Study on the mechanism of K-poisoning in Mn/TiO2 low temperature SCR catalysts
-
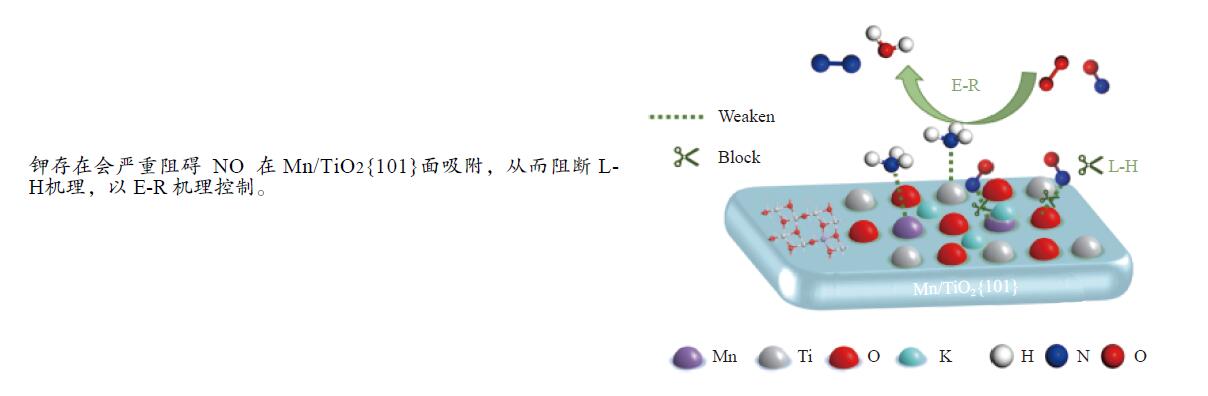
摘要: Mn/TiO2具有良好的低温NH3选择性催化还原NOx(SCR)的活性。烟气中存在的碱金属会从物理和化学上毒害催化剂导致Mn/TiO2催化剂中毒失活。论文以暴露{101}面TiO2为载体制备Mn/TiO2催化剂,采用浸渍法制备K中毒催化剂,研究了Mn/TiO2低温SCR催化剂钾中毒机理。实验发现,Mn/TiO2催化剂脱硝效率随K中毒浓度增加而减少;新鲜Mn/TiO2催化剂表面NH3-SCR反应由E-R和L-H机理共同控制;K吸附会导致催化剂比表面积降低,催化剂表面Mn4+、化学吸附氧比例降低,表面酸性位点数量减少,导致脱硝活性降低;同时K更易吸附在Mn顶位以及桥接O位附近,导致NO的吸附活化受到严重遏制,同时削弱NH3的吸附,使得L-H机理受到阻断,只能以E-R机理控制为主。Abstract: Mn/TiO2 has good low temperature NH3 selective catalytic reduction (SCR) activity for NOx. The presence of alkali metals in the flue gas can physically and chemically poison the catalyst leading to toxic deactivation of the Mn/TiO2 catalyst. This study investigated the mechanism of K-poisoning in Mn/TiO2 low temperature SCR catalysts by preparing K-poisoning Mn/TiO2 catalysts using exposed {101} surface TiO2 as a carrier. It was found that the denitrification efficiency of the Mn/TiO2 catalyst decreased with increasing K-poisoning concentration. Experimental characterisation and DFT calculations showed that the NH3-SCR reaction on the surface of the fresh Mn/TiO2 catalyst was controlled by both E-R and L-H mechanisms. K adsorption led to a reduction in the catalyst specific surface area, a decrease in the ratio of Mn4+ and chemisorbed oxygen on the catalyst surface and a decrease in the number of acidic sites on the surface, resulting in a decrease in denitrification activity; at the same time, K was more likely to adsorb near the Mn top site as well as the bridging O site, resulting in the activation of NO adsorption was severely curtailed and the adsorption of NH3 was weakened, making the L-H mechanism blocked and the E-R mechanism the main control.
-
Key words:
- low-temperature SCR /
- Mn/TiO2 /
- K-poisoning /
- catalyst
-
表 1 催化剂表面元素分析(EDS)
Table 1 Analysis of elemental concentrations on the surface of catalyst samples (EDS)
Sample K/% Mn/% O/% Ti/% Mn/TiO2 − 12.03 51.25 36.72 0.01K- Mn/TiO2 0.25 11.81 55.37 32.57 0.02K- Mn/TiO2 0.41 10.77 56.95 31.87 0.045K- Mn/TiO2 1.23 9.95 56.72 32.10 0.09K- Mn/TiO2 2.28 9.82 57.12 30.78 表 2 催化剂的BET参数
Table 2 BET parameters for catalyst samples
Catalyst BET surface
area /
(m2·g−1)Pore volume
×10−2/(cm3·g−1)Average pore
diameter/
nmMn/TiO2 52.7 12.1 9.2 0.01K- Mn/TiO2 44.1 13.0 11.8 0.02K- Mn/TiO2 44.4 12.9 11.7 0.045K- Mn/TiO2 45.0 11.6 9.1 0.09K- Mn/TiO2 42.3 11.3 9.1 表 3 催化剂表面元素分析(XPS)
Table 3 Analysis of elemental concentrations on the surface of catalyst samples (XPS)
Sample K/% Mn/% O/% Mn2+ Mn3++Mn4+ Oβ Oα Mn/TiO2 − 32.6 67.4 49.2 50.8 0.01K- Mn/TiO2 0.55 35.1 64.9 65.1 34.9 0.02K- Mn/TiO2 0.53 38.7 61.3 65.2 34.8 0.045K- Mn/TiO2 2.13 41.7 58.3 72.4 27.6 0.09K- Mn/TiO2 2.58 47.8 52.2 72.8 27.2 -
[1] ZHAO S, PENG J, GE R, et al. Research progress on selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts for NOx removal from coal-fired flue gas[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2022,236:107432. [2] WANG X, LI B, WANG Y, et al. Insight into the dynamic behaviors of reactants with temperature over a TiOx-based catalyst for NOx removal via NH3-SCR[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2022,605:154689. [3] 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 煤电节能减排升级与改造行动计划(2014−2022年) [EB/OL]. (2014-09-12) [2019-12-30]. http://www.sdpc.gov.cn/gzdt/201409/t20140919_626240.html.National Development and Reform Commission of the People's Republic of China. Action Plan for Energy Saving and Emission Reduction Upgrading and Retrofitting of Coal Power (2014−2022) [EB/OL]. (2014-09-12) [2019-12-30]. http://www.sdpc.gov.cn/gzdt/201409/t20140919_626240.html. [4] GB 4915—2013, 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 水泥工业大气污染物排放标准[S]. 2014.GB 4915—2013, Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Emission Standard for Air Pollutants in Cement Industry[S]. 2014. [5] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 关于推进实施钢铁行业超低排放的意见[EB/OL]. (2019-04-28)[2019-11-10]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/201904/t20190429_701463.html.Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Opinions on Promoting the Implementation of Ultra-Low Emission in the Iron and Steel Industry[EB/OL]. (2019-04-28)[2019-11-10]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/201904/t20190429_701463.html. [6] 沈伯雄, 卢凤菊, 高兰君, 等. 中温商业SCR催化剂碱和碱土中毒特性研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2016,44(4):500−506.SHEN Boxiong, LU Fengju, GAO Lanjun, et al. Characterisation of alkali and alkaline earth poisoning of medium temperature commercial SCR catalysts[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2016,44(4):500−506. [7] KONG M, LIU Q, WANG X, et al. Performance impact and poisoning mechanism of arsenic over commercial V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst[J]. Catal Commun,2015,72:121−126. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2015.09.029 [8] 马昊. 水泥炉窑烟气低温SCR 脱硝成型催化剂优化研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015.MA Hao. Optimisation of low temperature SCR denitrification catalyst for cement kiln flue gas[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015. [9] 石朝亭, 蔡军, 任强强, 等. 燃煤水泥窑炉低NOx 排放控制技术研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术,2020,26(1):174−183.SHI Chaoting, CAI Jun, REN Qiangqiang, et al. Research progress on low NOx emission control technology for coal-fired cement kilns[J]. Clean Coal Technol,2020,26(1):174−183. [10] DENG S, MENG T, XU B, et al. Advanced MnOx/TiO2 catalyst with preferentially exposed anatase {001} facet for low-temperature SCR of NO[J]. ACS Catal,2016,6(9):5807−5815. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01121 [11] CHEN L, LI J, GE M. The poisoning effect of alkali metals doping over nano V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Chem Eng J,2011,170(2):531−537. [12] 张成, 李君臣, 方鼎立, 等. Mn基低温SCR催化剂抗中毒研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术,2022,28(10):110−135.ZHANG Cheng, LI Junchen, FANG Dingli, et al. Progress of anti-poisoning research on Mn-based low-temperature SCR catalysts[J]. Clean Coal Technol,2022,28(10):110−135. [13] WAN Q, DUAN L, LI J, et al. Deactivation performance and mechanism of alkali (earth) metalson V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst for oxidation of gaseous elemental mercury in simulated coal-firedflue gas[J]. Catal Today,2011,175:189−195. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.011 [14] KANG K, YAO X, HUANG Y, et al. Insights into the co-doping effect of Fe3+ and Zr4+ on the anti-K performance of CeTiOx catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction[J]. J Hazard Mater,2021,416:125821. [15] GUO R-T, WANG Q-S, PAN W-G, et al. The poisoning effect of Na and K on Mn/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: A comparative study[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2014,317:111−116. [16] WEI L, CUI S, GUO H, et al. The effect of alkali metal over Mn/TiO2 for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 through DRIFT and DFT[J]. Comput Mater Sci,2018,(144):216−222. [17] ZHU N, SHAN W, SHAN Y, et al. Effects of alkali and alkaline earth metals on Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Chem Eng J,2020,388:124250. [18] JI J, TANG Y, HAN L, et al. Cerium manganese oxides coupled with ZSM-5: A novel SCR catalyst with superior K resistance[J]. Chem Eng J,2022,445:136530. [19] GAO E, FENG W, HUANG B, et al. The enhanced resistance to Na+-poisoning of MnCoCrOx SCR catalyst by acidity regulation: The mechanism of sulfuric acid pretreatment[J]. Mol Catal,2022,518:112084. [20] JIANG Y, HAN D, YANG L, et al. Improving the K resistance effectively of CeO2-TiO2 catalyst by Nb doping for NH3-SCR reaction[J]. Process Saf Environ Prot,2022,160:876−886. [21] SHI Q, LI Y, ZHOU Y, et al. The shape effect of TiO2 in VOx/TiO2 catalysts for selective reduction of NO by NH3[J]. J Mater Chem A,2015,3:14409−14415. [22] JIANG Y, LIU T, LAI C, et al. Deactivation of CeO2-TiO2 catalyst by K2SO4 for NH3-SCR: An experimental and DFT study[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2021,547:149196. [23] CHEN S, VASILIADES M A, YAN Q, et al. Remarkable N2-selectivity enhancement of practical NH3-SCR over Co0.5Mn1Fe0.25Al0.75Ox-LDO: The role of Co investigated by transient kinetic and DFT mechanistic studies[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2020,277:119186. [24] CHEN L, REN S, JIANG Y, et al. Effect of Mn and Ce oxides on low-temperature NH3-SCR performance over blast furnace slag-derived zeolite X supported catalysts[J]. Fuel,2022,320:123969. [25] FU Z, ZHANG G, HAN W, et al. The water resistance enhanced strategy of Mn based SCR catalyst by construction of TiO2 shell and superhydrophobic coating[J]. Chem Eng J,2021,426:131334. [26] XIE S, LI L, JIN L, et al. Low temperature high activity of M (M=Ce, Fe, Co, Ni) doped M-Mn/TiO2 catalysts for NH3-SCR and in situ DRIFTS for investigating the reaction mechanism[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2020,515:146014. [27] PAN W-G, ZHOU Y, GUO R-T, et al. Influence of calcination temperature on CeO2-CuO catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Environ Prog Sustainable,2014,33(2):385−389. doi: 10.1002/ep.11793 [28] WANG F, DAI H, DENG J, et al. Manganese oxides with rod-, wire-, tube-, and flower-like morphologies: Highly effective catalysts for the removal of toluene[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2012,46(7):4034−41. doi: 10.1021/es204038j [29] ZHANG S, LIU X, ZHONG Q, et al. Effect of Y doping on oxygen vacancies of TiO2 supported MnOx for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature[J]. Catal Commun,2012,25:7−11. [30] WEI L, WANG Z, LIU Y, et al. Support promotion effect on the SO2 and K+ co-poisoning resistance of MnO2/TiO2 for NH3-SCR of NO[J]. J Hazard Mater,2021,416:126117. [31] LI F, XIE J, FANG D, et al. Mechanistic study of Ce-modified MnOx/TiO2 catalysts with high NH3-SCR performance and SO2 resistance at low temperatures[J]. Res Chem Intermed,2017,43(10):5413−5432. doi: 10.1007/s11164-017-2937-0 [32] LI X, NIU Y, LI J, et al. Trace Co doping improves NH3-SCR performance and poisoning resistance of Ce-Mn-based catalysts[J]. Chem Eng J,2023,454:140180. [33] ZHOU X, WANG P, SHEN Z, et al. Low-temperature NOx reduction over hydrothermally stable SCR catalysts by engineering low-coordinated Mn active sites[J]. Chem Eng J,2022,442:136182. [34] CHEN L, REN S, PENG H, et al. Low-cost Mn-Ce/CuX catalyst from blast furnace slag waste for efficient low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2022,646:118868. [35] GAO X, DU X S, CUI L W, et al. A Ce-Cu-Ti oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Catal Commun,2010,12(4):255−258. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2010.09.029 -





 下载:
下载: