Study on the effect of active sites of ethanol synthesis from syngas over RhCu bimetallic catalyst
-
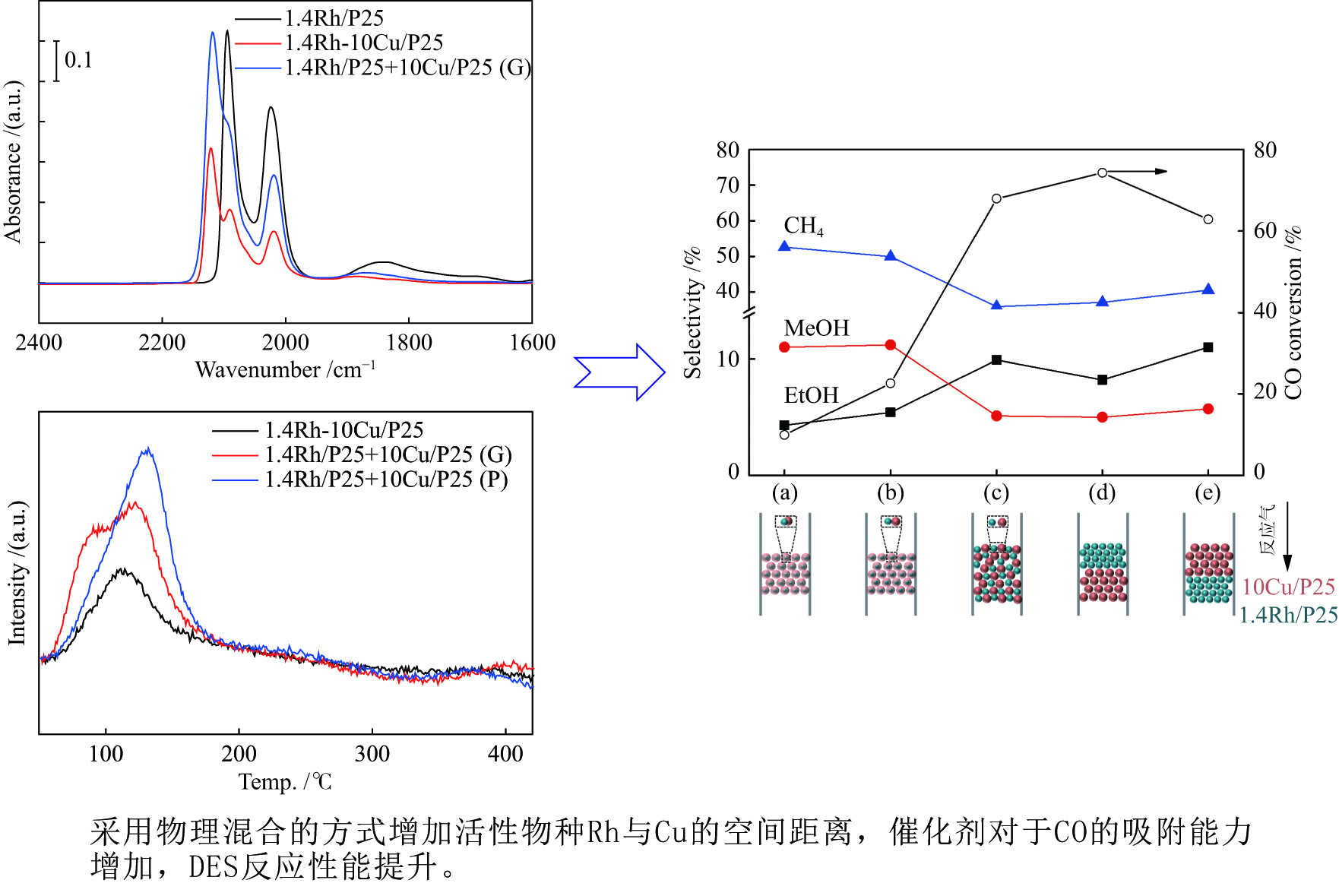
摘要: 稳定高效双金属催化剂的研究对于合成气直接合成乙醇具有重大意义,但也存在一定的挑战。本研究采用尿素辅助凝胶法和初湿浸渍法,制备了系列RhCu/P25双金属催化剂,并进行合成气直接制乙醇性能研究。研究表明,Rh改性的Cu基催化剂可以有效促进乙醇的生成,然而Rh和Cu活性位点之间紧密接触时,反应产物以甲烷和甲醇为主,乙醇含量甚微。RhCu/P25双金属催化剂反应性能的减弱与Rh和Cu活性位点上CO分子吸附受到抑制相关。当采用物理混合的方式增大Rh和Cu活性位点的空间距离时,CO分子的吸附明显增强,催化活性以及乙醇选择性提高。
-
关键词:
- RhCu双金属催化剂 /
- 乙醇 /
- 紧密接触 /
- 空间距离 /
- 活性位点
Abstract: Developing efficient and stable bimetallic catalysts has been a highly promising challenge for the direct synthesis of ethanol from syngas in recent years. In this study, a series of RhCu/P25 bimetallic catalysts with different Rh contents were prepared by combining the urea-assisted gel method and the impregnation method, and their performance in ethanol synthesis from syngas was studied. The results show that Rh-modified Cu-based catalyst can effectively promote the ethanol production. However, when the active sites of Rh and Cu are in close contact, the reaction products are mainly methane and methanol, and ethanol content is very low. This should be attributed to the inhibition of the adsorption of CO molecules on the Rh and Cu active sites. When the spatial distance between the Rh and Cu active sites is increased by physical mixing, the adsorption of CO molecules is significantly enhanced, and the catalytic activity and ethanol selectivity are improved.-
Key words:
- RhCu bimetallic catalysts /
- ethanol /
- close contact /
- spatial distance /
- active sites
-
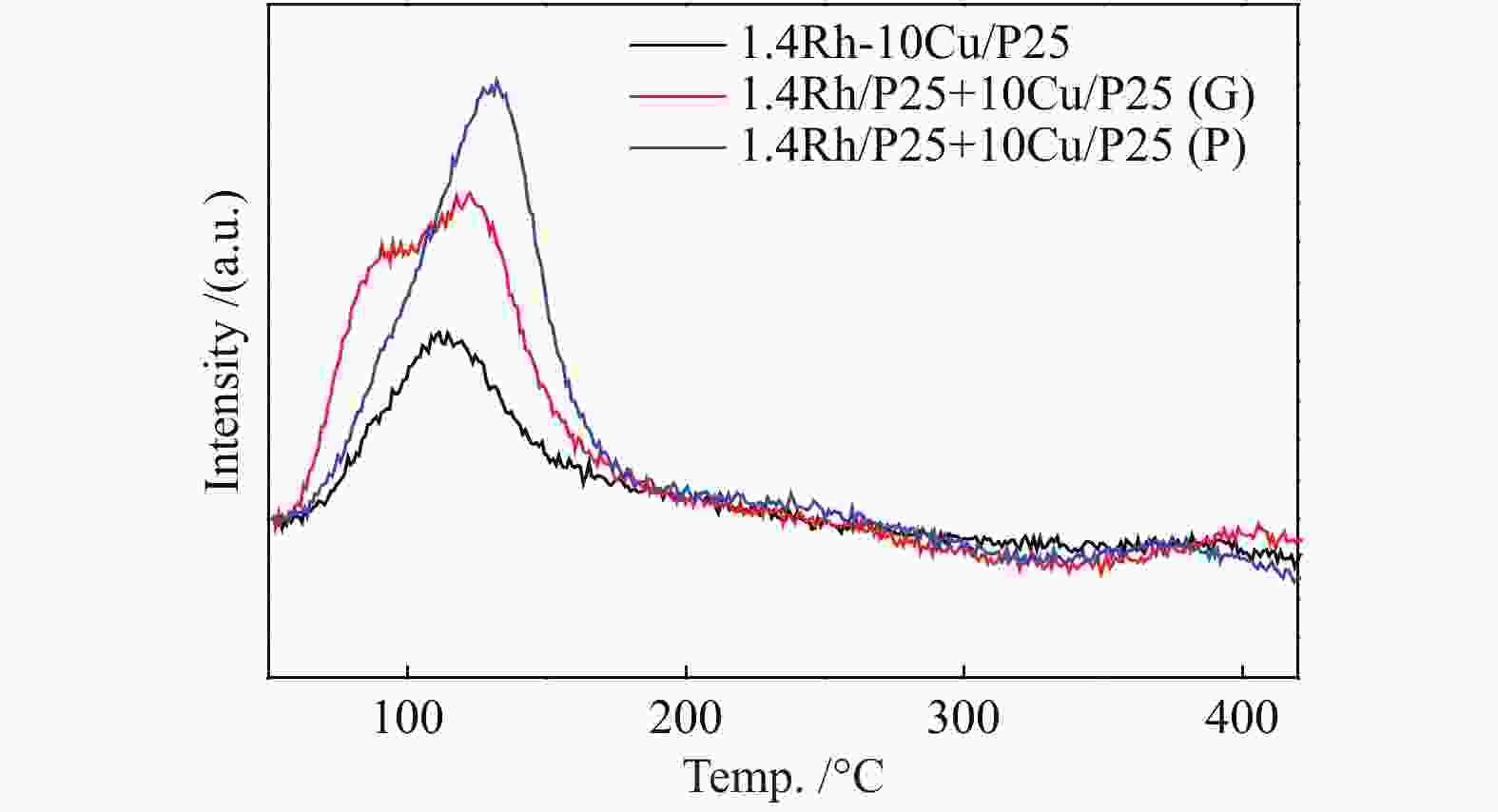
图 10 活性组分的混合方式对于合成乙醇性能的影响(a)尿素辅助凝胶和初湿浸渍法联用将Rh和Cu活性物种化学混合在一起;(b)在研钵中将1.4Rh/P25和10Cu/P25简单混合;(c)尺寸为250−420 μm的10Cu/P25和1.4Rh/P25颗粒混合;(d)上层1.4Rh/P25,下层10Cu/P25;(e)上层10Cu/P25,下层1.4Rh/P25
Figure 10 Effect of the integration methods of active components on the performance of ethanol synthesis (a) combined urea-assisted gel with incipient wetness impregnation method for chemical mixing of Rh and Cucomponents ; (b) physical mixing of Rh and Cu components in an agate mortar; (c) stacking of 10Cu/P25 and 1.4Rh/P25 granules with sizes of 250–420 μm; (d) 1.4Rh/P25|10Cu/P25; (e) 10Cu/P25|1.4Rh/P25
表 1 ICP测得的xRh-10Cu/P25催化剂中Rh和Cu的实际含量
Table 1 Actual content of Rh and Cu in xRh-10Cu/P25 catalysts measured by ICP
Sample Cu loading /%a Rh loading /%a 10Cu/P25 10.46 − 1.4Rh/P25 − 1.37 0.3Rh-10Cu/P25 10.03 0.28 1.4Rh-10Cu/P25 9.93 1.30 2.5Rh-10Cu/P25 9.80 2.62 3.6Rh-10Cu/P25 9.68 3.36 6.0Rh-10Cu/P25 9.92 5.89 a: determined by ICP analysis -
[1] GUO S X, LI S S, ZHONG H X, GONG D D, WANG J M, KANG N, ZHANG L H, LIU G L, LIU Y. Mixed oxides confined and tailored cobalt nanocatalyst for direct ethanol synthesis from syngas: A catalyst designing by using perovskite-type oxide as the precursor[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2018,57(6):2404−2415. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04336 [2] AO M, PHAM G H, SUNARSO J, TADE M O, LIU S M. Active centers of catalysts for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas: A review[J]. ACS Catal,2018,8(8):7025−7050. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b01391 [3] LUK H T, MONDELLI C, FERRE D C, STEWART J A, PEREZ-RAMIREZ J. Status and prospects in higher alcohols synthesis from syngas[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2017,46(5):1358−1426. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00324A [4] GU T J, WANG B C, CHEN S Y, YANG B. Automated generation and analysis of the complex catalytic reaction network of ethanol synthesis from syngas on Rh(111)[J]. ACS Catal,2020,10(11):6346−6355. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00630 [5] XIAO K, BAO Z H, QI X Z, WANG X X, ZHONG L S, FANG K G, LIN M G, SUN Y H. Advances in bifunctional catalysis for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas[J]. Chin J Catal,2013,34(1):116−129. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(11)60496-8 [6] ZHU Y, KONG X, LI X, DING G, ZHU Y, LI Y W. Cu Nanoparticles inlaid mesoporous Al2O3 as a high-performance bifunctional catalyst for ethanol synthesis via dimethyl oxalate hydrogenation[J]. ACS Catal,2014,4(10):3612−3620. doi: 10.1021/cs5009283 [7] PALOMINO R M, MAGEE J W, LLORCA J, SENANAYAKE S D, WHITE M G. The effect of Fe-Rh alloying on CO hydrogenation to C2+ oxygenates[J]. J Catal,2015,329:87−94. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.04.033 [8] GUPTA M, SMITH M L, SPIVEY J J. Heterogeneous catalytic conversion of dry syngas to ethanol and higher alcohols on Cu-based catalysts[J]. ACS Catal,2011,1(6):641−656. doi: 10.1021/cs2001048 [9] YIN A Y, GUO X Y, DAI W-L, FAN K N. The nature of active copper species in Cu-HMS catalyst for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol: New insights on the synergetic effect between Cu0 and Cu+[J]. J Phy Chem C,2009,113(25):11003−11013. [10] HUANG X, TESCHNER D, DIMITRAKOPOULOU M, FEDOROV A, FRANK B, KRAEHNERT R, ROSOWSKI F, KAISER H, SCHUNK S, KURETSCHKA C, SCHLOGL R, WILLINGER M G, TRUNSCHKE A. Atomic-scale observation of the metal-promoter interaction in Rh-based syngas-upgrading catalysts[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2019,58(26):8709−8713. doi: 10.1002/anie.201902750 [11] MATEEN M, SHAH K, CHEN Z, CHEN C, LI Y D. Selective hydrogenation of N-heterocyclic compounds over rhodium-copper bimetallic nanocrystals under ambient conditions[J]. Nano Res,2019,12(7):1631−1634. doi: 10.1007/s12274-019-2411-y [12] KRISHNAMURTHY R, CHUANG S S, GHOSAL K. Carbon monoxide adsorption and hydrogenation on Cu-Rh/SiO2 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,1994,114(1):109−125. doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(94)85111-5 [13] ZHAO Y H, YANG M M, SUN D P, SU H Y, SUN K J, MA X F, BAO X H, LI W-X. Rh-decorated cu alloy catalyst for improved C2 oxygenate formation from syngas[J]. J Phys Chem C,2011,115(37):18247−18256. doi: 10.1021/jp204961g [14] WEISZ P B. Polyfunctional heterogeneous catalysis[J]. Adv Catal,1962,13:137−190. [15] KIM J, KIM W, SEO Y, KIM J-C, RYOO R. n-Heptane hydroisomerization over Pt/MFI zeolite nanosheets: Effects of zeolite crystal thickness and platinum location[J]. J Catal,2013,301:187−197. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.02.015 [16] BATALHA N, PINARD L, BOUCHY C, GUILLON E, GUISNET M. n-Hexadecane hydroisomerization over Pt-HBEA catalysts. Quantification and effect of the intimacy between metal and protonic sites[J]. J Catal,2013,307:122−131. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.07.014 [17] ZECEVIC J, VANBUTSELE G, DE JONG K P, MARTENS J A. Nanoscale intimacy in bifunctional catalysts for selective conversion of hydrocarbons[J]. Nature,2015,528(7581):245−248. doi: 10.1038/nature16173 [18] CHENG K, ZHOU W, KANG J C, HE S, SHI S L, ZHANG Q H, PAN Y, WEN W, WANG Y. Bifunctional catalysts for one-step conversion of syngas into aromatics with excellent selectivity and stability[J]. Chem,2017,3(2):334−347. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2017.05.007 [19] CHENG K, GU B, LIU X L, KANG J C, ZHANG Q H, WANG Y. Direct and highly selective conversion of synthesis gas into lower olefins: design of a bifunctional catalyst combining methanol synthesis and carbon-carbon coupling[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2016,55(15):4725−4728. [20] KANG J C, HE S, ZHOU W, SHEN Z, LI Y Y, CHEN M S, ZHANG Q H, WANG Y. Single-pass transformation of syngas into ethanol with high selectivity by triple tandem catalysis[J]. Nat Commun,2020,11(1):1−11. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 [21] HANNAGAN R T, PATEL D A, CRAMER L A, SCHILLING A C, RYAN P T P, LARSON A M, ÇINAR V, WANG Y C, BALEMA T A, SYKES E C H. Combining STM, RAIRS and TPD to decipher the dispersion and interactions between active sites in RhCu single-atom alloys[J]. ChemCatChem,2019,12(2):488−493. [22] GONZALEZ S, SOUSA C, ILLAS F. Features and catalytic properties of RhCu: A review[J]. Int J Mod Phy B,2010,24(25/26):5128−5138. [23] LI C, LIU J, GAO W, ZHAO Y, WEI M. Ce-promoted Rh/TiO2 heterogeneous catalysts towards ethanol production from syngas[J]. Catal Lett,2013,143(11):1247−1254. doi: 10.1007/s10562-013-1100-9 [24] WANG B, CUI Y Y, WEN C, CHEN X, DONG Y, DAI W L. Role of copper content and calcination temperature in the structural evolution and catalytic performance of Cu/P25 catalysts in the selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2016,509:66−74. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.10.022 [25] KACIMI S, BARBIER, J. , TAHA, R. Oxygen storage capacity of promoted Rh/CeC2 catalysts. Exceptional behavior of RhCu/CeO2[J]. Catal Lett,1993,22:343−350. doi: 10.1007/BF00807243 [26] EGBEBI A, SCHWARTZ V, OVERBURY S H, SPIVEY J J. Effect of Li promoter on titania-supported Rh catalyst for ethanol formation from CO hydrogenation[J]. Cataly Today,2010,149(1-2):91−97. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2009.07.104 [27] JIANG B, KANI K, IQBAL M, ABE H, KIMURA T, HOSSAIN M S A, ANJANEYULU O, HENZIE J, YAMAUCHI Y. Mesoporous bimetallic RhCu alloy nanospheres using a sophisticated soft-templating strategy[J]. Chem Mater,2018,30(2):428−435. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04307 [28] GONG J L, YUE H R, ZHAO Y J, ZHAO S, ZHAO L, LV J, WANG S P, MA X B. Synthesis of ethanol via syngas on Cu/SiO2 catalysts with balanced Cu0-Cu+ sites[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2012,134(34):13922−13925. doi: 10.1021/ja3034153 [29] YIN A, GUO X, DAI W-L, FAN K. The nature of active copper species in Cu-HMS catalyst for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol: New insights on the synergetic effect between Cu0 and Cu+[J]. J Phys Chem C,2009,113(25):11003−11013. doi: 10.1021/jp902688b [30] LIU W C, MELAET G, RALSTON W T, ALAYOGLU S, HOROWITZ Y, YE R, HURLBURT T, MAO B, CRUMLIN E, SALMERON M, SOMORJAI G A. Co-Rh nanoparticles for the hydrogenation of carbon monoxide: Catalytic performance towards alcohol production and ambient pressure X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy study[J]. Catal Lett,2016,146(8):1574−1580. doi: 10.1007/s10562-016-1782-x [31] ZHENG X L, LIN H Q, ZHENG J W, DUAN X P, YUAN Y Z. Lanthanum oxide-modified Cu/SiO2 as a high-performance catalyst for chemoselective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol[J]. ACS Catal,2013,3(12):2738−2749. doi: 10.1021/cs400574v [32] HADJIIVANOV K, KNÖZINGER H. FTIR study of CO and NO adsorption and coadsorption on a Cu/SiO2 catalyst: Probing the oxidation state of copper[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys,2001,3(6):1132−1137. doi: 10.1039/b009649k [33] YANG A C, GARL C W. Infrared studies of carbon monoxide chemisorbed on rhodium[J]. J Phys Chem,1957,61(11):1504−1512. doi: 10.1021/j150557a013 [34] JIANG D H, DING Y J, PAN Z D, CHEN W M, LUO H Y. CO Hydrogenation to C2-oxygenates over Rh-Mn-Li/SiO2 catalyst: Effects of support pretreatment with nC1–C5 alcohols[J]. Catal Lett,2008,121(3):241−246. [35] FORCE C, BELZUNEGUI J, SANZ J, MARTıNEZ-ARIAS A, SORIA J. Influence of precursor salt on metal particle formation in Rh/CeO2 catalysts[J]. J Catal,2001,197(1):192−199. doi: 10.1006/jcat.2000.3067 [36] ANDERSON J A, ROCHESTER C H, WANG Z. IR study of CO adsorption on Cu–Rh/SiO2 catalysts, coked by reaction with methane[J]. J Mol Catal A: Chem,1999,139(2/3):285−303. doi: 10.1016/S1381-1169(98)00206-4 [37] QI J, CHRISTOPHER P. Atomically dispersed Rh active sites on oxide supports with controlled acidity for gas-phase halide-free methanol carbonylation to acetic acid[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2019,58(28):12632−12641. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b02289 -





 下载:
下载: