm Thick streamline length 30−60 μm Medium streamline length 10−30 μm Large-grain mosaic radius 5−10 μm Medium-grain mosaic radius 1.5−5 μm Fine-grain mosaic radius < 1.5 μm Isotropy no optical properties 表 3 不同温度下生焦各结构含量
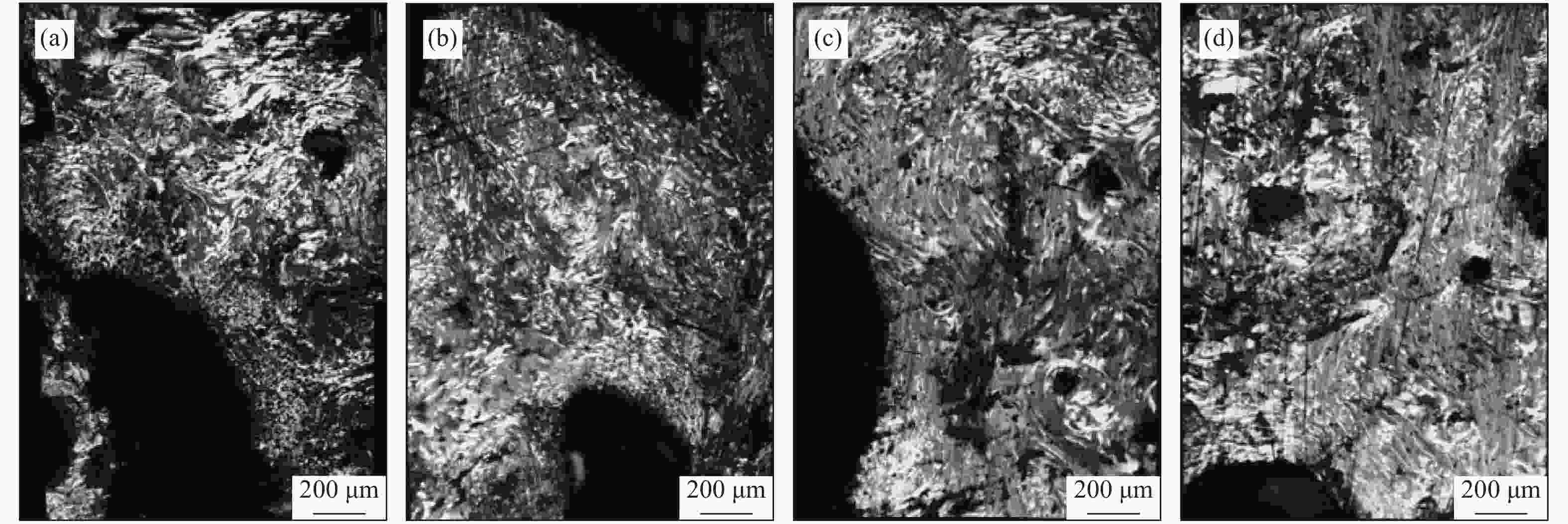
Table 3 Polarized structural content of green coke at different temperatures
Temperature
/℃Wide domain streamline /% Thick streamline /% Medium streamline /% Large-grain mosaic/% Medium-grain mosaic/% Fine-grained mosaic/% Isotropy /% Streamline total content/% Mosaic total content /% Total anisotropic structure content/% 470 43.4 1.2 0.1 2.9 0.5 4.4 47.5 44.5 7.8 52.5 480 56.6 13.7 3.2 1.4 0.5 2.1 22.6 73.5 4.0 77.4 490 84.6 8.8 1.8 0.6 1.5 0.6 2.1 95.2 2.7 97.9 500 82.4 14.4 1.4 0.7 1.1 0 0 98.2 1.8 100 510 75.8 19.2 4.0 0.6 0.4 0 0 99.1 1.0 100 表 4 不同压力下生焦各结构含量
Table 4 Polarized structural content of green coke at different pressures
Pressure/MPa Wide domain streamline /% Thick streamline /% Medium streamline /% Large-grain mosaic/% Medium-grain mosaic/% Fine-grained mosaic/% Isotropy /% Streamline total content/% Mosaic total content /% Total anisotropic structure content/% 0.1 87.1 6.3 1.1 0.0 0.9 0.5 4.1 94.5 1.4 95.9 0.2 87.8 8.1 2.2 0.7 0.6 0.6 0.0 98.1 1.9 100 0.3 87.3 8.9 2.0 0.4 0.6 0.5 0.3 98.2 1.5 99.7 0.4 84.6 8.8 1.8 0.6 1.5 0.6 2.1 95.2 2.7 97.9 表 5 不同炭化时间的生焦各结构含量
Table 5 Polarized structural content of green coke at different carbonization time
Carbonization time/h Wide domain streamline /% Thick streamline /% Medium streamline /% Large-grain mosaic/% Medium-grain mosaic/% Fine-grained mosaic/% Isotropy /% Streamline total content/% Mosaic total content /% Total anisotropic structure content/% 2 81.8 4.6 1.9 1.0 0.3 0.6 9.8 88.3 1.9 90.2 4 87.3 8.7 1.3 1.3 0.7 0.7 0.0 97.3 2.7 100 6 87.8 8.1 2.2 0.7 0.6 0.6 0.0 98.1 1.9 100 8 89.8 6.3 1.8 0.7 1.3 0.1 0.0 97.9 2.1 100 表 6 不同反应条件下的针状焦CTE
Table 6 CTE of needle coke under different reaction conditions
Parameter Value Temperature/℃ 490 490 490 490 490 Pressure/MPa 0.4 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.2 Carbonization time/h 6 6 6 4 8 CTE/(1 × 10−6/℃) 1.93 1.54 1.79 1.68 1.55 -
[1] MOCHIDA I, FEI Y Q, KORAI Y, FUJIMOTO K, YAMASHITA R. Carbonization in the tube bomb leading to needle coke: III. Carbonization properties of several coal-tar pitches[J]. Carbon,2016,27(3):375−380. [2] MOCHIDA I, FEI Y, KORAI Y, OISHI T. Co-carbonization of ethylene tar pitch and coal tar pitch to form needle coke[J]. Fuel,1990,69(6):672−677. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(90)90027-N [3] TODO Y, OYAMA T, MOCHIDA I, KORAL Y, SATOSHI A, KINYA S. Cocarbonization properties of solvent deasphalted oil from a petroleum vacuum residue in production of needle coke[J]. J Jpn Pet Inst,2008,34(1):96−100. [4] MOCHIDA I, KORAI Y, SAKANISHI K, TODO Y, OYAMA T. Cocarbonization properties of heat-treated petroleum vacuum residue with FCC decant oils in production of needle coke[J]. J Jpn Pet Inst,2008,34(1):101−106. [5] 李强, 李开喜, 王芙蓉, 孙国华. 针状焦基活性炭的制备及其作为EDLCs电极材料的电化学性能[J]. 新型炭材料,2005,20(4):335−342. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-8827.2005.04.009LI Qing, LI Kai-xi, WANG Fu-rong, SUN Guo-hua. Preparation of high porosity carbon electrodes from raw needle coke and their characterization for EDLCs[J]. New Carbon Mater,2005,20(4):335−342. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-8827.2005.04.009 [6] 许德平, 唐世波, 唐闲逸, 魏晓慧, 武欣. 针状焦制备过程中原料组分对中间相影响的研究进展[J]. 炭素技术,2016,35(1):34−39.XU De-ping, TANG Shi-bo, TANG Xian-yi, WEI Xiao-hui, WU Xin. Research advances of influence of components in feedstock on formation of mesophase in needle coke preparation[J]. Carbon Tech,2016,35(1):34−39. [7] ALVAREZ P, DIZE N, SANTAMARIA R, BLANCO C, MENENDEZ R, GRANDA M. Novel coal-based precursors for cokes with highly oriented microstructures[J]. Fuel,2012,95(1):400−406. [8] 张德保, 申海平, 范启明. 针状焦制备过程中的中间相研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2012,31(S2):175−181.ZHANG De-bao, SHEN Hai-ping, FAN Qi-ming. Research advances about mesophase in needle coke preparation[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2012,31(S2):175−181. [9] ZHU Y M, ZHAO C L, XU Y L, HU C S, ZHAO X F. Preparation and characterization of coal pitch-based needle coke (PartⅠ): theeffects of aromatic Index (f_a) in refined coal pitch[J]. Energy Fuels,2019,33(4):3456−3464. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b00160 [10] IM U, KIM J, LEE S H, LEE S M, LEE B R, PECK D H, JUNG D H. Preparation of activated carbon from needle coke via two-stage steam activation process[J]. Mater Lett,2019,237(15):22−25. [11] HALIM H, IM J, LEE C. Preparation of needle coke from petroleum by-products[J]. Carbon Lett,2013,14(3):152−161. doi: 10.5714/CL.2013.14.3.152 [12] 芦时林, 冯安祖. 针状焦热膨胀系数与显微结构的关系[J]. 炭素技术,1987,5(7):9−13.LU Shi-lin, FENG An-zu. Relationship between thermal expansion coefficient and microstructure of needle coke[J]. Carbon Tech,1987,5(7):9−13. [13] MOCHIDA I, OYAMA T, KORAI Y. Formation scheme of needle coke from FCC-decant oil[J]. Carbon,1988,26(1):49−55. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(88)90008-5 [14] PATRICK J W, REYNOLDS M J, SHAW F H. Development of optical anisotropy in vitrains during carbonization[J]. Fuel,1973,52(3):198−204. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(73)90079-3 [15] 钱树安, 李春锋, 周国英. 炭化原料的组成结构和中间相组织形态之间的关系[J]. 燃料化学学报,1984,12(4):62−74.QIAN Shu-an, LI Chun-feng, ZHOU Guo-ying. The relationship between the composition and molecular structure of carbonizing feedstocks and mesophase textures formed in pyrolysis[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,1984,12(4):62−74. [16] LEWIS R T, 彭颖. T. Lewis, 彭颖. 定量测定中间相沥青的各向异性区域的大小[J]. 新型炭材料,1986,5(3):48−50.LEWIS R T, PENG Ying. The anisotropic region of mesophase pitch was quantitatively determined[J]. New Carbon Mater,1986,5(3):48−50. [17] FLORES B D, BORREGO A G, DIEZ M A, SILVA D, GUILHERME L R, ZYMLA V, VILELA A C F, EDUARDO O. How coke optical texture became a relevant tool for understanding coal blending and coke quality[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2017,164:13−23. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.04.015 [18] MOCHIDA I, MARSH H. Carbonization and liquid-crystal (mesophase) development. 8. The co-carbonization of coals with acenaphthylene and decacyclene[J]. Fuel,1979,58(9):633−641. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(79)90216-3 [19] 杜亚平, 李峻海, 杨洋, 章真杰. 沥青中间相的光反射显微分析方法优化[J]. 燃料与化工,2014,45(6):49−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2014.06.018DU Ya-ping, LI Jun-hai, YANG Yang, ZHANG Zeng-jie. Optimization of light reflection microanalysis method for asphalt mesophase[J]. Fuel Chem Proc,2014,45(6):49−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3709.2014.06.018 [20] 侯先亮, 李铁虎, 庄强, 王珍, 程友亮, 赵廷凯. 图像处理技术在测定沥青中间相含量中的应用[J]. 炭素技术,2011,30(3):17−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3741.2011.03.005HONG You-liang, LI Tie-hu, ZHUANG Qiang, WANG Zhen, CHENG You-liang, ZHAO Ting-kai. Application of image processing technology in determination of asphalt mesophase content[J]. Carbon Tech,2011,30(3):17−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3741.2011.03.005 [21] NARCISO-ROMERO F J, RODRIGUEZ-REINOSO F, DIEZ M A. Influence of the carbon material on the synthesis of silicon carbide[J]. Carbon,1999,37(11):1771−1778. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(99)00045-7 [22] ZHU Y M, TANG S, ZHAO X, GAO L J. Co-carbonization of single coking coal and pyrolytic extracts from datong long-flame coal[J]. Metall Res Technol,2019,116(115):1−8. [23] WANG Z X, XUE P, CHEN K, GUO A J, LIN C H, KONG D H, SONG Z D, BO Y W. Correlation of temperature-programmed oxidation with microscopy for quantitative morphological characterization of thermal cokes produced from pilot and commercial delayed cokers[J]. Energy Fuels,2015,29(2):659−665. [24] 唐闲逸, 魏晓慧, 许德平, 张海永, 贺欣, 熊楚安, 唐瀚滢. 中温煤沥青喹啉不溶物的脱除及炭化制备针状焦[J]. 材料研究学报,2006,30(6):448−456.TANG Xian-yi, WEI Xiao-hui, XU De-ping, ZHANG Hai-yong, HE Xin, XIONG Chu-an, TANG Han-ying. Removal of QI from medium-temperature coal tar pitch and preparation of needle coke through carbonization[J]. Chin J Mater Res,2006,30(6):448−456. [25] 大谷杉郎, 真田雄三著. 炭化工学基础[M]. 张大名, 杨俊英, 译. 兰州: 兰州新华出版社, 1985: 31.OHGO S, MASADA Y. Basic of carbonization technics[M]. ZHANG Da-ming, YANG Jun-ying, trans. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Xinhua Printer, 1985: 31. -




 下载:
下载: