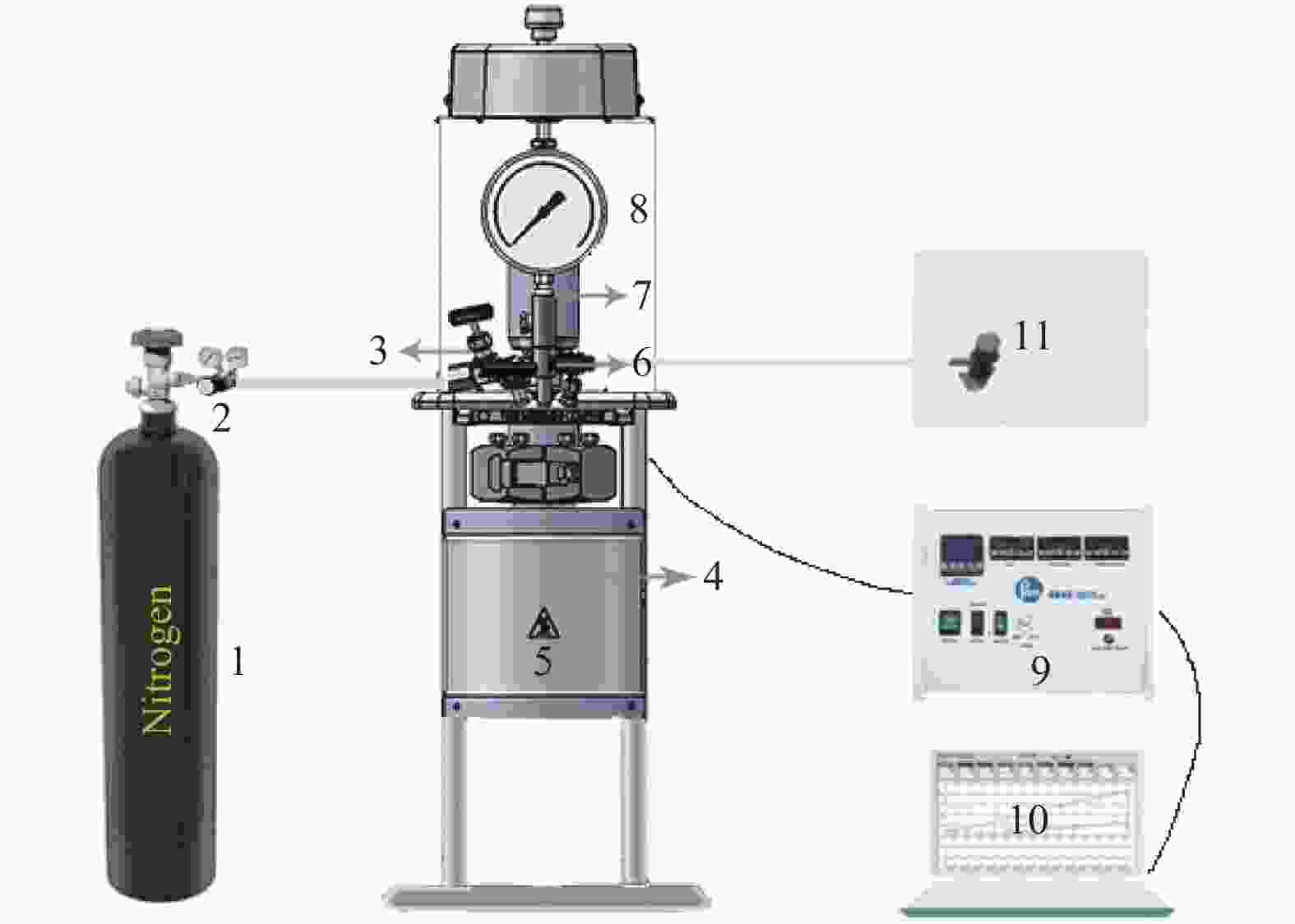
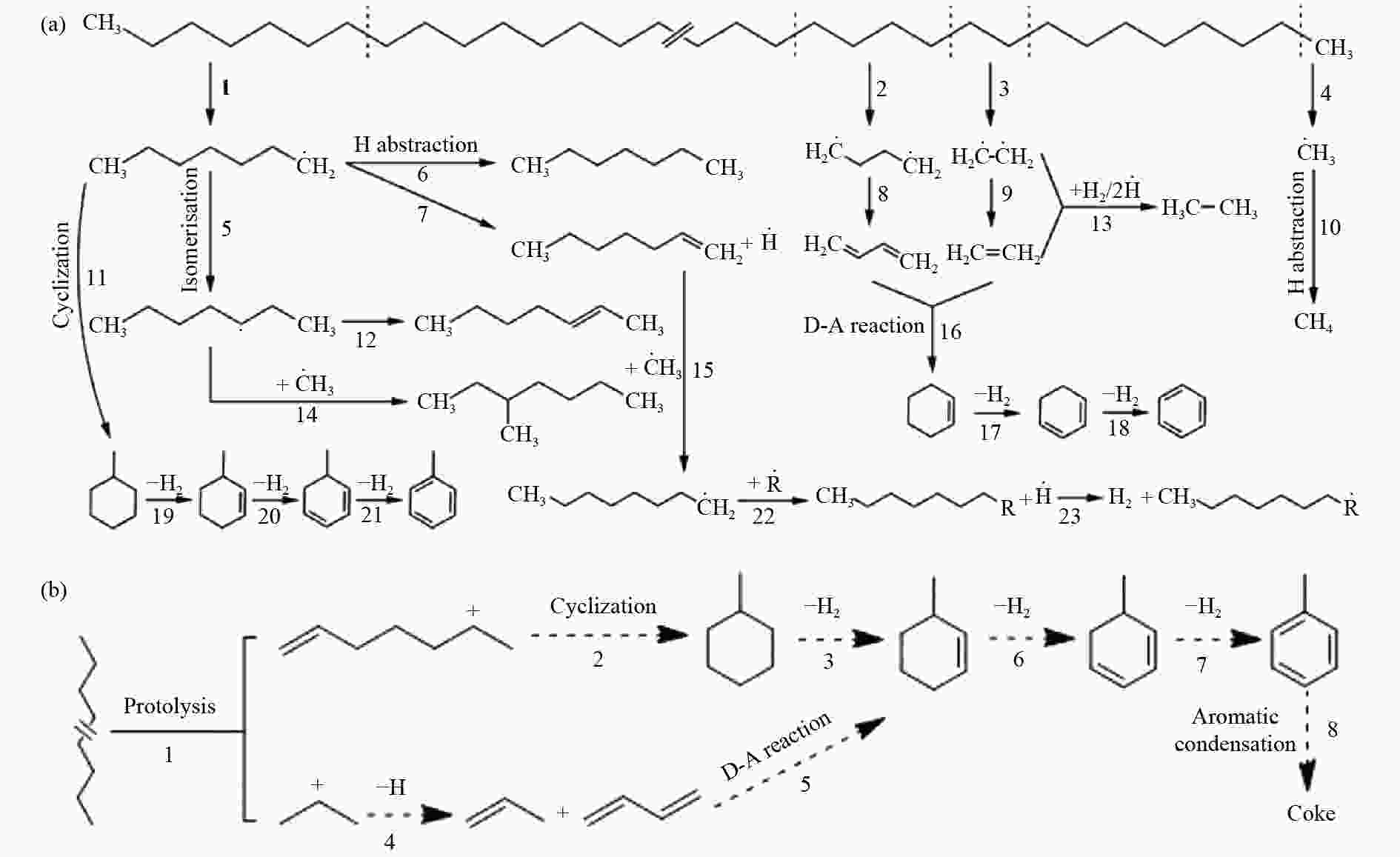
High-pressure pyrolysis and its mechanism of polyethylene
-
摘要: 塑料废弃物数量日益增加,实现低能耗、高值化利用是促进塑料废弃物回收利用的关键。在380 ℃设定温度和(1−5) ×105 Pa初始压力条件下分别开展聚乙烯高压热裂解和催化热解实验,记录反应过程温度曲线,分析聚乙烯高压热裂解/催化热解产物分布。研究结果表明,反应过程中反应物相态是影响热解反应历程的重要因素;因反应路径而异,压力变化对聚乙烯热裂解和催化热解产生不同程度的影响。聚乙烯高压热裂解实验过程中存在飞温现象,飞温峰值随初始压力的增加呈现单调增加的趋势;峰值温度的升高带来聚乙烯断链程度的加深,即获得更多小分子量产物。在相同设定温度和初始压力条件下的聚乙烯高压催化热解实验中不存在飞温现象,利用锌负载的ZSM-5催化剂实现聚乙烯高选择性制备芳香烃,液体产物中单环芳烃占比达82.53%,积炭产率在1.5%以下。Abstract: With the increasing waste disposal problems, high-value utilization technology using less energy is important to incentivize better recycling of plastic waste. Polyethylene high-pressure thermal cracking and catalytic pyrolysis experiments were conducted at a set temperature of 380 ℃ and low initial pressures (1−5) × 105 Pa. The process temperature curves were recorded and the hydrocarbon distribution of products was analyzed. The results suggest that the phase state in the pyrolysis system is a critical issue for reaction pathways. Thus, the pressure changes have different effects on the thermal cracking and catalytic pyrolysis of polyethylene. There is a phenomenon of thermal runaway during the polyethylene high-pressure pyrolysis process. The peak temperature represents a monotonous increase with the increasing initial pressure; the higher peak temperature leads to deeper cracking of polyethylene, giving more low-molecular-weight products. In the high-pressure catalytic pyrolysis experiments under the same other conditions, no thermal runaway is observed. The Zn-supported ZSM-5 catalyst converts polyethylene into aromatics, and the selectivity for monocyclic aromatics in the liquid phase is up to 82.53%. Moreover, the coke yield is less than 1.5%.
-
Key words:
- polyethylene /
- high pressure /
- thermal cracking /
- catalytic pyrolysis /
- thermal runaway
-
表 1 实验原料的LDPE特性
Table 1 Property of LDPE feedstock
Form Powder Molar mass average Mn ~ 1700 by GPC
average Mw ~ 4000 by GPCViscosity 1.5 Poise (25 ℃, Brookfield Thermosel) (lit.) Melting point 92 ℃ Acid number <0.05 mg KOH/g Transition temp softening point 106 ℃ (ring and ball) Density 0.92 g/mL at 25 ℃ 表 2 实验原料LDPE元素分析
Table 2 Ultimate analysis of LDPE feedstock
Raw material Ultimate analysis w/% C H N S O LDPE 85.22 14.08 0 0 0 表 3 聚乙烯高压热裂解/催化热解过程参数
Table 3 Process parameters of polyethylene high-pressure pyrolysis and high-pressure catalytic pyrolysis
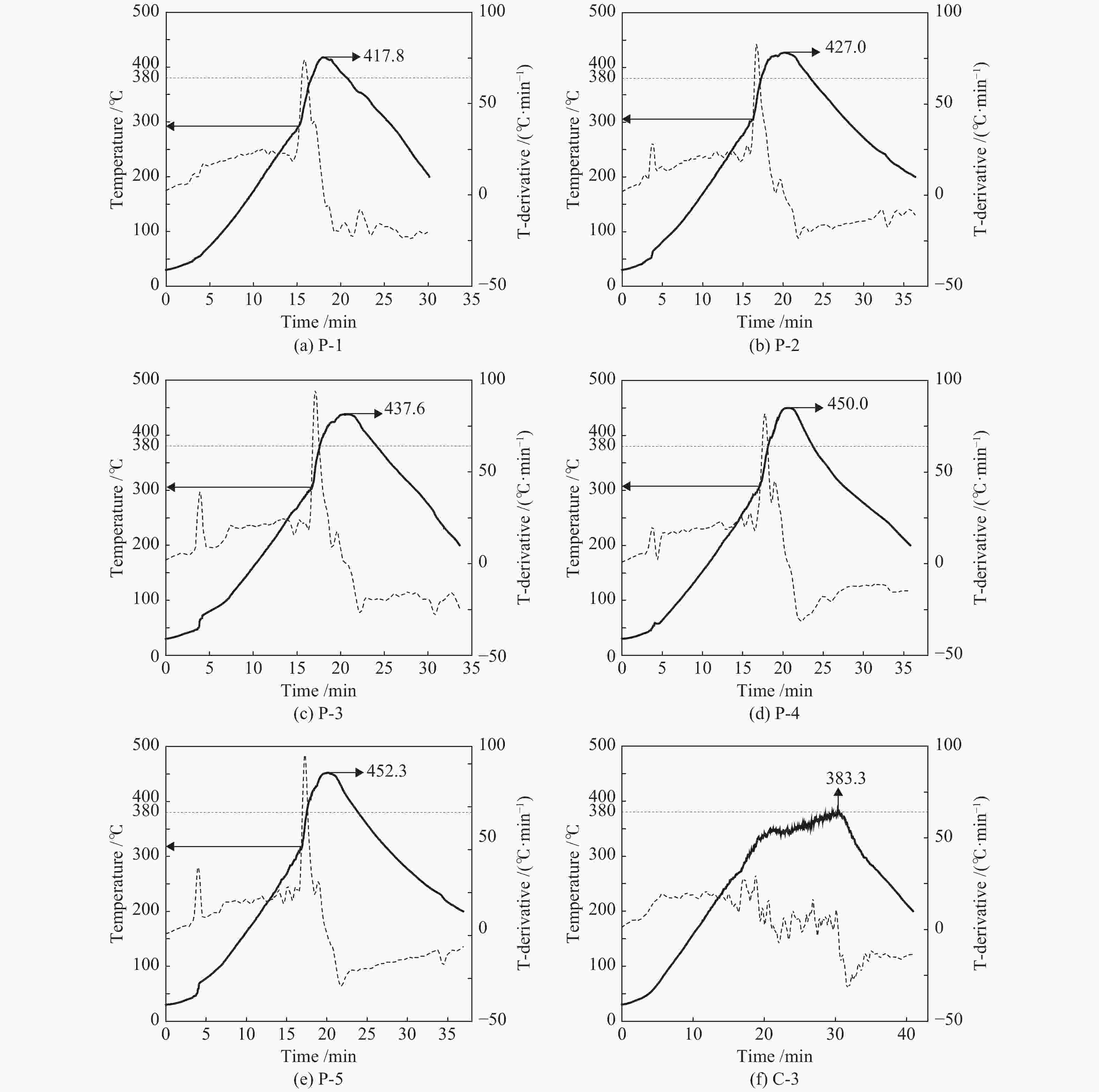
Entry Starting value of thermal runaway/℃ Peak temperature
/℃Peak pressure/
105 PaFinal pressure at room temperature/105 Pa Partial pressure of gaseous product at room temperature/105 Pa P-1 ~293 417.8 9.5 4 3 P-2 ~303 427.0 15 5 3 P-3 ~303 437.6 18 6.5 3.5 P-4 ~305 450.0 22 7.5 3.5 P-5 ~311 452.3 24 9 4 C-1 − 380.3 34.5 12 11 C-2 − 381.9 39 13 11 C-3 − 383.3 43.5 13.5 10.5 C-4 − 383.1 50 15 11 C-5 − 381.0 52 16.5 11.5 表 4 聚乙烯高压热裂解气体产物组分分布
Table 4 Gas products distribution obtained from the high-pressure pyrolysis of LDPE
Runs P-1 P-2 P-3 P-4 P-5 Hydrogen 3.84 5.04 5.88 7.54 8.61 Methane 24.26 25.69 26.74 26.28 29.00 Ethane 19.01 20.53 20.62 21.31 21.44 Ethylene 7.26 7.43 8.53 7.69 7.59 Propane 18.23 16.26 15.37 16.12 14.12 Propene 15.25 14.19 14.12 13.14 11.67 C4 alkanes 5.66 5.20 4.09 3.57 3.63 C4 olefins 5.56 4.85 3.75 3.64 3.11 C5+ hydrocarbons 0.94 0.81 0.91 0.71 0.83 note: the temperature set in the above table is 380 ℃; X in the label “P-X ” is the initial pressure value 表 5 聚乙烯高压热裂解液体产物组分分布
Table 5 Liquid products distribution obtained from the high-pressure pyrolysis of LDPE
Runs P-1 P-2 P-3 P-4 P-5 n-Paraffins 67.59 66.37 65.18 65.25 64.14 Isoparaffins − 0.38 0.95 1.14 1.18 Cycloparaffins 5.73 5.76 5.67 6.27 8.59 α-olefins 24.59 22.97 21.48 19.57 18.01 Cycloolefins − 1.56 2.58 3.41 3.27 Other olefins 2.09 2.23 2.49 2.19 2.54 Aromatics − 0.73 1.65 2.17 2.27 Average carbon number 14.12 13.57 12.84 11.16 11.05 note: the temperature set in the above table is 380 ℃; X in the label “P-X ” is the initial pressure value 表 6 聚乙烯催化热解气体产物组分分布
Table 6 Gas products distribution obtained from the catalytic pyrolysis of LDPE
Runs C-1 C-2 C-3 C-4 C-5 Hydrogen 26.27 24.98 23.51 19.82 20.26 Methane 6.82 6.29 5.37 6.03 5.88 Ethane 4.83 4.92 5.15 5.08 5.39 Ethylene 4.25 3.49 2.49 2.09 1.96 Propane 32.02 34.82 36.85 39.77 39.37 Propylene 7.58 5.28 4.26 3.92 3.00 Butane 5.18 6.26 6.44 7.09 7.26 Isobutane 7.17 9.18 10.49 11.52 11.56 C4 olefins 3.36 2.47 2.76 1.79 2.26 C5+ hydrocarbons 2.52 2.31 2.68 2.89 3.06 note: the temperature set in the above table is 380 ℃; X in the label “P-X ” is the initial pressure value 表 7 聚乙烯催化热解液体产物组分分布
Table 7 Liquid products distribution obtained from the catalytic pyrolysis of LDPE
Runs C-1 C-2 C-3 C-4 C-5 Aromatics 84.51 83.10 83.25 81.54 79.21 Benzene 5.62 4.84 5.32 4.28 4.36 Toluene 25.04 24.16 22.10 20.75 20.89 Ethylbenzene 4.63 4.53 4.46 4.39 4.40 Xylene 24.78 25.64 24.97 25.36 24.58 Other MAHs 22.46 21.87 24.25 24.75 23.29 PAHs 1.98 2.06 2.15 2.01 1.69 Other hydrocarbons 15.49 16.90 16.75 18.46 20.79 n-Paraffins 6.54 6.32 7.01 6.95 7.91 Isoparaffins 4.80 5.21 6.04 5.96 7.01 Olefins 0.74 0.83 0.98 1.26 1.44 Cycloparaffins 3.21 4.49 2.72 3.61 4.00 Cycloolefins 0.20 0.05 0.00 0.68 0.43 note: the temperature set in the above table is 380 ℃; X in the label “P-X ” is the initial pressure value -
[1] 汪刚, 余广炜, 谢胜禹, 江汝清, 汪印. 添加不同塑料与污泥混合热解对生物炭中重金属的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2019,47(5):611−620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.05.013WANG Gang, YU Guang-wei, XIE Sheng-yu, JIANG Ru-qing, WANG Yin. Effect of co-pyrolysis of different plastics with sewage sludge on heavy metals in the biochar[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2019,47(5):611−620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2019.05.013 [2] GEYER R, JAMBECK J R, LAW K L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made[J]. Sci Adv,2017,3(7):5. [3] MOHANRAJ C, SENTHILKUMAR T, CHANDRASEKAR M. A review on conversion techniques of liquid fuel from waste plastic materials[J]. Int J Energy Res,2017,41(11):1534−1552. doi: 10.1002/er.3720 [4] KUMAR A, VON WOLFF N, RAUCH M, ZOU Y-Q, SHMUL G, BEN-DAVID Y, LEITUS G, AVRAM L, MILSTEIN D. Hydrogenative Depolymerization of Nylons[J]. JACS,2020,142(33):14267−14275. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c05675 [5] KRATISH Y, LI J, LIU S, GAO Y, MARKS T J. Polyethylene terephthalate deconstruction catalyzed by a carbon-supported single-Site molybdenum-dioxo complex [J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2020. [6] TENNAKOON A, WU X, PATERSON A L, PATNAIK S, PEI Y, LAPOINTE A M, AMMAL S C, HACKLER R A, HEYDEN A, SLOWING I I, COATES G W, DELFERRO M, PETERS B, HUANG W, SADOW A D, PERRAS F A. Catalytic upcycling of high-density polyethylene via a processive mechanism[J]. Nat Catal, 2020. [7] GU F, GUO J F, ZHANG W J, SUMMERS P A, HALL P. From waste plastics to industrial raw materials: A life cycle assessment of mechanical plastic recycling practice based on a real-world case study[J]. Sci Total Environ,2017,601:1192−1207. [8] VASILE C, BREBU M A, KARAYILDIRIM T, YANIK J, DARIE H. Feedstock recycling from plastics and thermosets fractions of used computers. II. Pyrolysis oil upgrading[J]. Fuel,2007,86(4):477−485. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.08.010 [9] RAGAERT K, DELVA L, VAN GEEM K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste[J]. Waste Management,2017,69:24−58. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.07.044 [10] BAENA-GONZáLEZ J, SANTAMARIA-ECHART A, AGUIRRE J L, GONZÁLEZ S. Chemical recycling of plastic waste: Bitumen, solvents, and polystyrene from pyrolysis oil[J]. Waste Management,2020,118:139−149. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2020.08.035 [11] ACHILIAS D S, ROUPAKIAS C, MEGALOKONOMOS P, LAPPAS A A, ANTONAKOU Ε V. Chemical recycling of plastic wastes made from polyethylene (LDPE and HDPE) and polypropylene (PP)[J]. J Hazard Mater,2007,149(3):536−542. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.076 [12] GRAUSE G. Resource control by a sustainability based currency equivalent[J]. J Clean Prod,2018,200:533−541. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.297 [13] 孙锴, 王琬丽, 黄群星. 典型杂质掺混对废塑料热解油特性的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 1-11.SUN Kai, WANG Wan-li, HUANG Qun-xing. Effect of typical impurities on the pyrolysis oil of waste plastics[J]. Chem Ind Eng Pro (China), 2020, 1-11. [14] 孙艺蕾, 马跃, 李术元, 岳长涛. 聚烯烃塑料的热解和催化热解研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 1-21.SUN Yi-lei, MA Yue, LI Shu-yuan, YUE Chang-tao. Research progress in the pyrolysis and catalytic pyrolysis of waste polyolefin plastics[J]. Chem. Ind. & Eng. Pro. (China), 2020, 1-21. [15] AL-SALEM S M, ANTELAVA A, CONSTANTINOU A, MANOS G, DUTTA A. A review on thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of plastic solid waste (PSW)[J]. J Environ Manage,2017,197:177−98. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.084 [16] WONG S L, NGADI N, ABDULLAH T A T, INUWA I M. Current state and future prospects of plastic waste as source of fuel: A review[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2015,50:1167−80. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.063 [17] MURATA K, SATO K, SAKATA Y. Effect of pressure on thermal degradation of polyethylene[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2004, 71(2): 569-89. [18] KUMARI A, KUMAR S. Pyrolytic degradation of polyethylene in autoclave under high pressure to obtain fuel[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2017,124:298−302. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2017.01.020 [19] ONWUDILI J A, INSURA N, WILLIAMS P T. Composition of products from the pyrolysis of polyethylene and polystyrene in a closed batch reactor: Effects of temperature and residence time[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2009,86(2):293−303. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2009.07.008 [20] CHENG L, GU J, WANG Y, ZHANG J, YUAN H, CHEN Y. Polyethylene high-pressure pyrolysis: Better product distribution and process mechanism analysis[J]. Chem Eng J,2020,385:123866. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123866 [21] LOK C M, VAN DOORN J, ARANDA ALMANSA G. Promoted ZSM-5 catalysts for the production of bio-aromatics, a review[J]. Renew Sustainable Energy Rev,2019,113:109248. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.109248 [22] LÓPEZ A, DE MARCO I, CABALLERO B M, LARESGOITI M F, ADRADOS A. Influence of time and temperature on pyrolysis of plastic wastes in a semi-batch reactor[J]. Chem Eng J,2011,173(1):62−71. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.037 [23] MOSIO-MOSIEWSKI J, WARZALA M, MORAWSKI I, DOBRZANSKI T. High-pressure catalytic and thermal cracking of polyethylene[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2007,88(4):359−364. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2006.10.009 [24] SANTOS E, RIJO B, LEMOS F, LEMOS M A N D A. A catalytic reactive distillation approach to high density polyethylene pyrolysis – Part 2 – Middle olefin production[J]. Catal Today,2020,. [25] AKUBO K, NAHIL M A, WILLIAMS P T. Aromatic fuel oils produced from the pyrolysis-catalysis of polyethylene plastic with metal-impregnated zeolite catalysts[J]. J Energy Inst,2019,92(1):195−202. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2017.10.009 [26] SUN K, HUANG Q, CHI Y, YAN J. Effect of ZnCl2-activated biochar on catalytic pyrolysis of mixed waste plastics for producing aromatic-enriched oil[J]. Waste Management,2018,81:128−137. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.09.054 [27] SADRAMELI S M. Thermal/catalytic cracking of hydrocarbons for the production of olefins: A state-of-the-art review I: Thermal cracking review[J]. Fuel,2015,140:102−115. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.09.034 [28] SERRANO D P, AGUADO J, ESCOLA J M. Developing advanced catalysts for the conversion of polyolefinic waste plastics into fuels and chemicals[J]. ACS Catal,2012,2(9):1924−1941. doi: 10.1021/cs3003403 [29] 李传强, 刘思媛, 王东升, 刘书彬, 郑旭煦, 袁小亚. 压力反应釜中低温热裂解废旧LLDPE塑料制备PE蜡[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(12):4856−4863.LI Chuan-qiang, LIU Si-yuan, WANG dong-sheng, LIU Shu-bin, ZHENG Xu-xu, YUAN Xiao-ya. Preparation of PE wax by pyrolysis of LLDPE waste plastic in a pressure reactor under low temperature[J]. CIESC J,2019,70(12):4856−4863. -





 下载:
下载: