Study on the enhancement mechanism of low-temperature SCR performance of ammonium persulfate coupled transition metal oxides modified carbon-based catalysts
-
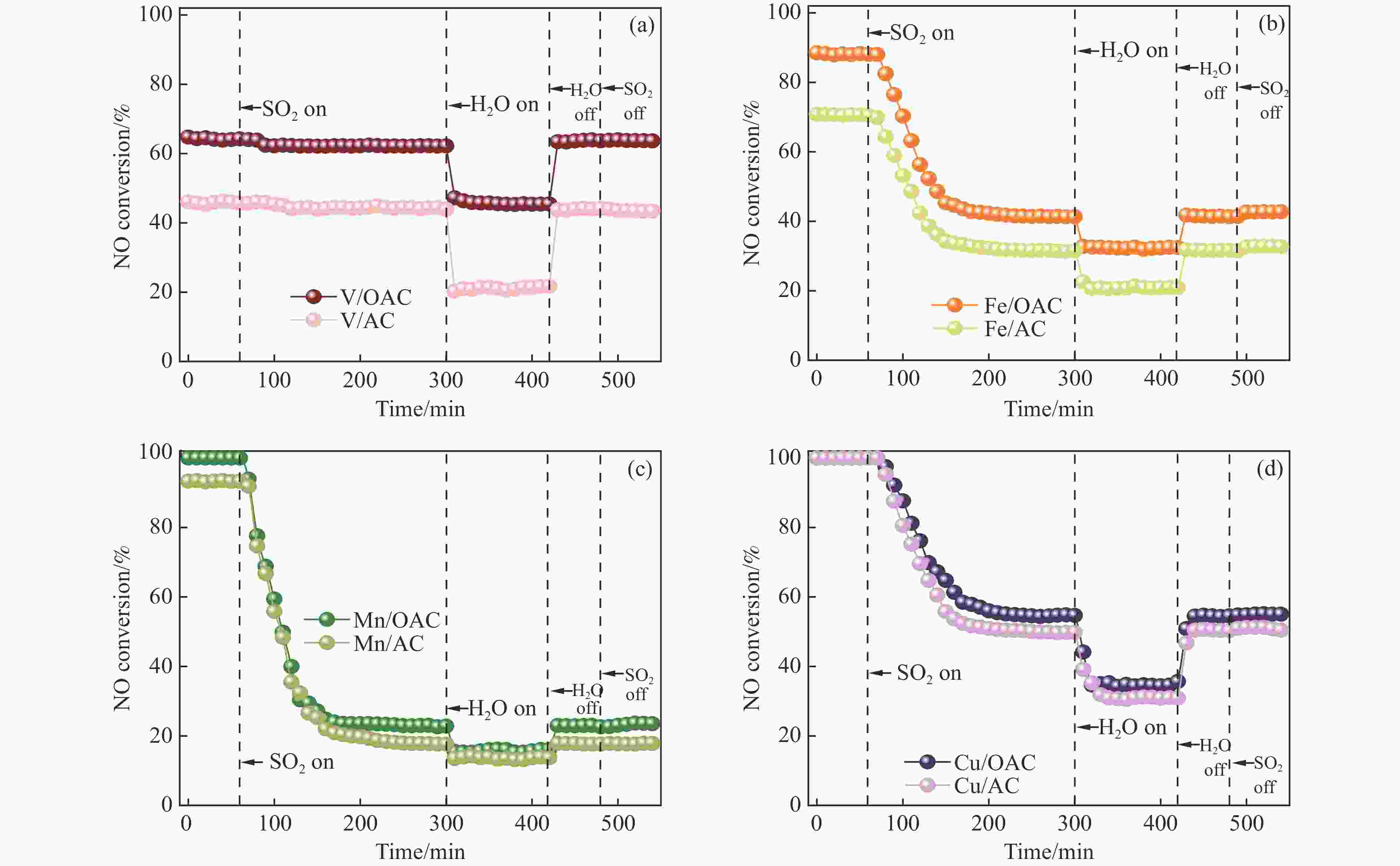
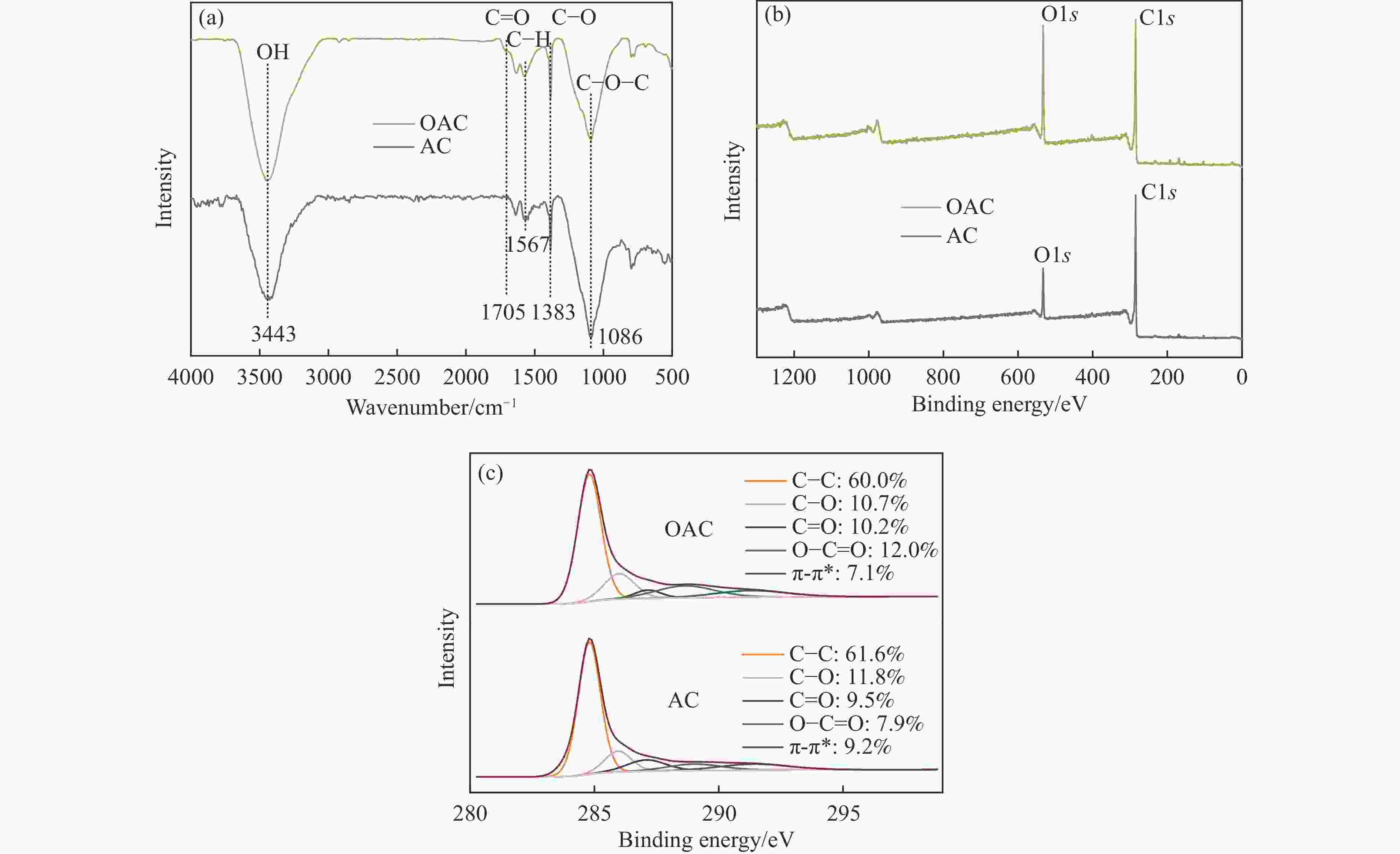
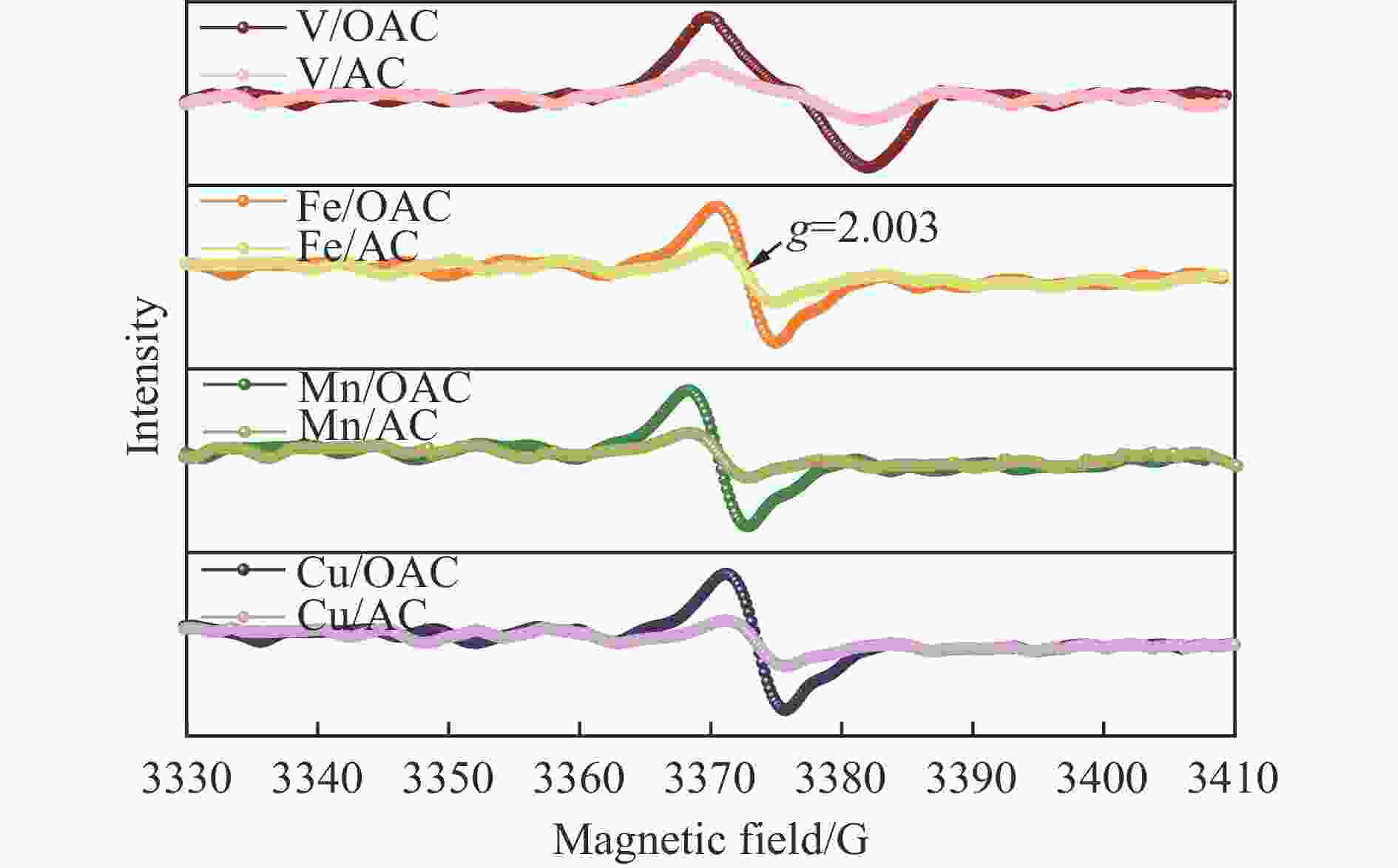
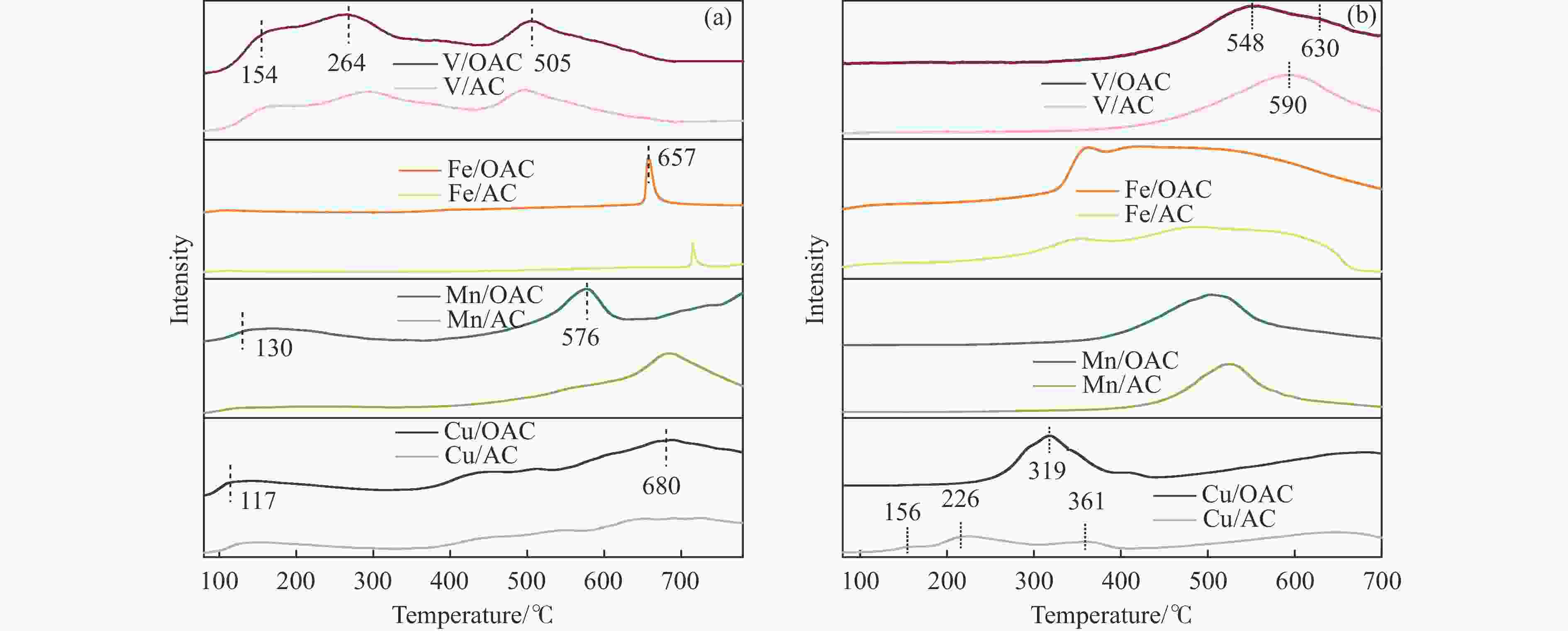
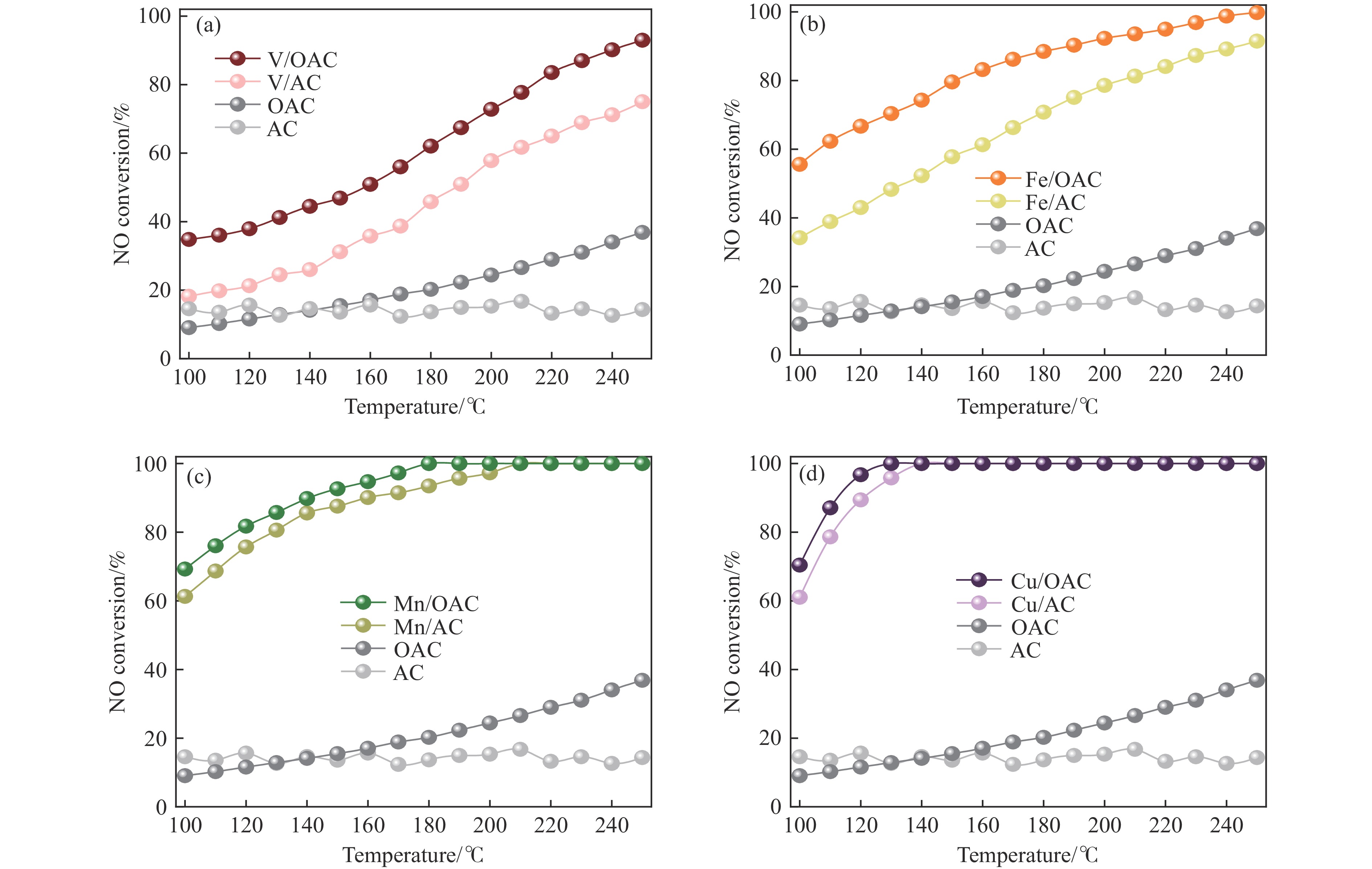
摘要: 本工作中利用过硫酸铵氧化耦合过渡金属氧化物改性制备V/OAC、Fe/OAC、Mn/OAC、Cu/OAC炭基催化剂,并通过催化活性测试和物理吸附、FT-IR、XPS、NH3-TPD、H2-TPR、EPR等表征手段探究改性炭基催化剂的低温SCR性能增强机制。结果表明,过硫酸铵氧化可向活性炭载体表面引入大量酸性含氧官能团,促进过渡金属氧化物中的氧空位形成,从而提升炭基催化剂的表面酸度和氧化还原性能,进而提升了炭基催化剂低温NH3-SCR性能。本工作发现,过硫酸铵氧化可诱导过渡金属元素(V、Fe、Mn、Cu)的低价态形成。因此,过硫酸铵氧化改性后,活性组分中低价态金属利于NH3-SCR反应的V/OAC、Fe/OAC催化剂性能提升显著,VOx/OAC和FeOx/OAC催化剂在100 ℃下的NO转化率分别从18.2%提升到34.8%和从34.2%提升到55.6%;而活性组分中高价态金属有利NH3-SCR反应的Mn/OAC和Cu/OAC催化剂性能提升有限,100 ℃下的NO转化率仅从61.4%提升到70.4%和61.3%提升到69.7%。本工作总结了过硫酸铵氧化改性对炭基催化剂表面金属价态的调控作用,有助于深入认识过硫酸铵氧化改性对炭基催化剂物化性质的调控规律,为高效炭基脱硝催化剂的开发提供指导和参考。Abstract: In recent years, carbon-based catalysts have received extensive attention in the field of NH3-SCR due to their unique advantages. In order to improve the performance of low-temperature NH3-SCR of carbon-based catalysts, V/OAC, Fe/OAC, Mn/OAC and Cu/OAC carbon-based catalysts were prepared by oxidizing and coupling transition metal oxides with ammonium persulfate. The mechanism of SCR performance enhancement of modified carbon-based catalysts was investigated by means of catalytic activity test, Physical adsorption, FT-IR, XPS, NH3-TPD, H2-TPR, EPR and other characterization methods. The results show that ammonium persulfate oxidation can introduce a large number of acidic oxygen-containing functional groups to the surface of activated carbon support, promote the formation of oxygen vacancy in transition metal oxides, and improve the surface acidity and redox performance of carbon-based catalysts, therefore the low temperature NH3-SCR performance of the carbon-based catalyst was improved. In particular, we found that oxidation of ammonium persulfate can induce the formation of lower valence states of transition metal elements (V, Fe, Mn,Cu ). Therefore, after oxidative modification of ammonium persulfate, the performance of V/OAC and Fe/OAC catalysts with low-priced metals in active components conducive to NH3-SCR reaction is significantly improved, the NO conversion of VOx/OAC and FeOx/OAC catalysts at 100 ℃ increased from 18.2% to 34.8% and from 34.2% to 55.6%, respectively; while the performance of Mn/OAC and Cu/OAC catalysts with high-priced metals in active components conducive to NH3-SCR reaction is limited, the conversion of NO at 100 ℃ only increased from 61.4% to 70.4% and from 61.3% to 69.7%. This work summarized the regulatory effect of ammonium persulfate oxidation modification on the surface metal states of carbon-based catalysts, which is helpful to deeply understand the regulation law of physical and chemical properties of carbon-based catalysts by oxidative modification of ammonium persulfate, and provide guidance and reference for the development of high-efficiency carbon-based denitrification catalysts.
-
Key words:
- NH3-SCR /
- carbon-based catalyst /
- transition metal /
- metal valence
-
表 1 催化剂的比表面积以及孔容和孔径
Table 1 Catalyst specific surface area and pore volume aperture
Sample BET surface area/(m2·g−1) Cumulitive pore volume/(cm3·g−1) Pore size/
nmVOx/AC 824 0.45 2.18 VOx/OAC 760 0.42 2.22 FeOx/AC 689 0.30 3.83 FeOx/OAC 602 0.29 3.81 MnOx/AC 803 0.44 2.53 MnOx/OAC 635 0.34 2.49 CuOx/AC 811 0.44 2.62 CuOx/OAC 657 0.36 2.52 表 2 催化剂的总酸量
Table 2 Total acid content of catalyst
Sample V/AC V/OAC Fe/AC Fe/OAC Mn/AC Mn/OAC Cu/AC Cu/OAC Total acid
(μmol·g−1)379.2 577.6 523.7 746.3 1190.7 1478.8 1325.3 1721.4 -
[1] GUO Q Q, JING W, HOU Y Q, et al. On the nature of oxygen groups for NH3-SCR of NO over carbon at low temperatures[J]. Chem Eng J,2015,270:41−49. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.086 [2] TANG X L, HAO J M, YI H H, et al. Low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 on Mn-based catalysts modified with cerium[J]. J Rare Earths,2007,25(1):240. [3] 谭月. Mn-Ce/活性焦低温脱硫脱硝催化剂的制备与再生实验研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2015Tan Y. Experimental study on preparation and regeneration of Mn-Ce/ Active Coke catalyst for desulfurization and denitrification at low temperature [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2015.) [4] KANG M, PARK E D, KIM J M, et al. Cu-Mn mixed oxides for low temperature NO reduction with NH3[J]. Catal Today,2006,111(3-4):236−241. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2005.10.032 [5] QI G, YANG R T, CHANG R, et al. Low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over USY-supported manganese oxide-based catalysts[J]. Catal lett,2003,87(1):67−71. [6] ZHU Z, LIU Z, LIU S, et al. A novel carbon-supported vanadium oxide catalyst for NO reduction with NH3 at low temperatures[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ,1999,23:L229−L233. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(99)00085-5 [7] LIU L, WANG B, YAO X, et al. Highly efficient MnO x /biochar catalysts obtained by air oxidation for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO[J]. Fuel,2021,283:119336. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119336 [8] LI S, HUANG Y, ZHU H, et al. Dual improvement in acid and redox properties of the FeO x /OAC catalyst via APS oxygen-functionalization: High low-temperature NH3-SCR activity, SO2 and H2O tolerance[J]. Fuel,2023,341:127716. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127716 [9] GUI R, YAN Q, XUE T, et al. The promoting/inhibiting effect of water vapor on the selective catalytic reduction of NO x [J]. J Hazard Mater,2022,439:129665. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129665 [10] GUO K, JI J, SONG W, et al. Conquering ammonium bisulfate poison over low-temperature NH3-SCR catalysts: A critical review[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ,2021,297:120388. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120388 [11] GUO K, JI J, OSUGA R, et al. Construction of Fe2O3 loaded and mesopore confined thin-layer titania catalyst for efficient NH3-SCR of NOx with enhanced H2O/SO2 tolerance[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ,2021,287:119982. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119982 [12] LIU C, CHEN L, LI J, et al. Enhancement of activity and sulfur resistance of CeO2 supported on TiO2-SiO2 for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2012,46(11):6182−6189. doi: 10.1021/es3001773 [13] WU Z, WEBLEY PA, ZHAO D, et al. Comprehensive study of pore evolution, mesostructural stability, and simultaneous surface functionalization of ordered mesoporous carbon (FDU-15) by wet oxidation as a promising adsorbent[J]. Langmuir,2010,26(12):10277−86. doi: 10.1021/la100455w [14] DU X, LI C, ZHAO L, et al. Promotional removal of HCHO from simulated flue gas over Mn-Fe oxides modified activated coke[J]. Appl Catal B:Envirol,2018,232:37−48. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.034 [15] CHEN L, YAO X, CAO J, et al. Effect of Ti4+ and Sn4+ co-incorporation on the catalytic performance of CeO2-MnO x catalyst for low temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2019,476:283−292. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.095 [16] MACÍAS-GARCÍA A, DIAZ-DIEZ M A, CUERDA-CORREA E M, et al. Study of the pore size distribution and fractal dimension of HNO3-treated activated carbons[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2006,252(17):5972−5975. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.11.010 [17] ZHANG X, YAO H, LEI X, et al. Synergistic adsorption and degradation of sulfamethoxazole from synthetic urine by hickory-sawdust-derived biochar: the critical role of the aromatic structure[J]. J Hazard Mater,2021,418:126366. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126366 [18] PUZIY AM, PODDUBNAYA OI, SOCHA RP, et al. studies of phosphoric acid activated carbons[J]. Carbon,2008,46(15):2113−23. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2008.09.010 [19] SHEN B, LIU Z, XU H, et al. Enhancing the absorption of elemental mercury using hydrogen peroxide modified bamboo carbons. [J] Fuel, 2019, 235 : 878-85. [20] XU Z, LI Y, GUO J, et al. An efficient and sulfur resistant K-modified activated carbon for SCR denitrification compared with acid- and Cu-modified activated carbon[J]. Chem Eng J,2020,395:125047. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125047 [21] LI N, Ma X, Zha Q, et al. Maximizing the number of oxygen-containing functional groups on activated carbon by using ammonium persulfate and improving the temperature-programmed desorption characterization of carbon surface chemistry[J]. Carbon,2011,49(15):5002−5013. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2011.07.015 [22] ZHANG N, WANG J, LI Q, et al. Enhanced selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over homoatomic dinuclear sites in defective α-Fe2O3[J]. Chem Eng J,2021,426:131845. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131845 [23] ZHAO X, YAN Y, MAO L, et al. A relationship between the V4+/V5+ ratio and the surface dispersion, surface acidity, and redox performance of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts[J]. RSC advances,2018,8(54):31081−31093. doi: 10.1039/C8RA02857E [24] LIU L, WU X, MA Y, et al. Potassium deactivation of Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for NH3-SCR: Evolution of salts, zeolite and copper species[J]. Chem Eng J,2020,383:123080. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123080 [25] BENDRICH M, SCHEUER A, HAYES R E, et al. Unified mechanistic model for Standard SCR, Fast SCR, and NO2 SCR over a copper chabazite catalyst[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ,2018,222:76−87. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.069 [26] LI S, HUANG Y, ZHAO L, et al. Oxygen-functionalized activated carbon supported vanadia catalysts: Unexpected improvement in low-temperature NH3-SCR performance[J]. Surf Interfaces,2022,33:102252. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102252 [27] LI Q, LIANG M, HAN X, et al. Insight into the enhancing activity and stability of Ce modified V2O5/AC during cyclic desulfurization-regeneration-denitrification[J]. J Hazard Mater,2022,424:127397. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127397 [28] BONINGARI T, ETTIREDDY P R, SOMOGYVARI A, et al. Influence of elevated surface texture hydrated titania on Ce-doped Mn/TiO2 catalysts for the low-temperature SCR of NOx under oxygen-rich conditions[J]. J Catal,2015,325:145−155. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.03.002 [29] YANG J, REN S, ZHANG T, et al. Iron doped effects on active sites formation over activated carbon supported Mn-Ce oxide catalysts for low-temperature SCR of NO[J]. Chem Eng J,2020,379:122398. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122398 [30] ZANG P, LIU J, HE Y, et al. LDH-derived preparation of CuMgFe layered double oxides for NH3-SCR and CO oxidation reactions: Performance study and synergistic mechanism[J]. Chem Eng J,2022,446:137414. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.137414 [31] LI J X, LIU F, REN L, et al. Excellent performance of one-pot synthesized Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2014,48(1):566−572. doi: 10.1021/es4032002 [32] LIU F, HE H, DING Y, et al. Effect of manganese substitution on the structure and activity of iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ,2009,93(1-2):194−204. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.09.029 -





 下载:
下载: