Effect of alkali treatment on ZnZrOx/SAPO-34 bifunctional catalyst for catalytic synthesis of light olefins from syngas
-
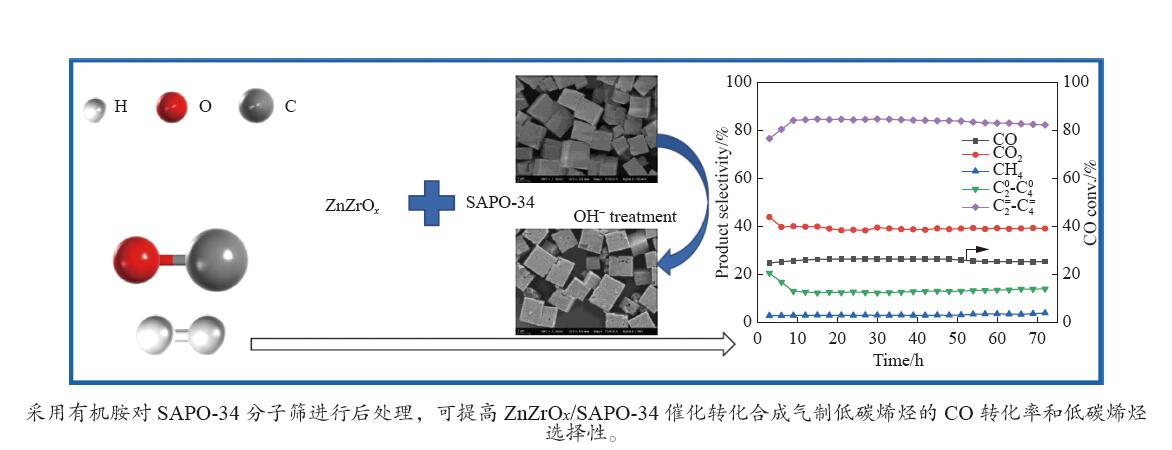
摘要: 采用ZnZrOx金属氧化物和SAPO-34分子筛物理混合制备了双功能催化剂,用于合成气一步法制低碳烯烃(STO)反应。考察了三乙胺、四甲基氢氧化铵和四乙基氢氧化铵三种有机碱溶液及不同浓度的三乙胺溶液处理对SAPO-34分子筛织构、结构和酸性的影响,采用XRD、SEM、N2吸附-脱附、NH3-TPD对分子筛进行了表征,并考察了碱处理后催化剂的STO反应性能。结果表明,采用0.06 mol/L的三种有机碱后处理均可在SAPO-34分子筛表面刻蚀出部分多级孔道,从而在STO反应中加速金属氧化物表面形成的中间过渡物种从金属氧化物表面扩散进入SAPO-34分子筛孔道,提高了催化剂在STO反应中CO的转化率,同时,三种碱处理均可降低SAPO-34分子筛的酸量及酸强度,从而提高催化剂在STO反应中低碳烯烃选择性;采用0.02−0.10 mol/L的三乙胺处理SAPO-34分子筛,均在SAPO-34分子筛表面刻蚀出的多级孔,提高了STO反应中CO的转化率,且0.02和0.06 mol/L的三乙胺溶液处理后的SAPO-34分子筛,酸强度和酸量的降低,抑制了甲烷的形成和烯烃的加氢,因此,随着碱处理浓度从0、0.02到0.06 mol/L逐步提高,催化剂对低碳烯烃的选择性逐步提高。其中,在400 ℃,3.0 MPa和GHSV=3600 mL/(g∙h)条件下,采用0.06 mol/L的三乙胺处理的SAPO-34物理混合ZnZrOx,与未经处理的SAPO-34分子筛相比,CO转化率从24.0%提升至26.4%,低碳烯烃选择性从78.2%提升至84.7%,且该催化剂具有较好的催化稳定性。
-
关键词:
- 合成气制低碳烯烃 /
- 双功能催化剂 /
- SAPO-34分子筛 /
- 碱处理
Abstract: A bifunctional catalyst was prepared by physical mixing of ZnZrOx metal oxide and SAPO-34 zeolite for the one-step conversion of synthesis gas to light olefins (STO) reaction. The effects of triethylamine, tetramethylammonium hydroxide and tetraethylammonium hydroxide solutions and different concentrations of triethylamine solution on the texture, structure and acidity of SAPO-34 zeolite were investigated. XRD, SEM, N2 adsorption and desorption, NH3-TPD were used to characterize the SAPO-34 zeolite and the STO reaction performance of the catalyst after alkali treatment was investigated. The results show that all three kinds of organic base with 0.06 mol/L post-treatment can etch some hierarchical channels on the surface of SAPO-34 zeolite, thus accelerating the diffusion of intermediate transition species formed on the surface of metal oxides into the channels of SAPO-34 zeolite in STO reaction, improving the CO conversion rate in STO reaction. At the same time, all three kinds of alkali treatments can reduce the acid amount and acid strength of SAPO-34 zeolite, thereby improving the selectivity for light olefins in the STO reaction. The treatment of SAPO-34 zeolite with 0.02−0.10 mol/L triethylamine resulted in the formation of hierarchical pores etched on the surface of SAPO-34 zeolite, which improved the conversion rate of CO in the STO reaction. Moreover, the acid strength and acidity of SAPO-34 zeolite treated with 0.02 and 0.06 mol/L triethylamine solutions decreased, inhibiting the formation of methane and the hydrogenation of light olefins. Therefore, as the concentration of alkali treatment gradually increased from 0, 0.02 to 0.06 mol/L, the selectivity for light olefins gradually increases. Under the reaction conditions of 400 ℃, 3.0 MPa and GHSV=3600 mL/(g·h), the CO conversion rate increased from 24.0% to 26.4%, and the selectivity of light olefins increased from 78.2% to 84.7% on the bifunctional catalyst composed of 0.06 mol/L triethylamine-treated SAPO-34 compared to untreated SAPO-34 zeolite, and the modified bifunctional catalyst had good catalytic stability.-
Key words:
- syngas to light olefins /
- bifunctional catalyst /
- SAPO-34 zeolite /
- alkali treatment
-
表 1 不同碱处理的SAPO-34分子筛的结构性质
Table 1 Structural properties of SAPO-34 after treatment with different alkalis
Sample ABET/
(m2·g−1)Amicro/
(m2·g−1)vtotal/
(cm3·g−1)vmicro/
(cm3·g−1)Relative
crystallinityaS-0 515 505 0.29 0.26 100 S-1-006 490 487 0.30 0.26 80.7 S-2-006 471 465 0.26 0.24 75.8 S-3-006 490 485 0.28 0.25 81.6 a : The crystallinity of S-0 is defined as 100%. 表 2 不同碱处理的SAPO-34分子筛的酸性
Table 2 Acid data of SAPO-34 zeolite treated with different alkalis
Sample Weak acid peak area Strong acid peak area Total acid peak area S-0 348 349 697 S-1-006 282 253 535 S-2-006 162 242 404 S-3-006 324 339 663 表 3 由不同碱处理SAPO-34分子筛和ZnZrOx 组成的双功能催化剂的催化性能
Table 3 Catalytic property of bifunctional catalysts composed of SAPO-34 treated with different alkalis and ZnZrOx
Catalyst CO
conversion/%CO2
selectivity/%Hydrocarbon distribution/% CH4 ${\rm{C} }_{2} ^{0}-{\rm{C} }_{4}^{0} $ ${\rm{C} }_{2} ^{=}-{\rm{C} }_{4}^{=} $ ZnZrOx/S-0 24.0 38.1 8.6 13.1 78.2 ZnZrOx/S-1-006 26.4 39.5 2.9 12.4 84.7 ZnZrOx/S-2-006 25.9 40.8 8.9 30.4 60.7 ZnZrOx/S-3-006 30.6 40.5 3.6 19.3 77.1 Reaction conditions: t=400 ℃, p=3.0 MPa, GHSV=3600 mL/(g∙h), CO:H2=1:2(vol/vol). 表 4 不同浓度三乙胺溶液处理的SAPO-34分子筛的结构性质
Table 4 Structural properties of SAPO-34 treated with different concentrations of triethylamine solutions
Sample ABET/(m2·g−1) Amicro/(m2·g−1) vtotal/(cm3·g−1) vmicro/(cm3·g−1) Relative crystallinitya S-0 515 505 0.29 0.26 100 S-1-002 511 505 0.29 0.26 90.4 S-1-006 490 587 0.30 0.26 80.7 S-1-010 473 465 0.27 0.24 78.3 a : The crystallinity of S-0 is defined as 100%. 表 5 不同浓度三乙胺溶液处理的SAPO-34分子筛的酸性
Table 5 Acid data of SAPO-34 zeolite treated with different concentrations of triethylamine solutions
Sample Weak acid peak area Strong acid peak area Total acid peak area S-0 348 349 697 S-1-002 328 340 668 S-1-006 282 253 535 S-1-010 277 245 522 表 6 由不同浓度三乙胺溶液处理SAPO-34分子筛和和ZnZrO x 组成的双功能催化剂的催化性能
Table 6 Catalytic property of bifunctional catalysts composed of SAPO-34 treated with different concentrations of triethylamine solutions and ZnZrOx
Catalyst CO
conversion/
%CO2
selectivity/
%Hydrocarbon
distribution/%CH4 ${\rm{C} }_{2} ^{0}-{\rm{C} }_{4}^{0}$ ${\rm{C} }_{2} ^{=}-{\rm{C} }_{4}^{=}$ ZnZrOx/S-0 24.0 38.1 8.6 13.1 78.2 ZnZrOx/S-1-002 25.2 38.8 2.4 15.5 82.1 ZnZrOx/S-1-006 26.4 39.5 2.9 12.4 84.7 ZnZrOx/S-1-010 25.4 40.5 6.9 17.4 75.7 Reaction conditions: t=400 ℃, p=3.0 MPa, GHSV=3600 mL/(g∙h), CO:H2=1:2(vol/vol). 表 7 不同双功能催化剂催化性能的比较
Table 7 Comparison of catalytic performance of different bifunctional catalysts
Catalyst Temperature
/℃Space velocity/(mL∙g−1∙h−1) Pressure/MPa CO conv./% ${\rm{C} }_{2} ^{=}-{\rm{C} }_{4}^{=}$ sel./% Ref. ZnZrOx/S-1-006 400 3600 3.0 26.4 84.7 this work MG-AH/SAPO-34 400 4875 2.5 19.5 81.2 [19] ZrCeZnOx/SAPO-34 400 3900 1.0 25.6 78.6 [28] ZnCr2O4/SAPO-34 400 4800 3.0 11 64 [29] ZnO-ZrO2/SAPO-34 400 4800 1.0 7.0 69 [30] ZnZrOx/SSZ-13 400 1800 3.0 23 75 [26] ZnZrO/MSAPO 400 7714 2.5 17 80 [13] ZnZrOx/AIPO-18 390 1200 4.0 25.2 45 [7] ZnAl2Ox/SAPO-18 400 4500 3.0 34.8 70.7 [6] -
[1] ZHANG P, MENG F, LI X, et al. Excellent selectivity for direct conversion of syngas to light olefins over a Mn-Ga oxide and SAPO-34 bifunctional catalyst[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2019,9(20):5577−5581. doi: 10.1039/C9CY01348B [2] FONSECA N, DOS SANTOS L R M, CERQUEIRA H S, et al. Olefins production from cracking of a Fischer-Tropsch naphtha[J]. Fuel,2021,95:183−189. [3] JOO E, PARK S, LEE M. Pyrolysis reaction mechanism for industrial naphtha cracking furnaces[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2001,40(11):2409−2415. doi: 10.1021/ie000774o [4] GONG F, YANG Z, HONG C, et al. Selective conversion of bio-oil to light olefins: Controlling catalytic cracking for maximum olefins[J]. Bioresour Technol,2011,102(19):9247−9254. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.009 [5] AL-SHAMMARI A A, ALI S A, AL-YASSIR N, et al. Catalytic cracking of heavy naphtha-range hydrocarbons over different zeolites structures[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2014,122:12−22. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.01.021 [6] 李保珍, 孟凡会, 王丽娜, 等. 合成气制低碳烯烃串联反应中Zn-Al氧化物的制备及性能[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(1):111−119.LI Baozhen, MENG Fanhui, WANG Lina, et al. Study on preparation and catalytic performance of Zn-Al oxides for tandem reaction of syngas conversion into light olefins[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(1):111−119. [7] SU J, ZHOU H, LIU S, et al. Syngas to light olefins conversion with high olefin/paraffin ratio using ZnCrOx/AlPO-18 bifunctional catalysts[J]. Nat Commun,2019,10(1):1297. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09336-1 [8] VAN DEELEN T W, HERNÁNDEZ MEJÍA C, DE JONG K P. Control of metal-support interactions in heterogeneous catalysts to enhance activity and selectivity[J]. Nat Catal,2019,2(11):955−970. doi: 10.1038/s41929-019-0364-x [9] LI S, LIU X, LU Y. Fischer-Trospch to olefins over hydrophobic FeMnOx@SiO2 catalysts: The effect of SiO2 shell content[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2022,635:118552. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2022.118552 [10] GONG K, LIN T, AN Y, et al. Fischer-Tropsch to olefins over CoMn-based catalysts: Effect of preparation methods[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2020,592:117414. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117414 [11] WANG M, WANG Z, LIU S, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical SAPO-34 to improve the catalytic performance of bifunctional catalysts for syngas-to-olefins reactions[J]. Chin J Catal,2021,349:181−192. [12] 刘赛赛, 姚金刚, 陈冠益, 等. 合成气一步法制备低碳烯烃和液体燃料催化剂研究进展[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(1):34−51.LIU Saisai, YAO Jingang, CHEN Guanyi, et al. One-step catalyst for the preparation of light olefins and liquid fuels from syngas[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(1):34−51. [13] JIAO F, LI J, PAN X, et al. Selective conversion of syngas to light olefins[J]. Science,2016,351(6277):1065−1068. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1835 [14] MENG F, LIANG X, WANG L, et al. Rational design of SAPO-34 zeolite in bifunctional catalysts for syngas conversion into light olefins[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2022,61(31):11397−11406. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.2c01111 [15] 皂辉杰, 姚金刚, 刘静, 等. 合成气一步法直接制低碳烯烃双功能催化剂研究新进展[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(1):19−33.ZAO Huijie, YAO Jingang, LIU Jing, et al. New research progress on bifunctional catalysts for one-step direct production of low carbon olefins from syngas[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(1):19−33. [16] 庹杰, 李石擎, 徐浩, 等. 分子筛结构设计及酸性调控在合成气催化转化中的应用进展[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(1):1−18. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(22)60035-5TUO Jie, LI Shiqing, XU Hao, et al. A progress of structure design and acidity tunning of zeolites in catalytic syngas conversion[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(1):1−18. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(22)60035-5 [17] HUANG Y, MA H, XU Z, et al. Role of nanosized sheet-like SAPO-34 in bifunctional catalyst for syngas-to-olefins reaction[J]. Fuel,2022,273:117771. [18] 魏晓娜, 李文双, 陈诗通, 等. 不同酸性SAPO-34分子的制备及催化合成气制低碳烯烃性能研究[J]. 工业催化,2022,30(2):41−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2022.02.007WEI Xiaona, LI Wenshuang, CHENG Shitong, et al. Synthesis of SAPO-34 zeolites with different acidity and their catalytic performance in syngas to olefins reaction[J]. Catal Ind,2022,30(2):41−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2022.02.007 [19] YANG G, MENG F, ZHANG P, et al. Effect of preparation method and precipitant on Mn-Ga oxide in combination with SAPO-34 for syngas conversion into light olefins[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2021,45(18):7967−6976. [20] LIU X, REN S, ZENG G, et al. Coke suppression in MTO over hierarchical SAPO-34 zeolites[J]. RSC Adv,2016,6(34):28787−28791. doi: 10.1039/C6RA02282K [21] VERBOEKEND D, MILINA M, PÉEZ-RAMÍREZ J. Hierarchical silicoaluminophosphates by postsynthetic modification: Influence of topology, composition, and silicon distribution[J]. Chem Mater,2014,26(15):4552−4562. doi: 10.1021/cm501774s [22] SUN C, WANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Fabrication of hierarchical ZnSAPO-34 by alkali treatment with improved catalytic performance in the methanol-to-olefin reaction[J]. C R Chim,2018,21(1):61−70. doi: 10.1016/j.crci.2017.11.006 [23] LI Z, MARTÍNEZ-TRIGUERO J, CONCEPCIÓN P, et al. Methanol to olefins: Activity and stability of nanosized SAPO-34 molecular sieves and control of selectivity by silicon distribution[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys,2013,15(35):14670−14680. doi: 10.1039/c3cp52247d [24] LIU X, ZHOU W, YANG Y, et al. Design of efficient bifunctional catalysts for direct conversion of syngas into lower olefins via methanol/dimethyl ether intermediates[J]. Chem Sci,2018,9(20):4708−4718. doi: 10.1039/C8SC01597J [25] KARGER J, RUTHVEN D M. Diffusion in nanoporous materials: Fundamental principles, insights and challenges[J]. New J Chem, 2016, 40(5): 4027-4048. [26] SCHNEIDER D, MEHLHORN D, ZEIGERMANN P. Transport properties of hierarchical micromesoporous materials[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2016,45(12):3439−3467. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00715A [27] JADAV D, BANDYOPADHYAY R, BANDYOPADHYAY M. Synthesis of hierarchical SAPO-5 & SAPO-34 materials by post‐synthetic alkali treatment and their enhanced catalytic activity in transesterification[J]. Eur J Inorg Chem,2020,2020(10):847−853. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201901250 [28] MENG F, LI X, ZHANG P, et al. Highly active ternary oxide ZrCeZnOx combined with SAPO-34 zeolite for direct conversion of syngas into light olefins[J]. Catal Today,2021,368:118−125. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.03.023 [29] ZHANG L, LIANG D, WANG Y, et al. Design of the core-shell catalyst: An effective strategy for suppressing side reactions in syngas to light olefins direct selective conversion[J]. Chem Sci,2020,11(16):4097−4105. doi: 10.1039/C9SC05544D [30] CHENG K, GU B, LIU X, et al. Direct and highly selective conversion of synthesis gas into lower olefins: Design of a bifunctional catalyst combining methanol synthesis and carbon-carbon coupling[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2016,55(15):4725−4728. doi: 10.1002/anie.201601208 -





 下载:
下载: